

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of exploration. In an era marked by rapid technological advancements and an ever-expanding knowledge base, refining the process of generating research recommendations becomes imperative.
But, what is a research recommendation?
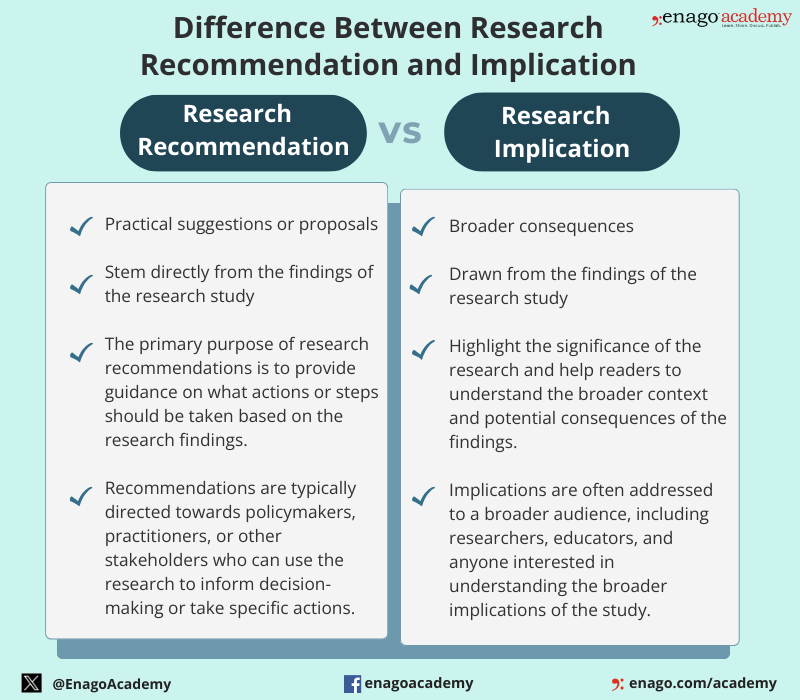
Research recommendations are suggestions or advice provided to researchers to guide their study on a specific topic . They are typically given by experts in the field. Research recommendations are more action-oriented and provide specific guidance for decision-makers, unlike implications that are broader and focus on the broader significance and consequences of the research findings. However, both are crucial components of a research study.
Difference Between Research Recommendations and Implication
Although research recommendations and implications are distinct components of a research study, they are closely related. The differences between them are as follows:
Types of Research Recommendations
Recommendations in research can take various forms, which are as follows:
These recommendations aim to assist researchers in navigating the vast landscape of academic knowledge.
Let us dive deeper to know about its key components and the steps to write an impactful research recommendation.
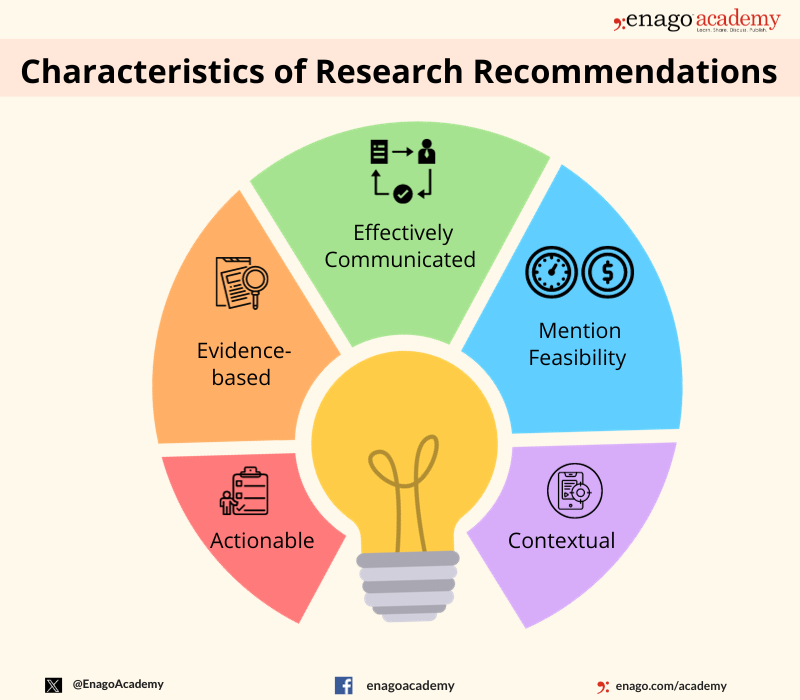
Key Components of Research Recommendations
The key components of research recommendations include defining the research question or objective, specifying research methods, outlining data collection and analysis processes, presenting results and conclusions, addressing limitations, and suggesting areas for future research. Here are some characteristics of research recommendations:
Research recommendations offer various advantages and play a crucial role in ensuring that research findings contribute to positive outcomes in various fields. However, they also have few limitations which highlights the significance of a well-crafted research recommendation in offering the promised advantages.
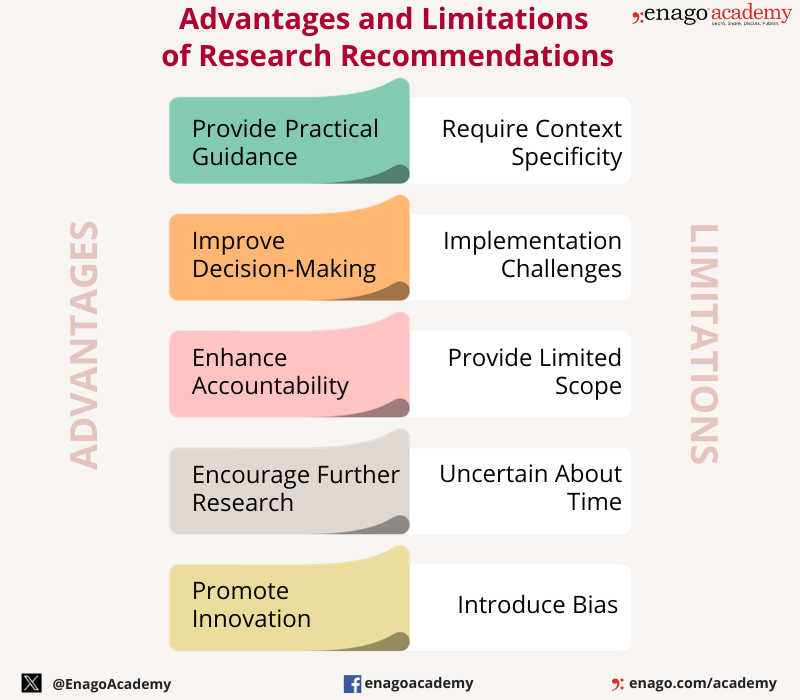
The importance of research recommendations ranges in various fields, influencing policy-making, program development, product development, marketing strategies, medical practice, and scientific research. Their purpose is to transfer knowledge from researchers to practitioners, policymakers, or stakeholders, facilitating informed decision-making and improving outcomes in different domains.
How to Write Research Recommendations?
Research recommendations can be generated through various means, including algorithmic approaches, expert opinions, or collaborative filtering techniques. Here is a step-wise guide to build your understanding on the development of research recommendations.
1. Understand the Research Question:
Understand the research question and objectives before writing recommendations. Also, ensure that your recommendations are relevant and directly address the goals of the study.
2. Review Existing Literature:
Familiarize yourself with relevant existing literature to help you identify gaps , and offer informed recommendations that contribute to the existing body of research.
3. Consider Research Methods:
Evaluate the appropriateness of different research methods in addressing the research question. Also, consider the nature of the data, the study design, and the specific objectives.
4. Identify Data Collection Techniques:
Gather dataset from diverse authentic sources. Include information such as keywords, abstracts, authors, publication dates, and citation metrics to provide a rich foundation for analysis.
5. Propose Data Analysis Methods:
Suggest appropriate data analysis methods based on the type of data collected. Consider whether statistical analysis, qualitative analysis, or a mixed-methods approach is most suitable.
6. Consider Limitations and Ethical Considerations:
Acknowledge any limitations and potential ethical considerations of the study. Furthermore, address these limitations or mitigate ethical concerns to ensure responsible research.
7. Justify Recommendations:
Explain how your recommendation contributes to addressing the research question or objective. Provide a strong rationale to help researchers understand the importance of following your suggestions.
8. Summarize Recommendations:
Provide a concise summary at the end of the report to emphasize how following these recommendations will contribute to the overall success of the research project.
By following these steps, you can create research recommendations that are actionable and contribute meaningfully to the success of the research project.
Download now to unlock some tips to improve your journey of writing research recommendations.
Example of a Research Recommendation
Here is an example of a research recommendation based on a hypothetical research to improve your understanding.
Research Recommendation: Enhancing Student Learning through Integrated Learning Platforms
Background:
The research study investigated the impact of an integrated learning platform on student learning outcomes in high school mathematics classes. The findings revealed a statistically significant improvement in student performance and engagement when compared to traditional teaching methods.
Recommendation:
In light of the research findings, it is recommended that educational institutions consider adopting and integrating the identified learning platform into their mathematics curriculum. The following specific recommendations are provided:
- Implementation of the Integrated Learning Platform:
Schools are encouraged to adopt the integrated learning platform in mathematics classrooms, ensuring proper training for teachers on its effective utilization.
- Professional Development for Educators:
Develop and implement professional programs to train educators in the effective use of the integrated learning platform to address any challenges teachers may face during the transition.
- Monitoring and Evaluation:
Establish a monitoring and evaluation system to track the impact of the integrated learning platform on student performance over time.
- Resource Allocation:
Allocate sufficient resources, both financial and technical, to support the widespread implementation of the integrated learning platform.
By implementing these recommendations, educational institutions can harness the potential of the integrated learning platform and enhance student learning experiences and academic achievements in mathematics.
This example covers the components of a research recommendation, providing specific actions based on the research findings, identifying the target audience, and outlining practical steps for implementation.
Using AI in Research Recommendation Writing
Enhancing research recommendations is an ongoing endeavor that requires the integration of cutting-edge technologies, collaborative efforts, and ethical considerations. By embracing data-driven approaches and leveraging advanced technologies, the research community can create more effective and personalized recommendation systems. However, it is accompanied by several limitations. Therefore, it is essential to approach the use of AI in research with a critical mindset, and complement its capabilities with human expertise and judgment.
Here are some limitations of integrating AI in writing research recommendation and some ways on how to counter them.
1. Data Bias
AI systems rely heavily on data for training. If the training data is biased or incomplete, the AI model may produce biased results or recommendations.
How to tackle: Audit regularly the model’s performance to identify any discrepancies and adjust the training data and algorithms accordingly.
2. Lack of Understanding of Context:
AI models may struggle to understand the nuanced context of a particular research problem. They may misinterpret information, leading to inaccurate recommendations.
How to tackle: Use AI to characterize research articles and topics. Employ them to extract features like keywords, authorship patterns and content-based details.
3. Ethical Considerations:
AI models might stereotype certain concepts or generate recommendations that could have negative consequences for certain individuals or groups.
How to tackle: Incorporate user feedback mechanisms to reduce redundancies. Establish an ethics review process for AI models in research recommendation writing.
4. Lack of Creativity and Intuition:
AI may struggle with tasks that require a deep understanding of the underlying principles or the ability to think outside the box.
How to tackle: Hybrid approaches can be employed by integrating AI in data analysis and identifying patterns for accelerating the data interpretation process.
5. Interpretability:
Many AI models, especially complex deep learning models, lack transparency on how the model arrived at a particular recommendation.
How to tackle: Implement models like decision trees or linear models. Provide clear explanation of the model architecture, training process, and decision-making criteria.
6. Dynamic Nature of Research:
Research fields are dynamic, and new information is constantly emerging. AI models may struggle to keep up with the rapidly changing landscape and may not be able to adapt to new developments.
How to tackle: Establish a feedback loop for continuous improvement. Regularly update the recommendation system based on user feedback and emerging research trends.
The integration of AI in research recommendation writing holds great promise for advancing knowledge and streamlining the research process. However, navigating these concerns is pivotal in ensuring the responsible deployment of these technologies. Researchers need to understand the use of responsible use of AI in research and must be aware of the ethical considerations.
Exploring research recommendations plays a critical role in shaping the trajectory of scientific inquiry. It serves as a compass, guiding researchers toward more robust methodologies, collaborative endeavors, and innovative approaches. Embracing these suggestions not only enhances the quality of individual studies but also contributes to the collective advancement of human understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
The purpose of recommendations in research is to provide practical and actionable suggestions based on the study's findings, guiding future actions, policies, or interventions in a specific field or context. Recommendations bridges the gap between research outcomes and their real-world application.
To make a research recommendation, analyze your findings, identify key insights, and propose specific, evidence-based actions. Include the relevance of the recommendations to the study's objectives and provide practical steps for implementation.
Begin a recommendation by succinctly summarizing the key findings of the research. Clearly state the purpose of the recommendation and its intended impact. Use a direct and actionable language to convey the suggested course of action.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
How to Effectively Cite a PDF (APA, MLA, AMA, and Chicago Style)
The pressure to “publish or perish” is a well-known reality for academics, striking fear into…

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
Using AI for Journal Selection — Simplifying your academic publishing journey in the smart way
Strategic journal selection plays a pivotal role in maximizing the impact of one’s scholarly work.…

- Career Corner
Recognizing the signs: A guide to overcoming academic burnout
As the sun set over the campus, casting long shadows through the library windows, Alex…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Reassessing the Lab Environment to Create an Equitable and Inclusive Space
The pursuit of scientific discovery has long been fueled by diverse minds and perspectives. Yet…

