Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples

What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 22 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Literature Review - A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
Curating and drafting a solid literature review section not only lends more credibility to your research paper but also makes your research tighter and better focused. But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye.
Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently synthesize and analyze a vast amount of information, identify key themes and trends, and uncover gaps in the existing research. Get real-time explanations, summaries, and answers to your questions for the paper you're reviewing, making navigating and understanding the complex literature landscape easier.
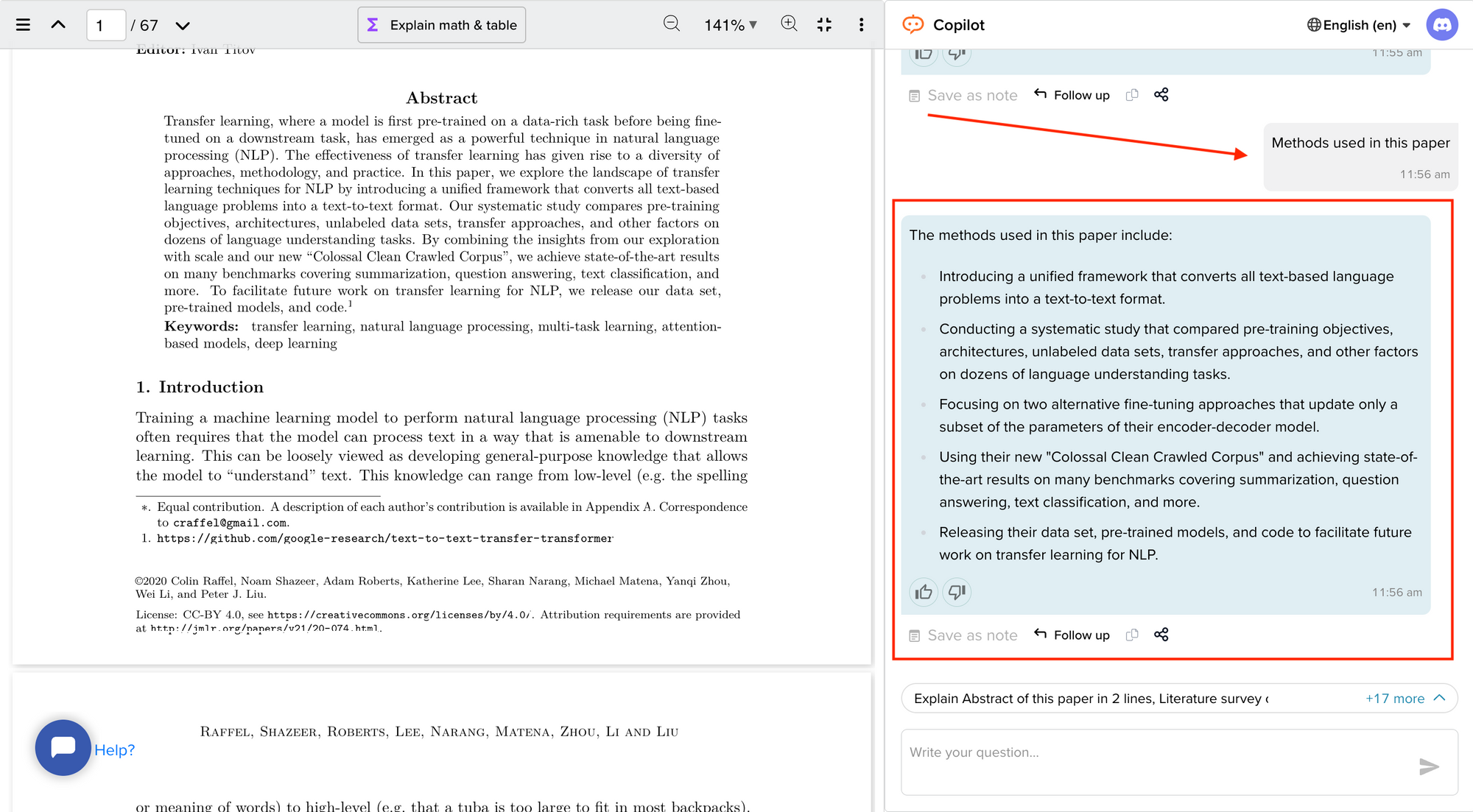
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything from the definition of a literature review, its appropriate length, various types of literature reviews, and how to write one.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a collation of survey, research, critical evaluation, and assessment of the existing literature in a preferred domain.
Eminent researcher and academic Arlene Fink, in her book Conducting Research Literature Reviews , defines it as the following:
“A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have explored while researching a particular topic, and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.”
