
Summarize any | in a click.
TLDR This helps you summarize any piece of text into concise, easy to digest content so you can free yourself from information overload.
Enter an Article URL or paste your Text
Browser extensions.
Use TLDR This browser extensions to summarize any webpage in a click.

Single platform, endless summaries
Transforming information overload into manageable insights — consistently striving for clarity.
100% Automatic Article Summarization with just a click
In the sheer amount of information that bombards Internet users from all sides, hardly anyone wants to devote their valuable time to reading long texts. TLDR This's clever AI analyzes any piece of text and summarizes it automatically, in a way that makes it easy for you to read, understand and act on.
Article Metadata Extraction
TLDR This, the online article summarizer tool, not only condenses lengthy articles into shorter, digestible content, but it also automatically extracts essential metadata such as author and date information, related images, and the title. Additionally, it estimates the reading time for news articles and blog posts, ensuring you have all the necessary information consolidated in one place for efficient reading.
- Automated author-date extraction
- Related images consolidation
- Instant reading time estimation

Distraction and ad-free reading
As an efficient article summarizer tool, TLDR This meticulously eliminates ads, popups, graphics, and other online distractions, providing you with a clean, uncluttered reading experience. Moreover, it enhances your focus and comprehension by presenting the essential content in a concise and straightforward manner, thus transforming the way you consume information online.