Simplifying the Literature Review Journey — A comparative analysis of 6 AI summarization tools
Imagine having to skim through and read mountains of research papers and books, only to…
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
Digital Citations: A comprehensive guide to citing of websites in APA, MLA, and CMOS…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
Published on 15 September 2022 by Tegan George .
Recommendations in research are a crucial component of your discussion section and the conclusion of your thesis , dissertation , or research paper .
As you conduct your research and analyse the data you collected , perhaps there are ideas or results that don’t quite fit the scope of your research topic . Or, maybe your results suggest that there are further implications of your results or the causal relationships between previously-studied variables than covered in extant research.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What should recommendations look like, building your research recommendation, how should your recommendations be written, recommendation in research example, frequently asked questions about recommendations.
Recommendations for future research should be:
- Concrete and specific
- Supported with a clear rationale
- Directly connected to your research
Overall, strive to highlight ways other researchers can reproduce or replicate your results to draw further conclusions, and suggest different directions that future research can take, if applicable.
Relatedly, when making these recommendations, avoid:
- Undermining your own work, but rather offer suggestions on how future studies can build upon it
- Suggesting recommendations actually needed to complete your argument, but rather ensure that your research stands alone on its own merits
- Using recommendations as a place for self-criticism, but rather as a natural extension point for your work
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
There are many different ways to frame recommendations, but the easiest is perhaps to follow the formula of research question conclusion recommendation. Here’s an example.
Conclusion An important condition for controlling many social skills is mastering language. If children have a better command of language, they can express themselves better and are better able to understand their peers. Opportunities to practice social skills are thus dependent on the development of language skills.
As a rule of thumb, try to limit yourself to only the most relevant future recommendations: ones that stem directly from your work. While you can have multiple recommendations for each research conclusion, it is also acceptable to have one recommendation that is connected to more than one conclusion.
These recommendations should be targeted at your audience, specifically toward peers or colleagues in your field that work on similar topics to yours. They can flow directly from any limitations you found while conducting your work, offering concrete and actionable possibilities for how future research can build on anything that your own work was unable to address at the time of your writing.
See below for a full research recommendation example that you can use as a template to write your own.
The current study can be interpreted as a first step in the research on COPD speech characteristics. However, the results of this study should be treated with caution due to the small sample size and the lack of details regarding the participants’ characteristics.
Future research could further examine the differences in speech characteristics between exacerbated COPD patients, stable COPD patients, and healthy controls. It could also contribute to a deeper understanding of the acoustic measurements suitable for e-health measurements.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
While it may be tempting to present new arguments or evidence in your thesis or disseration conclusion , especially if you have a particularly striking argument you’d like to finish your analysis with, you shouldn’t. Theses and dissertations follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the discussion section and results section .) The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation should include the following:
- A restatement of your research question
- A summary of your key arguments and/or results
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
For a stronger dissertation conclusion , avoid including:
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion…”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g. “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
In a thesis or dissertation, the discussion is an in-depth exploration of the results, going into detail about the meaning of your findings and citing relevant sources to put them in context.
The conclusion is more shorter and more general: it concisely answers your main research question and makes recommendations based on your overall findings.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2022, September 15). How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved 22 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/research-recommendations/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- How to formulate...
How to formulate research recommendations
- Related content
- Peer review
- Polly Brown ( pbrown{at}bmjgroup.com ) , publishing manager 1 ,
- Klara Brunnhuber , clinical editor 1 ,
- Kalipso Chalkidou , associate director, research and development 2 ,
- Iain Chalmers , director 3 ,
- Mike Clarke , director 4 ,
- Mark Fenton , editor 3 ,
- Carol Forbes , reviews manager 5 ,
- Julie Glanville , associate director/information service manager 5 ,
- Nicholas J Hicks , consultant in public health medicine 6 ,
- Janet Moody , identification and prioritisation manager 6 ,
- Sara Twaddle , director 7 ,
- Hazim Timimi , systems developer 8 ,
- Pamela Young , senior programme manager 6
- 1 BMJ Publishing Group, London WC1H 9JR,
- 2 National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence, London WC1V 6NA,
- 3 Database of Uncertainties about the Effects of Treatments, James Lind Alliance Secretariat, James Lind Initiative, Oxford OX2 7LG,
- 4 UK Cochrane Centre, Oxford OX2 7LG,
- 5 Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York, York YO10 5DD,
- 6 National Coordinating Centre for Health Technology Assessment, University of Southampton, Southampton SO16 7PX,
- 7 Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, Edinburgh EH2 1EN,
- 8 Update Software, Oxford OX2 7LG
- Correspondence to: PBrown
- Accepted 22 September 2006
“More research is needed” is a conclusion that fits most systematic reviews. But authors need to be more specific about what exactly is required
Long awaited reports of new research, systematic reviews, and clinical guidelines are too often a disappointing anticlimax for those wishing to use them to direct future research. After many months or years of effort and intellectual energy put into these projects, authors miss the opportunity to identify unanswered questions and outstanding gaps in the evidence. Most reports contain only a less than helpful, general research recommendation. This means that the potential value of these recommendations is lost.
Current recommendations
In 2005, representatives of organisations commissioning and summarising research, including the BMJ Publishing Group, the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, the National Coordinating Centre for Health Technology Assessment, the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence, the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, and the UK Cochrane Centre, met as members of the development group for the Database of Uncertainties about the Effects of Treatments (see bmj.com for details on all participating organisations). Our aim was to discuss the state of research recommendations within our organisations and to develop guidelines for improving the presentation of proposals for further research. All organisations had found weaknesses in the way researchers and authors of systematic reviews and clinical guidelines stated the need for further research. As part of the project, a member of the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination under-took a rapid literature search to identify information on research recommendation models, which found some individual methods but no group initiatives to attempt to standardise recommendations.
Suggested format for research recommendations on the effects of treatments
Core elements.
E Evidence (What is the current state of the evidence?)
P Population (What is the population of interest?)
I Intervention (What are the interventions of interest?)
C Comparison (What are the comparisons of interest?)
O Outcome (What are the outcomes of interest?)
T Time stamp (Date of recommendation)
Optional elements
d Disease burden or relevance
t Time aspect of core elements of EPICOT
s Appropriate study type according to local need
In January 2006, the National Coordinating Centre for Health Technology Assessment presented the findings of an initial comparative analysis of how different organisations currently structure their research recommendations. The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence and the National Coordinating Centre for Health Technology Assessment request authors to present recommendations in a four component format for formulating well built clinical questions around treatments: population, intervention, comparison, and outcomes (PICO). 1 In addition, the research recommendation is dated and authors are asked to provide the current state of the evidence to support the proposal.
Clinical Evidence , although not directly standardising its sections for research recommendations, presents gaps in the evidence using a slightly extended version of the PICO format: evidence, population, intervention, comparison, outcomes, and time (EPICOT). Clinical Evidence has used this inherent structure to feed research recommendations on interventions categorised as “unknown effectiveness” back to the National Coordinating Centre for Health Technology Assessment and for inclusion in the Database of Uncertainties about the Effects of Treatments ( http://www.duets.nhs.uk/ ).
We decided to propose the EPICOT format as the basis for its statement on formulating research recommendations and tested this proposal through discussion and example. We agreed that this set of components provided enough context for formulating research recommendations without limiting researchers. In order for the proposed framework to be flexible and more widely applicable, the group discussed using several optional components when they seemed relevant or were proposed by one or more of the group members. The final outcome of discussions resulted in the proposed EPICOT+ format (box).
A recent BMJ article highlighted how lack of research hinders the applicability of existing guidelines to patients in primary care who have had a stroke or transient ischaemic attack. 2 Most research in the area had been conducted in younger patients with a recent episode and in a hospital setting. The authors concluded that “further evidence should be collected on the efficacy and adverse effects of intensive blood pressure lowering in representative populations before we implement this guidance [from national and international guidelines] in primary care.” Table 1 outlines how their recommendations could be formulated using the EPICOT+ format. The decision on whether additional research is indeed clinically and ethically warranted will still lie with the organisation considering commissioning the research.
Research recommendation based on gap in the evidence identified by a cross sectional study of clinical guidelines for management of patients who have had a stroke
- View inline
Table 2 shows the use of EPICOT+ for an unanswered question on the effectiveness of compliance therapy in people with schizophrenia, identified by the Database of Uncertainties about the Effects of Treatments.
Research recommendation based on a gap in the evidence on treatment of schizophrenia identified by the Database of Uncertainties about the Effects of Treatments
Discussions around optional elements
Although the group agreed that the PICO elements should be core requirements for a research recommendation, intense discussion centred on the inclusion of factors defining a more detailed context, such as current state of evidence (E), appropriate study type (s), disease burden and relevance (d), and timeliness (t).
Initially, group members interpreted E differently. Some viewed it as the supporting evidence for a research recommendation and others as the suggested study type for a research recommendation. After discussion, we agreed that E should be used to refer to the amount and quality of research supporting the recommendation. However, the issue remained contentious as some of us thought that if a systematic review was available, its reference would sufficiently identify the strength of the existing evidence. Others thought that adding evidence to the set of core elements was important as it provided a summary of the supporting evidence, particularly as the recommendation was likely to be abstracted and used separately from the review or research that led to its formulation. In contrast, the suggested study type (s) was left as an optional element.
A research recommendation will rarely have an absolute value in itself. Its relative priority will be influenced by the burden of ill health (d), which is itself dependent on factors such as local prevalence, disease severity, relevant risk factors, and the priorities of the organisation considering commissioning the research.
Similarly, the issue of time (t) could be seen to be relevant to each of the core elements in varying ways—for example, duration of treatment, length of follow-up. The group therefore agreed that time had a subsidiary role within each core item; however, T as the date of the recommendation served to define its shelf life and therefore retained individual importance.
Applicability and usability
The proposed statement on research recommendations applies to uncertainties of the effects of any form of health intervention or treatment and is intended for research in humans rather than basic scientific research. Further investigation is required to assess the applicability of the format for questions around diagnosis, signs and symptoms, prognosis, investigations, and patient preference.
When the proposed format is applied to a specific research recommendation, the emphasis placed on the relevant part(s) of the EPICOT+ format may vary by author, audience, and intended purpose. For example, a recommendation for research into treatments for transient ischaemic attack may or may not define valid outcome measures to assess quality of life or gather data on adverse effects. Among many other factors, its implementation will also depend on the strength of current findings—that is, strong evidence may support a tightly focused recommendation whereas a lack of evidence would result in a more general recommendation.
The controversy within the group, especially around the optional components, reflects the different perspectives of the participating organisations—whether they were involved in commissioning, undertaking, or summarising research. Further issues will arise during the implementation of the proposed format, and we welcome feedback and discussion.
Summary points
No common guidelines exist for the formulation of recommendations for research on the effects of treatments
Major organisations involved in commissioning or summarising research compared their approaches and agreed on core questions
The essential items can be summarised as EPICOT+ (evidence, population, intervention, comparison, outcome, and time)
Further details, such as disease burden and appropriate study type, should be considered as required
We thank Patricia Atkinson and Jeremy Wyatt.
Contributors and sources All authors contributed to manuscript preparation and approved the final draft. NJH is the guarantor.
Competing interests None declared.
- Richardson WS ,
- Wilson MC ,
- Nishikawa J ,
- Hayward RSA
- McManus RJ ,
- Leonardi-Bee J ,
- PROGRESS Collaborative Group
- Warburton E
- Rothwell P ,
- McIntosh AM ,
- Lawrie SM ,
- Stanfield AC
- O'Donnell C ,
- Donohoe G ,
- Sharkey L ,
- Jablensky A ,
- Sartorius N ,
- Ernberg G ,