Simply put, a literature review can be defined as a critical discussion of relevant pre-existing research around your research question and carving out a definitive place for your study in the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews can be presented in multiple ways: a section of an article, the whole research paper itself, or a chapter of your thesis.
A literature review does function as a summary of sources, but it also allows you to analyze further, interpret, and examine the stated theories, methods, viewpoints, and, of course, the gaps in the existing content.
As an author, you can discuss and interpret the research question and its various aspects and debate your adopted methods to support the claim.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is meant to help your readers understand the relevance of your research question and where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. As a researcher, you should use it to set the context, build your argument, and establish the need for your study.
What is the importance of a literature review?
The literature review is a critical part of research papers because it helps you:
- Gain an in-depth understanding of your research question and the surrounding area
- Convey that you have a thorough understanding of your research area and are up-to-date with the latest changes and advancements
- Establish how your research is connected or builds on the existing body of knowledge and how it could contribute to further research
- Elaborate on the validity and suitability of your theoretical framework and research methodology
- Identify and highlight gaps and shortcomings in the existing body of knowledge and how things need to change
- Convey to readers how your study is different or how it contributes to the research area
How long should a literature review be?
Ideally, the literature review should take up 15%-40% of the total length of your manuscript. So, if you have a 10,000-word research paper, the minimum word count could be 1500.
Your literature review format depends heavily on the kind of manuscript you are writing — an entire chapter in case of doctoral theses, a part of the introductory section in a research article, to a full-fledged review article that examines the previously published research on a topic.
Another determining factor is the type of research you are doing. The literature review section tends to be longer for secondary research projects than primary research projects.
What are the different types of literature reviews?
All literature reviews are not the same. There are a variety of possible approaches that you can take. It all depends on the type of research you are pursuing.
Here are the different types of literature reviews:
Argumentative review
It is called an argumentative review when you carefully present literature that only supports or counters a specific argument or premise to establish a viewpoint.
Integrative review
It is a type of literature review focused on building a comprehensive understanding of a topic by combining available theoretical frameworks and empirical evidence.
Methodological review
This approach delves into the ''how'' and the ''what" of the research question — you cannot look at the outcome in isolation; you should also review the methodology used.
Systematic review
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research and collect, report, and analyze data from the studies included in the review.
Meta-analysis review
Meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects than those derived from the individual studies included within a review.
Historical review
Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, or phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and identify future research's likely directions.
Theoretical Review
This form aims to examine the corpus of theory accumulated regarding an issue, concept, theory, and phenomenon. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories exist, the relationships between them, the degree the existing approaches have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
Scoping Review
The Scoping Review is often used at the beginning of an article, dissertation, or research proposal. It is conducted before the research to highlight gaps in the existing body of knowledge and explains why the project should be greenlit.
State-of-the-Art Review
The State-of-the-Art review is conducted periodically, focusing on the most recent research. It describes what is currently known, understood, or agreed upon regarding the research topic and highlights where there are still disagreements.
Can you use the first person in a literature review?
When writing literature reviews, you should avoid the usage of first-person pronouns. It means that instead of "I argue that" or "we argue that," the appropriate expression would be "this research paper argues that."
Do you need an abstract for a literature review?
Ideally, yes. It is always good to have a condensed summary that is self-contained and independent of the rest of your review. As for how to draft one, you can follow the same fundamental idea when preparing an abstract for a literature review. It should also include:
- The research topic and your motivation behind selecting it
- A one-sentence thesis statement
- An explanation of the kinds of literature featured in the review
- Summary of what you've learned
- Conclusions you drew from the literature you reviewed
- Potential implications and future scope for research
Here's an example of the abstract of a literature review
Is a literature review written in the past tense?
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present perfect tenses.
How many sources for a literature review?
There are multiple approaches to deciding how many sources to include in a literature review section. The first approach would be to look level you are at as a researcher. For instance, a doctoral thesis might need 60+ sources. In contrast, you might only need to refer to 5-15 sources at the undergraduate level.
The second approach is based on the kind of literature review you are doing — whether it is merely a chapter of your paper or if it is a self-contained paper in itself. When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. In the second scenario, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
Quick tips on how to write a literature review
To know how to write a literature review, you must clearly understand its impact and role in establishing your work as substantive research material.
You need to follow the below-mentioned steps, to write a literature review:
- Outline the purpose behind the literature review
- Search relevant literature
- Examine and assess the relevant resources
- Discover connections by drawing deep insights from the resources
- Structure planning to write a good literature review
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review
As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications. You must be able to the answer below questions before you start:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What kind of sources should I analyze?