Avoid the Clickbait Trap
TLDR This smartly selects the most relevant points from a text, filtering out weak arguments and baseless speculation. It allows for quick comprehension of the essence, without needing to sift through all paragraphs. By focusing on core substance and disregarding fluff, it enhances efficiency in consuming information, freeing more time for valuable content.
- Filters weak arguments and speculation
- Highlights most relevant points
- Saves time by eliminating fluff
Who is TLDR This for?
TLDR This is a summarizing tool designed for students, writers, teachers, institutions, journalists, and any internet user who needs to quickly understand the essence of lengthy content.
Anyone with access to the Internet
TLDR This is for anyone who just needs to get the gist of a long article. You can read this summary, then go read the original article if you want to.
TLDR This is for students studying for exams, who are overwhelmed by information overload. This tool will help them summarize information into a concise, easy to digest piece of text.
TLDR This is for anyone who writes frequently, and wants to quickly summarize their articles for easier writing and easier reading.
TLDR This is for teachers who want to summarize a long document or chapter for their students.
Institutions
TLDR This is for corporations and institutions who want to condense a piece of content into a summary that is easy to digest for their employees/students.
Journalists
TLDR This is for journalists who need to summarize a long article for their newspaper or magazine.
Featured by the world's best websites
Our platform has been recognized and utilized by top-tier websites across the globe, solidifying our reputation for excellence and reliability in the digital world.
Focus on the Value, Not the Noise.
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
How to present and summarize a scientific journal article
Thomas cox , psyd, cristie columbus , md, dio, kashif ahmed , md, julie higginbotham , ma.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
The authors report no funding or conflicts of interest.
Corresponding author : Thomas Cox, PsyD, Faculty Development and Research Education, Baylor University Medical Center, 3500 Gaston Ave., Dallas, TX 75246 (e-mail: [email protected] ).
Received 2024 May 13; Accepted 2024 Jun 7; Collection date 2024.
The success of a journal club hinges on the presentation of articles that are both relevant and scientifically robust. It’s insufficient for presenters to merely read through an article and highlight a few points without a clear focus. A strong presentation should thoroughly describe the relevance and validity of the study, offer a critique, suggest how further research might address the issue, and discuss the implications for patient care. Selecting the right article is crucial. It is recommended to begin the presentation with a case scenario to emphasize the article’s clinical relevance and to revisit the case at the conclusion of the presentation. The components of the article presentation should include background information, methodology and results, and the authors’ discussion. Additionally, the presenter should critique the article’s validity, noting any potential biases, evaluating the risks and costs of the proposed intervention, and assessing how well the article supports its hypothesis. The presentation should conclude with a summary statement that includes conclusions, implications, and future directions. Having a structured process for journal club presentations guides presenters and ensures that attendees derive maximum benefit from the educational activity. This organized approach fosters a deeper understanding and encourages critical thinking among participants.
Keywords: Critique, graduate medical education, journal club, presentation, research
An important part of our training programs is to help trainees critically analyze and evaluate a journal article so they can consider its relevance and apply it to clinical practice. Being able to differentiate high-quality clinical scientific journal articles from low-quality articles is a valuable skill. To achieve this goal, it is helpful to utilize a didactic flow process for a formal presentation of a medical journal article. We begin with a history of medical journal clubs, followed by a method for article selection and presentation. Presentation components include a case-based scenario, article critique/summary, discussion, review of outcomes, conclusions, implications, and future directions. Table 1 reviews the steps necessary for preparation of a clinical article at journal club.
Key points for selection, appraisal, and presentation of an article
HISTORY OF MEDICAL JOURNAL CLUBS
The first recorded journal clubs were formed by Sir William Osler at McGill University in 1875. Dr. Osler, a Canadian physician known as the father of modern medicine, is best known for creating the foundation of the discipline of internal medicine and was instrumental in developing the system of clinical medical education. Also, Sir James Paget in the mid 19th century is credited for the first teaching-module type of journal club; he was a British surgeon and pathologist credited for discovering in human muscle the parasitic worm that causes trichinosis. Dr. Osler and Dr. Paget initiated medical journal clubs for different reasons.
The journal club as a formal educational modality was recorded in the early 1900s in Germany. The 20th century saw significant improvement in scientific reporting and research, with the development of journals for subspecialties. Journals also evolved into a forum for continuing medical education. Today journal clubs are designed to teach critical appraisal skills to physicians in training and offer continuing education for practicing physicians. While this educational tool is not formally incorporated into the undergraduate medical education curriculum, that could be considered, based on the value and importance of journal clubs at more advanced levels of medical training.
ARTICLE SELECTION
The foundation of an outstanding journal club presentation rests on the choice of an interesting and well-written paper. Before presenting a journal article, we recommend that a trainee have the proposed article reviewed by one or two program staff members to get feedback on the article’s educational significance, relevance for practice, and validity. Randomized controlled trials are typically the best to choose; however, other types of studies such as cohort studies, case-controlled studies, and meta-analyses can also be chosen. It is best to avoid case reports and review articles. Figure 1 reviews the various types of studies in medical research, both primary and secondary. While past landmark cases that provide some foundations of current clinical practice can be considered, the general recommendation is to choose an article published within the past 3 to 6 months. Look for articles that have provocative or unexpected results or that could lead to a dramatic shift in knowledge or clinical practice that will grab the audience’s attention.
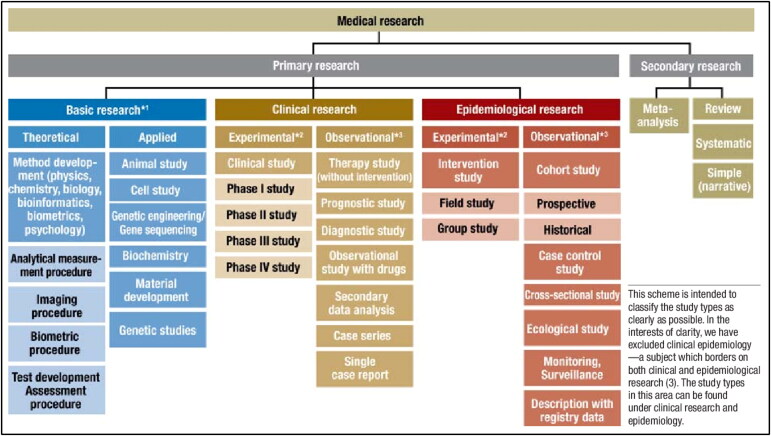
Classification of study types. +1 Sometimes known as experimental research; +2 analogous term: interventional; +3 analogous term: noninterventional or nonexperimental. Used with permission of Deutscher Ärzteverlag GmbH from Röhrig et al 1 ; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.
Numerous tools are available to aid in article selection, including tools from the American College of Physicians and the McMaster Online Rating of Evidence (MORE) system. Physicians can check online whether a potential article has been reviewed by experts. This process can help ensure that the paper meets the criteria for high scientific merit. In addition, articles that have passed this screening are rated on two 7-point scales by clinicians on relevance and value to their clinical discipline and newsworthiness. These scales can be used as informal guidelines to ensure that a chosen article merits presentation.
