

23 Advantages and Disadvantages of Qualitative Research
Investigating methodologies. Taking a closer look at ethnographic, anthropological, or naturalistic techniques. Data mining through observer recordings. This is what the world of qualitative research is all about. It is the comprehensive and complete data that is collected by having the courage to ask an open-ended question.
Print media has used the principles of qualitative research for generations. Now more industries are seeing the advantages that come from the extra data that is received by asking more than a “yes” or “no” question.
The advantages and disadvantages of qualitative research are quite unique. On one hand, you have the perspective of the data that is being collected. On the other hand, you have the techniques of the data collector and their own unique observations that can alter the information in subtle ways.
That’s why these key points are so important to consider.
What Are the Advantages of Qualitative Research?
1. Subject materials can be evaluated with greater detail. There are many time restrictions that are placed on research methods. The goal of a time restriction is to create a measurable outcome so that metrics can be in place. Qualitative research focuses less on the metrics of the data that is being collected and more on the subtleties of what can be found in that information. This allows for the data to have an enhanced level of detail to it, which can provide more opportunities to glean insights from it during examination.
2. Research frameworks can be fluid and based on incoming or available data. Many research opportunities must follow a specific pattern of questioning, data collection, and information reporting. Qualitative research offers a different approach. It can adapt to the quality of information that is being gathered. If the available data does not seem to be providing any results, the research can immediately shift gears and seek to gather data in a new direction. This offers more opportunities to gather important clues about any subject instead of being confined to a limited and often self-fulfilling perspective.
3. Qualitative research data is based on human experiences and observations. Humans have two very different operating systems. One is a subconscious method of operation, which is the fast and instinctual observations that are made when data is present. The other operating system is slower and more methodical, wanting to evaluate all sources of data before deciding. Many forms of research rely on the second operating system while ignoring the instinctual nature of the human mind. Qualitative research doesn’t ignore the gut instinct. It embraces it and the data that can be collected is often better for it.
4. Gathered data has a predictive quality to it. One of the common mistakes that occurs with qualitative research is an assumption that a personal perspective can be extrapolated into a group perspective. This is only possible when individuals grow up in similar circumstances, have similar perspectives about the world, and operate with similar goals. When these groups can be identified, however, the gathered individualistic data can have a predictive quality for those who are in a like-minded group. At the very least, the data has a predictive quality for the individual from whom it was gathered.
5. Qualitative research operates within structures that are fluid. Because the data being gathered through this type of research is based on observations and experiences, an experienced researcher can follow-up interesting answers with additional questions. Unlike other forms of research that require a specific framework with zero deviation, researchers can follow any data tangent which makes itself known and enhance the overall database of information that is being collected.
6. Data complexities can be incorporated into generated conclusions. Although our modern world tends to prefer statistics and verifiable facts, we cannot simply remove the human experience from the equation. Different people will have remarkably different perceptions about any statistic, fact, or event. This is because our unique experiences generate a different perspective of the data that we see. These complexities, when gathered into a singular database, can generate conclusions with more depth and accuracy, which benefits everyone.
7. Qualitative research is an open-ended process. When a researcher is properly prepared, the open-ended structures of qualitative research make it possible to get underneath superficial responses and rational thoughts to gather information from an individual’s emotional response. This is critically important to this form of researcher because it is an emotional response which often drives a person’s decisions or influences their behavior.
8. Creativity becomes a desirable quality within qualitative research. It can be difficult to analyze data that is obtained from individual sources because many people subconsciously answer in a way that they think someone wants. This desire to “please” another reduces the accuracy of the data and suppresses individual creativity. By embracing the qualitative research method, it becomes possible to encourage respondent creativity, allowing people to express themselves with authenticity. In return, the data collected becomes more accurate and can lead to predictable outcomes.
9. Qualitative research can create industry-specific insights. Brands and businesses today need to build relationships with their core demographics to survive. The terminology, vocabulary, and jargon that consumers use when looking at products or services is just as important as the reputation of the brand that is offering them. If consumers are receiving one context, but the intention of the brand is a different context, then the miscommunication can artificially restrict sales opportunities. Qualitative research gives brands access to these insights so they can accurately communicate their value propositions.
10. Smaller sample sizes are used in qualitative research, which can save on costs. Many qualitative research projects can be completed quickly and on a limited budget because they typically use smaller sample sizes that other research methods. This allows for faster results to be obtained so that projects can move forward with confidence that only good data is able to provide.
11. Qualitative research provides more content for creatives and marketing teams. When your job involves marketing, or creating new campaigns that target a specific demographic, then knowing what makes those people can be quite challenging. By going through the qualitative research approach, it becomes possible to congregate authentic ideas that can be used for marketing and other creative purposes. This makes communication between the two parties to be handled with more accuracy, leading to greater level of happiness for all parties involved.
12. Attitude explanations become possible with qualitative research. Consumer patterns can change on a dime sometimes, leaving a brand out in the cold as to what just happened. Qualitative research allows for a greater understanding of consumer attitudes, providing an explanation for events that occur outside of the predictive matrix that was developed through previous research. This allows the optimal brand/consumer relationship to be maintained.
What Are the Disadvantages of Qualitative Research?
1. The quality of the data gathered in qualitative research is highly subjective. This is where the personal nature of data gathering in qualitative research can also be a negative component of the process. What one researcher might feel is important and necessary to gather can be data that another researcher feels is pointless and won’t spend time pursuing it. Having individual perspectives and including instinctual decisions can lead to incredibly detailed data. It can also lead to data that is generalized or even inaccurate because of its reliance on researcher subjectivisms.
2. Data rigidity is more difficult to assess and demonstrate. Because individual perspectives are often the foundation of the data that is gathered in qualitative research, it is more difficult to prove that there is rigidity in the information that is collective. The human mind tends to remember things in the way it wants to remember them. That is why memories are often looked at fondly, even if the actual events that occurred may have been somewhat disturbing at the time. This innate desire to look at the good in things makes it difficult for researchers to demonstrate data validity.
3. Mining data gathered by qualitative research can be time consuming. The number of details that are often collected while performing qualitative research are often overwhelming. Sorting through that data to pull out the key points can be a time-consuming effort. It is also a subjective effort because what one researcher feels is important may not be pulled out by another researcher. Unless there are some standards in place that cannot be overridden, data mining through a massive number of details can almost be more trouble than it is worth in some instances.
4. Qualitative research creates findings that are valuable, but difficult to present. Presenting the findings which come out of qualitative research is a bit like listening to an interview on CNN. The interviewer will ask a question to the interviewee, but the goal is to receive an answer that will help present a database which presents a specific outcome to the viewer. The goal might be to have a viewer watch an interview and think, “That’s terrible. We need to pass a law to change that.” The subjective nature of the information, however, can cause the viewer to think, “That’s wonderful. Let’s keep things the way they are right now.” That is why findings from qualitative research are difficult to present. What a research gleans from the data can be very different from what an outside observer gleans from the data.
5. Data created through qualitative research is not always accepted. Because of the subjective nature of the data that is collected in qualitative research, findings are not always accepted by the scientific community. A second independent qualitative research effort which can produce similar findings is often necessary to begin the process of community acceptance.
6. Researcher influence can have a negative effect on the collected data. The quality of the data that is collected through qualitative research is highly dependent on the skills and observation of the researcher. If a researcher has a biased point of view, then their perspective will be included with the data collected and influence the outcome. There must be controls in place to help remove the potential for bias so the data collected can be reviewed with integrity. Otherwise, it would be possible for a researcher to make any claim and then use their bias through qualitative research to prove their point.
7. Replicating results can be very difficult with qualitative research. The scientific community wants to see results that can be verified and duplicated to accept research as factual. In the world of qualitative research, this can be very difficult to accomplish. Not only do you have the variability of researcher bias for which to account within the data, but there is also the informational bias that is built into the data itself from the provider. This means the scope of data gathering can be extremely limited, even if the structure of gathering information is fluid, because of each unique perspective.
8. Difficult decisions may require repetitive qualitative research periods. The smaller sample sizes of qualitative research may be an advantage, but they can also be a disadvantage for brands and businesses which are facing a difficult or potentially controversial decision. A small sample is not always representative of a larger population demographic, even if there are deep similarities with the individuals involve. This means a follow-up with a larger quantitative sample may be necessary so that data points can be tracked with more accuracy, allowing for a better overall decision to be made.
9. Unseen data can disappear during the qualitative research process. The amount of trust that is placed on the researcher to gather, and then draw together, the unseen data that is offered by a provider is enormous. The research is dependent upon the skill of the researcher being able to connect all the dots. If the researcher can do this, then the data can be meaningful and help brands and progress forward with their mission. If not, there is no way to alter course until after the first results are received. Then a new qualitative process must begin.
10. Researchers must have industry-related expertise. You can have an excellent researcher on-board for a project, but if they are not familiar with the subject matter, they will have a difficult time gathering accurate data. For qualitative research to be accurate, the interviewer involved must have specific skills, experiences, and expertise in the subject matter being studied. They must also be familiar with the material being evaluated and have the knowledge to interpret responses that are received. If any piece of this skill set is missing, the quality of the data being gathered can be open to interpretation.
11. Qualitative research is not statistically representative. The one disadvantage of qualitative research which is always present is its lack of statistical representation. It is a perspective-based method of research only, which means the responses given are not measured. Comparisons can be made and this can lead toward the duplication which may be required, but for the most part, quantitative data is required for circumstances which need statistical representation and that is not part of the qualitative research process.
The advantages and disadvantages of qualitative research make it possible to gather and analyze individualistic data on deeper levels. This makes it possible to gain new insights into consumer thoughts, demographic behavioral patterns, and emotional reasoning processes. When a research can connect the dots of each information point that is gathered, the information can lead to personalized experiences, better value in products and services, and ongoing brand development.
HARMONY PLATFORM .css-vxhqob{display:inline-block;line-height:1em;-webkit-flex-shrink:0;-ms-flex-negative:0;flex-shrink:0;color:currentColor;vertical-align:middle;fill:currentColor;stroke:none;margin-left:var(--chakra-space-4);height:var(--chakra-sizes-4);width:var(--chakra-sizes-2);margin-bottom:var(--chakra-space-1);}
Harmony platform.
Engage employees, inform customers and manage your workplace in one platform.
- Workplace Mobile App
HOW IT WORKS
- Omnichannel Feeds
- Integrations
- Analytics & Insights
- Workplace Management
- Consultancy

Find our how the Poppulo Harmony platform can help you to engage employees and customers, and deliver a great workplace experience.
- Employee Comms
- Customer Comms
- Workplace Experience
- Leadership Comms
- Change and Transformation
- Wayfinding & Directories
- Patient Comms
FEATURED CASE STUDIES

Using Digital Signage to Elevate the Workplace Experience

Aligning people and business goals through integrated employee communications

Valley Health
Launching an internal mobile app to keep frontline and back office employees informed
INDUSTRY OVERVIEW
Find out how our platform provides tailored support to your industry
- Hospitality & Entertainment
- Manufacturing
- Transportation
FEATURED CASE STUDY

Implementing an internal Mobile App in the software industry
OUR COMPANY
Our company overview.

- About Poppulo
RESOURCES OVERVIEW

We bring the best minds in employee comms together to share their knowledge and insights across our webinars, blogs, guides, and much more.
- Webinars & Guides
- Case Studies
- Maturity Model
FEATURED CONTENT

The Ultimate Guide to Internal Comms Strategy
The way we work, where we work, and how we work has fundamentally changed...