- How much should I critically evaluate each source?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or offer a critique of the sources?
- Do I need to include any background information or definitions?
Additionally, you should know that the narrower your research topic is, the swifter it will be for you to restrict the number of sources to be analyzed.
2. Search relevant literature
Dig deeper into search engines to discover what has already been published around your chosen topic. Make sure you thoroughly go through appropriate reference sources like books, reports, journal articles, government docs, and web-based resources.
You must prepare a list of keywords and their different variations. You can start your search from any library’s catalog, provided you are an active member of that institution. The exact keywords can be extended to widen your research over other databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Microsoft Academic
- Science.gov
Besides, it is not advisable to go through every resource word by word. Alternatively, what you can do is you can start by reading the abstract and then decide whether that source is relevant to your research or not.
Additionally, you must spend surplus time assessing the quality and relevance of resources. It would help if you tried preparing a list of citations to ensure that there lies no repetition of authors, publications, or articles in the literature review.
3. Examine and assess the sources
It is nearly impossible for you to go through every detail in the research article. So rather than trying to fetch every detail, you have to analyze and decide which research sources resemble closest and appear relevant to your chosen domain.
While analyzing the sources, you should look to find out answers to questions like:
- What question or problem has the author been describing and debating?
- What is the definition of critical aspects?
- How well the theories, approach, and methodology have been explained?
- Whether the research theory used some conventional or new innovative approach?
- How relevant are the key findings of the work?
- In what ways does it relate to other sources on the same topic?
- What challenges does this research paper pose to the existing theory
- What are the possible contributions or benefits it adds to the subject domain?
Be always mindful that you refer only to credible and authentic resources. It would be best if you always take references from different publications to validate your theory.
Always keep track of important information or data you can present in your literature review right from the beginning. It will help steer your path from any threats of plagiarism and also make it easier to curate an annotated bibliography or reference section.
4. Discover connections
At this stage, you must start deciding on the argument and structure of your literature review. To accomplish this, you must discover and identify the relations and connections between various resources while drafting your abstract.
A few aspects that you should be aware of while writing a literature review include:
- Rise to prominence: Theories and methods that have gained reputation and supporters over time.
- Constant scrutiny: Concepts or theories that repeatedly went under examination.
- Contradictions and conflicts: Theories, both the supporting and the contradictory ones, for the research topic.
- Knowledge gaps: What exactly does it fail to address, and how to bridge them with further research?
- Influential resources: Significant research projects available that have been upheld as milestones or perhaps, something that can modify the current trends
Once you join the dots between various past research works, it will be easier for you to draw a conclusion and identify your contribution to the existing knowledge base.
5. Structure planning to write a good literature review
There exist different ways towards planning and executing the structure of a literature review. The format of a literature review varies and depends upon the length of the research.
Like any other research paper, the literature review format must contain three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. The goals and objectives of the research question determine what goes inside these three sections.
Nevertheless, a good literature review can be structured according to the chronological, thematic, methodological, or theoretical framework approach.
Literature review samples
1. Standalone
2. As a section of a research paper
How SciSpace Discover makes literature review a breeze?
SciSpace Discover is a one-stop solution to do an effective literature search and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge. It is an excellent repository where you can find millions of only peer-reviewed articles and full-text PDF files. Here’s more on how you can use it:
Find the right information
Find what you want quickly and easily with comprehensive search filters that let you narrow down papers according to PDF availability, year of publishing, document type, and affiliated institution. Moreover, you can sort the results based on the publishing date, citation count, and relevance.
Assess credibility of papers quickly
When doing the literature review, it is critical to establish the quality of your sources. They form the foundation of your research. SciSpace Discover helps you assess the quality of a source by providing an overview of its references, citations, and performance metrics.
Get the complete picture in no time
SciSpace Discover’s personalized suggestion engine helps you stay on course and get the complete picture of the topic from one place. Every time you visit an article page, it provides you links to related papers. Besides that, it helps you understand what’s trending, who are the top authors, and who are the leading publishers on a topic.
Make referring sources super easy
To ensure you don't lose track of your sources, you must start noting down your references when doing the literature review. SciSpace Discover makes this step effortless. Click the 'cite' button on an article page, and you will receive preloaded citation text in multiple styles — all you've to do is copy-paste it into your manuscript.
Final tips on how to write a literature review
A massive chunk of time and effort is required to write a good literature review. But, if you go about it systematically, you'll be able to save a ton of time and build a solid foundation for your research.
We hope this guide has helped you answer several key questions you have about writing literature reviews.
Would you like to explore SciSpace Discover and kick off your literature search right away? You can get started here .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how to start a literature review.