ARTICLE APPRAISAL
Once an article is selected, it is time to critically appraise it. There are different approaches to critiquing articles. One recommended way is to apply JAMA’s series of users’ guides to the medical literature (see the list at https://guides.library.vcu.edu/ebm/criticalappraisal ). These guides provide fundamental questions that the reader should address. Key points to focus on in the assessment of the validity of the study include randomization of patients between control and treatment groups, concealment of allocation, use of the intention-to-treat principle, and follow-up of the study. If methodological flaws are found in the appraisal, it does not mean that the article should not be presented, because there is value in discussing points about research design and methodology.
Next, it is important to discuss the results of the study. Understanding basic statistics such as odds ratios and relative risks, as well as calculation of number needed to treat and/or number needed to harm, can help to quantify the results. In addition, it is just as important to evaluate the clinical significance of the results and applicability to patient care; statistical significance does not necessarily indicate clinical significance. Often the first table in an article describes study participant demographics, which can help the reader decide whether results, if clinically significant, can be applied to their own patient population. Finally, one should assess the article for bias, including funding and disclosures, which might affect the study’s credibility. Table 2 contains a summary of key questions a reader should reflect upon and attempt to answer as he or she analytically reads an article. If an editorial accompanies the paper, it is important to read it before the presentation, because editorials often emphasize key points and controversial topics that, together with the presenter’s own analysis, can be used to prompt discussion.
Key questions to address when analyzing an article
ARTICLE PRESENTATION
In preparation for a journal club presentation, one key suggestion is to avoid slide overload. The best approach is to focus only on several key areas and provide the relevant table or data. Be prepared on the day of the presentation. It is beneficial to practice beforehand or have an outline to follow during the presentation to avoid exceeding the time limit. Additionally, the presenter needs to know the audience. Some audiences may have all levels of learners—faculty, fellows, residents, and/or students—making it necessary to briefly explain or review some clinical techniques, processes, or terms in case an audience member is not familiar with it. Also, in preparing a presentation, remember that it is not necessary to provide a detailed description of the article. The audience should have already read the article, so all they need is a review of the main ideas.
The introduction of the article provides the audience with the necessary information in context so they can follow the article’s presentation. The presenter first needs to state why this article was selected. It is helpful to explicitly define the research question or hypothesis, the targeted objectives of the study, the study’s clinical relevance, and why the topic is worthy of study. A well-built research question has four basic components (PICO):.
P opulation: Who was studied
I ntervention or exposure: The therapy, risk factor, tests, etc.
C omparison or control: The alternative to intervention or exposure
O utcome: Clinical, functional, economic outcomes
It can also be useful to highlight any research done before the study to show the developmental process. This portion of the presentation concludes by describing informally what the authors hoped to prove with this research. It is also good practice to discuss the data supporting the current standard of care against which the study intervention is being measured.
Moving to the methodology , presenters should accurately describe the research tools and methods used in the study. Is it a randomized controlled trial? Is it prospective or retrospective? Is it blinded? Or is it cross-sectional or longitudinal? It is also important to describe the study population, including inclusion and exclusion criteria. A diagrammatic schema is recommended to construct and clearly illustrate treatment arms; software is available to help with this process. It is recommended that presenters broadly explain how the research question was addressed. Finally, the statistical methods and the power calculation to determine subject numbers should be presented.
The results can be highlighted using statistical methods that can be more quickly and easily grasped by the audience, such as means, medians, modes, standard deviations, and correlations. The goal is not to exclude any data but to avoid losing the audience with too much detail.
Following the presentation flow, the next major area is to review the authors’ discussion and their perspectives on the study results. This section should include explanations of inconsistent or unexpected results and consider whether the conclusions are supported by the data.
ARTICLE CRITIQUE
The next segment of the article presentation is a critique of the article from a viewpoint of validity. The audience wants to hear the presenter’s critique of the article. It is crucial at this point to present the support or criticisms of the study method and conclusions and point out any potential biases. It is also good practice to discuss the tradeoffs between the potential benefits of the study intervention versus the potential risks and costs. This element creates good discussion and debate in journal clubs. While a comprehensive discussion is often beyond the scope of an article presentation, the critique should define any incidence rates of clinically significant toxicities within the study. Finally, describe what the authors accomplished with their work. This may involve a sophisticated analysis of the study’s impact on clinical practice or new research methodology. One useful question is whether this study will impact or change the way you practice medicine. At this point, any study limitations can be outlined, even in bullet form.
Other questions that can be addressed during the critique are as follows: Were the authors successful in accomplishing their objectives? Did they answer their research question? Were their controls properly set up? Was the data accurately presented? Was this study powered correctly? What conclusions did the authors draw from the research? Was the research and study significant to impact change, or was it informational in its approach? Presenters can summarize the implications of the article for practice in their field, ensuring that the summary covers the research question. These are also features of a commentary that is solicited by the journal editor.
IMPLICATIONS AND CONCLUSION
There are two areas of focus for the conclusion of the discussion: (1) the implications for medicine, science, research, and health care; and (2) whether the journal article revealed any secondary results or endpoints that weren’t in the original research question. At the end, the presenters will want to restate the authors’ take-home message followed by their interpretation of the study and provide a personal perspective, detailing why they found the paper interesting and important. Then presenters can also reflect on whether they envision the study results redirecting research in this field and changing the landscape of clinical practice. Often the discussion leads to specific recommendations for future research. For example, how would you change the research question or change the study? How would you change the protocol to get a clear answer or to get an answer to a more appropriate question? For clinical practice, can this study yield results that can be applied to your patients? If the presenter began with a case scenario, in conclusion, he or she should return to that case and discuss whether it changed the decision-making process. Presenters should watch the time to allow for questions at the end. It is always beneficial to ensure a specific faculty member, maybe a mentor, can attend and make comments or pose audience questions to promote more discussion.