The Multi-Million Dollar Impact of Communication on Employee & Customer Experience
The stats speak for themselves—and the facts are unarguable...
10 Advantages and Disadvantages of Qualitative Research
— August 5th, 2021

Research is about gathering data so that it can inform meaningful decisions. In the workplace, this can be invaluable in allowing informed decision-making that will meet with wider strategic organizational goals.
However, research comes in a variety of guises and, depending on the methodologies applied, can achieve different ends. There are broadly two key approaches to research -- qualitative and quantitative.
Focus Group Guide: Top Tips and Traps for Employee Focus Groups
Qualitative v quantitative – what’s the difference.
Qualitative Research is at the touchy-feely end of the spectrum. It’s not so much about bean-counting and much more about capturing people’s opinions and emotions.
“Research following a qualitative approach is exploratory and seeks to explain ‘how’ and ‘why’ a particular phenomenon, or behavior, operates as it does in a particular context.” (simplypsychology.org)
Examples of the way qualitative research is often gathered includes:
Interviews are a conversation based inquiry where questions are used to obtain information from participants. Interviews are typically structured to meet the researcher’s objectives.
Focus Groups
Focus group discussions are a common qualitative research strategy . In a focus group discussion, the interviewer talks to a group of people about their thoughts, opinions, beliefs, and attitudes towards a topic. Participants are typically a group who are similar in some way, such as income, education, or career. In the context of a company, the group dynamic is likely their common experience of the workplace.
Observation
Observation is a systematic research method in which researchers look at the activity of their subjects in their typical environment. Observation gives direct information about your research. Using observation can capture information that participants may not think to reveal or see as important during interviews/focus groups.
Existing Documents
This is also called secondary data. A qualitative data collection method entails extracting relevant data from existing documents. This data can then be analyzed using a qualitative data analysis method called content analysis. Existing documents might be work documents, work email , or any other material relevant to the organization.
Quantitative Research is the ‘bean-counting’ bit of the research spectrum. This isn’t to demean its value. Now encompassed by the term ‘ People Analytics ’, it plays an equally important role as a tool for business decision-making.
Organizations can use a variety of quantitative data-gathering methods to track productivity. In turn, this can help:
- To rank employees and work units
- To award raises or promotions.
- To measure and justify termination or disciplining of staff
- To measure productivity
- To measure group/individual targets
Examples might include measuring workforce productivity. If Widget Makers Inc., has two production lines and Line A is producing 25% more per day than Line B, capturing this data immediately informs management/HR of potential issues. Is the slower production on Line B due to human factors or is there a production process issue?
Quantitative Research can help capture real-time activities in the workplace and point towards what needs management attention.
The Pros & Cons of the Qualitative approach
By its nature, qualitative research is far more experiential and focused on capturing people’s feelings and views. This undoubtedly has value, but it can also bring many more challenges than simply capturing quantitative data. Here are a few challenges and benefits to consider.
- Qualitative Research can capture changing attitudes within a target group such as consumers of a product or service, or attitudes in the workplace.
- Qualitative approaches to research are not bound by the limitations of quantitative methods. If responses don’t fit the researcher’s expectation that’s equally useful qualitative data to add context and perhaps explain something that numbers alone are unable to reveal .
- Qualitative Research provides a much more flexible approach . If useful insights are not being captured researchers can quickly adapt questions, change the setting or any other variable to improve responses.
- Qualitative data capture allows researchers to be far more speculative about what areas they choose to investigate and how to do so. It allows data capture to be prompted by a researcher’s instinctive or ‘gut feel’ for where good information will be found.
Qualitative research can be more targeted . If you want to compare productivity across an entire organization, all parts, process, and participants need to be accounted for. Qualitative research can be far more concentrated, sampling specific groups and key points in a company to gather meaningful data. This can both speed the process of data capture and keep the costs of data-gathering down.
Business acumen in internal communications – Why it matters and how to build it
- Sample size can be a big issue. If you seek to infer from a sample of, for example, 200 employees, based upon a sample of 5 employees, this raises the question of whether sampling will provide a true reflection of the views of the remaining 97.5% of the company?
- Sample bias - HR departments will have competing agendas. One argument against qualitative methods alone is that HR tasked with finding the views of the workforce may be influenced both consciously or unconsciously, to select a sample that favors an anticipated outcome .
- Self-selection bias may arise where companies ask staff to volunteer their views . Whether in a paper, online survey , or focus group, if an HR department calls for participants there will be the issue of staff putting themselves forward. The argument goes that this group, in self-selecting itself, rather than being a randomly selected snapshot of a department, will inevitably have narrowed its relevance to those that typically are willing to come forward with their views. Quantitative data is gathered whether someone volunteered or not.
- The artificiality of qualitative data capture. The act of bringing together a group is inevitably outside of the typical ‘norms ’ of everyday work life and culture and may influence the participants in unforeseen ways.
- Are the right questions being posed to participants? You can only get answers to questions you think to ask . In qualitative approaches, asking about “how” and “why” can be hugely informative, but if researchers don’t ask, that insight may be missed.
The reality is that any research approach has both pros and cons. The art of effective and meaningful data gathering is thus to be aware of the limitations and strengths of each method.
In the case of Qualitative research, its value is inextricably linked to the number-crunching that is Quantitative data. One is the Ying to the other’s Yang. Each can only provide half of the picture, but together, you get a more complete view of what’s occurring within an organization.
The best on communications delivered weekly to your inbox.

UPCOMING WEBINAR – APRIL 4TH
What’s possible with the poppulo harmony digital signage cloud.
Essay on Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research
Both qualitative and quantitative researches are valued in the research world and are often used together under a single project. This is despite the fact that they have significant differences in terms of their theoretical, epistemological, and methodological formations. Qualitative research is usually in form of words while quantitative research takes the numerical approach. This paper discusses the similarities, differences, advantages, and disadvantages of qualitative and quantitative research and provides a personal stand.
Similarities
Both qualitative and quantitative research approaches begin with a problem on which scholars seek to find answers. Without a research problem or question, there would be no reason for carrying out the study. Once a problem is formulated, researchers at their own discretion and depending on the nature of the question choose the appropriate type of research to employ. Just like in qualitative research, data obtained from quantitative analysis need to be analyzed (Miles & Huberman, 1994). This step is crucial for helping researchers to gain a deeper understanding of the issue under investigation. The findings of any research enjoy confirmability after undergoing a thorough examination and auditing process (Miles & Huberman, 1994).
Both types of research approaches require a concise plan before they are carried out. Once researchers formulate the study question, they must come up with a plan for investigating the matter (Yilmaz, 2013). Such plans include deciding the appropriate research technique to implement, estimating budgets, and deciding on the study areas. Failure to plan before embarking on the research project may compromise the research findings. In addition, both qualitative and quantitative research are dependent on each other and can be used for a single research project (Miles & Huberman, 1994). Quantitative data helps the qualitative research in finding a representative study sample and obtaining the background data. In the same way, qualitative research provides the quantitative side with the conceptual development and instrumentation (Miles & Huberman, 1994).
Differences
Qualitative research seeks to explain why things are the way they seem to be. It provides well-grounded descriptions and explanations of processes in identifiable local contexts (Miles & Huberman, 1994). Researchers use qualitative research to dig deeper into the problem and develop a relevant hypothesis for potential quantitative research. On the other hand, Quantitative research uses numerical data to state and quantify the problem (Yilmaz, 2013). Researchers in quantitative research use measurable data in formulating facts and uncovering the research pattern.
Quantitative research approach involves a larger number of participants for the purpose of gathering as much information as possible to summarize characteristics across large groups. This makes it a very expensive research approach. On the contrary, qualitative research approach describes a phenomenon in a more comprehensive manner. A relatively small number of participants take part in this type of research. This makes the overall process cheaper and time friendly.
Data collection methods differ significantly in the two research approaches. In quantitative research, scholars use surveys, questionnaires, and systematic measurements that involve numbers (Yilmaz, 2013). Moreover, they report their findings in impersonal third person prose by using numbers. This is different from the qualitative approach where only the participants’ observation and deep document analysis is necessary for conclusions to be drawn. Findings are disseminated in the first person’s narrative with sufficient quotations from the participants.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Qualitative Research
Qualitative data is based on human observations. Respondent’s observations connect the researcher to the most basic human experiences (Rahman, 2016). It gives a detailed production of participants’ opinions and feelings and helps in efficient interpretation of their actions (Miles & Huberman, 1994). Moreover, this research approach is interdisciplinary and entails a wide range of research techniques and epistemological viewpoints. Data collection methods in qualitative approach are both detailed and subjective (Rahman, 2016). Direct observations, unstructured interviews, and participant observation are the most common techniques employed in this type of research. Researchers have the opportunity to mingle directly with the respondents and obtain first-hand information.
On the negative side, the smaller population sample used in qualitative research raises credibility concerns (Rahman, 2016). The views of a small group of respondents may not necessarily reflect those of the entire population. Moreover, conducting this type of research on certain aspects such as the performance of students may be more challenging. In such instances, researchers prefer to use the quantitative approach instead (Rahman, 2016). Data analysis and interpretation in qualitative research is a more complex process. It is long, has elusive data, and has very stringent requirements for analysis (Rahman, 2016). In addition, developing a research question in this approach is a challenging task as the refining question mostly becomes continuous throughout the research process.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
The findings of a quantitative research can be generalized to a whole population as it involves larger samples that are randomly selected by researchers (Rahman, 2016). Moreover, the methods used allows for use of statistical software in test taking (Rahman, 2016). This makes the approach time effective and efficient for tackling complex research questions. Quantitative research allows for objectivity and accuracy of the study results. This approach is well designed to provide essential information that supports generalization of a phenomenon under study. It involves few variables and many cases that guarantee the validity and credibility of the study results.
This research approach, however, has some limitations. There is a limited direct connection between the researcher and respondents. Scholars who adopt this approach measure variables at specific moments in time and disregards the past experiences of the respondents (Rahman, 2016). As a result, deep information is often ignored and only the overall picture of the variables is represented. The quantitative approach uses standard questions set and administered by researchers (Rahman, 2016). This might lead to structural bias by respondents and false representation. In some instances, data may only reflect the views of the sample under study instead of revealing the real situation. Moreover, preset questions and answers limit the freedom of expression by the respondents.
Preferred Method
I would prefer quantitative research method over the qualitative approach. Data management in this technique is much familiar and more accessible to researchers’ contexts (Miles & Huberman, 1994). It is a more scientific process that involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of large amounts of data. Researchers have more control of the manner in which data is collected. Unlike qualitative data that requires descriptions, quantitative approach majors on numerical data (Yilmaz, 2013). With this type of data, I can use the various available software for classification and analyzes. Moreover, researchers are more flexible and free to interact with respondents. This gives an opportunity for obtaining first-hand information and learning more about other behavioral aspects of the population under study.
As highlighted above, qualitative and quantitative techniques are the two research approaches. Both seek to dig deeper into a particular problem, analyze the responses of a selected sample and make viable conclusions. However, qualitative research is much concerned with the description of peoples’ opinions, motivations, and reasons for a particular phenomenon. On the other hand, Quantitative research uses numerical data to state and explain research findings. Use of numerical data allows for objectivity and accuracy of the research results. However structural biases are common in this approach. Data collection and sampling in qualitative research is more detailed and subjective. Considering the different advantages and disadvantages of the two research approaches, I would go for the quantitative over qualitative research.
Miles, M., & Huberman, A. (1994). Qualitative data analysis (2nd Ed.). Beverly Hills: Sage.
Rahman, M. (2016). The Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches and Methods in Language “Testing and Assessment” Research: A Literature Review. Journal of Education and Learning , 6(1), 102.
Yilmaz, K. (2013). Comparison of Quantitative and Qualitative Research Traditions: epistemological, theoretical, and methodological differences. European Journal of Education , 48(2), 311-325.
Cite this page
Similar essay samples.
- Essay on Surrey Christmas Bureau
- Police Wearing Body Worn Cameras
- A multi-centre study of the risk factors and the impact of endometrios...
- Professional Development Plan
- Essay on Modifications Within a Company
- Essay on Creative Entrepreneurship

19 Advantages and Disadvantages of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a method that involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data to understand social phenomena.
This approach allows researchers to explore and gain in-depth insights into complex issues that cannot be easily measured or quantified.
However, like any research method, there are both advantages and disadvantages associated with qualitative research.