• What questions do you want to answer?
• What sources do you need to answer these questions?
• What information do these sources contain?
• How can you use this information to answer your questions?
2. What to include in a literature review?
• A brief background of the problem or issue
• What has previously been done to address the problem or issue
• A description of what you will do in your project
• How this study will contribute to research on the subject
3. Why literature review is important?
The literature review is an important part of any research project because it allows the writer to look at previous studies on a topic and determine existing gaps in the literature, as well as what has already been done. It will also help them to choose the most appropriate method for their own study.
4. How to cite a literature review in APA format?
To cite a literature review in APA style, you need to provide the author's name, the title of the article, and the year of publication. For example: Patel, A. B., & Stokes, G. S. (2012). The relationship between personality and intelligence: A meta-analysis of longitudinal research. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 16-21
5. What are the components of a literature review?
• A brief introduction to the topic, including its background and context. The introduction should also include a rationale for why the study is being conducted and what it will accomplish.
• A description of the methodologies used in the study. This can include information about data collection methods, sample size, and statistical analyses.
• A presentation of the findings in an organized format that helps readers follow along with the author's conclusions.
6. What are common errors in writing literature review?
• Not spending enough time to critically evaluate the relevance of resources, observations and conclusions.
• Totally relying on secondary data while ignoring primary data.
• Letting your personal bias seep into your interpretation of existing literature.
• No detailed explanation of the procedure to discover and identify an appropriate literature review.
7. What are the 5 C's of writing literature review?
• Cite - the sources you utilized and referenced in your research.
• Compare - existing arguments, hypotheses, methodologies, and conclusions found in the knowledge base.
• Contrast - the arguments, topics, methodologies, approaches, and disputes that may be found in the literature.
• Critique - the literature and describe the ideas and opinions you find more convincing and why.
• Connect - the various studies you reviewed in your research.
8. How many sources should a literature review have?
When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. if it is a self-contained paper in itself, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
9. Can literature review have diagrams?
• To represent an abstract idea or concept
• To explain the steps of a process or procedure
• To help readers understand the relationships between different concepts
10. How old should sources be in a literature review?
Sources for a literature review should be as current as possible or not older than ten years. The only exception to this rule is if you are reviewing a historical topic and need to use older sources.
11. What are the types of literature review?
• Argumentative review
• Integrative review
• Methodological review
• Systematic review
• Meta-analysis review
• Historical review
• Theoretical review
• Scoping review
• State-of-the-Art review
12. Is a literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research, and provide a background for the rest of your work.
But before you go,
- Six Online Tools for Easy Literature Review
- Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?

3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral

- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Harvard Graduate School of Design - Frances Loeb Library
Write and Cite
- Literature Review
- Academic Integrity
- Citing Sources
- Fair Use, Permissions, and Copyright
- Writing Resources
- Grants and Fellowships
- Last Updated: Apr 26, 2024 10:28 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/gsd/write
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
Literature reviews
A literature review is a research task that finds, evaluates and discusses information on a particular topic. You need to analyse multiple texts, and discuss key ideas that you find in the reading.
A literature review may also identify gaps for further research. It is not a process of summarising texts separately – that is done in an annotated bibliography .
A good literature review should:
- be well researched, planned and structured
- discuss a relevant issue, problem or practice that relates to your subject
- explain why your chosen topic is important
- identify key ideas or themes in the literature
- synthesise these findings into thematic paragraphs, using sufficient citations and correct referencing
- demonstrate your understanding of the topic and develop your knowledge and evidence-based practice.
Literature reviews differ across disciplines, so use your assessment instructions and marking criteria as your ultimate guide.
7 steps for writing a literature review
1. analyse the task.
Read the assessment instructions and marking rubric carefully. Note how many sources you need to include in your literature review and any guidelines on selecting the literature.
Choose a topic that interests you. A topic that is important to you will help you stay focused.
2. Establish a clear research question
A good research question will help you narrow down your topic so that it is manageable. If your question is too broad, you may be overwhelmed by the reading. If it is too narrow, you won’t find enough literature.
3. Search for relevant literature
Use keywords from your research question to begin searching .
In the research question "What factors impact student learning when on nursing placement?", the keywords are: student, learning, nursing and placement.
4. Read and review the literature, and take notes
When reading the literature, consider the following:
- Is the article relevant to your topic? For journal articles, read the abstract. For other sources, scan quickly and discard if you can’t see anything useful.
- Who is the author/s and what is their expertise?
- Is the source credible and scholarly ? Use any evaluation tools provided by your subject.