Undergraduate Research Experiences for STEM Students: Successes, Challenges, and Opportunities (2017)
Chapter: 9 conclusions and recommendations, 9 conclusions and recommendations.
Practitioners designing or improving undergraduate research experiences (UREs) can build on the experiences of colleagues and learn from the increasingly robust literature about UREs and the considerable body of evidence about how students learn. The questions practitioners ask themselves during the design process should include questions about the goals of the campus, program, faculty, and students. Other factors to consider when designing a URE include the issues raised in the conceptual framework for learning and instruction, the available resources, how the program or experience will be evaluated or studied, and how to design the program from the outset to incorporate these considerations, as well as how to build in opportunities to improve the experience over time in light of new evidence. (Some of these topics are addressed in Chapter 8 .)
Colleges and universities that offer or wish to offer UREs to their students should undertake baseline evaluations of their current offerings and create plans to develop a culture of improvement in which faculty are supported in their efforts to continuously refine UREs based on the evidence currently available and evidence that they and others generate in the future. While much of the evidence to date is descriptive, it forms a body of knowledge that can be used to identify research questions about UREs, both those designed around the apprenticeship model and those designed using the more recent course-based undergraduate research experience (CURE) model. Internships and other avenues by which undergraduates do research provide many of the same sorts of experiences but are not well studied. In any case, it is clear that students value these experiences; that many faculty do as well; and that they contribute to broadening participation in science,
technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education and careers. The findings from the research literature reported in Chapter 4 provide guidance to those designing both opportunities to improve practical and academic skills and opportunities for students to “try out” a professional role of interest.
Little research has been done that provides answers to mechanistic questions about how UREs work. Additional studies are needed to know which features of UREs are most important for positive outcomes with which students and to gain information about other questions of this type. This additional research is needed to better understand and compare different strategies for UREs designed for a diversity of students, mentors, and institutions. Therefore, the committee recommends steps that could increase the quantity and quality of evidence available in the future and makes recommendations for how faculty, departments, and institutions might approach decisions about UREs using currently available information. Multiple detailed recommendations about the kinds of research that might be useful are provided in the research agenda in Chapter 7 .
In addition to the specific research recommended in Chapter 7 , in this chapter the committee provides a series of interrelated conclusions and recommendations related to UREs for the STEM disciplines and intended to highlight the issues of primary importance to administrators, URE program designers, mentors to URE students, funders of UREs, those leading the departments and institutions offering UREs, and those conducting research about UREs. These conclusions and recommendations are based on the expert views of the committee and informed by their review of the available research, the papers commissioned for this report, and input from presenters during committee meetings. Table 9-1 defines categories of these URE “actors,” gives examples of specific roles included in each category, specifies key URE actions for which that category is responsible, and lists the conclusions and recommendations the committee views as most relevant to that actor category.
RESEARCH ON URES
Conclusion 1: The current and emerging landscape of what constitutes UREs is diverse and complex. Students can engage in STEM-based undergraduate research in many different ways, across a variety of settings, and along a continuum that extends and expands upon learning opportunities in other educational settings. The following characteristics define UREs. Due to the variation in the types of UREs, not all experiences include all of the following characteristics in the same way; experiences vary in how much a particular characteristic is emphasized.
TABLE 9-1 Audiences for Committee’s Conclusions and Recommendations
- They engage students in research practices including the ability to argue from evidence.
- They aim to generate novel information with an emphasis on discovery and innovation or to determine whether recent preliminary results can be replicated.
- They focus on significant, relevant problems of interest to STEM researchers and, in some cases, a broader community (e.g., civic engagement).
- They emphasize and expect collaboration and teamwork.
- They involve iterative refinement of experimental design, experimental questions, or data obtained.
- They allow students to master specific research techniques.
- They help students engage in reflection about the problems being investigated and the work being undertaken to address those problems.
- They require communication of results, either through publication or presentations in various STEM venues.
- They are structured and guided by a mentor, with students assuming increasing ownership of some aspects of the project over time.
UREs are generally designed to add value to STEM offerings by promoting an understanding of the ways that knowledge is generated in STEM fields and to extend student learning beyond what happens in the small group work of an inquiry-based course. UREs add value by enabling students to understand and contribute to the research questions that are driving the field for one or more STEM topics or to grapple with design challenges of interest to professionals. They help students understand what it means to be a STEM researcher in a way that would be difficult to convey in a lecture course or even in an inquiry-based learning setting. As participants in a URE, students can learn by engaging in planning, experimentation, evaluation, interpretation, and communication of data and other results in light of what is already known about the question of interest. They can pose relevant questions that can be solved only through investigative or design efforts—individually or in teams—and attempt to answer these questions despite the challenges, setbacks, and ambiguity of the process and the results obtained.
The diversity of UREs reflects the reality that different STEM disciplines operate from varying traditions, expectations, and constraints (e.g., lab safety issues) in providing opportunities for undergraduates to engage in research. In addition, individual institutions and departments have cultures that promote research participation to various degrees and at different stages in students’ academic careers. Some programs emphasize design and problem solving in addition to discovery. UREs in different disciplines can
take many forms (e.g., apprentice-style, course-based, internships, project-based), but the definitional characteristics described above are similar across different STEM fields.
Furthermore, students in today’s university landscape may have opportunities to engage with many different types of UREs throughout their education, including involvement in a formal program (which could include mentoring, tutoring, research, and seminars about research), an apprentice-style URE under the guidance of an individual or team of faculty members, an internship, or enrolling in one or more CUREs or in a consortium- or project-based program.
Conclusion 2: Research on the efficacy of UREs is still in the early stages of development compared with other interventions to improve undergraduate STEM education.
- The types of UREs are diverse, and their goals are even more diverse. Questions and methodologies used to investigate the roles and effectiveness of UREs in achieving those goals are similarly diverse.
- Most of the studies of UREs to date are descriptive case studies or use correlational designs. Many of these studies report positive outcomes from engagement in a URE.
- Only a small number of studies have employed research designs that can support inferences about causation. Most of these studies find evidence for a causal relationship between URE participation and subsequent persistence in STEM. More studies are needed to provide evidence that participation in UREs is a causal factor in a range of desired student outcomes.
Taking the entire body of evidence into account, the committee concludes that the published peer-reviewed literature to date suggests that participation in a URE is beneficial for students .
As discussed in the report’s Introduction (see Chapter 1 ) and in the research agenda (see Chapter 7 ), the committee considered descriptive, causal, and mechanistic questions in our reading of the literature on UREs. Scientific approaches to answering descriptive, causal, and mechanistic questions require deciding what to look for, determining how to examine it, and knowing appropriate ways to score or quantify the effect.
Descriptive questions ask what is happening without making claims as to why it is happening—that is, without making claims as to whether the research experience caused these changes. A descriptive statement about UREs only claims that certain changes occurred during or after the time the students were engaged in undergraduate research. Descriptive studies
cannot determine whether any benefits observed were caused by participation in the URE.
Causal questions seek to discover whether a specific intervention leads to a specific outcome, other things being equal. To address such questions, causal evidence can be generated from a comparison of carefully selected groups that do and do not experience UREs. The groups can be made roughly equivalent by random assignment (ensuring that URE and non-URE groups are the same on average as the sample size increases) or by controlling for an exhaustive set of characteristics and experiences that might render the groups different prior to the URE. Other quasi-experimental strategies can also be used. Simply comparing students who enroll in a URE with students who do not is not adequate for determining causality because there may be selection bias. For example, students already interested in STEM are more likely to seek out such opportunities and more likely to be selected for such programs. Instead the investigator would have to compare future enrollment patterns (or other measures) between closely matched students, some of whom enrolled in a URE and some of whom did not. Controlling for selection bias to enable an inference about causation can pose significant challenges.
Questions of mechanism or of process also can be explored to understand why a causal intervention leads to the observed effect. Perhaps the URE enhances a student’s confidence in her ability to succeed in her chosen field or deepens her commitment to the field by exposing her to the joy of discovery. Through these pathways that act on the participant’s purposive behavior, the URE enhances the likelihood that she persists in STEM. The question for the researcher then becomes what research design would provide support for this hypothesis of mechanism over other candidate explanations for why the URE is a causal factor in STEM persistence.
The committee has examined the literature and finds a rich descriptive foundation for testable hypotheses about the effects of UREs on student outcomes. These studies are encouraging; a few of them have generated evidence that a URE can be a positive causal factor in the progression and persistence of STEM students. The weight of the evidence has been descriptive; it relies primarily on self-reports of short-term gains by students who chose to participate in UREs and does not include direct measures of changes in the students’ knowledge, skills, or other measures of success across comparable groups of students who did and did not participate in UREs.
While acknowledging the scarcity of strong causal evidence on the benefits of UREs, the committee takes seriously the weight of the descriptive evidence. Many of the published studies of UREs show that students who participate report a range of benefits, such as increased understanding of the research process, encouragement to persist in STEM, and support that helps them sustain their identity as researchers and continue with their
plans to enroll in a graduate program in STEM (see Chapter 4 ). These are effective starting points for causal studies.
Conclusion 3: Studies focused on students from historically underrepresented groups indicate that participation in UREs improves their persistence in STEM and helps to validate their disciplinary identity.
Various UREs have been specifically designed to increase the number of historically underrepresented students who go on to become STEM majors and ultimately STEM professionals. While many UREs offer one or more supplemental opportunities to support students’ academic or social success, such as mentoring, tutoring, summer bridge programs, career or graduate school workshops, and research-oriented seminars, those designed for underrepresented students appear to emphasize such features as integral and integrated components of the program. In particular, studies of undergraduate research programs targeting underrepresented minority students have begun to document positive outcomes such as degree completion and persistence in interest in STEM careers ( Byars-Winston et al., 2015 ; Chemers et al., 2011 ; Jones et al., 2010 ; Nagda et al., 1998 ; Schultz et al., 2011 ). Most of these studies collected data on apprentice-style UREs, in which the undergraduate becomes a functioning member of a research group along with the graduate students, postdoctoral fellows, and mentor.
Recommendation 1: Researchers with expertise in education research should conduct well-designed studies in collaboration with URE program directors to improve the evidence base about the processes and effects of UREs. This research should address how the various components of UREs may benefit students. It should also include additional causal evidence for the individual and additive effects of outcomes from student participation in different types of UREs. Not all UREs need be designed to undertake this type of research, but it would be very useful to have some UREs that are designed to facilitate these efforts to improve the evidence base .
As the focus on UREs has grown, so have questions about their implementation. Many articles have been published describing specific UREs (see Chapter 2 ). Large amounts of research have also been undertaken to explore more generally how students learn, and the resulting body of evidence has led to the development and adoption of “active learning” strategies and experiences. If a student in a URE has an opportunity to, for example, analyze new data or to reformulate a hypothesis in light of the student’s analysis, this activity fits into the category that is described as active learning. Surveys of student participants and unpublished evaluations pro-
vide additional information about UREs but do not establish causation or determine the mechanism(s). Consequently, little is currently known about the mechanisms of precisely how UREs work and which aspects of UREs are most powerful. Important components that have been reported include student ownership of the URE project, time to tackle a question iteratively, and opportunities to report and defend one’s conclusions ( Hanauer and Dolan, 2014 ; Thiry et al., 2011 ).
There are many unanswered questions and opportunities for further research into the role and mechanism of UREs. Attention to research design as UREs are planned is important; more carefully designed studies are needed to understand the ways that UREs influence a student’s education and to evaluate the outcomes that have been reported for URE participants. Appropriate studies, which include matched samples or similar controls, would facilitate research on the ways that UREs benefit students, enabling both education researchers and implementers of UREs to determine optimal features for program design and giving the community a more robust understanding of how UREs work.
See the research agenda ( Chapter 7 ) for specific recommendations about research topics and approaches.
Recommendation 2: Funders should provide appropriate resources to support the design, implementation, and analysis of some URE programs that are specifically designed to enable detailed research establishing the effects on participant outcomes and on other variables of interest such as the consequences for mentors or institutions.
Not all UREs need to be the subject of extensive study. In many cases, a straightforward evaluation is adequate to determine whether the URE is meeting its goals. However, to achieve more widespread improvement in both the types and quality of the UREs offered in the future, additional evidence about the possible causal effects and mechanisms of action of UREs needs to be systematically collected and disseminated. This includes a better understanding of the implementation differences for a variety of institutions (e.g., community colleges, primarily undergraduate institutions, research universities) to ensure that the desired outcomes can translate across settings. Increasing the evidence about precisely how UREs work and which aspects of UREs are most powerful will require careful attention to study design during planning for the UREs.
Not all UREs need to be designed to achieve this goal; many can provide opportunities to students by relying on pre-existing knowledge and iterative improvement as that knowledge base grows. However, for the knowledge base to grow, funders must provide resources for some URE designers and social science researchers to undertake thoughtful and well-planned studies
on causal and mechanistic issues. This will maximize the chances for the creation and dissemination of information that can lead to the development of sustainable and effective UREs. These studies can result from a partnership formed as the URE is designed and funded, or evaluators and social scientists could identify promising and/or effective existing programs and then raise funds on their own to support the study of those programs to answer the questions of interest. In deciding upon the UREs that are chosen for these extensive studies, it will be important to consider whether, collectively, they are representative of UREs in general. For example, large and small UREs at large and small schools targeted at both introductory and advanced students and topics should be studied.
CONSTRUCTION OF URES
Conclusion 4: The committee was unable to find evidence that URE designers are taking full advantage of the information available in the education literature on strategies for designing, implementing, and evaluating learning experiences. STEM faculty members do not generally receive training in interpreting or conducting education research. Partnerships between those with expertise in education research and those with expertise in implementing UREs are one way to strengthen the application of evidence on what works in planning and implementing UREs.
As discussed in Chapters 3 and 4 , there is an extensive body of literature on pedagogy and how people learn; helping STEM faculty to access the existing literature and incorporate those concepts as they design UREs could improve student experiences. New studies that specifically focus on UREs may provide more targeted information that could be used to design, implement, sustain, or scale up UREs and facilitate iterative improvements. Information about the features of UREs that elicit particular outcomes or best serve certain populations of students should be considered when implementing a new instantiation of an existing model of a URE or improving upon an existing URE model.
Conclusion 5: Evaluations of UREs are often conducted to inform program providers and funders; however, they may not be accessible to others. While these evaluations are not designed to be research studies and often have small sample sizes, they may contain information that could be useful to those initiating new URE programs and those refining UREs. Increasing access to these evaluations and to the accumulated experience of the program providers may enable URE designers and implementers to build upon knowledge gained from earlier UREs.
As discussed in Chapter 1 , the committee searched for evaluations of URE programs in several different ways but was not able to locate many published evaluations to study. Although some evaluations were found in the literature, the committee could not determine a way to systematically examine the program evaluations that have been prepared. The National Science Foundation and other funders generally require grant recipients to submit evaluation data, but that information is not currently aggregated and shared publicly, even for programs that are using a common evaluation tool. 1
Therefore, while program evaluation likely serves a useful role in providing descriptive data about a program for the institutions and funders supporting the program, much of the summative evaluation work that has been done to date adds relatively little to the broader knowledge base and overall conversations around undergraduate research. Some of the challenges of evaluation include budget and sample size constraints.
Similarly, it is difficult for designers of UREs to benefit systematically from the work of others who have designed and run UREs in the past because of the lack of an easy and consistent mechanism for collecting, analyzing, and sharing data. If these evaluations were more accessible they might be beneficial to others designing and evaluating UREs by helping them to gather ideas and inspiration from the experiences of others. A few such stories are provided in this report, and others can be found among the many resources offered by the Council on Undergraduate Research 2 and on other websites such as CUREnet. 3
Recommendation 3: Designers of UREs should base their design decisions on sound evidence. Consultations with education and social science researchers may be helpful as designers analyze the literature and make decisions on the creation or improvement of UREs. Professional development materials should be created and made available to faculty. Educational and disciplinary societies should consider how they can provide resources and connections to those working on UREs.
Faculty and other organizers of UREs can use the expanding body of scholarship as they design or improve the programs and experiences offered to their students. URE designers will need to make decisions about how to adapt approaches reported in the literature to make the programs they develop more suitable to their own expertise, student population(s), and available resources. Disciplinary societies and other national groups, such as those focused on improving pedagogy, can play important roles in
___________________
1 Personal knowledge of Janet Branchaw, member of the Committee on Strengthening Research Experiences for Undergraduate STEM Students.
2 See www.cur.org [November 2016].
3 See ( curenet.cns.utexas.edu ) [November 2016].
bringing these issues to the forefront through events at their national and regional meetings and through publications in their journals and newsletters. They can develop repositories for various kinds of resources appropriate for their members who are designing and implementing UREs. The ability to travel to conferences and to access and discuss resources created by other individuals and groups is a crucial aspect of support (see Recommendations 7 and 8 for further discussion).
See Chapter 8 for specific questions to consider when one is designing or implementing UREs.
CURRENT OFFERINGS
Conclusion 6: Data at the institutional, state, or national levels on the number and type of UREs offered, or who participates in UREs overall or at specific types of institutions, have not been collected systematically. Although the committee found that some individual institutions track at least some of this type of information, we were unable to determine how common it is to do so or what specific information is most often gathered.
There is no one central database or repository that catalogs UREs at institutions of higher education, the nature of the research experiences they provide, or the relevant demographics (student, departmental, and institutional). The lack of comprehensive data makes it difficult to know how many students participate in UREs; where UREs are offered; and if there are gaps in access to UREs across different institutional types, disciplines, or groups of students. One of the challenges of describing the undergraduate research landscape is that students do not have to be enrolled in a formal program to have a research experience. Informal experiences, for example a work-study job, are typically not well documented. Another challenge is that some students participate in CUREs or other research experiences (such as internships) that are not necessarily labeled as such. Institutional administrators may be unaware of CUREs that are already part of their curriculum. (For example, establishment of CUREs may be under the purview of a faculty curriculum committee and may not be recognized as a distinct program.) Student participation in UREs may occur at their home institution or elsewhere during the summer. Therefore, it is very difficult for a science department, and likely any other STEM department, to know what percentage of their graduating majors have had a research experience, let alone to gather such information on students who left the major. 4
4 This point was made by Marco Molinaro, University of California, Davis, in a presentation to the Committee on Strengthening Research Experience for Undergraduate STEM Students, September 16, 2015.
Conclusion 7: While data are lacking on the precise number of students engaged in UREs, there is some evidence of a recent growth in course-based undergraduate research experiences (CUREs), which engage a cohort of students in a research project as part of a formal academic experience.
There has been an increase in the number of grants and the dollar amount spent on CUREs over the past decade (see Chapter 3 ). CUREs can be particularly useful in scaling UREs to reach a much larger population of students ( Bangera and Brownell, 2014 ). By using a familiar mechanism—enrollment in a course—a CURE can provide a more comfortable route for students unfamiliar with research to gain their first experience. CUREs also can provide such experiences to students with diverse backgrounds, especially if an institution or department mandates participation sometime during a student’s matriculation. Establishing CUREs may be more cost-effective at schools with little on-site research activity. However, designing a CURE is a new and time-consuming challenge for many faculty members. Connecting to nationally organized research networks can provide faculty with helpful resources for the development of a CURE based around their own research or a local community need, or these networks can link interested faculty to an ongoing collaborative project. Collaborative projects can provide shared curriculum, faculty professional development and community, and other advantages when starting or expanding a URE program. See the discussion in the report from a convocation on Integrating Discovery-based Research into the Undergraduate Curriculum ( National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, 2015 ).
Recommendation 4: Institutions should collect data on student participation in UREs to inform their planning and to look for opportunities to improve quality and access.
Better tracking of student participation could lead to better assessment of outcomes and improved quality of experience. Such metrics could be useful for both prospective students and campus planners. An integrated institutional system for research opportunities could facilitate the creation of tiered research experiences that allow students to progress in skills and responsibility and create support structures for students, providing, for example, seminars in communications, safety, and ethics for undergraduate researchers. Institutions could also use these data to measure the impact of UREs on student outcomes, such as student success rates in introductory courses, retention in STEM degree programs, and completion of STEM degrees.
While individual institutions may choose to collect additional information depending on their goals and resources, relevant student demographics
and the following design elements would provide baseline data. At a minimum, such data should include
- Type of URE;
- Each student’s discipline;
- Duration of the experience;
- Hours spent per week;
- When the student began the URE (e.g., first year, capstone);
- Compensation status (e.g., paid, unpaid, credit); and
- Location and format (e.g., on home campus, on another campus, internship, co-op).
National aggregation of some of the student participation variables collected by various campuses might be considered by funders. The existing Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System database, organized by the National Center for Education Statistics at the U.S. Department of Education, may be a suitable repository for certain aspects of this information.
Recommendation 5: Administrators and faculty at all types of colleges and universities should continually and holistically evaluate the range of UREs that they offer. As part of this process, institutions should:
- Consider how best to leverage available resources (including off-campus experiences available to students and current or potential networks or partnerships that the institution may form) when offering UREs so that they align with their institution’s mission and priorities;
- Consider whether current UREs are both accessible and welcoming to students from various subpopulations across campus (e.g., historically underrepresented students, first generation college students, those with disabilities, non-STEM majors, prospective kindergarten-through-12th-grade teachers); and
- Gather and analyze data on the types of UREs offered and the students who participate, making this information widely available to the campus community and using it to make evidence-based decisions about improving opportunities for URE participation. This may entail devising or implementing systems for tracking relevant data (see Conclusion 4 ).
Resources available for starting, maintaining, and expanding UREs vary from campus to campus. At some campuses, UREs are a central focus and many resources are devoted to them. At other institutions—for example, many community colleges—UREs are seen as extra, and new resources may be required to ensure availability of courses and facilities. Resource-
constrained institutions may need to focus more on ensuring that students are aware of potential UREs that already exist on campus and elsewhere in near proximity to campus. All institutional discussions about UREs must consider both the financial resources and physical resources (e.g., laboratories, field stations, engineering design studios) required, while remembering that faculty time is a crucial resource. The incentives and disincentives for faculty to spend time on UREs are significant. Those institutions with an explicit mission to promote undergraduate research may provide more recognition and rewards to departments and faculty than those with another focus. The culture of the institution with respect to innovation in pedagogy and support for faculty development also can have a major influence on the extent to which UREs are introduced or improved.
Access to UREs may vary across campus and by department, and participation in UREs may vary across student groups. It is important for campuses to consider the factors that may facilitate or discourage students from participation in UREs. Inconsistent procedures or a faculty preference for students with high grades or previous research experience may limit options for some student populations.
UREs often grow based on the initiative of individual faculty members and other personnel, and an institution may not have complete or even rudimentary knowledge of all of the opportunities available or whether there are gaps or inconsistencies in its offerings. A uniform method for tracking the UREs available on a given campus would be useful to students and would provide a starting point for analyzing the options. Tracking might consist of notations in course listings and, where feasible, on student transcripts. Analysis might consider the types of UREs offered, the resources available to each type of URE, and variations within or between various disciplines and programs. Attention to whether all students or groups of students have appropriate access to UREs would foster consideration of how to best allocate resources and programming on individual campuses, in order to focus resources and opportunities where they are most needed.
Conclusion 8: The quality of mentoring can make a substantial difference in a student’s experiences with research. However, professional development in how to be a good mentor is not available to many faculty or other prospective mentors (e.g., graduate students, postdoctoral fellows).
Engagement in quality mentored research experiences has been linked to self-reported gains in research skills and productivity as well as retention in STEM (see Chapter 5 ). Quality mentoring in UREs has been shown
to increase persistence in STEM for historically underrepresented students ( Hernandez et al., 2016 ). In addition, poor mentoring during UREs has been shown to decrease retention of students ( Hernandez et al., 2016 ).
More general research on good mentoring in the STEM environment has been positively associated with self-reported gains in identity as a STEM researcher, a sense of belonging, and confidence to function as a STEM researcher ( Byars-Winston et al., 2015 ; Chemers et al., 2011 ; Pfund et al., 2016 ; Thiry et al., 2011 ). The frequency and quality of mentee-mentor interactions has been associated with students’ reports of persistence in STEM, with mentoring directly or indirectly improving both grades and persistence in college. For students from historically underrepresented ethnic/racial groups, quality mentoring has been associated with self-reported enhanced recruitment into graduate school and research-related career pathways ( Byars-Winston et al., 2015 ). Therefore, it is important to ensure that faculty and mentors receive the proper development of mentoring skills.
Recommendation 6: Administrators and faculty at colleges and universities should ensure that all who mentor undergraduates in research experiences (this includes faculty, instructors, postdoctoral fellows, graduate students, and undergraduates serving as peer mentors) have access to appropriate professional development opportunities to help them grow and succeed in this role.
Although many organizations recognize effective mentors (e.g., the National Science Foundation’s Presidential Awards for Excellence in Science, Mathematics, and Engineering Mentoring), there currently are no standard criteria for selecting, evaluating, or recognizing mentors specifically for UREs. In addition, there are no requirements that mentors meet some minimum level of competency before engaging in mentoring or participate in professional development to obtain a baseline of knowledge and skills in mentoring, including cultural competence in mentoring diverse groups of students. Traditionally, the only experience required for being a mentor is having been mentored, regardless of whether the experience was negative or positive ( Handelsman et al., 2005 ; Pfund et al., 2015 ). Explicit consideration of how the relationships are formed, supported, and evaluated can improve mentor-mentee relationships. To ensure that the mentors associated with a URE are prepared appropriately, thereby increasing the chances of a positive experience for both mentors and mentees, all prospective mentors should prepare for their role. Available resources include the Entering Mentoring course (see Pfund et al., 2015 ) and the book Successful STEM Mentoring Initiative for Underrepresented Students ( Packard, 2016 ).
A person who is an ineffective mentor for one student might be inspiring for another, and the setting in which the mentoring takes place (e.g., a CURE or apprentice-style URE, a laboratory or field-research environment) may also influence mentor effectiveness. Thus, there should be some mechanism for monitoring such relationships during the URE, or there should be opportunity for a student who is unhappy with the relationship to seek other mentors. Indeed, cultivating a team of mentors with different experiences and expertise may be the best strategy for any student. A parallel volume to the Entering Mentoring curriculum mentioned above, Entering Research Facilitator’s Manual ( Branchaw et al., 2010 ), is designed to help students with their research mentor-mentee relationships and to coach them on building teams of mentors to guide them. As mentioned in Chapter 5 , the Entering Research curriculum also contains information designed to support a group of students as they go through their first apprentice-style research experience, each working in separate research groups and also meeting together as a cohort focused on learning about research.
PRIORITIES FOR THE FUTURE
Conclusion 9: The unique assets, resources, priorities, and constraints of the department and institution, in addition to those of individual mentors, impact the goals and structures of UREs. Schools across the country are showing considerable creativity in using unique resources, repurposing current assets, and leveraging student enthusiasm to increase research opportunities for their students.
Given current calls for UREs and the growing conversation about their benefits, an increasing number of two- and four-year colleges and universities are increasing their efforts to support undergraduate research. Departments, institutions, and individual faculty members influence the precise nature of UREs in multiple ways and at multiple levels. The physical resources available, including laboratories, field stations, and engineering design studios and testing facilities, make a difference, as does the ability to access resources in the surrounding community (including other parts of the campus). Institutions with an explicit mission to promote undergraduate research may provide more time, resources (e.g., financial, support personnel, space, equipment), and recognition and rewards to departments and faculty in support of UREs than do institutions without that mission. The culture of the institution with respect to innovation in pedagogy and support for faculty development also affects the extent to which UREs are introduced or improved.
Development of UREs requires significant time and effort. Whether or not faculty attempt to implement UREs can depend on whether departmental
or institutional reward and recognition systems compensate for or even recognize the time required to initiate and implement them. The availability of national consortia can help to alleviate many of the time and logistical problems but not those obstacles associated with recognition and resources.
It will be harder for faculty to find the time to develop UREs at institutions where they are required to teach many courses per semester, although in some circumstances faculty can teach CUREs that also advance their own research ( Shortlidge et al., 2016 ). Faculty at community colleges generally have the heaviest teaching expectations, little or no expectations or incentives to maintain a research program, limited access to lab or design space or to scientific and engineering journals, and few resources to undertake any kind of a research program. These constraints may limit the extent to which UREs can be offered to the approximately 40 percent of U.S. undergraduates who are enrolled in the nation’s community colleges (which collectively also serve the highest percentage of the nation’s underrepresented students). 5
Recommendation 7: Administrators and faculty at all types of colleges and universities should work together within and, where feasible, across institutions to create a culture that supports the development of evidence-based, iterative, and continuous refinement of UREs, in an effort to improve student learning outcomes and overall academic success. This should include the development, evaluation, and revision of policies and practices designed to create a culture supportive of the participation of faculty and other mentors in effective UREs. Policies should consider pedagogy, professional development, cross-cultural awareness, hiring practices, compensation, promotion (incentives, rewards), and the tenure process.
Colleges and universities that would like to expand or improve the UREs offered to their students should consider the campus culture and climate and the incentives that affect faculty choices. Those campuses that cultivate an environment supportive of the iterative and continuous refinement of UREs and that offer incentives for evaluation and evidence-based improvement of UREs seem more likely to sustain successful programs. Faculty and others who develop and implement UREs need support to be able to evaluate their courses or programs and to analyze evidence to make decisions about URE design. This kind of support may be fostered by expanding the mission of on-campus centers for learning and teaching to focus more on UREs or by providing incentives for URE developers from the natural sciences and engineering to collaborate with colleagues in the social sciences or colleges of education with expertise in designing studies
5 See http://nces.ed.gov/programs/coe/indicator_cha.asp [November 2016].
involving human subjects. Supporting closer communication between URE developers and the members of the campus Institutional Review Board may help projects to move forward more seamlessly. Interdepartmental and intercampus connections (especially those between two- and four-year institutions) can be valuable for linking faculty with the appropriate resources, colleagues, and diverse student populations. Faculty who have been active in professional development on how students learn in the classroom may have valuable experiences and expertise to share.
The refinement or expansion of UREs should build on evidence from data on student participation, pedagogy, and outcomes, which are integral components of the original design. As UREs are validated and refined, institutions should make efforts to facilitate connections among different departments and disciplines, including the creation of multidisciplinary UREs. Student engagement in learning in general, and with UREs more specifically, depends largely on the culture of the department and the institution and on whether students see their surroundings as inclusive and energetic places to learn and thrive. A study that examined the relationship between campus missions and the five benchmarks for effective educational practice (measured by the National Survey of Student Engagement) showed that different programs, policies, and approaches may work better, depending on the institution’s mission ( Kezar and Kinzie, 2006 ).
The Council on Undergraduate Research (2012) document Characteristics of Excellence in Undergraduate Research outlines several best practices for UREs based on the apprenticeship model (see Chapter 8 ). That document is not the result of a detailed analysis of the evidence but is based on the extensive experiences and expertise of the council’s members. It suggests that undergraduate research should be a normal part of the undergraduate experience regardless of the type of institution. It also identifies changes necessary to include UREs as part of the curriculum and culture changes necessary to support curricular reform, co-curricular activities, and modifications to the incentives and rewards for faculty to engage with undergraduate research. In addition, professional development opportunities specifically designed to help improve the pedagogical and mentoring skills of instructional staff in using evidence-based practices can be important for a supportive learning culture.
Recommendation 8: Administrators and faculty at all types of colleges and universities should work to develop strong and sustainable partnerships within and between institutions and with educational and professional societies for the purpose of sharing resources to facilitate the creation of sustainable URE programs.
Networks of faculty, institutions, regionally and nationally coordinated URE initiatives, professional societies, and funders should be strengthened
to facilitate the exchange of evidence and experience related to UREs. These networks could build on the existing work of professional societies that assist faculty with pedagogy. They can help provide a venue for considering the policy context and larger implications of increasing the number, size, and scope of UREs. Such networks also can provide a more robust infrastructure, to improve the sustainability and expansion of URE opportunities. The sharing of human, financial, scientific, and technical resources can strengthen the broad implementation of effective, high-quality, and more cost-efficient UREs. It may be especially important for community colleges and minority-serving institutions to engage in partnerships in order to expand the opportunities for undergraduates (both transfer and technical students) to participate in diverse UREs (see discussion in National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, 2015 , and Elgin et al., 2016 ). Consortia can facilitate the sharing of resources across disciplines and departments within the same institution or at different institutions, organizations, and agencies. Consortia that employ research methodologies in common can share curriculum, research data collected, and common assessment tools, lessening the time burden for individual faculty and providing a large pool of students from which to assess the efficacy of individual programs.
Changes in the funding climate can have substantial impacts on the types of programs that exist, iterative refinement of programs, and whether and how programs might be expanded to broaden participation by more undergraduates. For those institutions that have not yet established URE programs or are at the beginning phases of establishing one, mechanisms for achieving success and sustainability may include increased institutional ownership of programs of undergraduate research, development of a broad range of programs of different types and funding structures, formation of undergraduate research offices or repurposing some of the responsibilities and activities of those which already exist, and engagement in community promotion and dissemination of student accomplishments (e.g., student symposia, support for undergraduate student travel to give presentations at professional meetings).
Over time, institutions must develop robust plans for ensuring the long-term sustained funding of high-quality UREs. Those plans should include assuming that more fiscal responsibility for sustaining such efforts will be borne by the home institution as external support for such efforts decreases and ultimately ends. Building UREs into the curriculum and structure of a department’s courses and other programs, and thus its funding model, can help with sustainability. Partnerships with nonprofit organizations and industry, as well as seeking funding from diverse agencies, can also facilitate programmatic sustainability, especially if the UREs they fund can also support the mission and programs of the funders (e.g., through research internships or through CUREs that focus on community-
based research questions and challenges). Partnerships among institutions also may have greater potential to study and evaluate student outcomes from URE participation across broader demographic groups and to reduce overall costs through the sharing of administrative or other resources (such as libraries, microscopes, etc.).
Bangera, G., and Brownell, S.E. (2014). Course-based undergraduate research experiences can make scientific research more inclusive. CBE–Life Sciences Education , 13 (4), 602-606.
Branchaw, J.L., Pfund, C., and Rediske, R. (2010) Entering Research Facilitator’s Manual: Workshops for Students Beginning Research in Science . New York: Freeman & Company.
Byars-Winston, A.M., Branchaw, J., Pfund, C., Leverett, P., and Newton, J. (2015). Culturally diverse undergraduate researchers’ academic outcomes and perceptions of their research mentoring relationships. International Journal of Science Education , 37 (15), 2,533-2,554.
Chemers, M.M., Zurbriggen, E.L., Syed, M., Goza, B.K., and Bearman, S. (2011). The role of efficacy and identity in science career commitment among underrepresented minority students. Journal of Social Issues , 67 (3), 469-491.
Council on Undergraduate Research. (2012). Characteristics of Excellence in Undergraduate Research . Washington, DC: Council on Undergraduate Research.
Elgin, S.C.R., Bangera, G., Decatur, S.M., Dolan, E.L., Guertin, L., Newstetter, W.C., San Juan, E.F., Smith, M.A., Weaver, G.C., Wessler, S.R., Brenner, K.A., and Labov, J.B. 2016. Insights from a convocation: Integrating discovery-based research into the undergraduate curriculum. CBE–Life Sciences Education, 15 , 1-7.
Hanauer, D., and Dolan, E. (2014) The Project Ownership Survey: Measuring differences in scientific inquiry experiences, CBE–Life Sciences Education , 13 , 149-158.
Handelsman, J., Pfund, C., Lauffer, S.M., and Pribbenow, C.M. (2005). Entering Mentoring . Madison, WI: The Wisconsin Program for Scientific Teaching.
Hernandez, P.R., Estrada, M., Woodcock, A., and Schultz, P.W. (2016). Protégé perceptions of high mentorship quality depend on shared values more than on demographic match. Journal of Experimental Education. Available: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00220973.2016.1246405 [November 2016].
Jones, P., Selby, D., and Sterling, S.R. (2010). Sustainability Education: Perspectives and Practice Across Higher Education . New York: Earthscan.
Kezar, A.J., and Kinzie, J. (2006). Examining the ways institutions create student engagement: The role of mission. Journal of College Student Development , 47 (2), 149-172.
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. (2015). Integrating Discovery-Based Research into the Undergraduate Curriculum: Report of a Convocation . Washington, DC: National Academies Press.
Nagda, B.A., Gregerman, S.R., Jonides, J., von Hippel, W., and Lerner, J.S. (1998). Undergraduate student-faculty research partnerships affect student retention. Review of Higher Education, 22 , 55-72. Available: http://scholar.harvard.edu/files/jenniferlerner/files/nagda_1998_paper.pdf [February 2017].
Packard, P. (2016). Successful STEM Mentoring Initiatives for Underrepresented Students: A Research-Based Guide for Faculty and Administrators . Sterling, VA: Stylus.
Pfund, C., Branchaw, J.L., and Handelsman, J. (2015). Entering Mentoring: A Seminar to Train a New Generation of Scientists (2nd ed). New York: Macmillan Learning.
Pfund, C., Byars-Winston, A., Branchaw, J.L., Hurtado, S., and Eagan, M.K. (2016). Defining attributes and metrics of effective research mentoring relationships. AIDS and Behavior, 20 , 238-248.
Schultz, P.W., Hernandez, P.R., Woodcock, A., Estrada, M., Chance, R.C., Aguilar, M., and Serpe, R.T. (2011). Patching the pipeline reducing educational disparities in the sciences through minority training programs. Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis , 33 (1), 95-114.
Shortlidge, E.E., Bangera, G., and Brownell, S.E. (2016). Faculty perspectives on developing and teaching course-based undergraduate research experiences. BioScience, 66 (1), 54-62.
Thiry, H., Laursen, S.L., and Hunter, A.B. (2011). What experiences help students become scientists? A comparative study of research and other sources of personal and professional gains for STEM undergraduates. Journal of Higher Education, 82 (4), 358-389.
This page intentionally left blank.
Undergraduate research has a rich history, and many practicing researchers point to undergraduate research experiences (UREs) as crucial to their own career success. There are many ongoing efforts to improve undergraduate science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education that focus on increasing the active engagement of students and decreasing traditional lecture-based teaching, and UREs have been proposed as a solution to these efforts and may be a key strategy for broadening participation in STEM. In light of the proposals questions have been asked about what is known about student participation in UREs, best practices in UREs design, and evidence of beneficial outcomes from UREs.
Undergraduate Research Experiences for STEM Students provides a comprehensive overview of and insights about the current and rapidly evolving types of UREs, in an effort to improve understanding of the complexity of UREs in terms of their content, their surrounding context, the diversity of the student participants, and the opportunities for learning provided by a research experience. This study analyzes UREs by considering them as part of a learning system that is shaped by forces related to national policy, institutional leadership, and departmental culture, as well as by the interactions among faculty, other mentors, and students. The report provides a set of questions to be considered by those implementing UREs as well as an agenda for future research that can help answer questions about how UREs work and which aspects of the experiences are most powerful.
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
Switch between the Original Pages , where you can read the report as it appeared in print, and Text Pages for the web version, where you can highlight and search the text.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.
Implications or Recommendations in Research: What's the Difference?
- Peer Review
High-quality research articles that get many citations contain both implications and recommendations. Implications are the impact your research makes, whereas recommendations are specific actions that can then be taken based on your findings, such as for more research or for policymaking.
Updated on August 23, 2022