- Redaction Team
- September 9, 2023
- Professional Development , Thesis Writing
Advantages of Qualitative Research
- Rich and In-Depth Data : Qualitative research provides rich and detailed data, allowing researchers to explore complex social phenomena, experiences, and contexts in depth.
- Contextual Understanding : It emphasizes the importance of context, enabling researchers to understand the social, cultural, and environmental factors that influence behavior and perceptions.
- Flexibility : Qualitative research is flexible and adaptable, allowing researchers to change their research focus, questions, or methods based on emerging insights during the study.
- Exploratory Nature : It is well-suited for generating hypotheses and theories by exploring new or under-researched topics. Researchers can uncover unexpected findings.
- Participant Perspectives : Qualitative research prioritizes the voices and perspectives of participants, providing insight into their lived experiences, beliefs, and worldviews.
- Holistic Understanding : Researchers can capture the complexity of human behavior and experiences, including emotions, motivations, and interpersonal dynamics.
- Useful for Small Sample Sizes : Qualitative research can be effective with small sample sizes when a deep understanding of a specific group or context is required.
- Complementary to Quantitative Research : It can complement quantitative research by providing qualitative insights that help explain or interpret numerical data.
- Validity and Authenticity : Qualitative research often focuses on establishing the validity and authenticity of findings, emphasizing the importance of rigor and transparency in the research process.
Disadvantages of Qualitative Research
- Subjectivity : Qualitative research is subjective in nature, and findings can be influenced by the researcher's biases, interpretations, and values.
- Limited Generalizability : The small sample sizes and context-specific nature of qualitative research may limit the generalizability of findings to broader populations or contexts.
- Time-Consuming : Qualitative research can be time-consuming, as it involves data collection methods such as interviews, participant observation, and content analysis, which require significant time and effort.
- Data Analysis Complexity : Analyzing qualitative data can be complex, requiring skills in coding, thematic analysis, and interpretation. It can be challenging to ensure intercoder reliability.
- Resource-Intensive : Qualitative research may require more resources than quantitative research, particularly when conducting in-depth interviews or ethnographic fieldwork.
- Ethical Considerations : Researchers must navigate ethical considerations, such as informed consent, confidentiality, and ensuring the well-being of participants, which can be complex in qualitative studies.
- Interpretation Challenges : Qualitative research findings are open to interpretation, and different researchers may draw different conclusions from the same data.
- Limited Quantification : Qualitative research does not produce numerical data, which can make it challenging to quantify and compare findings across studies.
- Potential for Researcher Influence : Researchers may inadvertently influence participant responses or behaviors through their presence or questioning, leading to potential bias.
- Difficulty in Sampling : Choosing a representative sample can be challenging in qualitative research, as the emphasis is on depth rather than breadth.
In practice, the choice between qualitative and quantitative research methods depends on the research objectives, questions, and the nature of the phenomenon being studied.
Often, researchers use mixed methods, combining both qualitative and quantitative approaches, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of a research topic.
Conclusion of Pros and Cons of Qualitative Research Method
In conclusion, qualitative research offers several advantages, such as capturing rich, detailed data, providing flexibility in data collection methods, and allowing for exploratory studiesfrom market research, focus group, interviews with follow-up questions and open-ended questions by the interviewer.
However, it also has limitations, including small sample sizes, subjective data analysis, resource-intensiveness, and challenges in establishing validity and reliability, as in contrast from quantitative methods with quantitative data.
Therefore, researchers should consider both the strengths and weaknesses of qualitative research and advantages and disadvantages of quantitative research approach when selecting the appropriate type of research methodology for their study.
By understanding these advantages and disadvantages, researchers can make informed decisions and maximize the potential of qualitative research in generating meaningful insights.
Read more here on how to write a Master Thesis .