- What is the main topic and what themes are discussed?
Pay attention to important information, such as the abstract, introduction, headings/subheadings, graphs/tables and conclusion.
Take notes using the Cornell method or a note-taking grid. Keeping notes that help you remember the content and relevance of each source is vital for writing a literature review.
- Example note-taking grid for a literature review [Word - 14KB]
5. Identify common themes or areas for further research
It's important to understand the relationships between the sources you've read. Look out for:
- themes: what questions, ideas or topics recur across the literature? Where do authors agree or disagree?
- areas for further research: what is missing from the literature? Are there any weaknesses?
6. Plan the structure of the literature review
Before you start writing, plan how your literature review will be organised.
Literature reviews are usually organised thematically, meaning they discuss one theme after another. You can also organise your ideas chronologically (from past to present) or by methodology (e.g. comparing findings from qualitative and quantitative research).
7. Write, edit, proofread, submit
It's easy to get lost in the reading and not leave enough time for polishing your writing. Use the Assessment Planner to make a clear study plan that includes time for writing, editing and proofreading.
Structure of a literature review
Introduction.
The introduction should include:
- context or background : give a brief summary of the context for your research question and explain why it is important
- purpose (thesis statement): state the purpose of the literature review. This is a statement generated from the research question
- scope (roadmap): outline the specific themes the literature review will focus on and give the reader a sense of how your writing is organised.
Each body paragraph focuses on a specific theme and draws on several pieces of literature.
Paragraphs should include:
- topic sentence: start with the theme of the paragraph
- synthesis of evidence: make connections between multiple sources by comparing and contrasting their views. Use summaries, paraphrases and quotes , and don't forget to properly reference your sources
- analysis or evaluation: add your own interpretation of the findings and comment on any strengths, weaknesses, gaps or areas for further research in the literature
- link: end the paragraph by either linking back to your main topic or to the following paragraph.
Conclusions should include:
- restate the purpose of the review
- summary of the main findings : remind your reader of the main points. Make sure you paraphrase your ideas, so you don’t use the same wording as elsewhere in the literature review
- implications of the findings: suggest how the findings might be important for practice in your field
- areas for further research : provide suggestions for future research to address the problem, issue or question.
The conclusion is followed by a Reference list or Bibliography. Consult the Style notes page of the Academic Referencing Tool for examples.
For complete sample literature reviews with further annotations, see the Word and PDF documents below.
- Example Literature Review - Allied Health [PDF 245KB]
- Example Literature Review - Allied Health [Word 69KB]
- Example Literature Review - Education [PDF 283KB]
- Example Literature Review - Education [Word 104KB]
Further resources
- Using a reading to choose a research topic worksheet
- Manchester Academic Phrasebank - Phrases for academic writing and reporting on research
- Turn a stack of papers into a literature review: Useful tool for beginners (Journal article)
Pathfinder link
Still have questions? Do you want to talk to an expert? Peer Learning Advisors or Academic Skills and Language Advisors are available.
Cant R., Ryan, C., Hughes, L., Luders, E., & Cooper, S. (2021). What helps, what hinders? Undergraduate nursing students’ perceptions of clinical placements based on a thematic synthesis of literature. SAGE Open Nursing, 7, 1-20. https://doi.org/10.1177/23779608211035845 Adapted and used under CC BY-NC 4.0 license
- << Previous: Annotated bibliographies
- Next: Presentations >>
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.

Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet].
Chapter 9 methods for literature reviews.
Guy Paré and Spyros Kitsiou .
9.1. Introduction
Literature reviews play a critical role in scholarship because science remains, first and foremost, a cumulative endeavour ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). As in any academic discipline, rigorous knowledge syntheses are becoming indispensable in keeping up with an exponentially growing eHealth literature, assisting practitioners, academics, and graduate students in finding, evaluating, and synthesizing the contents of many empirical and conceptual papers. Among other methods, literature reviews are essential for: (a) identifying what has been written on a subject or topic; (b) determining the extent to which a specific research area reveals any interpretable trends or patterns; (c) aggregating empirical findings related to a narrow research question to support evidence-based practice; (d) generating new frameworks and theories; and (e) identifying topics or questions requiring more investigation ( Paré, Trudel, Jaana, & Kitsiou, 2015 ).
Literature reviews can take two major forms. The most prevalent one is the “literature review” or “background” section within a journal paper or a chapter in a graduate thesis. This section synthesizes the extant literature and usually identifies the gaps in knowledge that the empirical study addresses ( Sylvester, Tate, & Johnstone, 2013 ). It may also provide a theoretical foundation for the proposed study, substantiate the presence of the research problem, justify the research as one that contributes something new to the cumulated knowledge, or validate the methods and approaches for the proposed study ( Hart, 1998 ; Levy & Ellis, 2006 ).