That seems clear enough, but the two are commonly confused.
This confusion is especially true if you come from a so-called high-context culture in which information is often implied based on the situation, as in many Asian cultures. High-context cultures are different from low-context cultures where information is more direct and explicit (as in North America and many European cultures).
Let's set these two straight in a low-context way; i.e., we'll be specific and direct! This is the best way to be in English academic writing because you're writing for the world.
Implications and recommendations in a research article
The standard format of STEM research articles is what's called IMRaD:
- Introduction
- Discussion/conclusions
Some journals call for a separate conclusions section, while others have the conclusions as the last part of the discussion. You'll write these four (or five) sections in the same sequence, though, no matter the journal.
The discussion section is typically where you restate your results and how well they confirmed your hypotheses. Give readers the answer to the questions for which they're looking to you for an answer.
At this point, many researchers assume their paper is finished. After all, aren't the results the most important part? As you might have guessed, no, you're not quite done yet.
The discussion/conclusions section is where to say what happened and what should now happen
The discussion/conclusions section of every good scientific article should contain the implications and recommendations.
The implications, first of all, are the impact your results have on your specific field. A high-impact, highly cited article will also broaden the scope here and provide implications to other fields. This is what makes research cross-disciplinary.
Recommendations, however, are suggestions to improve your field based on your results.
These two aspects help the reader understand your broader content: How and why your work is important to the world. They also tell the reader what can be changed in the future based on your results.
These aspects are what editors are looking for when selecting papers for peer review.

Implications and recommendations are, thus, written at the end of the discussion section, and before the concluding paragraph. They help to “wrap up” your paper. Once your reader understands what you found, the next logical step is what those results mean and what should come next.
Then they can take the baton, in the form of your work, and run with it. That gets you cited and extends your impact!
The order of implications and recommendations also matters. Both are written after you've summarized your main findings in the discussion section. Then, those results are interpreted based on ongoing work in the field. After this, the implications are stated, followed by the recommendations.
Writing an academic research paper is a bit like running a race. Finish strong, with your most important conclusion (recommendation) at the end. Leave readers with an understanding of your work's importance. Avoid generic, obvious phrases like "more research is needed to fully address this issue." Be specific.
The main differences between implications and recommendations (table)

Now let's dig a bit deeper into actually how to write these parts.
What are implications?
Research implications tell us how and why your results are important for the field at large. They help answer the question of “what does it mean?” Implications tell us how your work contributes to your field and what it adds to it. They're used when you want to tell your peers why your research is important for ongoing theory, practice, policymaking, and for future research.
Crucially, your implications must be evidence-based. This means they must be derived from the results in the paper.
Implications are written after you've summarized your main findings in the discussion section. They come before the recommendations and before the concluding paragraph. There is no specific section dedicated to implications. They must be integrated into your discussion so that the reader understands why the results are meaningful and what they add to the field.
A good strategy is to separate your implications into types. Implications can be social, political, technological, related to policies, or others, depending on your topic. The most frequently used types are theoretical and practical. Theoretical implications relate to how your findings connect to other theories or ideas in your field, while practical implications are related to what we can do with the results.
Key features of implications
- State the impact your research makes
- Helps us understand why your results are important
- Must be evidence-based
- Written in the discussion, before recommendations
- Can be theoretical, practical, or other (social, political, etc.)
Examples of implications
Let's take a look at some examples of research results below with their implications.
The result : one study found that learning items over time improves memory more than cramming material in a bunch of information at once .
The implications : This result suggests memory is better when studying is spread out over time, which could be due to memory consolidation processes.
The result : an intervention study found that mindfulness helps improve mental health if you have anxiety.
The implications : This result has implications for the role of executive functions on anxiety.
The result : a study found that musical learning helps language learning in children .
The implications : these findings suggest that language and music may work together to aid development.
What are recommendations?
As noted above, explaining how your results contribute to the real world is an important part of a successful article.
Likewise, stating how your findings can be used to improve something in future research is equally important. This brings us to the recommendations.
Research recommendations are suggestions and solutions you give for certain situations based on your results. Once the reader understands what your results mean with the implications, the next question they need to know is "what's next?"
Recommendations are calls to action on ways certain things in the field can be improved in the future based on your results. Recommendations are used when you want to convey that something different should be done based on what your analyses revealed.
Similar to implications, recommendations are also evidence-based. This means that your recommendations to the field must be drawn directly from your results.
The goal of the recommendations is to make clear, specific, and realistic suggestions to future researchers before they conduct a similar experiment. No matter what area your research is in, there will always be further research to do. Try to think about what would be helpful for other researchers to know before starting their work.
Recommendations are also written in the discussion section. They come after the implications and before the concluding paragraphs. Similar to the implications, there is usually no specific section dedicated to the recommendations. However, depending on how many solutions you want to suggest to the field, they may be written as a subsection.
Key features of recommendations
- Statements about what can be done differently in the field based on your findings
- Must be realistic and specific
- Written in the discussion, after implications and before conclusions
- Related to both your field and, preferably, a wider context to the research
Examples of recommendations
Here are some research results and their recommendations.
A meta-analysis found that actively recalling material from your memory is better than simply re-reading it .
- The recommendation: Based on these findings, teachers and other educators should encourage students to practice active recall strategies.
A medical intervention found that daily exercise helps prevent cardiovascular disease .
- The recommendation: Based on these results, physicians are recommended to encourage patients to exercise and walk regularly. Also recommended is to encourage more walking through public health offices in communities.
A study found that many research articles do not contain the sample sizes needed to statistically confirm their findings .
The recommendation: To improve the current state of the field, researchers should consider doing power analysis based on their experiment's design.
What else is important about implications and recommendations?
When writing recommendations and implications, be careful not to overstate the impact of your results. It can be tempting for researchers to inflate the importance of their findings and make grandiose statements about what their work means.
Remember that implications and recommendations must be coming directly from your results. Therefore, they must be straightforward, realistic, and plausible.
Another good thing to remember is to make sure the implications and recommendations are stated clearly and separately. Do not attach them to the endings of other paragraphs just to add them in. Use similar example phrases as those listed in the table when starting your sentences to clearly indicate when it's an implication and when it's a recommendation.
When your peers, or brand-new readers, read your paper, they shouldn't have to hunt through your discussion to find the implications and recommendations. They should be clear, visible, and understandable on their own.
That'll get you cited more, and you'll make a greater contribution to your area of science while extending the life and impact of your work.

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"

How to write recommendations in a research paper
Many students put in a lot of effort and write a good report however they are not able to give proper recommendations. Recommendations in the research paper should be included in your research. As a researcher, you display a deep understanding of the topic of research. Therefore you should be able to give recommendations. Here are a few tips that will help you to give appropriate recommendations.
Recommendations in the research paper should be the objective of the research. Therefore at least one of your objectives of the paper is to provide recommendations to the parties associated or the parties that will benefit from your research. For example, to encourage higher employee engagement HR department should make strategies that invest in the well-being of employees. Additionally, the HR department should also collect regular feedback through online surveys.
Recommendations in the research paper should come from your review and analysis For example It was observed that coaches interviewed were associated with the club were working with the club from the past 2-3 years only. This shows that the attrition rate of coaches is high and therefore clubs should work on reducing the turnover of coaches.
Recommendations in the research paper should also come from the data you have analysed. For example, the research found that people over 65 years of age are at greater risk of social isolation. Therefore, it is recommended that policies that are made for combating social isolation should target this specific group.
Recommendations in the research paper should also come from observation. For example, it is observed that Lenovo’s income is stable and gross revenue has displayed a negative turn. Therefore the company should analyse its marketing and branding strategy.
Recommendations in the research paper should be written in the order of priority. The most important recommendations for decision-makers should come first. However, if the recommendations are of equal importance then it should come in the sequence in which the topic is approached in the research.
Recommendations in a research paper if associated with different categories then you should categorize them. For example, you have separate recommendations for policymakers, educators, and administrators then you can categorize the recommendations.
Recommendations in the research paper should come purely from your research. For example, you have written research on the impact on HR strategies on motivation. However, nowhere you have discussed Reward and recognition. Then you should not give recommendations for using rewards and recognition measures to boost employee motivation.
The use of bullet points offers better clarity rather than using long paragraphs. For example this paragraph “ It is recommended that Britannia Biscuit should launch and promote sugar-free options apart from the existing product range. Promotion efforts should be directed at creating a fresh and healthy image. A campaign that conveys a sense of health and vitality to the consumer while enjoying biscuit is recommended” can be written as:
- The company should launch and promote sugar-free options
- The company should work towards creating s fresh and healthy image
- The company should run a campaign to convey its healthy image
The inclusion of an action plan along with recommendation adds more weightage to your recommendation. Recommendations should be clear and conscience and written using actionable words. Recommendations should display a solution-oriented approach and in some cases should highlight the scope for further research.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER COLUMN
- 20 July 2020
Writing the perfect recommendation letter
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Undergraduates need them for graduate-school applications; PhD students and postdocs use them to apply for fellowships and jobs; senior scientists often have to have them to apply for awards and promotions. But writing an effective and personal recommendation letter can be time-consuming, especially for academics who must juggle grant applications, manuscripts, teaching and student supervision. And some might struggle to say the right things to support a former employee or student in their career move, while sounding original and unique.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 584 , 158 (2020)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-02186-8
These interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Related Articles

- Research management

Londoners see what a scientist looks like up close in 50 photographs
Career News 18 APR 24
Deadly diseases and inflatable suits: how I found my niche in virology research
Spotlight 17 APR 24

How young people benefit from Swiss apprenticeships

Ready or not, AI is coming to science education — and students have opinions
Career Feature 08 APR 24

After the genocide: what scientists are learning from Rwanda
News Feature 05 APR 24

Researchers want a ‘nutrition label’ for academic-paper facts
Nature Index 17 APR 24