This article has outlined a formal process for presenting journal articles, which can greatly benefit both presenters and audience members. By adhering to this structured approach, presenters can better prepare their presentations, ensuring they are clear and comprehensive. Audience members, in turn, will know what to expect, making these sessions more productive and engaging. Implementing a formal presentation process in journal clubs can enhance their effectiveness, contributing more significantly to collective understanding and education.
Moreover, presenting journal articles not only facilitates peer discussion on new developments or landmark cases in a specialty but also enhances the analytical and presentation skills of the presenters. These skills are integral to clinical practice, as they enable practitioners to critically evaluate new information and communicate their insights effectively. Thus, the practice of presenting journal articles serves as a valuable exercise in professional development within the clinical community.
DISCLOSURE STATEMENT
- 1. Röhrig B, Du Prel JB, Wachtlin D, Blettner M.. Types of study in medical research: part 3 of a series on evaluation of scientific publications. Dtsch Arztebl Int . 2009;106(15):262–268. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2009.0262. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 2. Syed AF, Ahmed J.. How to prepare an outstanding journal club presentation in Unani post graduation. Int J Adv Health Sci . 2016;3(3):208–212. [ Google Scholar ]
- 3. Linzer M. The journal club and medical education: over one hundred years of unrecorded history. Postgrad Med J . 1987;63(740):475–478. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.63.740.475. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 4. Judd S, Antaki F.. Approach to presenting a clinical journal club. Gastroenterology . 2014;146(7):1591–1593. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.04.024. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 5. McMaster University . McMaster health knowledge refinery: our process. Accessed June 17, 2024. https://hiru.mcmaster.ca/MORE/physicians/sentinel_reader.html .
- 6. Schwartz MD, Dowell D, Aperi J, Kalet AL.. Improving journal club presentations, or, I can present that paper in under 10 minutes. Evid Based Med . 2007;12(3):66–68. doi: 10.1136/ebm.12.3.66-a. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- View on publisher site
- PDF (474.6 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Summary
Definition:
A research summary is a brief and concise overview of a research project or study that highlights its key findings, main points, and conclusions. It typically includes a description of the research problem, the research methods used, the results obtained, and the implications or significance of the findings. It is often used as a tool to quickly communicate the main findings of a study to other researchers, stakeholders, or decision-makers.
Structure of Research Summary
The Structure of a Research Summary typically include:
- Introduction : This section provides a brief background of the research problem or question, explains the purpose of the study, and outlines the research objectives.
- Methodology : This section explains the research design, methods, and procedures used to conduct the study. It describes the sample size, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- Results : This section presents the main findings of the study, including statistical analysis if applicable. It may include tables, charts, or graphs to visually represent the data.
- Discussion : This section interprets the results and explains their implications. It discusses the significance of the findings, compares them to previous research, and identifies any limitations or future directions for research.
- Conclusion : This section summarizes the main points of the research and provides a conclusion based on the findings. It may also suggest implications for future research or practical applications of the results.
- References : This section lists the sources cited in the research summary, following the appropriate citation style.
How to Write Research Summary
Here are the steps you can follow to write a research summary:
- Read the research article or study thoroughly: To write a summary, you must understand the research article or study you are summarizing. Therefore, read the article or study carefully to understand its purpose, research design, methodology, results, and conclusions.
- Identify the main points : Once you have read the research article or study, identify the main points, key findings, and research question. You can highlight or take notes of the essential points and findings to use as a reference when writing your summary.
- Write the introduction: Start your summary by introducing the research problem, research question, and purpose of the study. Briefly explain why the research is important and its significance.
- Summarize the methodology : In this section, summarize the research design, methods, and procedures used to conduct the study. Explain the sample size, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- Present the results: Summarize the main findings of the study. Use tables, charts, or graphs to visually represent the data if necessary.
- Interpret the results: In this section, interpret the results and explain their implications. Discuss the significance of the findings, compare them to previous research, and identify any limitations or future directions for research.
- Conclude the summary : Summarize the main points of the research and provide a conclusion based on the findings. Suggest implications for future research or practical applications of the results.
- Revise and edit : Once you have written the summary, revise and edit it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors. Make sure that your summary accurately represents the research article or study.
- Add references: Include a list of references cited in the research summary, following the appropriate citation style.
Example of Research Summary
Here is an example of a research summary:
Title: The Effects of Yoga on Mental Health: A Meta-Analysis
Introduction: This meta-analysis examines the effects of yoga on mental health. The study aimed to investigate whether yoga practice can improve mental health outcomes such as anxiety, depression, stress, and quality of life.
Methodology : The study analyzed data from 14 randomized controlled trials that investigated the effects of yoga on mental health outcomes. The sample included a total of 862 participants. The yoga interventions varied in length and frequency, ranging from four to twelve weeks, with sessions lasting from 45 to 90 minutes.
Results : The meta-analysis found that yoga practice significantly improved mental health outcomes. Participants who practiced yoga showed a significant reduction in anxiety and depression symptoms, as well as stress levels. Quality of life also improved in those who practiced yoga.