The second form of literature review, which is the focus of this chapter, constitutes an original and valuable work of research in and of itself ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Rather than providing a base for a researcher’s own work, it creates a solid starting point for all members of the community interested in a particular area or topic ( Mulrow, 1987 ). The so-called “review article” is a journal-length paper which has an overarching purpose to synthesize the literature in a field, without collecting or analyzing any primary data ( Green, Johnson, & Adams, 2006 ).
When appropriately conducted, review articles represent powerful information sources for practitioners looking for state-of-the art evidence to guide their decision-making and work practices ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, high-quality reviews become frequently cited pieces of work which researchers seek out as a first clear outline of the literature when undertaking empirical studies ( Cooper, 1988 ; Rowe, 2014 ). Scholars who track and gauge the impact of articles have found that review papers are cited and downloaded more often than any other type of published article ( Cronin, Ryan, & Coughlan, 2008 ; Montori, Wilczynski, Morgan, Haynes, & Hedges, 2003 ; Patsopoulos, Analatos, & Ioannidis, 2005 ). The reason for their popularity may be the fact that reading the review enables one to have an overview, if not a detailed knowledge of the area in question, as well as references to the most useful primary sources ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Although they are not easy to conduct, the commitment to complete a review article provides a tremendous service to one’s academic community ( Paré et al., 2015 ; Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Most, if not all, peer-reviewed journals in the fields of medical informatics publish review articles of some type.
The main objectives of this chapter are fourfold: (a) to provide an overview of the major steps and activities involved in conducting a stand-alone literature review; (b) to describe and contrast the different types of review articles that can contribute to the eHealth knowledge base; (c) to illustrate each review type with one or two examples from the eHealth literature; and (d) to provide a series of recommendations for prospective authors of review articles in this domain.
9.2. Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
As explained in Templier and Paré (2015) , there are six generic steps involved in conducting a review article:
- formulating the research question(s) and objective(s),
- searching the extant literature,
- screening for inclusion,
- assessing the quality of primary studies,
- extracting data, and
- analyzing data.
Although these steps are presented here in sequential order, one must keep in mind that the review process can be iterative and that many activities can be initiated during the planning stage and later refined during subsequent phases ( Finfgeld-Connett & Johnson, 2013 ; Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ).
Formulating the research question(s) and objective(s): As a first step, members of the review team must appropriately justify the need for the review itself ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ), identify the review’s main objective(s) ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ), and define the concepts or variables at the heart of their synthesis ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ; Webster & Watson, 2002 ). Importantly, they also need to articulate the research question(s) they propose to investigate ( Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ). In this regard, we concur with Jesson, Matheson, and Lacey (2011) that clearly articulated research questions are key ingredients that guide the entire review methodology; they underscore the type of information that is needed, inform the search for and selection of relevant literature, and guide or orient the subsequent analysis. Searching the extant literature: The next step consists of searching the literature and making decisions about the suitability of material to be considered in the review ( Cooper, 1988 ). There exist three main coverage strategies. First, exhaustive coverage means an effort is made to be as comprehensive as possible in order to ensure that all relevant studies, published and unpublished, are included in the review and, thus, conclusions are based on this all-inclusive knowledge base. The second type of coverage consists of presenting materials that are representative of most other works in a given field or area. Often authors who adopt this strategy will search for relevant articles in a small number of top-tier journals in a field ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In the third strategy, the review team concentrates on prior works that have been central or pivotal to a particular topic. This may include empirical studies or conceptual papers that initiated a line of investigation, changed how problems or questions were framed, introduced new methods or concepts, or engendered important debate ( Cooper, 1988 ). Screening for inclusion: The following step consists of evaluating the applicability of the material identified in the preceding step ( Levy & Ellis, 2006 ; vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). Once a group of potential studies has been identified, members of the review team must screen them to determine their relevance ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). A set of predetermined rules provides a basis for including or excluding certain studies. This exercise requires a significant investment on the part of researchers, who must ensure enhanced objectivity and avoid biases or mistakes. As discussed later in this chapter, for certain types of reviews there must be at least two independent reviewers involved in the screening process and a procedure to resolve disagreements must also be in place ( Liberati et al., 2009 ; Shea et al., 2009 ). Assessing the quality of primary studies: In addition to screening material for inclusion, members of the review team may need to assess the scientific quality of the selected studies, that is, appraise the rigour of the research design and methods. Such formal assessment, which is usually conducted independently by at least two coders, helps members of the review team refine which studies to include in the final sample, determine whether or not the differences in quality may affect their conclusions, or guide how they analyze the data and interpret the findings ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Ascribing quality scores to each primary study or