Privacy Overview
16 Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Qualitative Research Methods
Qualitative research is the process of natural inquisitiveness which wants to find an in-depth understanding of specific social phenomena within a regular setting. It is a process that seeks to find out why people act the way that they do in specific situations. By relying on the direct experiences that each person has every day, it becomes possible to define the meaning of a choice – or even a life.
Researchers who use the qualitative process are looking at multiple methods of inquiry to review human-related activities. This process is a way to measure the very existence of humanity. Multiple options are available to complete the work, including discourse analysis, biographies, case studies, and various other theories.
This process results in three primary areas of focus, which are individual actions, overall communication, and cultural influence. Each option must make the common assumption that knowledge is subjective instead of objective, which means the researchers must learn from their participants to understand what is valuable and what is not in their studies.
List of the Pros of Qualitative Research
1. Qualitative research is a very affordable method of research. Qualitative research is one of the most affordable ways to glean information from individuals who are being studied. Focus groups tend to be the primary method of collecting information using this process because it is fast and effective. Although there are research studies that require an extensive period of observation to produce results, using a group interview session can produce usable information in under an hour. That means you can proceed faster with the ideas you wish to pursue when compared to other research methods.
2. Qualitative research provides a predictive element. The data which researchers gather when using the qualitative research process provides a predictive element to the project. This advantage occurs even though the experiences or perspectives of the individuals participating in the research can vary substantially from person-to-person. The goal of this work is not to apply the information to the general public, but to understand how specific demographics react in situations where there are challenges to face. It is a process which allows for product development to occur because the pain points of the population have been identified.
3. Qualitative research focuses on the details of personal choice. The qualitative research process looks at the purpose of the decision that an individual makes as the primary information requiring collection. It does not take a look at the reasons why someone would decide to make the choices that they do in the first place. Other research methods preferred to look at the behavior, but this method wants to know the entire story behind each individual choice so that the entire population or society can benefit from the process.
4. Qualitative research uses fluid operational structures. The qualitative research process relies on data gathering based on situations that researchers are watching and experiencing personally. Instead of relying on a specific framework to collect and preserve information under rigid guidelines, this process finds value in the human experience. This method makes it possible to include the intricacies of the human experience with the structures required to find conclusions that are useful to the demographics involved – and possible to the rest of society as well.
5. Qualitative research uses individual choices as workable data. When we have an understanding of why individual choices occurred, then we can benefit from the diversity that the human experience provides. Each unique perspective makes it possible for every other person to gather more knowledge about a situation because there are differences to examine. It is a process which allows us to discover more potential outcomes because there is more information present from a variety of sources. Researchers can then take the perspectives to create guidelines that others can follow if they find themselves stuck in a similar situation.
6. Qualitative research is an open-ended process. One of the most significant advantages of qualitative research is that it does not rely on specific deadlines, formats, or questions to create a successful outcome. This process allows researchers to ask open-ended questions whenever they feel it is appropriate because there may be more data to collect. There are not the same time elements involved in this process either, as qualitative research can continue indefinitely until those working on the project feel like there is nothing more to glean from the individuals participating.
Because of this unique structure, researchers can look for data points that other methods might overlook because a greater emphasis is often placed on the interview or observational process with firm deadlines.
7. Qualitative research works to remove bias from its collected information. Unconscious bias is a significant factor in every research project because it relies on the ability of the individuals involved to control their thoughts, emotions, and reactions. Everyone has preconceived notions and stereotypes about specific demographics and nationalities which can influence the data collected. No one is 100% immune to this process. The format of qualitative research allows for these judgments to be set aside because it prefers to look at the specific structures behind each choice of person makes.
This research method also collects information about the events which lead up to a specific decision instead of trying to examine what happens after the fact. That’s why this advantage allows the data to be more accurate compared to the other research methods which are in use.
8. Qualitative research provides specific insight development. The average person tends to make a choice based on comfort, convenience, or both. We also tend to move forward in our circumstances based on what we feel is comfortable to our spiritual, moral, or ethical stances. Every form of communication that we use becomes a potential foundation for researchers to understand the demographics of humanity in better ways. By looking at the problems we face in everyday situations, it becomes possible to discover new insights that can help us to solve do you need problems which can come up. It is a way for researchers to understand the context of what happens in society instead of only looking at the outcomes.
9. Qualitative research requires a smaller sample size. Qualitative research studies wrap up faster that other methods because a smaller sample size is possible for data collection with this method. Participants can answer questions immediately, creating usable and actionable information that can lead to new ideas. This advantage makes it possible to move forward with confidence in future choices because there is added predictability to the results which are possible.
10. Qualitative research provides more useful content. Authenticity is highly demanded in today’s world because there is no better way to understand who we are as an individual, a community, or a society. Qualitative research works hard to understand the core concepts of how each participant defines themselves without the influence of outside perspectives. It wants to see how people structure their lives, and then take that data to help solve whatever problems they might have. Although no research method can provide guaranteed results, there is always some type of actionable information present with this approach.
List of the Cons of Qualitative Research
1. Qualitative research creates subjective information points. The quality of the information collected using the qualitative research process can sometimes be questionable. This approach requires the researchers to connect all of the data points which they gather to find the answers to their questions. That means the results are dependent upon the skills of those involved to read the non-verbal cues of each participate, understand when and where follow-up questions are necessary, and remember to document each response. Because individuals can interpret this data in many different ways, there can sometimes be differences in the conclusion because each researcher has a different take on what they receive.
2. Qualitative research can involve significant levels of repetition. Although the smaller sample sizes found in qualitative research can be an advantage, this structure can also be a problem when researchers are trying to collect a complete data profile for a specific demographic. Multiple interviews and discovery sessions become necessary to discover what the potential consequences of a future choice will be. When you only bring in a handful of people to discuss a situation, then these individuals may not offer a complete representation of the group being studied. Without multiple follow-up sessions with other participants, there is no way to prove the authenticity of the information collected.
3. Qualitative research is difficult to replicate. The only way that research can turn into fact is through a process of replication. Other researchers must be able to come to the similar conclusions after the initial project publishers the results. Because the nature of this work is subjective, finding opportunities to duplicate the results are quite rare. The scope of information which a project collects is often limited, which means there is always some doubt found in the data. That is why you will often see a margin of error percentage associated with research that uses this method. Because it never involves every potential member of a demographic, it will always be incomplete.
4. Qualitative research relies on the knowledge of the researchers. The only reason why opportunities are available in the first place when using qualitative research is because there are researchers involved which have expertise that relates to the subject matter being studied. When interviewers are unfamiliar with industry concepts, then it is much more challenging to identify follow-up opportunities that would be if the individual conducting the session was familiar with the ideas under discussion. There is no way to correctly interpret the data if the perspective of the researcher is skewed by a lack of knowledge.
5. Qualitative research does not offer statistics. The goal of qualitative research is to seek out moments of commonality. That means you will not find statistical data within the results. It looks to find specific areas of concern or pain points that are usable to the organization funding to research in the first place. The amount of data collected using this process can be extreme, but there is no guarantee that it will ever be usable. You do not have the same opportunities to compare information as you would with other research methods.
6. Qualitative research still requires a significant time investment. It is true that there are times when the qualitative research process is significantly faster than other methods. There is also the disadvantage in the fact that the amount of time necessary to collect accurate data can be unpredictable using this option. It may take months, years, or even decades to complete a research project if there is a massive amount of data to review. That means the researchers involve must make a long-term commitment to the process to ensure the results can be as accurate as possible.
These qualitative research pros and cons review how all of us come to the choices that we make each day. When researchers understand why we come to specific conclusions, then it becomes possible to create new goods and services that can make our lives easier. This process then concludes with solutions which can benefit a significant majority of the people, leading to better best practices in the future.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Qualitative study.
Steven Tenny ; Janelle M. Brannan ; Grace D. Brannan .
Affiliations
Last Update: September 18, 2022 .
- Introduction
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems. [1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences, perceptions, and behavior. It answers the hows and whys instead of how many or how much. It could be structured as a stand-alone study, purely relying on qualitative data or it could be part of mixed-methods research that combines qualitative and quantitative data. This review introduces the readers to some basic concepts, definitions, terminology, and application of qualitative research.
Qualitative research at its core, ask open-ended questions whose answers are not easily put into numbers such as ‘how’ and ‘why’. [2] Due to the open-ended nature of the research questions at hand, qualitative research design is often not linear in the same way quantitative design is. [2] One of the strengths of qualitative research is its ability to explain processes and patterns of human behavior that can be difficult to quantify. [3] Phenomena such as experiences, attitudes, and behaviors can be difficult to accurately capture quantitatively, whereas a qualitative approach allows participants themselves to explain how, why, or what they were thinking, feeling, and experiencing at a certain time or during an event of interest. Quantifying qualitative data certainly is possible, but at its core, qualitative data is looking for themes and patterns that can be difficult to quantify and it is important to ensure that the context and narrative of qualitative work are not lost by trying to quantify something that is not meant to be quantified.
However, while qualitative research is sometimes placed in opposition to quantitative research, where they are necessarily opposites and therefore ‘compete’ against each other and the philosophical paradigms associated with each, qualitative and quantitative work are not necessarily opposites nor are they incompatible. [4] While qualitative and quantitative approaches are different, they are not necessarily opposites, and they are certainly not mutually exclusive. For instance, qualitative research can help expand and deepen understanding of data or results obtained from quantitative analysis. For example, say a quantitative analysis has determined that there is a correlation between length of stay and level of patient satisfaction, but why does this correlation exist? This dual-focus scenario shows one way in which qualitative and quantitative research could be integrated together.
Examples of Qualitative Research Approaches
Ethnography
Ethnography as a research design has its origins in social and cultural anthropology, and involves the researcher being directly immersed in the participant’s environment. [2] Through this immersion, the ethnographer can use a variety of data collection techniques with the aim of being able to produce a comprehensive account of the social phenomena that occurred during the research period. [2] That is to say, the researcher’s aim with ethnography is to immerse themselves into the research population and come out of it with accounts of actions, behaviors, events, etc. through the eyes of someone involved in the population. Direct involvement of the researcher with the target population is one benefit of ethnographic research because it can then be possible to find data that is otherwise very difficult to extract and record.
Grounded Theory
Grounded Theory is the “generation of a theoretical model through the experience of observing a study population and developing a comparative analysis of their speech and behavior.” [5] As opposed to quantitative research which is deductive and tests or verifies an existing theory, grounded theory research is inductive and therefore lends itself to research that is aiming to study social interactions or experiences. [3] [2] In essence, Grounded Theory’s goal is to explain for example how and why an event occurs or how and why people might behave a certain way. Through observing the population, a researcher using the Grounded Theory approach can then develop a theory to explain the phenomena of interest.
Phenomenology
Phenomenology is defined as the “study of the meaning of phenomena or the study of the particular”. [5] At first glance, it might seem that Grounded Theory and Phenomenology are quite similar, but upon careful examination, the differences can be seen. At its core, phenomenology looks to investigate experiences from the perspective of the individual. [2] Phenomenology is essentially looking into the ‘lived experiences’ of the participants and aims to examine how and why participants behaved a certain way, from their perspective . Herein lies one of the main differences between Grounded Theory and Phenomenology. Grounded Theory aims to develop a theory for social phenomena through an examination of various data sources whereas Phenomenology focuses on describing and explaining an event or phenomena from the perspective of those who have experienced it.
Narrative Research
One of qualitative research’s strengths lies in its ability to tell a story, often from the perspective of those directly involved in it. Reporting on qualitative research involves including details and descriptions of the setting involved and quotes from participants. This detail is called ‘thick’ or ‘rich’ description and is a strength of qualitative research. Narrative research is rife with the possibilities of ‘thick’ description as this approach weaves together a sequence of events, usually from just one or two individuals, in the hopes of creating a cohesive story, or narrative. [2] While it might seem like a waste of time to focus on such a specific, individual level, understanding one or two people’s narratives for an event or phenomenon can help to inform researchers about the influences that helped shape that narrative. The tension or conflict of differing narratives can be “opportunities for innovation”. [2]
Research Paradigm
Research paradigms are the assumptions, norms, and standards that underpin different approaches to research. Essentially, research paradigms are the ‘worldview’ that inform research. [4] It is valuable for researchers, both qualitative and quantitative, to understand what paradigm they are working within because understanding the theoretical basis of research paradigms allows researchers to understand the strengths and weaknesses of the approach being used and adjust accordingly. Different paradigms have different ontology and epistemologies . Ontology is defined as the "assumptions about the nature of reality” whereas epistemology is defined as the “assumptions about the nature of knowledge” that inform the work researchers do. [2] It is important to understand the ontological and epistemological foundations of the research paradigm researchers are working within to allow for a full understanding of the approach being used and the assumptions that underpin the approach as a whole. Further, it is crucial that researchers understand their own ontological and epistemological assumptions about the world in general because their assumptions about the world will necessarily impact how they interact with research. A discussion of the research paradigm is not complete without describing positivist, postpositivist, and constructivist philosophies.
Positivist vs Postpositivist
To further understand qualitative research, we need to discuss positivist and postpositivist frameworks. Positivism is a philosophy that the scientific method can and should be applied to social as well as natural sciences. [4] Essentially, positivist thinking insists that the social sciences should use natural science methods in its research which stems from positivist ontology that there is an objective reality that exists that is fully independent of our perception of the world as individuals. Quantitative research is rooted in positivist philosophy, which can be seen in the value it places on concepts such as causality, generalizability, and replicability.
Conversely, postpositivists argue that social reality can never be one hundred percent explained but it could be approximated. [4] Indeed, qualitative researchers have been insisting that there are “fundamental limits to the extent to which the methods and procedures of the natural sciences could be applied to the social world” and therefore postpositivist philosophy is often associated with qualitative research. [4] An example of positivist versus postpositivist values in research might be that positivist philosophies value hypothesis-testing, whereas postpositivist philosophies value the ability to formulate a substantive theory.
Constructivist
Constructivism is a subcategory of postpositivism. Most researchers invested in postpositivist research are constructivist as well, meaning they think there is no objective external reality that exists but rather that reality is constructed. Constructivism is a theoretical lens that emphasizes the dynamic nature of our world. “Constructivism contends that individuals’ views are directly influenced by their experiences, and it is these individual experiences and views that shape their perspective of reality”. [6] Essentially, Constructivist thought focuses on how ‘reality’ is not a fixed certainty and experiences, interactions, and backgrounds give people a unique view of the world. Constructivism contends, unlike in positivist views, that there is not necessarily an ‘objective’ reality we all experience. This is the ‘relativist’ ontological view that reality and the world we live in are dynamic and socially constructed. Therefore, qualitative scientific knowledge can be inductive as well as deductive.” [4]
So why is it important to understand the differences in assumptions that different philosophies and approaches to research have? Fundamentally, the assumptions underpinning the research tools a researcher selects provide an overall base for the assumptions the rest of the research will have and can even change the role of the researcher themselves. [2] For example, is the researcher an ‘objective’ observer such as in positivist quantitative work? Or is the researcher an active participant in the research itself, as in postpositivist qualitative work? Understanding the philosophical base of the research undertaken allows researchers to fully understand the implications of their work and their role within the research, as well as reflect on their own positionality and bias as it pertains to the research they are conducting.
Data Sampling
The better the sample represents the intended study population, the more likely the researcher is to encompass the varying factors at play. The following are examples of participant sampling and selection: [7]
- Purposive sampling- selection based on the researcher’s rationale in terms of being the most informative.
- Criterion sampling-selection based on pre-identified factors.
- Convenience sampling- selection based on availability.
- Snowball sampling- the selection is by referral from other participants or people who know potential participants.
- Extreme case sampling- targeted selection of rare cases.
- Typical case sampling-selection based on regular or average participants.
Data Collection and Analysis
Qualitative research uses several techniques including interviews, focus groups, and observation. [1] [2] [3] Interviews may be unstructured, with open-ended questions on a topic and the interviewer adapts to the responses. Structured interviews have a predetermined number of questions that every participant is asked. It is usually one on one and is appropriate for sensitive topics or topics needing an in-depth exploration. Focus groups are often held with 8-12 target participants and are used when group dynamics and collective views on a topic are desired. Researchers can be a participant-observer to share the experiences of the subject or a non-participant or detached observer.
While quantitative research design prescribes a controlled environment for data collection, qualitative data collection may be in a central location or in the environment of the participants, depending on the study goals and design. Qualitative research could amount to a large amount of data. Data is transcribed which may then be coded manually or with the use of Computer Assisted Qualitative Data Analysis Software or CAQDAS such as ATLAS.ti or NVivo. [8] [9] [10]
After the coding process, qualitative research results could be in various formats. It could be a synthesis and interpretation presented with excerpts from the data. [11] Results also could be in the form of themes and theory or model development.
Dissemination
To standardize and facilitate the dissemination of qualitative research outcomes, the healthcare team can use two reporting standards. The Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research or COREQ is a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. [12] The Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is a checklist covering a wider range of qualitative research. [13]
Examples of Application
Many times a research question will start with qualitative research. The qualitative research will help generate the research hypothesis which can be tested with quantitative methods. After the data is collected and analyzed with quantitative methods, a set of qualitative methods can be used to dive deeper into the data for a better understanding of what the numbers truly mean and their implications. The qualitative methods can then help clarify the quantitative data and also help refine the hypothesis for future research. Furthermore, with qualitative research researchers can explore subjects that are poorly studied with quantitative methods. These include opinions, individual's actions, and social science research.
A good qualitative study design starts with a goal or objective. This should be clearly defined or stated. The target population needs to be specified. A method for obtaining information from the study population must be carefully detailed to ensure there are no omissions of part of the target population. A proper collection method should be selected which will help obtain the desired information without overly limiting the collected data because many times, the information sought is not well compartmentalized or obtained. Finally, the design should ensure adequate methods for analyzing the data. An example may help better clarify some of the various aspects of qualitative research.
A researcher wants to decrease the number of teenagers who smoke in their community. The researcher could begin by asking current teen smokers why they started smoking through structured or unstructured interviews (qualitative research). The researcher can also get together a group of current teenage smokers and conduct a focus group to help brainstorm factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke (qualitative research).
In this example, the researcher has used qualitative research methods (interviews and focus groups) to generate a list of ideas of both why teens start to smoke as well as factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke. Next, the researcher compiles this data. The research found that, hypothetically, peer pressure, health issues, cost, being considered “cool,” and rebellious behavior all might increase or decrease the likelihood of teens starting to smoke.
The researcher creates a survey asking teen participants to rank how important each of the above factors is in either starting smoking (for current smokers) or not smoking (for current non-smokers). This survey provides specific numbers (ranked importance of each factor) and is thus a quantitative research tool.
The researcher can use the results of the survey to focus efforts on the one or two highest-ranked factors. Let us say the researcher found that health was the major factor that keeps teens from starting to smoke, and peer pressure was the major factor that contributed to teens to start smoking. The researcher can go back to qualitative research methods to dive deeper into each of these for more information. The researcher wants to focus on how to keep teens from starting to smoke, so they focus on the peer pressure aspect.
The researcher can conduct interviews and/or focus groups (qualitative research) about what types and forms of peer pressure are commonly encountered, where the peer pressure comes from, and where smoking first starts. The researcher hypothetically finds that peer pressure often occurs after school at the local teen hangouts, mostly the local park. The researcher also hypothetically finds that peer pressure comes from older, current smokers who provide the cigarettes.
The researcher could further explore this observation made at the local teen hangouts (qualitative research) and take notes regarding who is smoking, who is not, and what observable factors are at play for peer pressure of smoking. The researcher finds a local park where many local teenagers hang out and see that a shady, overgrown area of the park is where the smokers tend to hang out. The researcher notes the smoking teenagers buy their cigarettes from a local convenience store adjacent to the park where the clerk does not check identification before selling cigarettes. These observations fall under qualitative research.
If the researcher returns to the park and counts how many individuals smoke in each region of the park, this numerical data would be quantitative research. Based on the researcher's efforts thus far, they conclude that local teen smoking and teenagers who start to smoke may decrease if there are fewer overgrown areas of the park and the local convenience store does not sell cigarettes to underage individuals.
The researcher could try to have the parks department reassess the shady areas to make them less conducive to the smokers or identify how to limit the sales of cigarettes to underage individuals by the convenience store. The researcher would then cycle back to qualitative methods of asking at-risk population their perceptions of the changes, what factors are still at play, as well as quantitative research that includes teen smoking rates in the community, the incidence of new teen smokers, among others. [14] [15]
Qualitative research functions as a standalone research design or in combination with quantitative research to enhance our understanding of the world. Qualitative research uses techniques including structured and unstructured interviews, focus groups, and participant observation to not only help generate hypotheses which can be more rigorously tested with quantitative research but also to help researchers delve deeper into the quantitative research numbers, understand what they mean, and understand what the implications are. Qualitative research provides researchers with a way to understand what is going on, especially when things are not easily categorized. [16]
- Issues of Concern
As discussed in the sections above, quantitative and qualitative work differ in many different ways, including the criteria for evaluating them. There are four well-established criteria for evaluating quantitative data: internal validity, external validity, reliability, and objectivity. The correlating concepts in qualitative research are credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability. [4] [11] The corresponding quantitative and qualitative concepts can be seen below, with the quantitative concept is on the left, and the qualitative concept is on the right:
- Internal validity--- Credibility
- External validity---Transferability
- Reliability---Dependability
- Objectivity---Confirmability
In conducting qualitative research, ensuring these concepts are satisfied and well thought out can mitigate potential issues from arising. For example, just as a researcher will ensure that their quantitative study is internally valid so should qualitative researchers ensure that their work has credibility.
Indicators such as triangulation and peer examination can help evaluate the credibility of qualitative work.
- Triangulation: Triangulation involves using multiple methods of data collection to increase the likelihood of getting a reliable and accurate result. In our above magic example, the result would be more reliable by also interviewing the magician, back-stage hand, and the person who "vanished." In qualitative research, triangulation can include using telephone surveys, in-person surveys, focus groups, and interviews as well as surveying an adequate cross-section of the target demographic.
- Peer examination: Results can be reviewed by a peer to ensure the data is consistent with the findings.
‘Thick’ or ‘rich’ description can be used to evaluate the transferability of qualitative research whereas using an indicator such as an audit trail might help with evaluating the dependability and confirmability.
- Thick or rich description is a detailed and thorough description of details, the setting, and quotes from participants in the research. [5] Thick descriptions will include a detailed explanation of how the study was carried out. Thick descriptions are detailed enough to allow readers to draw conclusions and interpret the data themselves, which can help with transferability and replicability.
- Audit trail: An audit trail provides a documented set of steps of how the participants were selected and the data was collected. The original records of information should also be kept (e.g., surveys, notes, recordings).
One issue of concern that qualitative researchers should take into consideration is observation bias. Here are a few examples:
- Hawthorne effect: The Hawthorne effect is the change in participant behavior when they know they are being observed. If a researcher was wanting to identify factors that contribute to employee theft and tells the employees they are going to watch them to see what factors affect employee theft, one would suspect employee behavior would change when they know they are being watched.
- Observer-expectancy effect: Some participants change their behavior or responses to satisfy the researcher's desired effect. This happens in an unconscious manner for the participant so it is important to eliminate or limit transmitting the researcher's views.
- Artificial scenario effect: Some qualitative research occurs in artificial scenarios and/or with preset goals. In such situations, the information may not be accurate because of the artificial nature of the scenario. The preset goals may limit the qualitative information obtained.
- Clinical Significance
Qualitative research by itself or combined with quantitative research helps healthcare providers understand patients and the impact and challenges of the care they deliver. Qualitative research provides an opportunity to generate and refine hypotheses and delve deeper into the data generated by quantitative research. Qualitative research does not exist as an island apart from quantitative research, but as an integral part of research methods to be used for the understanding of the world around us. [17]
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Qualitative research is important for all members of the health care team as all are affected by qualitative research. Qualitative research may help develop a theory or a model for health research that can be further explored by quantitative research. Much of the qualitative research data acquisition is completed by numerous team members including social works, scientists, nurses, etc. Within each area of the medical field, there is copious ongoing qualitative research including physician-patient interactions, nursing-patient interactions, patient-environment interactions, health care team function, patient information delivery, etc.
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Steven Tenny declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Janelle Brannan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Grace Brannan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Tenny S, Brannan JM, Brannan GD. Qualitative Study. [Updated 2022 Sep 18]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Suicidal Ideation. [StatPearls. 2024] Suicidal Ideation. Harmer B, Lee S, Duong TVH, Saadabadi A. StatPearls. 2024 Jan
- Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. [Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022] Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1; 2(2022). Epub 2022 Feb 1.
- Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012). [Phys Biol. 2013] Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012). Foffi G, Pastore A, Piazza F, Temussi PA. Phys Biol. 2013 Aug; 10(4):040301. Epub 2013 Aug 2.
- Review Evidence Brief: The Effectiveness Of Mandatory Computer-Based Trainings On Government Ethics, Workplace Harassment, Or Privacy And Information Security-Related Topics [ 2014] Review Evidence Brief: The Effectiveness Of Mandatory Computer-Based Trainings On Government Ethics, Workplace Harassment, Or Privacy And Information Security-Related Topics Peterson K, McCleery E. 2014 May
- Review Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review. [Campbell Syst Rev. 2021] Review Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review. Mugellini G, Della Bella S, Colagrossi M, Isenring GL, Killias M. Campbell Syst Rev. 2021 Jun; 17(2):e1173. Epub 2021 May 24.
Recent Activity
- Qualitative Study - StatPearls Qualitative Study - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