Discussion : The findings of this study suggest that yoga can be an effective intervention for improving mental health outcomes. The study supports the growing body of evidence that suggests that yoga can have a positive impact on mental health. Limitations of the study include the variability of the yoga interventions, which may affect the generalizability of the findings.
Conclusion : Overall, the findings of this meta-analysis support the use of yoga as an effective intervention for improving mental health outcomes. Further research is needed to determine the optimal length and frequency of yoga interventions for different populations.
References :
- Cramer, H., Lauche, R., Langhorst, J., Dobos, G., & Berger, B. (2013). Yoga for depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Depression and anxiety, 30(11), 1068-1083.
- Khalsa, S. B. (2004). Yoga as a therapeutic intervention: a bibliometric analysis of published research studies. Indian journal of physiology and pharmacology, 48(3), 269-285.
- Ross, A., & Thomas, S. (2010). The health benefits of yoga and exercise: a review of comparison studies. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 16(1), 3-12.
Purpose of Research Summary
The purpose of a research summary is to provide a brief overview of a research project or study, including its main points, findings, and conclusions. The summary allows readers to quickly understand the essential aspects of the research without having to read the entire article or study.
Research summaries serve several purposes, including:
- Facilitating comprehension: A research summary allows readers to quickly understand the main points and findings of a research project or study without having to read the entire article or study. This makes it easier for readers to comprehend the research and its significance.
- Communicating research findings: Research summaries are often used to communicate research findings to a wider audience, such as policymakers, practitioners, or the general public. The summary presents the essential aspects of the research in a clear and concise manner, making it easier for non-experts to understand.
- Supporting decision-making: Research summaries can be used to support decision-making processes by providing a summary of the research evidence on a particular topic. This information can be used by policymakers or practitioners to make informed decisions about interventions, programs, or policies.
- Saving time: Research summaries save time for researchers, practitioners, policymakers, and other stakeholders who need to review multiple research studies. Rather than having to read the entire article or study, they can quickly review the summary to determine whether the research is relevant to their needs.
Characteristics of Research Summary
The following are some of the key characteristics of a research summary:
- Concise : A research summary should be brief and to the point, providing a clear and concise overview of the main points of the research.
- Objective : A research summary should be written in an objective tone, presenting the research findings without bias or personal opinion.
- Comprehensive : A research summary should cover all the essential aspects of the research, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions.
- Accurate : A research summary should accurately reflect the key findings and conclusions of the research.
- Clear and well-organized: A research summary should be easy to read and understand, with a clear structure and logical flow.
- Relevant : A research summary should focus on the most important and relevant aspects of the research, highlighting the key findings and their implications.
- Audience-specific: A research summary should be tailored to the intended audience, using language and terminology that is appropriate and accessible to the reader.
- Citations : A research summary should include citations to the original research articles or studies, allowing readers to access the full text of the research if desired.
When to write Research Summary
Here are some situations when it may be appropriate to write a research summary:
- Proposal stage: A research summary can be included in a research proposal to provide a brief overview of the research aims, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
- Conference presentation: A research summary can be prepared for a conference presentation to summarize the main findings of a study or research project.
- Journal submission: Many academic journals require authors to submit a research summary along with their research article or study. The summary provides a brief overview of the study’s main points, findings, and conclusions and helps readers quickly understand the research.
- Funding application: A research summary can be included in a funding application to provide a brief summary of the research aims, objectives, and expected outcomes.
- Policy brief: A research summary can be prepared as a policy brief to communicate research findings to policymakers or stakeholders in a concise and accessible manner.
Advantages of Research Summary
Research summaries offer several advantages, including:
- Time-saving: A research summary saves time for readers who need to understand the key findings and conclusions of a research project quickly. Rather than reading the entire research article or study, readers can quickly review the summary to determine whether the research is relevant to their needs.
- Clarity and accessibility: A research summary provides a clear and accessible overview of the research project’s main points, making it easier for readers to understand the research without having to be experts in the field.
- Improved comprehension: A research summary helps readers comprehend the research by providing a brief and focused overview of the key findings and conclusions, making it easier to understand the research and its significance.
- Enhanced communication: Research summaries can be used to communicate research findings to a wider audience, such as policymakers, practitioners, or the general public, in a concise and accessible manner.
- Facilitated decision-making: Research summaries can support decision-making processes by providing a summary of the research evidence on a particular topic. Policymakers or practitioners can use this information to make informed decisions about interventions, programs, or policies.
- Increased dissemination: Research summaries can be easily shared and disseminated, allowing research findings to reach a wider audience.
Limitations of Research Summary
Limitations of the Research Summary are as follows:
- Limited scope: Research summaries provide a brief overview of the research project’s main points, findings, and conclusions, which can be limiting. They may not include all the details, nuances, and complexities of the research that readers may need to fully understand the study’s implications.
- Risk of oversimplification: Research summaries can be oversimplified, reducing the complexity of the research and potentially distorting the findings or conclusions.
- Lack of context: Research summaries may not provide sufficient context to fully understand the research findings, such as the research background, methodology, or limitations. This may lead to misunderstandings or misinterpretations of the research.
- Possible bias: Research summaries may be biased if they selectively emphasize certain findings or conclusions over others, potentially distorting the overall picture of the research.
- Format limitations: Research summaries may be constrained by the format or length requirements, making it challenging to fully convey the research’s main points, findings, and conclusions.
- Accessibility: Research summaries may not be accessible to all readers, particularly those with limited literacy skills, visual impairments, or language barriers.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Implications in Research – Types, Examples and...