considering through domain-based evaluations which study components have or have not been designed and executed appropriately makes it possible to reflect on the extent to which the selected study addresses possible biases and maximizes validity ( Shea et al., 2009 ). Extracting data: The following step involves gathering or extracting applicable information from each primary study included in the sample and deciding what is relevant to the problem of interest ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Indeed, the type of data that should be recorded mainly depends on the initial research questions ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ). However, important information may also be gathered about how, when, where and by whom the primary study was conducted, the research design and methods, or qualitative/quantitative results ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Analyzing and synthesizing data : As a final step, members of the review team must collate, summarize, aggregate, organize, and compare the evidence extracted from the included studies. The extracted data must be presented in a meaningful way that suggests a new contribution to the extant literature ( Jesson et al., 2011 ). Webster and Watson (2002) warn researchers that literature reviews should be much more than lists of papers and should provide a coherent lens to make sense of extant knowledge on a given topic. There exist several methods and techniques for synthesizing quantitative (e.g., frequency analysis, meta-analysis) and qualitative (e.g., grounded theory, narrative analysis, meta-ethnography) evidence ( Dixon-Woods, Agarwal, Jones, Young, & Sutton, 2005 ; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic. Our classification scheme is largely inspired from Paré and colleagues’ (2015) typology. Below we present and illustrate those review types that we feel are central to the growth and development of the eHealth domain.
9.3.1. Narrative Reviews
The narrative review is the “traditional” way of reviewing the extant literature and is skewed towards a qualitative interpretation of prior knowledge ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). Put simply, a narrative review attempts to summarize or synthesize what has been written on a particular topic but does not seek generalization or cumulative knowledge from what is reviewed ( Davies, 2000 ; Green et al., 2006 ). Instead, the review team often undertakes the task of accumulating and synthesizing the literature to demonstrate the value of a particular point of view ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ). As such, reviewers may selectively ignore or limit the attention paid to certain studies in order to make a point. In this rather unsystematic approach, the selection of information from primary articles is subjective, lacks explicit criteria for inclusion and can lead to biased interpretations or inferences ( Green et al., 2006 ). There are several narrative reviews in the particular eHealth domain, as in all fields, which follow such an unstructured approach ( Silva et al., 2015 ; Paul et al., 2015 ).
Despite these criticisms, this type of review can be very useful in gathering together a volume of literature in a specific subject area and synthesizing it. As mentioned above, its primary purpose is to provide the reader with a comprehensive background for understanding current knowledge and highlighting the significance of new research ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Faculty like to use narrative reviews in the classroom because they are often more up to date than textbooks, provide a single source for students to reference, and expose students to peer-reviewed literature ( Green et al., 2006 ). For researchers, narrative reviews can inspire research ideas by identifying gaps or inconsistencies in a body of knowledge, thus helping researchers to determine research questions or formulate hypotheses. Importantly, narrative reviews can also be used as educational articles to bring practitioners up to date with certain topics of issues ( Green et al., 2006 ).
Recently, there have been several efforts to introduce more rigour in narrative reviews that will elucidate common pitfalls and bring changes into their publication standards. Information systems researchers, among others, have contributed to advancing knowledge on how to structure a “traditional” review. For instance, Levy and Ellis (2006) proposed a generic framework for conducting such reviews. Their model follows the systematic data processing approach comprised of three steps, namely: (a) literature search and screening; (b) data extraction and analysis; and (c) writing the literature review. They provide detailed and very helpful instructions on how to conduct each step of the review process. As another methodological contribution, vom Brocke et al. (2009) offered a series of guidelines for conducting literature reviews, with a particular focus on how to search and extract the relevant body of knowledge. Last, Bandara, Miskon, and Fielt (2011) proposed a structured, predefined and tool-supported method to identify primary studies within a feasible scope, extract relevant content from identified articles, synthesize and analyze the findings, and effectively write and present the results of the literature review. We highly recommend that prospective authors of narrative reviews consult these useful sources before embarking on their work.
Darlow and Wen (2015) provide a good example of a highly structured narrative review in the eHealth field. These authors synthesized published articles that describe the development process of mobile health ( m-health ) interventions for patients’ cancer care self-management. As in most narrative reviews, the scope of the research questions being investigated is broad: (a) how development of these systems are carried out; (b) which methods are used to investigate these systems; and (c) what conclusions can be drawn as a result of the development of these systems. To provide clear answers to these questions, a literature search was conducted on six electronic databases and Google Scholar . The search was performed using several terms and free text words, combining them in an appropriate manner. Four inclusion and three exclusion criteria were utilized during the screening process. Both authors independently reviewed each of the identified articles to determine eligibility and extract study information. A flow diagram shows the number of studies identified, screened, and included or excluded at each stage of study selection. In terms of contributions, this review provides a series of practical recommendations for m-health intervention development.