Online Plagiarism Checker for Academic Assignments
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for your Academic Assignments
Get it proofread now
Free Express Delivery to All Places in Canada
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Research paper structure & sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Qualitative Research – Advantages & Disadvantages
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Qualitative research, as a unique methodology , facilitates the gathering of information while simultaneously investigating the rationale behind the provided data. This piece illuminates the applications of this form of research, its primary users, the strategies for qualitative data acquisition and analysis, along with the principal benefits and potential drawbacks associated with this research approach.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Qualitative Research – In a Nutshell
- 2 Qualitative Research – Definition
- 3 Qualitative Research Methods
- 4 Qualitative Research: How to Analyze the Data?
- 5 Pros & cons
Qualitative Research – In a Nutshell
- Qualitative research collects complex data based on participants’ opinions and the reasons behind these opinions.
- It can be used in any field but is found most commonly in subjects like the social sciences.
- The sample sizes are generally smaller than in other forms of research.
- The most popular methods are interviews, focus groups, and ethnographic research.
- Data analysis generally divided into developing codes, identifying themes, and creating summaries.
Qualitative Research – Definition
Qualitative research involves gathering and then analyzing data that is recorded non-numerically, such as video, audio, or text. The data is used to understand complex concepts, experiences, and opinions. Qualitative research is used to develop new insights into problems or to generate new research ideas.
As such, qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research . This latter form of research utilizes numerical data to search for patterns and perform statistical analysis.
Qualitative data can be used in any field, but it is most commonly employed by the humanities and social sciences. This research method is popular in subjects like anthropology, history, sociology, and so on.
Qualitative Research Methods
The most common types of qualitative research are interviews, focus groups, and ethnographic research.
1. Interviews Interviews are the most common form of qualitative research. They are generally conducted on a one-to-one basis and are purely conversational. During the interview, the interviewer aims to obtain detailed answers on specific topics from the research participant.
Interviews are an effective tool for gathering data on people’s beliefs and their motivations. Skilled researchers are capable of asking useful follow-up questions to gain more data on useful topics.
Interviews can be performed face-to-face, over the phone, or via a video chat application. They generally last anywhere from 30 minutes to over two hours. Face-to-face interviews grant the most opportunities for gathering data since they provide opportunities to gain extra information from things like body language.
2. Focus Groups A focus group involves gathering around six to ten people and asking them questions as a collective. Participants should be chosen based on their knowledge or experience with the research question.
Focus groups ask questions centered around ‘how’, ‘what’ and ‘why’. One of the advantages of these groups is that researchers can ask an initial question and then let the ensuing conversation between group members occur naturally.
Focus groups are one of the more difficult to organize qualitative research methods since they require a large number of people with similar experiences to be available at the same time. However, focus groups are an effective way of letting research participants explore concepts that are too complex for individuals to grasp effectively.
3. Ethnographic Research
Ethnographic research is the most in-depth form of qualitative research and involved studying people in their natural environment. Researchers aim to observe their audiences while remaining undetected by adapting to their audiences’ environments.
Instead of relying on people’s testimonies about their experiences, ethnographic research seeks to interpret these experiences directly as they occur. Studying audiences this way makes ethnographic research one of the slowest ways to collect data. A study of this type can require anything from a few days to a few years. Ethnographic research is also heavily dependent on the capabilities of the researcher to infer useful data from their observations.
Qualitative Research: How to Analyze the Data?
Qualitative data analysis can be carried out using these three steps:
1. Develop and Apply Codes. Codes can be thought of as categories of data. Every created code needs a meaningful title consisting of a word or short phrase. Events, behaviors, activities meanings, and more can all be assigned one of these three types of code.
Open coding. The initial sorting of all the raw data into some kind of order. Axial coding. Creating links between categories of codes. Selective coding. Connecting categories together in order to formulate a story.
2. Identify Themes, Patterns, and Relationships
There are no universal methods for identifying patterns in qualitative research data. However, there is a set of techniques for identifying common themes and relationships with reference to the previously created codes. These are the most popular techniques for interpreting qualitative data:
- Scanning the data for words or phrases that are commonly used during responses.
- Comparing results from primary data gathering sessions with results in secondary sources and analyzing the differences between the two sets.
- Scanning the data for words or phrases that were expected but did not appear. The lack of a discussion about an aspect also provides information.
- Comparing the primary research data and comparing it to phenomena from a different area using relevant metaphors and analogs.
3. Summarize the Data
The final step is connecting the research data to the hypotheses. Highlight major themes and trends by utilizing noteworthy quotations from the data as well as possible contradictions.
One of the key aspects of qualitative data is that there is no unified, formal approach to collecting and analyzing data. Each research project will require its own set of methods and techniques. The key lies in examining the unique requirements of each project and adjusting the research methodology accordingly.
Pros & cons
Who uses qualitative research.
This type of research is used by people who seek subjective answers that will allow them to explore ideas. It is often used to explore the meaning behind quantitative data. Alternatively, qualitative data can provide direction before quantitative research is utilized.
What are the advantages of qualitative research?
Qualitative research focuses on gaining as much data as possible from a relatively small sample size. It is a more flexible approach than quantitative research since it enables participants to express themselves while providing data.
What are the main approaches of qualitative research?
The most common approaches to qualitative data gathering include action research, ethnography, grounded theory, narrative research, and phenomenological research.
How big should the sample size be?
Qualitative research studies seek between 20 and 60 participants. The research results are used to provide actionable direction and cannot be quantified.
How many questions should be asked?
The number of questions depends on the research format. When leading a focus group, there should be three to eight questions that guide the discussion.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
Home Essay Examples Science Qualitative Research
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Research Methodologies: Qualitative Research
- Category Science
- Subcategory Scientific Method
- Topic Qualitative Research