Data Analysis – Process, Methods and Types

Dissertation – Format, Example and Template

Survey Instruments – List and Their Uses

Research Techniques – Methods, Types and Examples

Significance of the Study – Examples and Writing...

Research Paper Summarizer
Ai-powered tool for summarizing research papers.
- Quickly understand a research paper: Get a concise summary of a research paper without having to read the entire document.
- Prepare for a presentation or discussion: Understand the key points of a research paper to confidently present or discuss it.
- Write a literature review: Get summaries of multiple research papers to easily compare and contrast their findings.
- Stay updated on the latest research: Quickly understand the latest research in your field without having to read every paper in detail.
New & Trending Tools
Wedding toast generator, ai answer science questions, ai text analyzer and highlights.

Research faster with genei
Automatically summarise background reading and produce blogs, articles, and reports faster.

"I could totally see this startup playing the same role as a Grammarly: a helpful extension of workflows that optimizes the way people who write for a living, write." Natasha Mascarenhas Senior Reporter at TechCrunch
Y-combinator summer 2021.
Genei is part of Y-Combinator, a US startup accelerator with over 2000 companies including Stripe, Airbnb, Reddit and Twitch.

TechCrunch favourite startups 2021
Genei was recently named among Tech Crunch's favourite startups of summer 2021.
Oxford University All Innovate 2020
Prize winning company in Oxford University's prestigious "All Innovate" startup competition.
Trusted by thought leaders and experts
"genei is a company that excites me a lot. Their AI has the potential to offer massive productivity boosts in research and writing."
"We can perform research using genei's keyword extraction tool to optimize our article content better than before."
"Genei’s summarisation provides a whole new dimension to our research and reporting, and helps contribute towards the clarity and conciseness of our work."