How we landed job interviews for professorships straight out of our PhD programmes
Career Column 08 APR 24
Postdoctoral Associate- Artificial Intelligence
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Postdoctoral Research Fellow
Looking for postdoctoral fellowship candidates to advance genomic research in the study of lung diseases at Brigham and Women's Hospital and HMS.
Boston, Massachusetts
Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH)
Position Opening for Principal Investigator GIBH
We aim to foster cutting-edge scientific and technological advancements in the field of molecular tissue biology at the single-cell level.
Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health(GIBH), Chinese Academy of Sciences
PostDoc grant- 3D histopathology image analysis
Join a global pharmaceutical company as a Postdoctoral researcher and advance 3D histopathology image analysis! Apply with your proposals today.
Biberach an der Riß, Baden-Württemberg (DE)
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
Postdoctoral Position
We are seeking highly motivated and skilled candidates for postdoctoral fellow positions
Boston, Massachusetts (US)
Boston Children's Hospital (BCH)
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » References in Research – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
References in Research – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

References in Research
Definition:
References in research are a list of sources that a researcher has consulted or cited while conducting their study. They are an essential component of any academic work, including research papers, theses, dissertations, and other scholarly publications.
Types of References
There are several types of references used in research, and the type of reference depends on the source of information being cited. The most common types of references include:
References to books typically include the author’s name, title of the book, publisher, publication date, and place of publication.
Example: Smith, J. (2018). The Art of Writing. Penguin Books.
Journal Articles
References to journal articles usually include the author’s name, title of the article, name of the journal, volume and issue number, page numbers, and publication date.
Example: Johnson, T. (2021). The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health. Journal of Psychology, 32(4), 87-94.
Web sources
References to web sources should include the author or organization responsible for the content, the title of the page, the URL, and the date accessed.
Example: World Health Organization. (2020). Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) advice for the public. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease/novel-coronavirus-2019/advice-for-public
Conference Proceedings
References to conference proceedings should include the author’s name, title of the paper, name of the conference, location of the conference, date of the conference, and page numbers.
Example: Chen, S., & Li, J. (2019). The Future of AI in Education. Proceedings of the International Conference on Educational Technology, Beijing, China, July 15-17, pp. 67-78.
References to reports typically include the author or organization responsible for the report, title of the report, publication date, and publisher.
Example: United Nations. (2020). The Sustainable Development Goals Report. United Nations.
Formats of References
Some common Formates of References with their examples are as follows:
APA (American Psychological Association) Style
The APA (American Psychological Association) Style has specific guidelines for formatting references used in academic papers, articles, and books. Here are the different reference formats in APA style with examples:
Author, A. A. (Year of publication). Title of book. Publisher.
Example : Smith, J. K. (2005). The psychology of social interaction. Wiley-Blackwell.
Journal Article
Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (Year of publication). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), page numbers.
Example : Brown, L. M., Keating, J. G., & Jones, S. M. (2012). The role of social support in coping with stress among African American adolescents. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 22(1), 218-233.
Author, A. A. (Year of publication or last update). Title of page. Website name. URL.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020, December 11). COVID-19: How to protect yourself and others. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html
Magazine article
Author, A. A. (Year, Month Day of publication). Title of article. Title of Magazine, volume number(issue number), page numbers.
Example : Smith, M. (2019, March 11). The power of positive thinking. Psychology Today, 52(3), 60-65.
Newspaper article:
Author, A. A. (Year, Month Day of publication). Title of article. Title of Newspaper, page numbers.
Example: Johnson, B. (2021, February 15). New study shows benefits of exercise on mental health. The New York Times, A8.
Edited book
Editor, E. E. (Ed.). (Year of publication). Title of book. Publisher.
Example : Thompson, J. P. (Ed.). (2014). Social work in the 21st century. Sage Publications.
Chapter in an edited book:
Author, A. A. (Year of publication). Title of chapter. In E. E. Editor (Ed.), Title of book (pp. page numbers). Publisher.
Example : Johnson, K. S. (2018). The future of social work: Challenges and opportunities. In J. P. Thompson (Ed.), Social work in the 21st century (pp. 105-118). Sage Publications.
MLA (Modern Language Association) Style
The MLA (Modern Language Association) Style is a widely used style for writing academic papers and essays in the humanities. Here are the different reference formats in MLA style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication year.
Example : Smith, John. The Psychology of Social Interaction. Wiley-Blackwell, 2005.
Journal article
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, volume number, issue number, Publication year, page numbers.
Example : Brown, Laura M., et al. “The Role of Social Support in Coping with Stress among African American Adolescents.” Journal of Research on Adolescence, vol. 22, no. 1, 2012, pp. 218-233.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Webpage.” Website Name, Publication date, URL.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “COVID-19: How to Protect Yourself and Others.” CDC, 11 Dec. 2020, https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Magazine, Publication date, page numbers.
Example : Smith, Mary. “The Power of Positive Thinking.” Psychology Today, Mar. 2019, pp. 60-65.
Newspaper article
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Newspaper, Publication date, page numbers.
Example : Johnson, Bob. “New Study Shows Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health.” The New York Times, 15 Feb. 2021, p. A8.
Editor’s Last name, First name, editor. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication year.
Example : Thompson, John P., editor. Social Work in the 21st Century. Sage Publications, 2014.
Chapter in an edited book
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Chapter.” Title of Book, edited by Editor’s First Name Last name, Publisher, Publication year, page numbers.
Example : Johnson, Karen S. “The Future of Social Work: Challenges and Opportunities.” Social Work in the 21st Century, edited by John P. Thompson, Sage Publications, 2014, pp. 105-118.
Chicago Manual of Style
The Chicago Manual of Style is a widely used style for writing academic papers, dissertations, and books in the humanities and social sciences. Here are the different reference formats in Chicago style:
Example : Smith, John K. The Psychology of Social Interaction. Wiley-Blackwell, 2005.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal volume number, no. issue number (Publication year): page numbers.
Example : Brown, Laura M., John G. Keating, and Sarah M. Jones. “The Role of Social Support in Coping with Stress among African American Adolescents.” Journal of Research on Adolescence 22, no. 1 (2012): 218-233.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Webpage.” Website Name. Publication date. URL.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “COVID-19: How to Protect Yourself and Others.” CDC. December 11, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Magazine, Publication date.
Example : Smith, Mary. “The Power of Positive Thinking.” Psychology Today, March 2019.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Newspaper, Publication date.
Example : Johnson, Bob. “New Study Shows Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health.” The New York Times, February 15, 2021.
Example : Thompson, John P., ed. Social Work in the 21st Century. Sage Publications, 2014.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Chapter.” In Title of Book, edited by Editor’s First Name Last Name, page numbers. Publisher, Publication year.
Example : Johnson, Karen S. “The Future of Social Work: Challenges and Opportunities.” In Social Work in the 21st Century, edited by John P. Thompson, 105-118. Sage Publications, 2014.

Harvard Style
The Harvard Style, also known as the Author-Date System, is a widely used style for writing academic papers and essays in the social sciences. Here are the different reference formats in Harvard Style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher.
Example : Smith, John. 2005. The Psychology of Social Interaction. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal volume number (issue number): page numbers.
Example: Brown, Laura M., John G. Keating, and Sarah M. Jones. 2012. “The Role of Social Support in Coping with Stress among African American Adolescents.” Journal of Research on Adolescence 22 (1): 218-233.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. “Title of Webpage.” Website Name. URL. Accessed date.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2020. “COVID-19: How to Protect Yourself and Others.” CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html. Accessed April 1, 2023.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. “Title of Article.” Title of Magazine, month and date of publication.
Example : Smith, Mary. 2019. “The Power of Positive Thinking.” Psychology Today, March 2019.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. “Title of Article.” Title of Newspaper, month and date of publication.
Example : Johnson, Bob. 2021. “New Study Shows Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health.” The New York Times, February 15, 2021.
Editor’s Last name, First name, ed. Year of publication. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher.
Example : Thompson, John P., ed. 2014. Social Work in the 21st Century. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. “Title of Chapter.” In Title of Book, edited by Editor’s First Name Last Name, page numbers. Place of publication: Publisher.
Example : Johnson, Karen S. 2014. “The Future of Social Work: Challenges and Opportunities.” In Social Work in the 21st Century, edited by John P. Thompson, 105-118. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Vancouver Style
The Vancouver Style, also known as the Uniform Requirements for Manuscripts Submitted to Biomedical Journals, is a widely used style for writing academic papers in the biomedical sciences. Here are the different reference formats in Vancouver Style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Book. Edition number. Place of publication: Publisher; Year of publication.
Example : Smith, John K. The Psychology of Social Interaction. 2nd ed. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell; 2005.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Article. Abbreviated Journal Title. Year of publication; volume number(issue number):page numbers.
Example : Brown LM, Keating JG, Jones SM. The Role of Social Support in Coping with Stress among African American Adolescents. J Res Adolesc. 2012;22(1):218-233.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Webpage. Website Name [Internet]. Publication date. [cited date]. Available from: URL.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19: How to Protect Yourself and Others [Internet]. 2020 Dec 11. [cited 2023 Apr 1]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Article. Title of Magazine. Year of publication; month and day of publication:page numbers.
Example : Smith M. The Power of Positive Thinking. Psychology Today. 2019 Mar 1:32-35.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Article. Title of Newspaper. Year of publication; month and day of publication:page numbers.
Example : Johnson B. New Study Shows Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health. The New York Times. 2021 Feb 15:A4.
Editor’s Last name, First name, editor. Title of Book. Edition number. Place of publication: Publisher; Year of publication.
Example: Thompson JP, editor. Social Work in the 21st Century. 1st ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications; 2014.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Chapter. In: Editor’s Last name, First name, editor. Title of Book. Edition number. Place of publication: Publisher; Year of publication. page numbers.
Example : Johnson KS. The Future of Social Work: Challenges and Opportunities. In: Thompson JP, editor. Social Work in the 21st Century. 1st ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications; 2014. p. 105-118.
Turabian Style
Turabian style is a variation of the Chicago style used in academic writing, particularly in the fields of history and humanities. Here are the different reference formats in Turabian style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher, Year of publication.
Example : Smith, John K. The Psychology of Social Interaction. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell, 2005.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal volume number, no. issue number (Year of publication): page numbers.
Example : Brown, LM, Keating, JG, Jones, SM. “The Role of Social Support in Coping with Stress among African American Adolescents.” J Res Adolesc 22, no. 1 (2012): 218-233.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Webpage.” Name of Website. Publication date. Accessed date. URL.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “COVID-19: How to Protect Yourself and Others.” CDC. December 11, 2020. Accessed April 1, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Magazine, Month Day, Year of publication, page numbers.
Example : Smith, M. “The Power of Positive Thinking.” Psychology Today, March 1, 2019, 32-35.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Newspaper, Month Day, Year of publication.
Example : Johnson, B. “New Study Shows Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health.” The New York Times, February 15, 2021.
Editor’s Last name, First name, ed. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher, Year of publication.
Example : Thompson, JP, ed. Social Work in the 21st Century. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2014.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Chapter.” In Title of Book, edited by Editor’s Last name, First name, page numbers. Place of publication: Publisher, Year of publication.
Example : Johnson, KS. “The Future of Social Work: Challenges and Opportunities.” In Social Work in the 21st Century, edited by Thompson, JP, 105-118. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2014.
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Style
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) style is commonly used in engineering, computer science, and other technical fields. Here are the different reference formats in IEEE style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Book Title. Place of Publication: Publisher, Year of publication.
Example : Oppenheim, A. V., & Schafer, R. W. Discrete-Time Signal Processing. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2010.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Abbreviated Journal Title, vol. number, no. issue number, pp. page numbers, Month year of publication.
Example: Shannon, C. E. “A Mathematical Theory of Communication.” Bell System Technical Journal, vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 379-423, July 1948.
Conference paper
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Paper.” In Title of Conference Proceedings, Place of Conference, Date of Conference, pp. page numbers, Year of publication.
Example: Gupta, S., & Kumar, P. “An Improved System of Linear Discriminant Analysis for Face Recognition.” In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Science and Network Technology, Harbin, China, Dec. 2011, pp. 144-147.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Webpage.” Name of Website. Date of publication or last update. Accessed date. URL.
Example : National Aeronautics and Space Administration. “Apollo 11.” NASA. July 20, 1969. Accessed April 1, 2023. https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/apollo/apollo11.html.
Technical report
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Report.” Name of Institution or Organization, Report number, Year of publication.
Example : Smith, J. R. “Development of a New Solar Panel Technology.” National Renewable Energy Laboratory, NREL/TP-6A20-51645, 2011.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Patent.” Patent number, Issue date.
Example : Suzuki, H. “Method of Producing Carbon Nanotubes.” US Patent 7,151,019, December 19, 2006.
Standard Title. Standard number, Publication date.
Example : IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic. IEEE Std 754-2008, August 29, 2008
ACS (American Chemical Society) Style
ACS (American Chemical Society) style is commonly used in chemistry and related fields. Here are the different reference formats in ACS style:
Author’s Last name, First name; Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Article. Abbreviated Journal Title Year, Volume, Page Numbers.
Example : Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cui, Y.; Ma, Y. Facile Preparation of Fe3O4/graphene Composites Using a Hydrothermal Method for High-Performance Lithium Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2715-2721.
Author’s Last name, First name. Book Title; Publisher: Place of Publication, Year of Publication.
Example : Carey, F. A. Organic Chemistry; McGraw-Hill: New York, 2008.
Author’s Last name, First name. Chapter Title. In Book Title; Editor’s Last name, First name, Ed.; Publisher: Place of Publication, Year of Publication; Volume number, Chapter number, Page Numbers.
Example : Grossman, R. B. Analytical Chemistry of Aerosols. In Aerosol Measurement: Principles, Techniques, and Applications; Baron, P. A.; Willeke, K., Eds.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, 2001; Chapter 10, pp 395-424.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Webpage. Website Name, URL (accessed date).
Example : National Institute of Standards and Technology. Atomic Spectra Database. https://www.nist.gov/pml/atomic-spectra-database (accessed April 1, 2023).
Author’s Last name, First name. Patent Number. Patent Date.
Example : Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W. US Patent 9,999,999, December 31, 2022.
Author’s Last name, First name; Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Article. In Title of Conference Proceedings, Publisher: Place of Publication, Year of Publication; Volume Number, Page Numbers.
Example : Jia, H.; Xu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Huang, X. Fast Adsorption of Organic Pollutants by Graphene Oxide. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, 2017; Volume 1, pp 223-228.
AMA (American Medical Association) Style
AMA (American Medical Association) style is commonly used in medical and scientific fields. Here are the different reference formats in AMA style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Article Title. Journal Abbreviation. Year; Volume(Issue):Page Numbers.
Example : Jones, R. A.; Smith, B. C. The Role of Vitamin D in Maintaining Bone Health. JAMA. 2019;321(17):1765-1773.
Author’s Last name, First name. Book Title. Edition number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Example : Guyton, A. C.; Hall, J. E. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2015.
Author’s Last name, First name. Chapter Title. In: Editor’s Last name, First name, ed. Book Title. Edition number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year: Page Numbers.
Example: Rajakumar, K. Vitamin D and Bone Health. In: Holick, M. F., ed. Vitamin D: Physiology, Molecular Biology, and Clinical Applications. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Springer; 2010:211-222.
Author’s Last name, First name. Webpage Title. Website Name. URL. Published date. Updated date. Accessed date.
Example : National Cancer Institute. Breast Cancer Prevention (PDQ®)–Patient Version. National Cancer Institute. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/breast-prevention-pdq. Published October 11, 2022. Accessed April 1, 2023.
Author’s Last name, First name. Conference presentation title. In: Conference Title; Conference Date; Place of Conference.
Example : Smith, J. R. Vitamin D and Bone Health: A Meta-Analysis. In: Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research; September 20-23, 2022; San Diego, CA.
Thesis or dissertation
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Thesis or Dissertation. Degree level [Doctoral dissertation or Master’s thesis]. University Name; Year.
Example : Wilson, S. A. The Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on Bone Health in Postmenopausal Women [Doctoral dissertation]. University of California, Los Angeles; 2018.
ASCE (American Society of Civil Engineers) Style
The ASCE (American Society of Civil Engineers) style is commonly used in civil engineering fields. Here are the different reference formats in ASCE style:
Author’s Last name, First name. “Article Title.” Journal Title, volume number, issue number (year): page numbers. DOI or URL (if available).
Example : Smith, J. R. “Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Sustainable Drainage Systems in Urban Areas.” Journal of Environmental Engineering, vol. 146, no. 3 (2020): 04020010. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001668.
Example : McCuen, R. H. Hydrologic Analysis and Design. 4th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education; 2013.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Chapter Title.” In: Editor’s Last name, First name, ed. Book Title. Edition number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year: page numbers.
Example : Maidment, D. R. “Floodplain Management in the United States.” In: Shroder, J. F., ed. Treatise on Geomorphology. San Diego, CA: Academic Press; 2013: 447-460.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Paper Title.” In: Conference Title; Conference Date; Location. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year: page numbers.
Example: Smith, J. R. “Sustainable Drainage Systems for Urban Areas.” In: Proceedings of the ASCE International Conference on Sustainable Infrastructure; November 6-9, 2019; Los Angeles, CA. Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers; 2019: 156-163.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Report Title.” Report number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Example : U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. “Hurricane Sandy Coastal Risk Reduction Program, New York and New Jersey.” Report No. P-15-001. Washington, DC: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers; 2015.
CSE (Council of Science Editors) Style
The CSE (Council of Science Editors) style is commonly used in the scientific and medical fields. Here are the different reference formats in CSE style:
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Article Title.” Journal Title. Year;Volume(Issue):Page numbers.
Example : Smith, J.R. “Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Sustainable Drainage Systems in Urban Areas.” Journal of Environmental Engineering. 2020;146(3):04020010.
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. Book Title. Edition number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Chapter Title.” In: Editor’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial., ed. Book Title. Edition number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year:Page numbers.
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Paper Title.” In: Conference Title; Conference Date; Location. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Example : Smith, J.R. “Sustainable Drainage Systems for Urban Areas.” In: Proceedings of the ASCE International Conference on Sustainable Infrastructure; November 6-9, 2019; Los Angeles, CA. Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers; 2019.
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Report Title.” Report number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Bluebook Style
The Bluebook style is commonly used in the legal field for citing legal documents and sources. Here are the different reference formats in Bluebook style:
Case citation
Case name, volume source page (Court year).
Example : Brown v. Board of Education, 347 U.S. 483 (1954).
Statute citation
Name of Act, volume source § section number (year).
Example : Clean Air Act, 42 U.S.C. § 7401 (1963).
Regulation citation
Name of regulation, volume source § section number (year).
Example: Clean Air Act, 40 C.F.R. § 52.01 (2019).
Book citation
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. Book Title. Edition number (if applicable). Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Example: Smith, J.R. Legal Writing and Analysis. 3rd ed. New York, NY: Aspen Publishers; 2015.
Journal article citation
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Article Title.” Journal Title. Volume number (year): first page-last page.
Example: Garcia, C. “The Right to Counsel: An International Comparison.” International Journal of Legal Information. 43 (2015): 63-94.
Website citation
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Page Title.” Website Title. URL (accessed month day, year).
Example : United Nations. “Universal Declaration of Human Rights.” United Nations. https://www.un.org/en/universal-declaration-human-rights/ (accessed January 3, 2023).
Oxford Style
The Oxford style, also known as the Oxford referencing system or the documentary-note citation system, is commonly used in the humanities, including literature, history, and philosophy. Here are the different reference formats in Oxford style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Book Title. Place of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication.
Example : Smith, John. The Art of Writing. New York: Penguin, 2020.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Article Title.” Journal Title volume, no. issue (year): page range.
Example: Garcia, Carlos. “The Role of Ethics in Philosophy.” Philosophy Today 67, no. 3 (2019): 53-68.
Chapter in an edited book citation
Author’s Last name, First name. “Chapter Title.” In Book Title, edited by Editor’s Name, page range. Place of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication.
Example : Lee, Mary. “Feminism in the 21st Century.” In The Oxford Handbook of Feminism, edited by Jane Smith, 51-69. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2018.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Page Title.” Website Title. URL (accessed day month year).
Example : Jones, David. “The Importance of Learning Languages.” Oxford Language Center. https://www.oxfordlanguagecenter.com/importance-of-learning-languages/ (accessed 3 January 2023).
Dissertation or thesis citation
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Dissertation/Thesis.” PhD diss., University Name, Year of Publication.
Example : Brown, Susan. “The Art of Storytelling in American Literature.” PhD diss., University of Oxford, 2020.
Newspaper article citation
Author’s Last name, First name. “Article Title.” Newspaper Title, Month Day, Year.
Example : Robinson, Andrew. “New Developments in Climate Change Research.” The Guardian, September 15, 2022.
AAA (American Anthropological Association) Style
The American Anthropological Association (AAA) style is commonly used in anthropology research papers and journals. Here are the different reference formats in AAA style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. Book Title. Place of Publication: Publisher.
Example : Smith, John. 2019. The Anthropology of Food. New York: Routledge.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Article Title.” Journal Title volume, no. issue: page range.
Example : Garcia, Carlos. 2021. “The Role of Ethics in Anthropology.” American Anthropologist 123, no. 2: 237-251.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Chapter Title.” In Book Title, edited by Editor’s Name, page range. Place of Publication: Publisher.
Example: Lee, Mary. 2018. “Feminism in Anthropology.” In The Oxford Handbook of Feminism, edited by Jane Smith, 51-69. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Page Title.” Website Title. URL (accessed day month year).
Example : Jones, David. 2020. “The Importance of Learning Languages.” Oxford Language Center. https://www.oxfordlanguagecenter.com/importance-of-learning-languages/ (accessed January 3, 2023).
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Title of Dissertation/Thesis.” PhD diss., University Name.
Example : Brown, Susan. 2022. “The Art of Storytelling in Anthropology.” PhD diss., University of California, Berkeley.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Article Title.” Newspaper Title, Month Day.
Example : Robinson, Andrew. 2021. “New Developments in Anthropology Research.” The Guardian, September 15.
AIP (American Institute of Physics) Style
The American Institute of Physics (AIP) style is commonly used in physics research papers and journals. Here are the different reference formats in AIP style:
Example : Johnson, S. D. 2021. “Quantum Computing and Information.” Journal of Applied Physics 129, no. 4: 043102.
Example : Feynman, Richard. 2018. The Feynman Lectures on Physics. New York: Basic Books.
Example : Jones, David. 2020. “The Future of Quantum Computing.” In The Handbook of Physics, edited by John Smith, 125-136. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Conference proceedings citation
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Title of Paper.” Proceedings of Conference Name, date and location: page range. Place of Publication: Publisher.
Example : Chen, Wei. 2019. “The Applications of Nanotechnology in Solar Cells.” Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Nanotechnology, July 15-17, Tokyo, Japan: 224-229. New York: AIP Publishing.
Example : American Institute of Physics. 2022. “About AIP Publishing.” AIP Publishing. https://publishing.aip.org/about-aip-publishing/ (accessed January 3, 2023).
Patent citation
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. Patent Number.
Example : Smith, John. 2018. US Patent 9,873,644.
References Writing Guide
Here are some general guidelines for writing references:
- Follow the citation style guidelines: Different disciplines and journals may require different citation styles (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). It is important to follow the specific guidelines for the citation style required.
- Include all necessary information : Each citation should include enough information for readers to locate the source. For example, a journal article citation should include the author(s), title of the article, journal title, volume number, issue number, page numbers, and publication year.
- Use proper formatting: Citation styles typically have specific formatting requirements for different types of sources. Make sure to follow the proper formatting for each citation.
- Order citations alphabetically: If listing multiple sources, they should be listed alphabetically by the author’s last name.
- Be consistent: Use the same citation style throughout the entire paper or project.
- Check for accuracy: Double-check all citations to ensure accuracy, including correct spelling of author names and publication information.
- Use reputable sources: When selecting sources to cite, choose reputable and authoritative sources. Avoid sources that are biased or unreliable.
- Include all sources: Make sure to include all sources used in the research, including those that were not directly quoted but still informed the work.
- Use online tools : There are online tools available (e.g., citation generators) that can help with formatting and organizing references.
Purpose of References in Research
References in research serve several purposes:
- To give credit to the original authors or sources of information used in the research. It is important to acknowledge the work of others and avoid plagiarism.
- To provide evidence for the claims made in the research. References can support the arguments, hypotheses, or conclusions presented in the research by citing relevant studies, data, or theories.
- To allow readers to find and verify the sources used in the research. References provide the necessary information for readers to locate and access the sources cited in the research, which allows them to evaluate the quality and reliability of the information presented.
- To situate the research within the broader context of the field. References can show how the research builds on or contributes to the existing body of knowledge, and can help readers to identify gaps in the literature that the research seeks to address.
Importance of References in Research
References play an important role in research for several reasons:
- Credibility : By citing authoritative sources, references lend credibility to the research and its claims. They provide evidence that the research is based on a sound foundation of knowledge and has been carefully researched.
- Avoidance of Plagiarism : References help researchers avoid plagiarism by giving credit to the original authors or sources of information. This is important for ethical reasons and also to avoid legal repercussions.
- Reproducibility : References allow others to reproduce the research by providing detailed information on the sources used. This is important for verification of the research and for others to build on the work.
- Context : References provide context for the research by situating it within the broader body of knowledge in the field. They help researchers to understand where their work fits in and how it builds on or contributes to existing knowledge.
- Evaluation : References provide a means for others to evaluate the research by allowing them to assess the quality and reliability of the sources used.
Advantages of References in Research
There are several advantages of including references in research:
- Acknowledgment of Sources: Including references gives credit to the authors or sources of information used in the research. This is important to acknowledge the original work and avoid plagiarism.
- Evidence and Support : References can provide evidence to support the arguments, hypotheses, or conclusions presented in the research. This can add credibility and strength to the research.
- Reproducibility : References provide the necessary information for others to reproduce the research. This is important for the verification of the research and for others to build on the work.
- Context : References can help to situate the research within the broader body of knowledge in the field. This helps researchers to understand where their work fits in and how it builds on or contributes to existing knowledge.
- Evaluation : Including references allows others to evaluate the research by providing a means to assess the quality and reliability of the sources used.
- Ongoing Conversation: References allow researchers to engage in ongoing conversations and debates within their fields. They can show how the research builds on or contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
- Table of Contents
AI, Ethics & Human Agency
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process.
- Recommendation Reports
- © 2023 by Joseph M. Moxley - University of South Florida , Julie Staggers - Washington State University
Recommendation reports are texts that advise audiences about the best ways to solve a problem. Recommendation reports are a type of formal report that is widely used across disciplines and professions. Subject Matter Experts aim to make recommendations based on the best available theory, research and practice.
Different disciplines and professions have different research methods for assessing knowledge claims and defining knowledge . Thus, there is no one perfect way to write a recommendation report.
As always, when composing—especially when you’re planning your report—it’s strategic to focus on your audience, rhetorical analysis, and rhetorical reasoning. At center, keep the focus on what you want your audience to feel, think, and do.
While writers, speakers, and knowledge workers . . . may choose a variety of ways to organize their reports, below are some fairly traditional sections to formal recommendations reports:
- Letter of transmittal
- Problem Definition
- Potential solutions to the problem
- Empirical Research Methods used to investigate the problem
- Recommendations
- List of Illustrations
Report Body
Note: your specific rhetorical context will determine what headings you use in your Recommendation Report. That said, the following sections are fairly typical for this genre, and they are required, as appropriate, for this assignment.
Report back matter
Collect material for the appendices as you go. The report back matter will include:
- Bibliography, which is sometimes referred to as Works Cited or References (Use a citation format appropriate for your field (APA, MLA, Chicago, IEEE, etc.)
- Appendices, if necessary (e.g., letters of support, financial projections)
Formatting and design
Employ a professional writing style throughout, including:
- Page layout: Appropriate to audience, purpose, and context. 8.5 x 11 with 1-inch margins is a fail-safe default.
- Typography: Choose business-friendly fonts appropriate to your audience, purpose, and context; Arial for headers and Times New Roman for body text is a safe, neutral default.
- Headings and subheadings: Use a numbered heading and subheading system, formatted using the Styles function on your word processor.
- Bulleted and numbered lists: Use lists that are formatted correctly using the list buttons on your word processor with a blank line before the first bullet and after the last bullet
- Graphics and figures: Support data findings and arguments with appropriate visuals – charts, tables, graphics; Include numbered titles and captions
- Page numbering: use lower-case Roman numerals for pages before the table of contents, Arabic numerals; no page number on the TOC.
Additional Resources
- Final Reports by Angela Eward-Mangione and Katherine McGee
- Professional Writing Style