“Qualitative research is multi-method in focus, involving an interpretive and naturalistic approach to its subject matter” (Denzin & Lincoln 2000). The research aims at constructing empirically-oriented theories through an inductive approach. It illustrates multiple perspectives combining subjective and social aspects. Qualitative research acquires the data in-depth, without an external structure of responses from the research subjects. Thus, the data obtained is rich in detail, though in an unstructured format; which results in the complexity of analysis. The data collection significantly involves determining sample design as it’s the foundation. The data is obtained from certain qualitative methods –personal interview/ discussions, focus groups, case study research, ethnographic research, and qualitative observation. Meanwhile, the ethical dilemma is crucial in qualitative research due to the factors such as informed consent, confidentiality, justice to participant responses, and issues of harm while collecting data. Comment by Rony, Sidharth (2018): abstract
This study proffers a critical review of qualitative research, particularly in ‘case study’ and ‘focus groups. It analyses the advantages and disadvantages of the methodologies as utilized in the following papers. I intend to examine the papers, (Hengstler, et al., 2016) and (James, et al., 2013) Comment by HP: Add title of papers?
Our writers can write you a new plagiarism-free essay on any topic
Focus Group
Historically, the technique was developed during World War II to examine the responses of the population towards radio programs (Stewart & Shamdasani 1990). The focus group is a small selected section of people, whose responses are studied for the purpose of research. It is led by a trained moderator who is equipped to garner information.
The groups include natural groups (existing in everyday lives), artificial group (selected for the research purpose), and real groups. Furthermore, it’s classified into homogenous and heterogeneous groups. The homogenous group is an analogous sample with the same background whereas heterogeneous contain dissimilar groups with different characteristics.
It generally consists of about six to eight participants (Guest et al. 2016), mediating discussions between the groups. It is imperative for the interviewer to possess the characteristics such as empathy, good listening, and flexibility. Such focus groups lead people into group discussions, in which the dynamics of the group will be of highlighted. The merit of such kind of group discussions allows opinions and thought patterns which are expressed in our every day lives unlike the interviews that are relatively formal and well-thought.
- The group interviews are cost-effective yet produce data in large amount.
- The benefit of using “discussion stimulus” like relevant inventories, images, short film, PPTs, and lectures.
- The provision for audio recording provides an accurate summary. Technically, the selection of correct microphones enables high-quality record videos. The omnidirectional microphones are well-suited to record the focus groups.
- The dynamics of the group while developing arguments/ points as found in group discussion is an essential source of knowledge/ data collection.
- The heterogeneity of a group especially facilitates dynamics in the discussion with myriad perspectives at hand.
- The corrections by the group in terms of their viewpoints aid to polish the individual opinion and further validating statements.
- A discussion allows identifying the process of problem-solving.
Disadvantages
- The questions may be limited due to the inefficiency in taking notes.
- The problem of contradictory viewpoints during group discussion may cause confusion within the researcher, further adhering to conclude with subjective/ personal decisions.
- Severe heterogeneity may pave way for deficiency in ‘common’ discussions.
- The opinions/ views of a biased moderator may affect the discussions process and content of the group.
- The unfamiliarity of members with one another under the chosen discussion group may sometimes deteriorate the efficiency of the discussions. It also leads to domination of one member while others hold inhibitions to express themselves.
- Unlike the personal interviews, it is unfavorable to formulate a definite framework and pattern in the group discussions.
- It is also exasperating to elucidate the tasks and conducts for the moderators beyond single group.
- In a semi-structured interview, it is difficult to mediate between the course of the discussion and the moderator’s input.
Case study is a predominant research approach that emphasis on careful study of a unit/ section. It emerged in several disciplines as suitable for large studies in tracing the theories of individual perceptions and hegemonic discourses; and thereby achieving descriptive research goals. It majorly depended on time and even produced desired historical accounts. Qualitative researchers asserted case studies are identified in configuration context and path-dependent. The study utilizes a “case-centered” approach instead of “variable centered”, advocating in-depth strategies such as “thick description” and “process tracing” (ed. Given 2008). It also stresses on the internal complexity and nuances of a case as the researches may be influential to the real world.
Though the observation is highly focused on a single phenomenon/ unit, it doesn’t necessarily confine it’s observation towards a sole case observation. However, the case-study researchers are clearly aware of the observations’ limitations. The case studies usually exempt those research studies having temporal and spatial variations or limitations, allowing to research on a specific hostage population.
The case studies are categorized into naturalism, positivism, and constructivism types. The naturalists attempt to produce pragmatic and elaborate knowledge whereas the positivist creates models or propositions enabling conjectures for the study. Constructivists focus at empirical evidence supplying to theoretical discourses. Thus, case studies principally offer a medium for theoretical constructions for many types of research.
- The collected data was available for strong comparisons about the in-depth analysis, offering it a natural, empirical totality along the notion of theoretical consistency.
- The naturalist case study reveals the authentic nature of those phenomena or unit through a close analysis. Therefore, offering a descriptive narrative through an inductive approach.
- The positivist case study presents an objective reality, unveiling the correspondences between the individual case and the selected population. Example: – Cross case analysis, dividing multiple cases, temporal sequencing,
- The constructivist approach uses the interpretive technique, narrowing the disparities between the concrete observations and abstract concepts.
- The findings of those research generalizations could be later accessed by other researchers.
- The information collected can serve as questionnaires or schedules to later deduce conclusions.
- The generalizations inferred may be false as the information collection do not follow any guidelines.
- It consumes time as it extends to longer time periods even including the history of the research topic and therefore, multiplying the expenditures.
- It inculcates various assumptions, holding a tendency to obtain unrealistic data.
Analysis of Focus Group: “The impact of automation on pharmacy staff experience of workplace stressors”
Rapid demands for health- care sectors have been flourishing due to an expanding aging population. However, the associated pressures led to the incapability of the staffs to deliver efficient services to the patients. The introduction of an automated dispensing system claimed to improve the nature of work among pharmacists. The impact of automation on the pharmacy staff experience was aimed in the paper by examining the effect of the installation of an automated dispensing system (ADS). Survey responses of pre-and post- automation were conducted on pharmacy staff in the National Health Service Hospital in Wales, UK. The paper identifies a quantitative relation and corroborates it with the qualitative focus group approach.
In order to observe the pre-and post- automation regarding staffs’ gender, mean age, and mean contracted hours of work, the quantitative method of questionnaire and surveys were utilized. Descriptive statistics was developed to analyze the respondent demographics using the occupational stressor questionnaire. This method mediated evidence that occupational stress to be less during post- automation in contrast to the pre-automation period.
The focus group methodology was undertaken to understand the opinions/ standpoints of the participants on the impact of automation. The study focused on four focus groups, 1. two groups allocated to check the technicians, 2. pharmacists, and 3. group based on post-automation staff experiences and occupational stressors. The homogeneity of the group having similar occupational backgrounds, i.e., pharmacists and accredited checking technicians (ACTs) aided to produce a large amount of information. The data were collected regarding the workload, dispensing errors, job autonomy, related stress and satisfaction, work-life conflict, and discussion to enhance career growth. Such homogeneity benefitted upon concentrated attentiveness, which necessarily stimulated an effective group discussion. The discussions were audio-recorded and prepared into notes by an assistant moderator that later obliterated any kind of biased interpretations by the researcher. The transcribed audio-recording is an illustrative resource use throughout the research, beginning from data collection until its conclusion. However, audio recording is bound by ethical formalities. The ethics review board has made it mandatory that recordings are restricted of usage without informed consent from the participants. The recordings must be preserved safely. Further, no discussion can be recorded without the permission of respective participants and the researcher must hold an ethical obligation in case of denial of permission. Even it may affect the data quality, it must be necessarily avoided.
Furthermore, the information collected were further scrutinized under the ‘framework analysis’ since its approach focused on specific questions in a pre-designed sample within a stipulated time limit. Despite its merits, the anonymity made it impossible to carry comparisons between the responses of pre-and post- automation of the questionnaire data.
Importantly, ethics in research is significant as it’s fundamental in protecting the respondent/participants’ information. The data collected through such techniques as sampling, focus groups, interviews must ensure voluntary informed consent and confidentiality. While transcription, the researchers maintained the anonymity of the participants as they shared public-sensitive and personal information. Though the primary interviewers were familiar of the respondents, its autonomy was compelled to censorship while transcribing. In the paper, the implementation of anonymity has provided authentic viewpoints as they could express without inhibitions or any form of threats. Simultaneously, what researchers perhaps fail to understand is that sometimes the respondents may want their information to be acknowledged and seek ownership of their contributions.
It is imperative for the qualitative research to receive an ethics certificate approved by the institutional review board for their research accessibility. The approval will specify the sites data collection, recruitment and benefits of participants, process of consent, and confidentiality. This study was approved by the North East Wales Research Ethics Committee and NHS Trust Research.
The major limitation of this methodology is its information being narrowed to a single focus group i.e. the experiences of pharmacy staff from a single hospital. The effect of ADS may be different to other hospital staff. In addition, the sample size was relatively meager as merely pharmacists from dispensaries were eligible to participate. The participation within the group was again reduced to less than 95%, which may also have caused the process and content to be slightly biased. Moreover, the reliability of both questionnaire focus group discussions may be questionable as the pharmacy staff remained reluctant to share their opinions on the impact of the ADS on occupational stressors.
Analysis of Case study: “Applied Artificial Intelligence and trust in the case of autonomous vehicles and medical assistance devices” by Monika Hengstler, Ellen Enkel, Selina Duelli
The emerging diverse applications such as autonomous vehicles and medical device assistance utilize the inherent artificial intelligence technology. The nine case studies were analyzed in the transportation and medical industries to illustrate trust as a main constituent of AI. The paper elaborates the symbiotic relations of trust towards technology, innovating firms, and its communications. The democratic development of the AI process is inferred by providing approaches to enhance trust. The paper has utilized case study as the main research approach and done a cross-case analysis of multiple case studies. The major strength of the case study is its flexibility to combine various such research techniques such as discussions and semi-structured interviews to further complement the data collection for the research.
To identify an appropriate case study, the researchers were required to select certain participants depending on its criteria. As the study essentially focuses on trust and is mainly examined through case studies, the theoretical sampling or purposive sampling allowed to particularly selection such AI industries within the given criteria, unlike random sampling. Further, the nine suitable case studies were obtained through semi-structured Interviews that offered a detailed overview of transportation and medical industry case studies. It provided a description of the applications and status of the market introduction. The case studies included semi/ fully autonomous cars, Future Trucks project, Deutsche Bahn semi/ fully autonomous trains, VAG Nurnberg underground train, IBM’s Watson (cognitive system), HP’s automated fraud detection, AiCure, and Fraunhofer IPA. This diversified case study presented comparability and enhanced the potential of sub-methods utilized in the paper.
The semi-structured interview is advantageous as it enabled the ‘subjective theory’ wherein the interviewees held a complex amount of knowledge about their industry. The prior knowledge about their own sector allowed them to be informal in their language. The informality as innate is an important key in the method as it established a rapport and security wherein the industries weren’t threatened of the companies’ confidentiality, policies, and time pressures. It led to companies declaring their contribution for the research work, having nine case studies. In fact, the semi-structured interview allowed to structure the interviews into three main categories using questionnaires that were theory-driven or hypotheses-oriented questions, but fundamentally open-ended. However, each of the interviews took about 30- 65 minutes from March to April, showing a high level of time consumption. But, the provision of recording interviews eliminated this drawback and aided inaccurate data collection.
Importantly, the cross-case analysis serves the purpose of mobilizing between individual case studies to produce case knowledge, compare/contrast case studies, and thereby led to conclude the discussions. The cross-case analysis was performed in the paper in order to examine the trust-building strategies in the innovating firms. In this particular study, the analysis combines with a heuristic case study wherein a theory development was instrumental. It infers the concepts such as performance, process, and purpose that formed the foundation of trust in automation. The insights gained from a cross-case analysis included the notions of operational safety, data security, and privacy protection. Those three determinants were identified as major elements influencing trust in technology. This led to construct validity and especially allowing it as concretely reliable data due to its multitude number of case study evidences. Furthermore, the cross-case analysis revealed the significant disparity between the applied technology and society, especially influencing the trust in technology. Techniques such as cross-case examination and within-case examination along with literature review help ensure external validity. Despite the biased tendencies of this research approach, it is an important tool to researchers.
This research puts forth a variety of ethical challenges as this type of research is directly associated to social policies and real-time activities. Here, the ethical issues are prominent with the methodologies as much as it is with the subject matter. For instance, the AiCure application used in the health care sector uses much sensitive health information of patients logged to it, therefore it provides video tutorials to narrate their privacy-related information of the application. Similarly, the methods like semi-structured interviews require confidentiality to be maintained along with identifying whom to acknowledge.
My research
Industrial revolutions have always been significant steps in a society’s economic evolution. Starting from transitioning of manufacturing processes, industrial revolutions have changed society’s way of life, thinking, and economic transactions. Each of these revolutions changed the way of life from that of their previous era but was not without its risks. The fourth industrial revolution, which focuses on cyber-physical systems which greatly enhance Industrial process automation, is expected to increase the efficiency of the manufacturing sector. But with large-scale affordable automation, the need for human labor has reduced. This can lead to a loss of employment opportunities. In the United States, within a gap of 17 years from 2000, even though production has increased by 30 percent, the number of manufacturing jobs has reduced by 20 percent. This anomaly makes it necessary to find ways by which the risk of unemployment can be prevented. Comment by Rony, Sidharth (2018): Harvard referencing
The Ph.D. project centers upon understanding the risks involved in Industrial Automation and strategies of the industry to mitigate those risks involved. It can be dealt with two-fold: Pieces of training can be provided by the industries to their employees to substitute or complement automation in the field. By training as substitution, I mean, some industries can choose to develop the skill set of human capital to improve the efficacy but not opt for automation. By training as a compliment, it intends that a different industry can choose to empower the human capital to adapt to automation. I wish to lead a case study research on those two different set of industries from the employees’ perspective. In the first case study, I shall analyze the employee satisfaction when they receive training as substitution and the second case study looks at understanding the same when they receive training as a compliment. I shall further conduct a cross-case analysis of the two different case studies to compare the two different contexts of training and its effectiveness. Comment by Rony, Sidharth (2018): need to rephrase
The study aimed to critically understand the advantages and disadvantages of research methodologies based on two vital research paradigms, in relation to automation. The elaboration of case study and focus group enables to inform research designs, enhancing its visibility under the qualitative research study. It also discusses in length, of several methods and techniques of qualitative data collection, analysis, and its generation.
Although ethical aspects aren’t a methodology, it becomes an important element in research. The notion of ethics combines aspects of ethical inquiries, its approaches, ethical codes, and committees. Also, it was found how an ethical framework ensures equality among the participants and the researchers.
- Hengstler, M., Enkel, E. & Duelli, S., 2016. Applied artificial intelligence and trust—The case of autonomous vehicles and medical assistance devices. Technological Forecasting & Social Change, Issue 105, pp. 105-120.
- James, K. L. et al., 2013. The impact of automation on pharmacy staff experience of workplace stressors. International Journal of Pharmacy Practice, Issue 21, p. 105–116.
- Guest, G., Namey, E. & McKenna, K., 2016, ‘How Many Focus Groups Are Enough? Building an Evidence Base for Non-probability Sample Sizes’, SAGE journals, viewed on 10 February 2019, from https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1525822X16639015.
- Denzin, N. K. & Lincoln, Y.S., 2000, ‘Handbook of Qualitative Research, Thousand Oaks, SAGE.
- Stewart, D. & Shamdasani, P.,1990. ‘Focus groups: Theory and Practice’. London, SAGE.
- Given, L.M. ed., 2008, Qualitative Research Methods. California, SAGE.
We have 98 writers available online to start working on your essay just NOW!
Related Topics
Related essays.
By clicking "Send essay" you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
By clicking "Receive essay" you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
We can edit this one and make it plagiarism-free in no time
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Interesting
- Scholarships
- UGC-CARE Journals
Advantages and Disadvantages of Qualitative Research Methodologies