Add, organise, and manage information with ease.
95% of users say genei enables them work more productively. Documents can be stored in customisable projects and folders, whilst content can be linked to any part of a document to generate automatic references.

Ask questions and our AI will find answers.
95% of users say they find greater answers and insights from their work when using genei.

Finish your reading list faster.
AI-powered summarisation and keyword extraction for any group of PDFs or webpages. 98% of users say genei saves them time by paraphrasing complex ideas and enabling them to find crucial information faster.
.png)
Improve the quality & efficiency of your research today
Never miss important reading again.
Our chrome extension add-on means you can summarize webpages or save them for later reading as you browse.

- Import, view, summarise & analyse PDFs and webpages
- Document management and file storage system
- Full notepad & annotation capabilities
- In-built citation management and reference generator
- Export functionality
- Everything in basic
- 70% higher quality AI
- Access to GPT3 - the world's most advanced language based AI
- Multi-document summarisation, search, and question answering
- Rephrasing and Paraphrasing functionality
Loved by thousands of users worldwide
Find out how genei can benefit you.
Empower Your Academic Journey
AI Summarizer & Summary Generator
Jenni AI stands as a comprehensive academic writing assistant, encompassing an AI summarizer and summary generator among its key features. This specialized functionality is meticulously crafted to facilitate the creation of concise summaries, effectively condensing extensive research papers, articles, or essays. Jenni AI simplifies the process, enabling you to focus more on your analysis and less on summarization. Our tool is built with the ethos of promoting authentic academic endeavors, not replacing them.

Loved by over 3 million academics

Trusted By Academics Worldwide
Academics from leading institutions rely on Jenni AI for efficient summary generation

Crafting Quality Academic Writing Solutions with Our Text Summarizer
Discover how Jenni AI stands out as the solution for your summarization needs
Effortless Summarization
Jenni AI takes the hassle out of summarization. Just paste your text, and watch as Jenni AI distills the core ideas into a clear, concise summary.
Get started

Interactive Editing
Don’t just settle for the first draft. Interact with the summary, tweak, and refine it to meet your specific requirements, ensuring that every summary is precisely what you need.
Learning and Improvement
Jenni AI is not just a tool, but a companion in your academic journey. Learn from the summarization process and improve your writing skills with every interaction.

Our Commitment to Academic Integrity
At Jenni AI, we uphold the principle of academic integrity with the utmost regard. Our tool is devised to assist, not to replace your original work.
How Does Jenni AI Summarizing Tool Work?
Navigating the Realm of Academic Writing Has Never Been Easier
Create Your Account
Sign up for a free Jenni AI account to embark on a simplified summarization journey.
Paste Your Text
Copy and paste the text you wish to summarize. Whether it's a research article, essay, or a complex thesis, Jenni AI is here to assist.
Generate Your Summary
Ask Jenni to summarize and watch as it employs advanced algorithms to distill the core essence of your text, presenting a coherent and concise summary.
Review and edit your summary. Jenni AI's interactive platform allows you to tweak and refine the summary to align perfectly with your academic objectives.
What Scholars Are Saying
Hear from our satisfied users and elevate your writing to the next level

I thought AI writing was useless. Then I found Jenni AI, the AI-powered assistant for academic writing. It turned out to be much more advanced than I ever could have imagined. Jenni AI = ChatGPT x 10.

Charlie Cuddy
@sonofgorkhali
Love this use of AI to assist with, not replace, writing! Keep crushing it @Davidjpark96 💪

Waqar Younas, PhD
@waqaryofficial
4/9 Jenni AI's Outline Builder is a game-changer for organizing your thoughts and structuring your content. Create detailed outlines effortlessly, ensuring your writing is clear and coherent. #OutlineBuilder #WritingTools #JenniAI

I started with Jenni-who & Jenni-what. But now I can't write without Jenni. I love Jenni AI and am amazed to see how far Jenni has come. Kudos to http://Jenni.AI team.

Jenni is perfect for writing research docs, SOPs, study projects presentations 👌🏽

Stéphane Prud'homme
http://jenni.ai is awesome and super useful! thanks to @Davidjpark96 and @whoisjenniai fyi @Phd_jeu @DoctoralStories @WriteThatPhD
Frequently asked questions
How does jenni ai generate summaries, is jenni ai suitable for all academic fields.
How does the citation helper work?
Can I use Jenni AI for professional or non-academic writing?
How does Jenni AI help with writer’s block?
How does Jenni AI compare to other summarization tools?
Choosing the Right Academic Writing Companion
Get ready to make an informed decision and uncover the key reasons why Jenni AI is your ultimate tool for academic excellence.
Feature Featire
COMPETITORS
Academic Orientation
Designed with academic rigor in mind, ensuring your summaries uphold scholarly standards.
Often lack academic focus, potentially diluting the essence of scholarly texts.
Contextual Understanding
Employs advanced AI to grasp the context, ensuring summaries are meaningful and coherent.
May struggle with contextual understanding, leading to disjointed or misleading summaries.
Customization
Offers customization options to tailor summaries according to your specific needs and preferences.
Generic summarization often with limited customization, risking loss of critical information.
User-Friendly Interface
Intuitive interface makes summarization a breeze, enhancing the user experience.
Clunky interfaces can hinder the summarization process, making it less user-friendly.
Promotes an interactive learning environment, aiding in improving your summarization skills over time.
Merely provide summarization with no added value in terms of learning or skill enhancement.
Ready to Elevate Your Academic Writing?
Create your free Jenni AI account today and discover a new horizon of academic excellence!
'ZDNET Recommends': What exactly does it mean?
ZDNET's recommendations are based on many hours of testing, research, and comparison shopping. We gather data from the best available sources, including vendor and retailer listings as well as other relevant and independent reviews sites. And we pore over customer reviews to find out what matters to real people who already own and use the products and services we’re assessing.
When you click through from our site to a retailer and buy a product or service, we may earn affiliate commissions. This helps support our work, but does not affect what we cover or how, and it does not affect the price you pay. Neither ZDNET nor the author are compensated for these independent reviews. Indeed, we follow strict guidelines that ensure our editorial content is never influenced by advertisers.
ZDNET's editorial team writes on behalf of you, our reader. Our goal is to deliver the most accurate information and the most knowledgeable advice possible in order to help you make smarter buying decisions on tech gear and a wide array of products and services. Our editors thoroughly review and fact-check every article to ensure that our content meets the highest standards. If we have made an error or published misleading information, we will correct or clarify the article. If you see inaccuracies in our content, please report the mistake via this form .
How to use ChatGPT to summarize a book, article, or research paper