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority – How to Establish Credibility in Speech & Writing
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

Writing an Effective & Supportive Recommendation Letter
Sarvenaz sarabipour.
1 Institute for Computational Medicine and Department of Biomedical Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, United States
Sarah J. Hainer
2 Department of Biological Sciences, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
Emily Furlong
3 Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
Nafisa M. Jadavji
4 Department of Biomedical Sciences, Midwestern University, Glendale, United States
5 Department of Neuroscience, Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada
Charlotte M. de Winde
6 MRC Laboratory for Molecular Cell Biology, University College London, London, United Kingdom
7 Department of Molecular Cell Biology & Immunology, Amsterdam UMC Locatie VUmc, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Natalia Bielczyk
8 Welcome Solutions, Nijmegen, the Netherlands
9 Stichting Solaris Onderzoek en Ontwikkeling, Nijmegen, the Netherlands
Aparna P. Shah
10 The Solomon H. Snyder Department of Neuroscience, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, United States
Author Contributions
Writing recommendation letters on behalf of students and other early-career researchers is an important mentoring task within academia. An effective recommendation letter describes key candidate qualities such as academic achievements, extracurricular activities, outstanding personality traits, participation in and dedication to a particular discipline, and the mentor’s confidence in the candidate’s abilities. In this Words of Advice, we provide guidance to researchers on composing constructive and supportive recommendation letters, including tips for structuring and providing specific and effective examples, while maintaining a balance in language and avoiding potential biases.
Introduction
A letter of recommendation or a reference letter is a statement of support for a student or an early-career researcher (ECR; a non-tenured scientist who may be a research trainee, postdoctoral fellow, laboratory technician, or junior faculty colleague) who is a candidate for future employment, promotion, education, or funding opportunities. Letters of recommendation are commonly requested at different stages of an academic research career and sometimes for transitioning to a non-academic career. Candidates need to request letters early on and prepare relevant information for the individual who is approached for recommendation [ 1 , 2 ]. Writing recommendation letters in support of ECRs for career development opportunities is an important task undertaken frequently by academics. ECRs can also serve as mentors during their training period and may be asked to write letters for their mentees. This offers the ECRs an excellent opportunity to gain experience in drafting these important documents, but may present a particular challenge for individuals with little experience. In general, a letter of recommendation should present a well-documented evaluation and provide sufficient evidence and information about an individual to assist a person or a selection committee in making their decision on an application [ 1 ]. Specifically, the letter should address the purpose for which it is written (which is generally to provide support of the candidate’s application and recommendation for the opportunity) and describe key candidate qualities, the significance of the work performed, the candidate’s other accomplishments and the mentor’s confidence in the candidate’s abilities. It should be written in clear and unbiased language. While a poorly written letter may not result in loss of the opportunity for the candidate, a well-written one can help an application stand out from the others, thus well-enhancing the candidate’s chances for the opportunity.
Letter readers at review, funding, admissions, hiring and promotion committees need to examine the letter objectively with a keenness for information on the quality of the candidate’s work and perspective on their scientific character [ 6 ]. However well-intentioned, letters can fall short of providing a positive, effective, and supportive document [ 1 , 3 – 5 ]. To prevent this, it is important to make every letter personal; thus, writing letters requires time and careful consideration. This article draws from our collective experiences as ECRs and the literature to highlight best practices and key elements for those asked to provide recommendation letters for their colleagues, students, or researchers who have studied or trained in their classroom or research laboratory. We hope that these guidelines will be helpful for letter writers to provide an overall picture of the candidate’s capabilities, potential and professional promise.
Decide on whether to write the letter
Before you start, it is important to evaluate your relationship with the candidate and ability to assess their skills and abilities honestly. Consider how well and in what context you know the person, as well as whether you can be supportive of their application [ 7 ]. Examine the description of the opportunity for which the letter is being requested ( Figure 1 ). Often you will receive a request by a student or a researcher whom you know very well and have interacted with in different settings – in and out of the classroom, your laboratory or that of a colleague, or within your department – and whose performance you find to be consistently satisfactory or excellent. Sometimes a mentee may request a recommendation letter when still employed or working with you, their research advisor. This can come as an unpleasant surprise if you are unaware that the trainee was seeking other opportunities (for instance, if they haven’t been employed with you for long, or have just embarked on a new project). While the mentee should be transparent about their goals and searching for opportunities, you should as a mentor offer to provide the letter for your mentee (see Table 1 ).