Table of contents
advantages of qualitative research methodologies, disadvantages of qualitative research methodologies, 10 key points of qualitative research methodologies.
Qualitative research methodologies offer unique advantages and disadvantages that researchers should consider when choosing their approach
- Authentic Answers : Qualitative research allows participants to express their thoughts and views freely, leading to authentic responses.
- Trustworthiness : Information gathered in qualitative studies is based on participants’ thoughts and experiences, making it more trustworthy and accurate.
- In-depth Questioning : Qualitative methods like focus groups and interviews enable researchers to delve deeply into topics, providing rich insights.
- Flexibility : Qualitative research offers a flexible approach, allowing researchers to adapt questions or settings quickly to improve responses.
- Creativity : This methodology encourages creativity and genuine ideas to be collected from specific demographics, fostering innovation.
- Not Statistically Representative : Qualitative research does not provide statistical representation, limiting the ability to make quantitative comparisons.
- Data Duplication : Responses in qualitative research cannot usually be measured, leading to potential data duplication over time.
- Time-Consuming : Qualitative research can be time-consuming and labor-intensive due to the detailed nature of data collection and analysis.
- Difficulty in Replicating Results : Due to the subjective nature of qualitative data, replicating results can be challenging, impacting the reliability of findings.
- Dependence on Researchers’ Experience : The quality of data collected in qualitative research relies heavily on the experience and skills of the researchers involved.
- Rich understanding: Uncovers the “why” behind phenomena through detailed exploration of experiences and motivations.
- Flexibility: Adapts to emerging themes during research, ensuring relevant data collection.
- Exploring new areas: Suitable for initial investigations in under-researched fields.
- Individual focus: Captures the nuances of individual experiences within diverse populations.
- Subjectivity: Researcher interpretation can introduce bias, requiring careful design and reporting.
- Limited generalizability: Findings may not apply to entire populations due to smaller sample sizes.
- Time-consuming: Data collection, analysis, and interpretation can be lengthy compared to quantitative methods.
- Potential for influence: Researcher presence can influence participant responses, requiring objectivity.
- Complementary approach: Often used alongside quantitative methods for a more comprehensive understanding.
- Valuable insights: Offers valuable qualitative data for understanding complex human behavior and experiences
In conclusion, while qualitative research methodologies offer valuable insights into human behavior and social interactions, researchers must carefully weigh these advantages and disadvantages to ensure the effectiveness and reliability of their studies
- advantages of qualitative research
- disadvantages of qualitative research
- human behavior research
- qualitative analysis
- qualitative data
- qualitative research
- research design
- Research Methodology
- research methods
- Social Science Research
Scientists Are Working on THIS in 2024? Top 10 Research Areas Revealed!
14 websites to download research paper for free – 2024, how to write a research paper research paper format, email subscription.