AI chatbots like ChatGPT can be used to make summarizing long articles, research papers, and books an easier job. If you're tasked with writing a summary for school or work about a body of written text, and you're pinched for time, ChatGPT can help you understand the necessary components.
You should remember that ChatGPT is a tool that can help you further understand a topic, and it may not be in your best interest to have it write your work for you.
Also: How to make ChatGPT provide sources and citations
If you're a student writing a research paper, someone who is keen to discover more about a lengthy article, or someone who wants to dive into a complicated subject, you can use ChatGPT to simplify the process.
How ChatGPT can create summaries for you
Materials needed : You'll need a device that can connect to the internet, an OpenAI account , and a basic understanding of the article, research paper, or book you want to summarize.
Also: This AI chatbot can sum up any PDF and answer any question you have about it
The process should take about one to three minutes.
1. Find your article, paper, or book to summarize
If you need ChatGPT to help summarize an article or research paper, find the body of text online and keep it open in a separate tab.
2. Open your web browser and log in to OpenAI
Open your web browser of choice and type in chat.openai.com/chat .
Also: How to use ChatGPT to write Excel formulas
Log in or sign up for an account.
3. Type your request
In the chat box, type in TLDR: followed by the title of the book you want summarized. TLDR stands for too long, didn't read.
Also: How to use ChatGPT: Everything you need to know
You can also ask ChatGPT: "Summarize [book title]."
You cannot paste a URL into ChatGPT. If you do so, you'll get a response explaining that the chatbot cannot access websites. If you want ChatGPT to summarize research, you'll need a basic understanding of the topic to ensure you aren't including inaccurate information in your report.
For example, if you're writing a paper about how twin sibling dynamics affect their marriages, you can ask ChatGPT: "Explain how twin relationships affect their marriages."
Also: The best AI chatbots: ChatGPT and other noteworthy alternatives
ChatGPT will offer you a few bullet points of both positive and negative effects a twin bond can have on the twins' marriages. You'll still need to read key points of the research, as ChatGPT won't provide you with specific statistics or scientific conclusions. But ChatGPT can help you understand the context surrounding the research you're interested in.
If you're having trouble comprehending specific passages in an article, book, or research paper, you can copy parts of the text and paste them into ChatGPT.
Think of this method as reshuffling the words you're currently reading to help you make more sense of the text in front of you.
This is an accurate summary of 'The Hunger Games: Mockingjay'.
What are ChatGPT's limitations?
If you're using ChatGPT to summarize an article, book, or piece of research, keep in mind that ChatGPT isn't aware of events that occurred after September 2021.
Also: 4 things Claude AI can do that ChatGPT can't
ChatGPT is a large language model that uses queues and millions of data points to mimic human responses. This form of mimicry is why ChatGPT will answer questions even when it doesn't output the correct answer. So, make sure you're not using any information from ChatGPT without fact-checking it.
If you try to get around this obstacle and provide ChatGPT with an article that contains information post-2021, it might hallucinate. Here, I asked the chatbot to summarize an article about a new app I wrote about , and it made up a few details.
Lemon8 is a new app from TikTok's parent company, ByteDance. Although the TikTok trend may exist, that's not what the article is about.
Can ChatGPT summarize a PDF?
Copying and pasting a URL into ChatGPT won't yield you the best results. If there is a specific paragraph or sentence you're struggling with, you can copy and paste it into ChatGPT and ask it to explain it to you. Still, it's best to read the PDF and use the chatbot as a summary tool and not as an educator.
Also: How to use ChatGPT to write code
If you're looking for an AI chatbot that you can regularly rely on to give you an accurate summary of a PDF, consider using ChatPDF . You can summarize up to three PDFs of up to 120 pages per day, and an upgraded plan is available for $5 per month.
Can ChatGPT summarize an email thread?
Sort of. If you want to copy and paste every single email, ChatGPT can summarize the thread's contents for you. It would be more helpful to scan an email thread yourself and ask ChatGPT to help you write a response based on the key points you know about the conversation.
Editor's note: We've added additional context to the step concerning ChatGPT summarizing articles by URL.
More on AI tools
How to use chatgpt to write a better cover letter, i'm a google docs power user, and this new feature is genuinely helpful - here's why, how to subscribe to your favorite writers online: 4 easy ways.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Features built for scholars like you, trusted by researchers and students around the world. Any format. Summarize papers, PDFs, book chapters, online articles and more. Easy import. Drag and drop files, enter the url of a page, paste a block of text, or use our browser extension. Enhanced summary.
Summarize long texts, documents, articles and papers in 1 click with Scribbr's free summarizer tool. Get the most important information quickly and easily with the AI summarizer. ... Speed up your academic research by extracting key points. Every day use. Reduce your reading time by summarizing long blocks of text within seconds. Business.
Table of contents. When to write a summary. Step 1: Read the text. Step 2: Break the text down into sections. Step 3: Identify the key points in each section. Step 4: Write the summary. Step 5: Check the summary against the article. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about summarizing.
Article Metadata Extraction. TLDR This, the online article summarizer tool, not only condenses lengthy articles into shorter, digestible content, but it also automatically extracts essential metadata such as author and date information, related images, and the title. Additionally, it estimates the reading time for news articles and blog posts ...
A research paper summary is a short overview of a research paper. Generally, a research paper summary is about 300-400 words long, though with longer papers, they're usually no more than 10 percent the length of the original paper. Research paper summaries play an important role in academia.
A research article usually has seven major sections: Title, Abstract, Introduction, Method, Results, Discussion, and References. The first thing you should do is to decide why you need to summarize the article. If the purpose of the summary is to take notes to later remind yourself about the article you may want to write a longer summary ...
Presentation components include a case-based scenario, article critique/summary, discussion, review of outcomes, conclusions, implications, and future directions. ... Presenters can summarize the implications of the article for practice in their field, ensuring that the summary covers the research question. These are also features of a ...
Article Summarizer—Read Faster and Improve Comprehension. Boost your productivity, save time, and work more efficiently with QuillBot's article summarizer. This free tool will instantly give you the key points of any long text, such as blogs, research papers, news or research articles, and more.
The analysis shows that you can evaluate the evidence presented in the research and explain why the research could be important. Summary. The summary portion of the paper should be written with enough detail so that a reader would not have to look at the original research to understand all the main points. At the same time, the summary section ...
Summarize, analyze and organize your research . Summarize anything. Understand complex research. Organize your knowledge. Try for free. Flashcard summary. Scroll. Try it yourself. Try for free. Used by people studying at. ... Summarize any paper, article or textbook. You can summarize videos too! Scholarcy converts long complex texts into ...
The purpose of a research summary is to provide a brief overview of a research project or study, including its main points, findings, and conclusions. The summary allows readers to quickly understand the essential aspects of the research without having to read the entire article or study. Research summaries serve several purposes, including:
Reads, understands, and summarizes the main points and conclusions of a research paper. HyperWrite's Research Paper Summarizer is an AI-powered tool designed to read and summarize research papers. It identifies the main points, arguments, and conclusions, providing a clear and concise summary. This tool is perfect for students, researchers, and professionals who need to quickly understand the ...
Cite the article in your summary and, if you use AI to generate your summary, acknowledge your use of AI. Grammarly's citation generator makes this easy. Don't repeat the original article's text verbatim. Instead, summarize it in your own words. Use Grammarly's plagiarism checker to detect plagiarism in your text.
Academic Research and Study: Students, researchers, and academics can benefit from Ahrefs' Summarizer Tool when conducting literature reviews or researching specific topics. Reading and summarizing numerous research papers, articles, and studies can be time-consuming. The Summarizer Tool can help researchers quickly extract the main points, methodologies, and findings from academic papers ...
Our research into the best summary generators (aka summarizers or summarizing tools) found that the best summarizer available is the one offered by QuillBot. While many summarizers just pick out some sentences from the text, QuillBot generates original summaries that are creative, clear, accurate, and concise. It can summarize texts of up to ...
A total of 10,584 participants had complete baseline information and at least one pain entry, with 6850 (65%) participants remaining in the study beyond their first week and 4692 (44%) beyond their first month (Fig. 2 b). Further description of engagement clusters is provided in Supplementary Table 2 and Supplementary Figs 1 -3.
genei is a intelligent research tool enabling you to improve productivity by using a custom AI algorithm to summarise articles, analyse research and find key information, instantly. ... Our chrome extension add-on means you can summarize webpages or save them for later reading as you browse.
The introduction should provide an overview of the paper, a brief summary description, and state the main idea. 6. Introducing the Report's Purpose. Include a brief description of the paper's purpose in the research paper summary. State the thesis statement and briefly overview the paper's main points. 7.
Jenni AI stands as a comprehensive academic writing assistant, encompassing an AI summarizer and summary generator among its key features. This specialized functionality is meticulously crafted to facilitate the creation of concise summaries, effectively condensing extensive research papers, articles, or essays.
Journal Article Request If you can't find the free full text version of a research article, please complete and submit this form. An Learning Commons staff member will then place an interlibrary loan request on your behalf. Summarizing an Article. The following websites offer advice and instruction on summarizing articles:
AI chatbots like ChatGPT can be used to make summarizing long articles, research papers, and books an easier job. If you're tasked with writing a summary for school or work about a body of written ...