First, it is important to establish whether you are equipped to write a strong letter of support. If not, it is best to have a candid conversation with the applicant and discuss alternative options or opportunities. If you are in a position to write a strong letter of support, first acquire information regarding the application and the candidate, draft a letter in advance (see Box 1 ) and submit the letter on time. When drafting the letter, incorporate specific examples, avoid biases, and discuss the letter with the candidate (see Tables 1 – 2 for specific examples). After submission, store a digital copy for potential future use for the same candidate.
Key do’s and don’ts when being asked to write a letter of recommendation
Other requests may be made by a candidate who has made no impression on you, or only a negative one. In this case, consider the candidate’s potential and future goals, and be fair in your evaluation. Sending a negative letter or a generic positive letter for individuals you barely know is not helpful to the selection committee and can backfire for the candidate. It can also, in some instances, backfire for you if a colleague accepts a candidate based on your generic positive letter when you did not necessarily fully support that individual. For instance, letter writers sometimes stretch the truth to make a candidate sound better than they really are, thinking it is helpful. If you do not know the applicant well enough or feel that you cannot be supportive, you are not in a strong position to write the recommendation letter and should decline the request, being open about why you are declining to write the letter. Also, be selective about writing on behalf of colleagues who may be in one’s field but whose work is not well known to you. If you have to read the candidate’s curriculum vitae to find out who they are and what they have done, then you may not be qualified to write the letter [ 8 ].
When declining a request to provide a letter of support, it is important to explain your reasoning to the candidate and suggest how they might improve their prospects for the future [ 8 ]. If the candidate is having a similar problem with other mentors, try to help them identify a more appropriate referee or to explore whether they are making an appropriate application in the first place. Suggest constructive steps to improve relationships with mentors to identify individuals to provide letters in the future. Most importantly, do not let the candidate assume that all opportunities for obtaining supportive letters of recommendation have been permanently lost. Emphasize the candidate’s strengths by asking them to share a favourite paper, assignment, project, or other positive experience that may have taken place outside of your class or lab, to help you identify their strengths. Finally, discuss with the candidate their career goals to help them realize what they need to focus on to become more competitive or steer them in a different career direction. This conversation can mark an important step and become a great interaction and mentoring opportunity for ECRs.
Examine the application requirements
Once you decide to write a recommendation letter, it is important to know what type and level of opportunity the candidate is applying for, as this will determine what should be discussed in the letter ( Figure 1 ). You should carefully read the opportunity posting description and/or ask the candidate to summarize the main requirements and let you know the specific points that they find important to highlight. Pay close attention to the language of the position announcement to fully address the requested information and tailor the letter to the specific needs of the institution, employer, or funding organisation. In some instances, a waiver form or an option indicating whether or not the candidate waives their right to see the recommendation document is provided. If the candidate queries a waiver decision, note that often referees are not allowed to send a letter that is not confidential and that there may be important benefits to maintaining the confidentiality of letters (see Table 1 ). Specifically, selection committees may view confidential letters as having greater credibility and, value and some letter writers may feel less reserved in their praise of candidates in confidential letters.
Acquire candidate information and discuss letter content
To acquire appropriate information about the candidate, one or more of the following documents may be valuable: a resume or curriculum vitae (CV), a publication or a manuscript, an assignment or exam written for your course, a copy of the application essay or personal statement, a transcript of academic records, a summary of current work, and specific recommendation forms or questionnaires (if provided) [ 9 ]. Alternatively, you may ask the candidate to complete a questionnaire asking for necessary information and supporting documents [ 10 ]. Examine the candidate’s CV and provide important context to the achievements listed therein. Tailor the letter for the opportunity using these documents as a guide, but do not repeat their contents as the candidate likely submits them separately. Even the most articulate of candidates may find it difficult to describe their qualities in writing [ 11 ]. Furthermore, a request may be made by a person who has made a good impression, but for whom you lack significant information to be able to write a strong letter. Thus, even if you know a candidate well, schedule a brief in-person, phone, or virtual meeting with them to 1) fill in gaps in your knowledge about them, 2) understand why they are applying for this particular opportunity, 3) help bring their past accomplishments into sharper focus, and 4) discuss their short- and long-term goals and how their current studies or research activities relate to the opportunity they are applying for and to these goals. Other key information to gather from the applicant includes the date on which the recommendation letter is due, as well as details on how to submit it.
For most applications (for both academic and non-academic opportunities), a letter of recommendation will need to cover both scholarly capabilities and achievements as well as a broader range of personal qualities and experiences beyond the classroom or the laboratory. This includes extracurricular experiences and traits such as creativity, tenacity, and collegiality. If necessary, discuss with the candidate what they would like to see additionally highlighted. As another example of matching a letter with its purpose, a letter for a fellowship application for a specific project should discuss the validity and feasibility of the project, as well as the candidate’s qualifications for fulfilling the project.
Draft the letter early and maintain a copy
Another factor that greatly facilitates letter writing is drafting one as soon as possible after you have taught or trained the candidate, while your impressions are still clear. You might consider encouraging the candidate to make their requests early [ 11 ]. These letters can be placed in the candidate’s portfolio and maintained in your own files for future reference. If you are writing a letter in response to a request, start drafting it well in advance and anticipate multiple rounds of revision before submission. Once you have been asked by a candidate to write a letter, that candidate may return frequently, over a number of years, for additional letters. Therefore, maintain a digital copy of the letter for your records and for potential future applications for the same candidate.
Structure your letter
In the opening, you should introduce yourself and the candidate, state your qualifications and explain how you became acquainted with the candidate, as well as the purpose of the letter, and a summary of your recommendation ( Table 2 ). To explain your relationship with the candidate you should fully describe the capacity in which you know them: the type of experience, the period during which you worked with the candidate, and any special assignments or responsibilities that the candidate performed under your guidance. For instance, the letter may start with: “This candidate completed their postdoctoral training under my supervision. I am pleased to be able to provide my strongest support in recommending them for this opportunity.” You may also consider ranking the candidate among similar level candidates within the opening section to give an immediate impression of your thoughts. Depending on the position, ranking the candidate may also be desired by selection committees, and may be requested within the letter. For instance, the recommendation form or instructions may ask you to rank the candidate in the top 1%, 5%, 10%, etc., of applicants. You could write "the student is in the top 5% of undergraduate students I have trained" Or “There are currently x graduate students in our department and I rank this candidate at the top 1%. Their experimental/computational skills are the best I have ever had in my own laboratory.”. Do not forget to include with whom or what group you are comparing the individual. If you have not yet trained many individuals in your own laboratory, include those that you trained previously as a researcher as reference. Having concentrated on the candidate’s individual or unique strengths, you might find it difficult to provide a ranking. This is less of an issue if a candidate is unambiguously among the top 10% that you have mentored but not all who come to you for a letter will fall within that small group. If you wish to offer a comparative perspective, you might more readily be able to do so in more specific areas such as whether the candidate is one of the most articulate, original, clear-thinking, motivated, or intellectually curious.
Key do’s and don’ts when writing a letter of recommendation
The body of the recommendation letter should provide specific information about the candidate and address any questions or requirements posed in the selection criteria (see sections above). Some applications may ask for comments on a candidate’s scholarly performance. Refer the reader to the candidate’s CV and/or transcript if necessary but don’t report grades, unless to make an exceptional point (such as they were the only student to earn a top grade in your class). The body of the recommendation letter will contain the majority of the information including specific examples, relevant candidate qualities, and your experiences with the candidate, and therefore the majority of this manuscript focuses on what to include in this section.
The closing paragraph of the letter should briefly 1) summarize your opinions about the candidate, 2) clearly state your recommendation and strong support of the candidate for the opportunity that they are seeking, and 3) offer the recipient of the letter the option to contact you if they need any further information. Make sure to provide your email address and phone number in case the recipient has additional questions. The overall tone of the letter can represent your confidence in the applicant. If opportunity criteria are detailed and the candidate meets these criteria completely, include this information. Do not focus on what you may perceive as a candidate’s negative qualities as such tone may do more harm than intended ( Table 2 ). Finally, be aware of the Forer’s effect, a cognitive error, in which a very general description, that fits almost everyone, is used to describe a person [ 20 ]. Such generalizations can be harmful, as they provide the candidate the impression that they received a valuable, positive letter, but for the committee, who receive hundreds of similar letters, this is non-informative and unhelpful to the application.
Describe relevant candidate qualities with specific examples and without overhyping
In discussing a candidate’s qualities and character, proceed in ways similar to those used for intellectual evaluation ( Box 1 ). Information to specifically highlight may include personal characteristics, such as integrity, resilience, poise, confidence, dependability, patience, creativity, enthusiasm, teaching capabilities, problem-solving abilities, ability to manage trainees and to work with colleagues, curriculum development skills, collaboration skills, experience in grant writing, ability to organize events and demonstrate abilities in project management, and ability to troubleshoot (see section “ Use ethical principles, positive and inclusive language within the letter ” below for tips on using inclusive terminology). The candidate may also have a specific area of knowledge, strengths and experiences worth highlighting such as strong communication skills, expertise in a particular scientific subfield, an undergraduate degree with a double major, relevant work or research experience, coaching, and/or other extracurricular activities. Consider whether the candidate has taught others in the lab, or shown particular motivation and commitment in their work. When writing letters for mentees who are applying for (non-)academic jobs or admission to academic institutions, do not merely emphasize their strengths, achievements and potential, but also try to 1) convey a sense of what makes them a potential fit for that position or funding opportunity, and 2) fill in the gaps. Gaps may include an insufficient description of the candidate’s strengths or research given restrictions on document length. Importantly, to identify these gaps, one must have carefully reviewed both the opportunity posting as well as the application materials (see Box 1 , Table 2 ).
Recommendations for Letter Writers
- Consider characteristics that excite & motivate this candidate.
- Include qualities that you remember most about the candidate.
- Detail their unusual competence, talent, mentorship, teaching or leadership abilities.
- Explain the candidate’s disappointments or failures & the way they reacted & overcame.
- Discuss if they demonstrated a willingness to take intellectual risks beyond the normal research & classroom experience.
- Ensure that you have knowledge of the institution that the candidate is applying for.
- Consider what makes you believe this particular opportunity is a good match for this candidate.
- Consider how they might fit into the institution’s community & grow from their experience.
- Describe their personality & social skills.
- Discuss how the candidate interacts with teachers & peers.
- Use ethical principles, positive & inclusive language within the letter.
- Do not list facts & details, every paper, or discovery of the candidate’s career.
- Only mention unusual family or community circumstances after consulting the candidate.
- A thoughtful letter from a respective colleague with a sense of perspective can be quite valuable.
- Each letter takes time & effort, take it seriously.
When writing letters to nominate colleagues for promotion or awards, place stronger emphasis on their achievements and contributions to a field, or on their track record of teaching, mentorship and service, to aid the judging panel. In addition to describing the candidate as they are right now, you can discuss the development the person has undergone (for specific examples see Table 2 ).
A letter of recommendation can also explain weaknesses or ambiguities in the candidate’s record. If appropriate – and only after consulting the candidate - you may wish to mention a family illness, financial hardship, or other factors that may have resulted in a setback or specific portion of the candidate’s application perceived weakness (such as in the candidate’s transcript). For example, sometimes there are acceptable circumstances for a gap in a candidate’s publication record—perhaps a medical condition or a family situation kept them out of the lab for a period of time. Importantly, being upfront about why there is a perceived gap or blemish in the application package can strengthen the application. Put a positive spin on the perceived negatives using terms such as “has taken steps to address gaps in knowledge”, “has worked hard to,” and “made great progress in” (see Table 2 ).
Describe a candidate’s intellectual capabilities in terms that reflect their distinctive or individual strengths and be prepared to support your judgment with field-specific content [ 12 ] and concrete examples. These can significantly strengthen a letter and will demonstrate a strong relationship between you and the candidate. Describe what the candidate’s strengths are, moments they have overcome adversity, what is important to them. For example: “candidate x is exceptionally intelligent. They proved to be a very quick study, learning the elements of research design and technique y in record time. Furthermore, their questions are always thoughtful and penetrating.”. Mention the candidate’s diligence, work ethic, and curiosity and do not merely state that “the applicant is strong” without specific examples. Describing improvements to candidate skills over time can help highlight their work ethic, resolve, and achievements over time. However, do not belabor a potential lower starting point.
Provide specific examples for when leadership was demonstrated, but do not include leadership qualities if they have not been demonstrated. For example, describe the candidate’s qualities such as independence, critical thinking, creativity, resilience, ability to design and interpret experiments; ability to identify the next steps and generate interesting questions or ideas, and what you were especially impressed by. Do not generically list the applicant as independent with no support or if this statement would be untrue.
Do not qualify candidate qualities based on a stereotype for specific identities. Quantify the candidate’s abilities, especially with respect to other scientists who have achieved success in the field and who the letter reader might know. Many letter writers rank applicants according to their own measure of what makes a good researcher, graduate trainee, or technician according to a combination of research strengths, leadership skills, writing ability, oral communication, teaching ability, and collegiality. Describe what the role of the candidate was in their project and eventual publication and do not assume letter readers will identify this information on their own (see Table 2 ). Including a description about roles and responsibilities can help to quantify a candidate’s contribution to the listed work. For example, “The candidate is the first author of the paper, designed, and led the project.”. Even the best mentor can overlook important points, especially since mentors typically have multiple mentees under their supervision. Thus, it can help to ask the candidate what they consider their strengths or traits, and accomplishments of which they are proud.
If you lack sufficient information to answer certain questions about the candidate, it is best to maintain the integrity and credibility of your letter - as the recommending person, you are potentially writing to a colleague and/or someone who will be impacted by your letter; therefore, honesty is key above all. Avoid the misconception that the more superlatives you use, the stronger the letter. Heavy use of generic phrases or clichés is unhelpful. Your letter can only be effective if it contains substantive information about the specific candidate and their qualifications for the opportunity. A recommendation that paints an unrealistic picture of a candidate may be discounted. All information in a letter of recommendation should be, to the best of your knowledge, accurate. Therefore, present the person truthfully but positively. Write strongly and specifically about someone who is truly excellent (explicitly describe how and why they are special). Write a balanced letter without overhyping the candidate as it will not help them.
Be careful about what you leave out of the letter
Beware of what you leave out of the recommendation letter. For most opportunities, there are expectations of what should be included in a letter, and therefore what is not said can be just as important as what is said. Importantly, do not assume all the same information is necessary for every opportunity. In general, you should include the information stated above, covering how you know the candidate, their strengths, specific examples to support your statements, and how the candidate fits well for the opportunity. For example, if you don’t mention a candidate’s leadership skills or their ability to work well with others, the letter reader may wonder why, if the opportunity requires these skills. Always remember that opportunities are sought by many individuals, so evaluators may look for any reason to disregard an application, such as a letter not following instructions or discussing the appropriate material. Also promote the candidate by discussing all of their scholarly and non-scholarly efforts, including non-peer reviewed research outputs such as preprints, academic and non-academic service, and advocacy work which are among their broader impact and all indicative of valuable leadership qualities for both academic and non-academic environments ( Table 2 ).
Provide an even-handed judgment of scholarly impact, be fair and describe accomplishments fairly by writing a balanced letter about the candidate’s attributes that is thoughtful and personal (see Table 2 ). Submitting a generic, hastily written recommendation letter is not helpful and can backfire for both the candidate and the letter writer as you will often leave out important information for the specific opportunity; thus, allow for sufficient time and effort on each candidate/application.
Making the letter memorable by adding content that the reader will remember, such as an unusual anecdote, or use of a unique term to describe the candidate. This will help the application stand out from all the others. Tailor the letter to the candidate, including as much unique, relevant information as possible and avoid including personal information unless the candidate gives consent. Provide meaningful examples of achievements and provide stories or anecdotes that illustrate the candidate’s strengths. Say what the candidate specifically did to give you that impression ( Box 1 ). Don’t merely praise the candidate using generalities such as “candidate x is a quick learner”.
Use ethical principles, positive and inclusive language within the letter
Gender affects scientific careers. Avoid providing information that is irrelevant to the opportunity, such as ethnicity, age, hobbies, or marital status. Write about professional attributes that pertain to the application. However, there are qualities that might be important to the job or funding opportunity. For instance, personal information may illustrate the ability to persevere and overcome adversity - qualities that are helpful in academia and other career paths. It is critical to pay attention to biases and choices of words while writing the letter [ 13 , 14 ]. Advocacy bias (a letter writer is more likely to write a strong letter for someone similar to themselves) has been identified as an issue in academic environments [ 3 ]. Studies have also shown that there are often differences in the choice of words used in letters for male and female scientists [ 3 , 5 ]. For instance, letters for women have been found not to contain much specific and descriptive language. Descriptions often pay greater attention to the personal lives or personal characteristics of women than men, focusing on items that have little relevance in a letter of recommendation. When writing recommendation letters, employers have a tendency to focus on scholarly capabilities in male candidates and personality features in female candidates; for instance, female candidates tend to be depicted in letters as teachers and trainees, whereas male candidates are described as researchers and professionals [ 15 ]. Also, letters towards males often contain more standout words such as “superb”, “outstanding”, and “excellent”. Furthermore, letters for women had been found to contain more doubt-raising statements, including negative or unexplained comments [ 3 , 15 , 16 ]. This is discriminative towards women and gives a less clear picture of women as professionals. Keep the letter gender neutral. Do not write statements such as “candidate x is a kind woman” or “candidate y is a fantastic female scientist” as these have no bearing on whether someone will do well in graduate school or in a job. One way to reduce gender bias is by checking your reference letter with a gender bias calculator [ 17 , 18 ]. Test for gender biases by writing a letter of recommendation for any candidate, male or female, and then switch all the pronouns to the opposite gender. Read the letter over and ask yourself if it sounds odd. If it does, you should probably change the terms used [ 17 ]. Other biases also exist, and so while gender bias has been the most heavily investigated, bias based on other identities (race, nationality, ethnicity, among others) should also be examined and assessed in advance and during letter writing to ensure accurate and appropriate recommendations for all.
Revise and submit on time
The recommendation letter should be written using language that is straightforward and concise [ 19 ]. Avoid using jargon or language that is too general or effusive ( Table 1 ). Formats and styles of single and co-signed letters are also important considerations. In some applications, the format is determined by the application portal itself in which the recommender is asked to answer a series of questions. If these questions do not cover everything you would like to address you could inquire if there is the option to provide a letter as well. Conversely, if the recommendation questionnaire asks for information that you cannot provide, it is best to explicitly mention this in writing. The care with which you write the letter will also influence the effectiveness of the letter - writing eloquently is another way of registering your support for the candidate. Letters longer than two pages can be counterproductive, and off-putting as reviewers normally have a large quantity of letters to read. In special cases, longer letters may be more favourable depending on the opportunity. On the other hand, anything shorter than a page may imply a lack of interest or knowledge, or a negative impression on the candidate. In letter format, write at least 3-4 paragraphs. It is important to note that letters from different sectors, such as academia versus industry tend to be of different lengths. Ensure that your letter is received by the requested method (mail or e-mail) and deadline, as a late submission could be detrimental for the candidate. Write and sign the letter on your department letterhead which is a further form of identification.
Conclusions
Recommendation letters can serve as important tools for assessing ECRs as potential candidates for a job, course, or funding opportunity. Candidates need to request letters in advance and provide relevant information for the recommender. Readers at selection committees need to examine the letter objectively with an eye for information on the quality of the candidate’s scholarly and non-scholarly endeavours and scientific traits. As a referee, it is important that you are positive, candid, yet helpful, as you work with the candidate in drafting a letter in their support. In writing a recommendation letter, summarize your thoughts on the candidate and emphasize your strong support for their candidacy. A successful letter communicates the writer’s enthusiasm for an individual, but does so realistically, sympathetically, and with concrete examples to support the writer’s associations. Writing recommendation letters can help mentors examine their interactions with their mentee and know them in different light. Express your willingness to help further by concluding the letter with an offer to be contacted should the reader need more information. Remember that a letter writer’s judgment and credibility are at stake thus do spend the time and effort to present yourself as a recommender in the best light and help ECRs in their career path.
Acknowledgements
S.J.H. was supported by the National Institutes of Health grant R35GM133732. A.P.S. was partially supported by the NARSAD Young Investigator Grant 27705.
Abbreviations:
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Reference List: Textual Sources

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Basic Format for Books
Edited book, no author, edited book with an author or authors, a translation.
Note : When you cite a republished work, like the one above, in your text, it should appear with both dates: Plato (385-378/1989)
Edition Other Than the First
Article or chapter in an edited book.
Note : When you list the pages of the chapter or essay in parentheses after the book title, use "pp." before the numbers: (pp. 1-21). This abbreviation, however, does not appear before the page numbers in periodical references, except for newspapers. List any edition number in the same set of parentheses as the page numbers, separated by a comma: (2nd ed., pp. 66-72).
Multivolume Work
Articles in periodicals.
APA style dictates that authors are named with their last name followed by their initials; publication year goes between parentheses, followed by a period. The title of the article is in sentence-case, meaning only the first word and proper nouns in the title are capitalized. The periodical title is run in title case, and is followed by the volume number which, with the title, is also italicized. If a DOI has been assigned to the article that you are using, you should include this after the page numbers for the article. If no DOI has been assigned and you are accessing the periodical online, use the URL of the website from which you are retrieving the periodical.
Article in Print Journal
Note: APA 7 advises writers to include a DOI (if available), even when using the print source. The example above assumes no DOI is available.
Article in Electronic Journal
Note : This content also appears on Reference List: Online Media .
As noted above, when citing an article in an electronic journal, include a DOI if one is associated with the article.
DOIs may not always be available. In these cases, use a URL. Many academic journals provide stable URLs that function similarly to DOIs. These are preferable to ordinary URLs copied and pasted from the browser's address bar.
Article in a Magazine
Article in a newspaper.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
What the data says about Americans’ views of climate change