iLovePhD is a research education website to know updated research-related information. It helps researchers to find top journals for publishing research articles and get an easy manual for research tools. The main aim of this website is to help Ph.D. scholars who are working in various domains to get more valuable ideas to carry out their research. Learn the current groundbreaking research activities around the world, love the process of getting a Ph.D.
WhatsApp Channel
Join iLovePhD WhatsApp Channel Now!
Contact us: [email protected]
Copyright © 2019-2024 - iLovePhD
- Artificial intelligence
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What is Secondary Research? | Definition, Types, & Examples
What is Secondary Research? | Definition, Types, & Examples
Published on January 20, 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on January 12, 2024.
Secondary research is a research method that uses data that was collected by someone else. In other words, whenever you conduct research using data that already exists, you are conducting secondary research. On the other hand, any type of research that you undertake yourself is called primary research .
Secondary research can be qualitative or quantitative in nature. It often uses data gathered from published peer-reviewed papers, meta-analyses, or government or private sector databases and datasets.
Table of contents
When to use secondary research, types of secondary research, examples of secondary research, advantages and disadvantages of secondary research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions.
Secondary research is a very common research method, used in lieu of collecting your own primary data. It is often used in research designs or as a way to start your research process if you plan to conduct primary research later on.
Since it is often inexpensive or free to access, secondary research is a low-stakes way to determine if further primary research is needed, as gaps in secondary research are a strong indication that primary research is necessary. For this reason, while secondary research can theoretically be exploratory or explanatory in nature, it is usually explanatory: aiming to explain the causes and consequences of a well-defined problem.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Secondary research can take many forms, but the most common types are:
Statistical analysis
Literature reviews, case studies, content analysis.
There is ample data available online from a variety of sources, often in the form of datasets. These datasets are often open-source or downloadable at a low cost, and are ideal for conducting statistical analyses such as hypothesis testing or regression analysis .
Credible sources for existing data include:
- The government
- Government agencies
- Non-governmental organizations
- Educational institutions
- Businesses or consultancies
- Libraries or archives
- Newspapers, academic journals, or magazines
A literature review is a survey of preexisting scholarly sources on your topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant themes, debates, and gaps in the research you analyze. You can later apply these to your own work, or use them as a jumping-off point to conduct primary research of your own.
Structured much like a regular academic paper (with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion), a literature review is a great way to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject. It is usually qualitative in nature and can focus on a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. A case study is a great way to utilize existing research to gain concrete, contextual, and in-depth knowledge about your real-world subject.
You can choose to focus on just one complex case, exploring a single subject in great detail, or examine multiple cases if you’d prefer to compare different aspects of your topic. Preexisting interviews , observational studies , or other sources of primary data make for great case studies.
Content analysis is a research method that studies patterns in recorded communication by utilizing existing texts. It can be either quantitative or qualitative in nature, depending on whether you choose to analyze countable or measurable patterns, or more interpretive ones. Content analysis is popular in communication studies, but it is also widely used in historical analysis, anthropology, and psychology to make more semantic qualitative inferences.
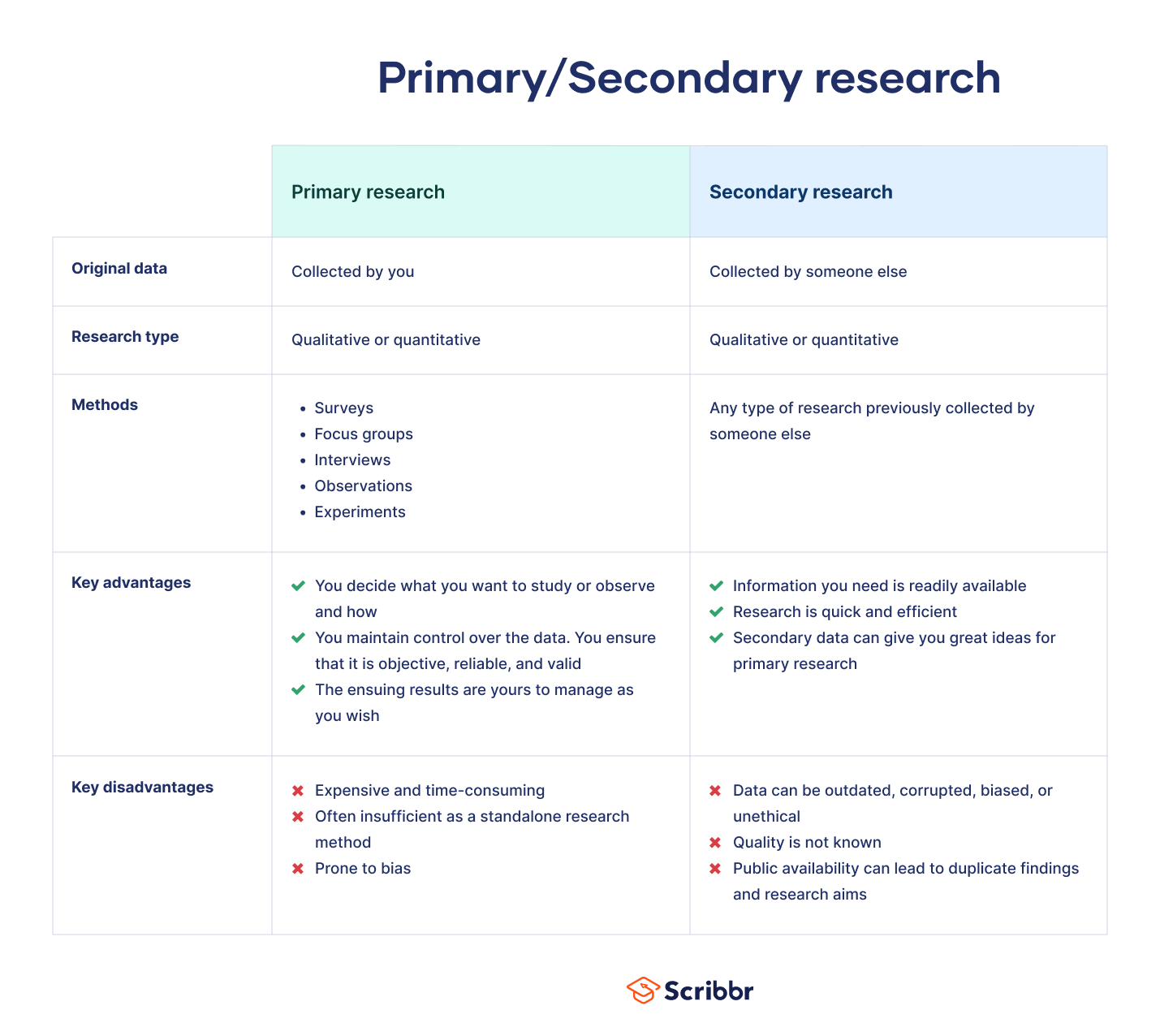
Secondary research is a broad research approach that can be pursued any way you’d like. Here are a few examples of different ways you can use secondary research to explore your research topic .
Secondary research is a very common research approach, but has distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of secondary research
Advantages include:
- Secondary data is very easy to source and readily available .
- It is also often free or accessible through your educational institution’s library or network, making it much cheaper to conduct than primary research .
- As you are relying on research that already exists, conducting secondary research is much less time consuming than primary research. Since your timeline is so much shorter, your research can be ready to publish sooner.
- Using data from others allows you to show reproducibility and replicability , bolstering prior research and situating your own work within your field.
Disadvantages of secondary research
Disadvantages include:
- Ease of access does not signify credibility . It’s important to be aware that secondary research is not always reliable , and can often be out of date. It’s critical to analyze any data you’re thinking of using prior to getting started, using a method like the CRAAP test .
- Secondary research often relies on primary research already conducted. If this original research is biased in any way, those research biases could creep into the secondary results.
Many researchers using the same secondary research to form similar conclusions can also take away from the uniqueness and reliability of your research. Many datasets become “kitchen-sink” models, where too many variables are added in an attempt to draw increasingly niche conclusions from overused data . Data cleansing may be necessary to test the quality of the research.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
A systematic review is secondary research because it uses existing research. You don’t collect new data yourself.
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyze a large amount of readily-available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how it is generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
George, T. (2024, January 12). What is Secondary Research? | Definition, Types, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/secondary-research/
Largan, C., & Morris, T. M. (2019). Qualitative Secondary Research: A Step-By-Step Guide (1st ed.). SAGE Publications Ltd.
Peloquin, D., DiMaio, M., Bierer, B., & Barnes, M. (2020). Disruptive and avoidable: GDPR challenges to secondary research uses of data. European Journal of Human Genetics , 28 (6), 697–705. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-020-0596-x
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, primary research | definition, types, & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, what is a case study | definition, examples & methods, what is your plagiarism score.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
9. Unseen data can disappear during the qualitative research process. The amount of trust that is placed on the researcher to gather, and then draw together, the unseen data that is offered by a provider is enormous. The research is dependent upon the skill of the researcher being able to connect all the dots.
Organizations can use a variety of quantitative data-gathering methods to track productivity. In turn, this can help: To rank employees and work units. To award raises or promotions. To measure and justify termination or disciplining of staff. To measure productivity. To measure group/individual targets.
Keywords: qualitative and quantitative research, advantages, disadvantages, testing and assessment 1. Introduction Qualitative and quantitative research approaches and methods are usually found to be utilised rather frequently in different disciplines of education such as sociology, psychology, history, and so on. Concerning the research
There are many advantages and disadvantages of using a qualitative research when investigating our social world. Qualitative research can provide a more in depth and detailed account of why things happen and how they affect the people concerned. On the other hand though, qualitative research deals with small numbers and fewer people are studied ...
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Qualitative research instead focuses on obtaining deep and rich data and aims to identify the specific contents, dynamics, and processes inherent within the phenomenon and situation. There are clear distinctions in the advantages, disadvantages, and goals of quantitative and qualitative research.
Disadvantages of Qualitative Research Methodologies. Qualitative research does not provide statistical representation, limiting the ability to make quantitative comparisons. 1 . Data Duplication. Responses in qualitative research cannot usually be measured, leading to potential data duplication over time. 2 .
However structural biases are common in this approach. Data collection and sampling in qualitative research is more detailed and subjective. Considering the different advantages and disadvantages of the two research approaches, I would go for the quantitative over qualitative research. References. Miles, M., & Huberman, A. (1994).
Disadvantages of Qualitative Research. Subjectivity: Qualitative research is subjective in nature, and findings can be influenced by the researcher's biases, interpretations, and values. Limited Generalizability: The small sample sizes and context-specific nature of qualitative research may limit the generalizability of findings to broader ...
Through the analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of each method, it becomes possible to formulate a more accurate, informed and complete choice. Mind map representation for qualitative ...
Qualitative research study has lots of advantages, but just like all good things, there are disadvantages to it as well. One major disadvantage in qualitative research is that it cannot quantify how many participants will answer one way or another, which can make it difficult to create a solid statistic on the participants.
It is a way for researchers to understand the context of what happens in society instead of only looking at the outcomes. 9. Qualitative research requires a smaller sample size. Qualitative research studies wrap up faster that other methods because a smaller sample size is possible for data collection with this method.
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems.[1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants ...
As qualitative research has evolved, researchers in the field have struggled with a persistent tension between a need for both methodological flexibility and structure (Holloway & Todres, 2003).In the development of qualitative research, three major methodologies are discussed most frequently and are often viewed as foundational: phenomenology, ethnography, and grounded theory (Holloway ...
Qualitative Research - Definition. Qualitative research involves gathering and then analyzing data that is recorded non-numerically, such as video, audio, or text. The data is used to understand complex concepts, experiences, and opinions. Qualitative research is used to develop new insights into problems or to generate new research ideas.
There are many advantages and disadvantages of using a qualitative research when investigating our social world. Qualitative research can provide a more in depth and detailed account of why things happen and how they affect the people concerned. On the other hand though, qualitative research deals with small numbers and fewer people are studied ...
Advantages and disadvantages of primary research. Primary research is a great choice for many research projects, but it has distinct advantages and disadvantages. Advantages of primary research. Advantages include: The ability to conduct really tailored, thorough research, down to the "nitty-gritty" of your topic. You decide what you want ...
The study aimed to critically understand the advantages and disadvantages of research methodologies based on two vital research paradigms, in relation to automation. The elaboration of case study and focus group enables to inform research designs, enhancing its visibility under the qualitative research study.
The research also uses qualitative research design because of its multi-dimensional and plurastic respect to paradigms. Moreover, it allows different researchers to conduct a similar research and yet produce different results as it incorporates people's emotions, prejudice and perceptions. Major disadvantages of qualitative research stem.
Ethnography is a type of qualitative research that involves immersing yourself in a particular community or organization to observe their behavior and interactions up close. The word "ethnography" also refers to the written report of the research that the ethnographer produces afterwards. Ethnography is a flexible research method that ...
Advantages: Authentic Answers: Qualitative research allows participants to express their thoughts and views freely, leading to authentic responses. Trustworthiness: Information gathered in qualitative studies is based on participants' thoughts and experiences, making it more trustworthy and accurate. In-depth Questioning: Qualitative methods ...
This essay will initially present the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative research and briefly quantitative research. It will then go on to critique a qualitative research article yet due to the word count only several factors of this will be critiqued and the article is by Wills ' et al (2005).
It often uses data gathered from published peer-reviewed papers, meta-analyses, ... Advantages and disadvantages of secondary research. Secondary research is a very common research approach, but has distinct advantages and disadvantages. ... Qualitative Secondary Research: A Step-By-Step Guide (1st ed.). SAGE Publications Ltd.