A recent report from the United Nations’ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has underscored the need for international action to avoid increasingly severe climate impacts in the years to come. Steps outlined in the report, and by climate experts, include major reductions in greenhouse gas emissions from sectors such as energy production and transportation.
But how do Americans feel about climate change, and what steps do they think the United States should take to address it? Here are eight charts that illustrate Americans’ views on the issue, based on recent Pew Research Center surveys.
Pew Research Center published this collection of survey findings as part of its ongoing work to understand attitudes about climate change and energy issues. The most recent survey was conducted May 30-June 4, 2023, among 10,329 U.S. adults. Earlier findings have been previously published, and methodological information, including the sample sizes and field dates, can be found by following the links in the text.
Everyone who took part in the June 2023 survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way, nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and its methodology .
A majority of Americans support prioritizing the development of renewable energy sources. Two-thirds of U.S. adults say the country should prioritize developing renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, over expanding the production of oil, coal and natural gas, according to a survey conducted in June 2023.
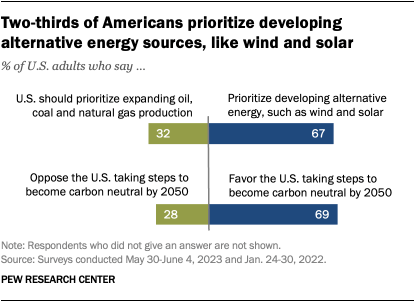
In a previous Center survey conducted in 2022, nearly the same share of Americans (69%) favored the U.S. taking steps to become carbon neutral by 2050 , a goal outlined by President Joe Biden at the outset of his administration. Carbon neutrality means releasing no more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than is removed.
Nine-in-ten Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents say the U.S. should prioritize developing alternative energy sources to address America’s energy supply. Among Republicans and Republican leaners, 42% support developing alternative energy sources, while 58% say the country should prioritize expanding exploration and production of oil, coal and natural gas.
There are important differences by age within the GOP. Two-thirds of Republicans under age 30 (67%) prioritize the development of alternative energy sources. By contrast, 75% of Republicans ages 65 and older prioritize expanding the production of oil, coal and natural gas.
Americans are reluctant to phase out fossil fuels altogether, but younger adults are more open to it. Overall, about three-in-ten adults (31%) say the U.S. should completely phase out oil, coal and natural gas. More than twice as many (68%) say the country should use a mix of energy sources, including fossil fuels and renewables.
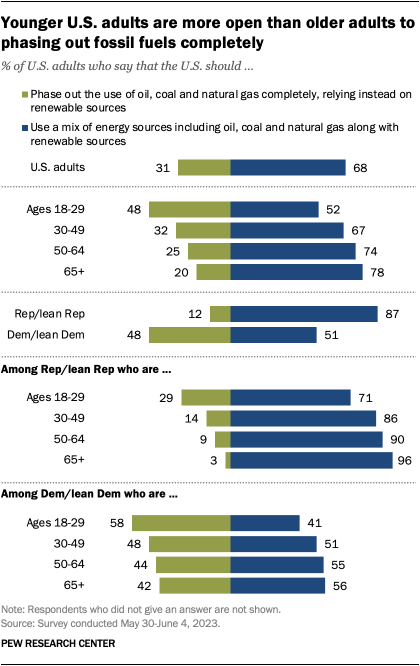
While the public is generally reluctant to phase out fossil fuels altogether, younger adults are more supportive of this idea. Among Americans ages 18 to 29, 48% say the U.S. should exclusively use renewables, compared with 52% who say the U.S. should use a mix of energy sources, including fossil fuels.
There are age differences within both political parties on this question. Among Democrats and Democratic leaners, 58% of those ages 18 to 29 favor phasing out fossil fuels entirely, compared with 42% of Democrats 65 and older. Republicans of all age groups back continuing to use a mix of energy sources, including oil, coal and natural gas. However, about three-in-ten (29%) Republicans ages 18 to 29 say the U.S. should phase out fossil fuels altogether, compared with fewer than one-in-ten Republicans 50 and older.
There are multiple potential routes to carbon neutrality in the U.S. All involve major reductions to carbon emissions in sectors such as energy and transportation by increasing the use of things like wind and solar power and electric vehicles. There are also ways to potentially remove carbon from the atmosphere and store it, such as capturing it directly from the air or using trees and algae to facilitate carbon sequestration.
The public supports the federal government incentivizing wind and solar energy production. In many sectors, including energy and transportation, federal incentives and regulations significantly influence investment and development.
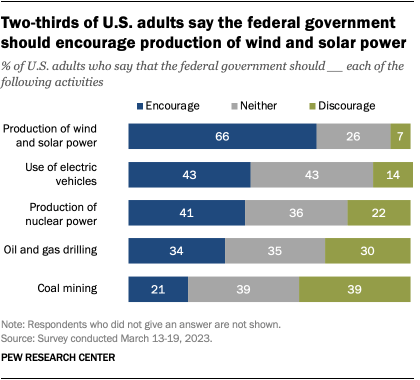
Two-thirds of Americans think the federal government should encourage domestic production of wind and solar power. Just 7% say the government should discourage this, while 26% think it should neither encourage nor discourage it.
Views are more mixed on how the federal government should approach other activities that would reduce carbon emissions. On balance, more Americans think the government should encourage than discourage the use of electric vehicles and nuclear power production, though sizable shares say it should not exert an influence either way.
When it comes to oil and gas drilling, Americans’ views are also closely divided: 34% think the government should encourage drilling, while 30% say it should discourage this and 35% say it should do neither. Coal mining is the one activity included in the survey where public sentiment is negative on balance: More say the federal government should discourage than encourage coal mining (39% vs. 21%), while 39% say it should do neither.
Americans see room for multiple actors – including corporations and the federal government – to do more to address the impacts of climate change. Two-thirds of adults say large businesses and corporations are doing too little to reduce the effects of climate change. Far fewer say they are doing about the right amount (21%) or too much (10%).
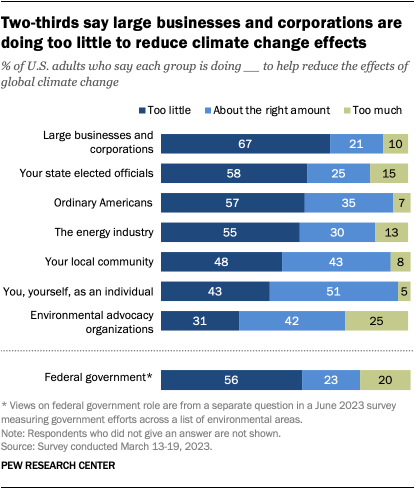
Majorities also say their state elected officials (58%) and the energy industry (55%) are doing too little to address climate change, according to a March 2023 survey.
In a separate Center survey conducted in June 2023, a similar share of Americans (56%) said the federal government should do more to reduce the effects of global climate change.
When it comes to their own efforts, about half of Americans (51%) think they are doing about the right amount as an individual to help reduce the effects of climate change, according to the March 2023 survey. However, about four-in-ten (43%) say they are doing too little.
Democrats and Republicans have grown further apart over the last decade in their assessments of the threat posed by climate change. Overall, a majority of U.S. adults (54%) describe climate change as a major threat to the country’s well-being. This share is down slightly from 2020 but remains higher than in the early 2010s.
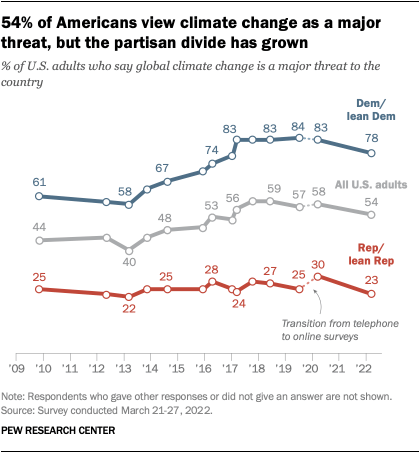
Nearly eight-in-ten Democrats (78%) describe climate change as a major threat to the country’s well-being, up from about six-in-ten (58%) a decade ago. By contrast, about one-in-four Republicans (23%) consider climate change a major threat, a share that’s almost identical to 10 years ago.
Concern over climate change has also risen internationally, as shown by separate Pew Research Center polling across 19 countries in 2022. People in many advanced economies express higher levels of concern than Americans . For instance, 81% of French adults and 73% of Germans describe climate change as a major threat.
Climate change is a lower priority for Americans than other national issues. While a majority of adults view climate change as a major threat, it is a lower priority than issues such as strengthening the economy and reducing health care costs.
Overall, 37% of Americans say addressing climate change should be a top priority for the president and Congress in 2023, and another 34% say it’s an important but lower priority. This ranks climate change 17th out of 21 national issues included in a Center survey from January.
As with views of the threat that climate change poses, there’s a striking contrast between how Republicans and Democrats prioritize the issue. For Democrats, it falls in the top half of priority issues, and 59% call it a top priority. By comparison, among Republicans, it ranks second to last, and just 13% describe it as a top priority.
Our analyses have found that partisan gaps on climate change are often widest on questions – such as this one – that measure the salience or importance of the issue. The gaps are more modest when it comes to some specific climate policies. For example, majorities of Republicans and Democrats alike say they would favor a proposal to provide a tax credit to businesses for developing technologies for carbon capture and storage.
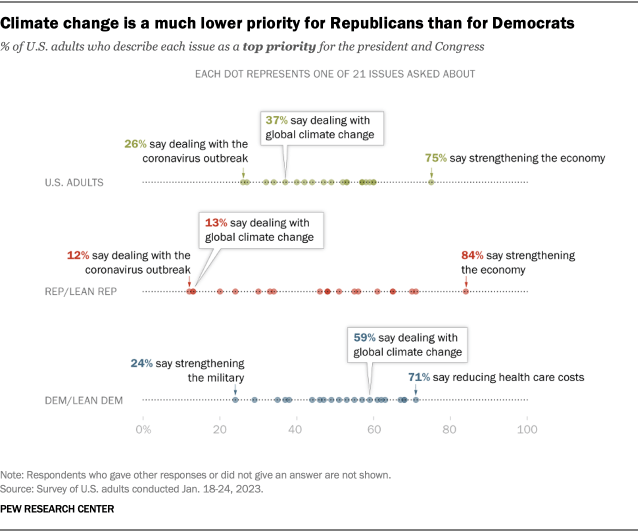
Perceptions of local climate impacts vary by Americans’ political affiliation and whether they believe that climate change is a serious problem. A majority of Americans (61%) say that global climate change is affecting their local community either a great deal or some. About four-in-ten (39%) see little or no impact in their own community.
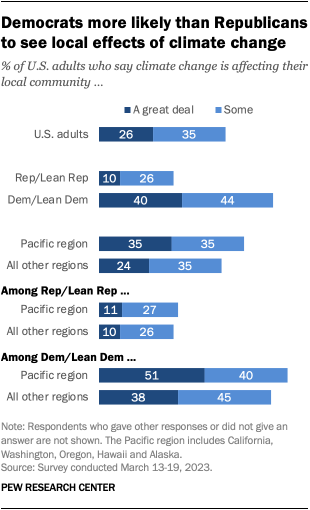
The perception that the effects of climate change are happening close to home is one factor that could drive public concern and calls for action on the issue. But perceptions are tied more strongly to people’s beliefs about climate change – and their partisan affiliation – than to local conditions.
For example, Americans living in the Pacific region – California, Washington, Oregon, Hawaii and Alaska – are more likely than those in other areas of the country to say that climate change is having a great deal of impact locally. But only Democrats in the Pacific region are more likely to say they are seeing effects of climate change where they live. Republicans in this region are no more likely than Republicans in other areas to say that climate change is affecting their local community.
Our previous surveys show that nearly all Democrats believe climate change is at least a somewhat serious problem, and a large majority believe that humans play a role in it. Republicans are much less likely to hold these beliefs, but views within the GOP do vary significantly by age and ideology. Younger Republicans and those who describe their views as moderate or liberal are much more likely than older and more conservative Republicans to describe climate change as at least a somewhat serious problem and to say human activity plays a role.
Democrats are also more likely than Republicans to report experiencing extreme weather events in their area over the past year – such as intense storms and floods, long periods of hot weather or droughts – and to see these events as connected with climate change.
About three-quarters of Americans support U.S. participation in international efforts to reduce the effects of climate change. Americans offer broad support for international engagement on climate change: 74% say they support U.S. participation in international efforts to reduce the effects of climate change.
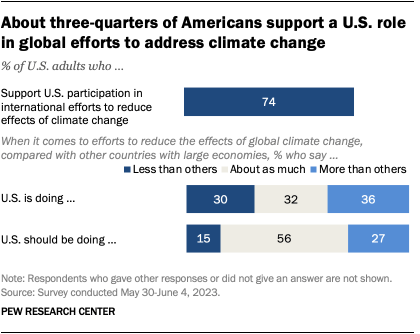
Still, there’s little consensus on how current U.S. efforts stack up against those of other large economies. About one-in-three Americans (36%) think the U.S. is doing more than other large economies to reduce the effects of global climate change, while 30% say the U.S. is doing less than other large economies and 32% think it is doing about as much as others. The U.S. is the second-largest carbon dioxide emitter , contributing about 13.5% of the global total.
When asked what they think the right balance of responsibility is, a majority of Americans (56%) say the U.S. should do about as much as other large economies to reduce the effects of climate change, while 27% think it should do more than others.
A previous Center survey found that while Americans favor international cooperation on climate change in general terms, their support has its limits. In January 2022 , 59% of Americans said that the U.S. does not have a responsibility to provide financial assistance to developing countries to help them build renewable energy sources.
In recent years, the UN conference on climate change has grappled with how wealthier nations should assist developing countries in dealing with climate change. The most recent convening in fall 2022, known as COP27, established a “loss and damage” fund for vulnerable countries impacted by climate change.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published April 22, 2022. Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and its methodology .
- Climate, Energy & Environment
- Environment & Climate
- Partisanship & Issues
- Political Issues

How Republicans view climate change and energy issues
How americans view future harms from climate change in their community and around the u.s., americans continue to have doubts about climate scientists’ understanding of climate change, growing share of americans favor more nuclear power, why some americans do not see urgency on climate change, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Recommendations for future research should be: Concrete and specific. Supported with a clear rationale. Directly connected to your research. Overall, strive to highlight ways other researchers can reproduce or replicate your results to draw further conclusions, and suggest different directions that future research can take, if applicable.
Research recommendations may be provided by experts in the field, such as professors, researchers, or consultants, and are intended to help guide the researcher towards the most appropriate and effective approach to their research project. ... Example of Research Recommendations sample for students: Further investigate the effects of X on Y by ...
Here is a step-wise guide to build your understanding on the development of research recommendations. 1. Understand the Research Question: Understand the research question and objectives before writing recommendations. Also, ensure that your recommendations are relevant and directly address the goals of the study. 2.
Recommendation in research example. See below for a full research recommendation example that you can use as a template to write your own. Recommendation section. The current study can be interpreted as a first step in the research on COPD speech characteristics. However, the results of this study should be treated with caution due to the small ...
Make sure your solutions cover all relevant areas within your research scope. Consider different contexts, stakeholders, and perspectives affected by the recommendations. Be thorough in identifying potential improvement areas and offering appropriate actions. Don't add new information to this part of your paper.
How to formulate research recommendations. "More research is needed" is a conclusion that fits most systematic reviews. But authors need to be more specific about what exactly is required. Long awaited reports of new research, systematic reviews, and clinical guidelines are too often a disappointing anticlimax for those wishing to use them ...
For this reason you need to support your conclusions with structured, logical reasoning. Having drawn your conclusions you can then make recommendations. These should flow from your conclusions. They are suggestions about action that might be taken by people or organizations in the light of the conclusions that you have drawn from the results ...
OVERVIEW OF WRITING RESEARCH RECOMMENDATIONS 1. Once you have finished your research, and coded and analyzed your data, you are ready to start ... are many different venues, audiences, and formats to do this, and in each case, you should ask yourself whether the format best fits the venue and the audience. 2. Your research will have both ...
When the proposed format is applied to a specific research recommendation, the emphasis placed on the relevant part(s) of the EPICOT+ format may vary by author, audience, and intended purpose. For example, a recommendation for research into treatments for transient ischaemic attack may or may not define valid outcome measures to assess quality ...
Recommendations are a key part of most reports. Their role is to tell your reader what they (or others) need to do based upon the findings in a report. These should be written with the mindset that each recommendation will prompt a change. Make Your Points Action-Based. Since we are telling the reader (or others) what to do, use action verbs.
The formatting of a research paper is different depending on which style guide you're following. In addition to citations, APA, MLA, and Chicago provide format guidelines for things like font choices, page layout, format of headings and the format of the reference page. Scribbr offers free Microsoft Word templates for the most common formats.
Step 1: Restate the problem. The first task of your conclusion is to remind the reader of your research problem. You will have discussed this problem in depth throughout the body, but now the point is to zoom back out from the details to the bigger picture. While you are restating a problem you've already introduced, you should avoid phrasing ...
Recommendation 1: Researchers with expertise in education research should conduct well-designed studies in collaboration with URE program directors to improve the evidence base about the processes and effects of UREs. This research should address how the various components of UREs may benefit students.
High-quality research articles that get many citations contain both implications and recommendations. Implications are the impact your research makes, whereas recommendations are specific actions that can then be taken based on your findings, such as for more research or for policymaking. That seems clear enough, but the two are commonly confused.
the research recommendations are relevant to current practice. we communicate well with the research community. This process and methods guide has been developed to help guidance-producing centres make research recommendations. It describes a step-by-step approach to identifying uncertainties, formulating research recommendations and research ...
The inclusion of an action plan along with recommendation adds more weightage to your recommendation. Recommendations should be clear and conscience and written using actionable words. Recommendations should display a solution-oriented approach and in some cases should highlight the scope for further research.
The conclusions are as stated below: i. Students' use of language in the oral sessions depicted their beliefs and values. based on their intentions. The oral sessions prompted the students to be ...
Writing recommendation letters is great fun — it allows me to reflect on my interactions with pupils, remember the creative times together and promote them in their future careers. It is like ...
The initially stated overarching aim of this research was to identify the contextual factors and mechanisms that are regularly associated with effective and cost-effective public involvement in research. While recognising the limitations of our analysis, we believe we have largely achieved this in our revised theory of public involvement in research set out in Chapter 8. We have developed and ...
Journal Articles. References to journal articles usually include the author's name, title of the article, name of the journal, volume and issue number, page numbers, and publication date. Example: Johnson, T. (2021). The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health. Journal of Psychology, 32 (4), 87-94.
Recommendation reports are texts that advise audiences about the best ways to solve a problem. Recommendation reports are a type of formal report that is widely used across disciplines and professions. Subject Matter Experts aim to make recommendations based on the best available theory, research and practice. Different disciplines and professions have different research methods
the purpose, research questions and results of the study. The implications of these findings and the resultant recommendations will also be explained. Recommendations were based on the conclusions and purpose of the study. 5.2 OVERVIEW OF THE STUDY The study was an exploratory, descriptive and contextual qualitative study. The
Writing recommendation letters on behalf of students and other early-career researchers is an important mentoring task within academia. An effective recommendation letter describes key candidate qualities such as academic achievements, extracurricular activities, outstanding personality traits, participation in and dedication to a particular discipline, and the mentor's confidence in the ...
Title of chapter. In E. E. Editor & F. F. Editor (Eds.), Title of work: Capital letter also for subtitle (pp. pages of chapter). Publisher. Note: When you list the pages of the chapter or essay in parentheses after the book title, use "pp." before the numbers: (pp. 1-21). This abbreviation, however, does not appear before the page numbers in ...
Pew Research Center published this collection of survey findings as part of its ongoing work to understand attitudes about climate change and energy issues. ... 10,329 U.S. adults. Earlier findings have been previously published, and methodological information, including the sample sizes and field dates, can be found by following the links in ...