9.3.2. Descriptive or Mapping Reviews
The primary goal of a descriptive review is to determine the extent to which a body of knowledge in a particular research topic reveals any interpretable pattern or trend with respect to pre-existing propositions, theories, methodologies or findings ( King & He, 2005 ; Paré et al., 2015 ). In contrast with narrative reviews, descriptive reviews follow a systematic and transparent procedure, including searching, screening and classifying studies ( Petersen, Vakkalanka, & Kuzniarz, 2015 ). Indeed, structured search methods are used to form a representative sample of a larger group of published works ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, authors of descriptive reviews extract from each study certain characteristics of interest, such as publication year, research methods, data collection techniques, and direction or strength of research outcomes (e.g., positive, negative, or non-significant) in the form of frequency analysis to produce quantitative results ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). In essence, each study included in a descriptive review is treated as the unit of analysis and the published literature as a whole provides a database from which the authors attempt to identify any interpretable trends or draw overall conclusions about the merits of existing conceptualizations, propositions, methods or findings ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In doing so, a descriptive review may claim that its findings represent the state of the art in a particular domain ( King & He, 2005 ).
In the fields of health sciences and medical informatics, reviews that focus on examining the range, nature and evolution of a topic area are described by Anderson, Allen, Peckham, and Goodwin (2008) as mapping reviews . Like descriptive reviews, the research questions are generic and usually relate to publication patterns and trends. There is no preconceived plan to systematically review all of the literature although this can be done. Instead, researchers often present studies that are representative of most works published in a particular area and they consider a specific time frame to be mapped.
An example of this approach in the eHealth domain is offered by DeShazo, Lavallie, and Wolf (2009). The purpose of this descriptive or mapping review was to characterize publication trends in the medical informatics literature over a 20-year period (1987 to 2006). To achieve this ambitious objective, the authors performed a bibliometric analysis of medical informatics citations indexed in medline using publication trends, journal frequencies, impact factors, Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) term frequencies, and characteristics of citations. Findings revealed that there were over 77,000 medical informatics articles published during the covered period in numerous journals and that the average annual growth rate was 12%. The MeSH term analysis also suggested a strong interdisciplinary trend. Finally, average impact scores increased over time with two notable growth periods. Overall, patterns in research outputs that seem to characterize the historic trends and current components of the field of medical informatics suggest it may be a maturing discipline (DeShazo et al., 2009).
9.3.3. Scoping Reviews
Scoping reviews attempt to provide an initial indication of the potential size and nature of the extant literature on an emergent topic (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Daudt, van Mossel, & Scott, 2013 ; Levac, Colquhoun, & O’Brien, 2010). A scoping review may be conducted to examine the extent, range and nature of research activities in a particular area, determine the value of undertaking a full systematic review (discussed next), or identify research gaps in the extant literature ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In line with their main objective, scoping reviews usually conclude with the presentation of a detailed research agenda for future works along with potential implications for both practice and research.
Unlike narrative and descriptive reviews, the whole point of scoping the field is to be as comprehensive as possible, including grey literature (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005). Inclusion and exclusion criteria must be established to help researchers eliminate studies that are not aligned with the research questions. It is also recommended that at least two independent coders review abstracts yielded from the search strategy and then the full articles for study selection ( Daudt et al., 2013 ). The synthesized evidence from content or thematic analysis is relatively easy to present in tabular form (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
One of the most highly cited scoping reviews in the eHealth domain was published by Archer, Fevrier-Thomas, Lokker, McKibbon, and Straus (2011) . These authors reviewed the existing literature on personal health record ( phr ) systems including design, functionality, implementation, applications, outcomes, and benefits. Seven databases were searched from 1985 to March 2010. Several search terms relating to phr s were used during this process. Two authors independently screened titles and abstracts to determine inclusion status. A second screen of full-text articles, again by two independent members of the research team, ensured that the studies described phr s. All in all, 130 articles met the criteria and their data were extracted manually into a database. The authors concluded that although there is a large amount of survey, observational, cohort/panel, and anecdotal evidence of phr benefits and satisfaction for patients, more research is needed to evaluate the results of phr implementations. Their in-depth analysis of the literature signalled that there is little solid evidence from randomized controlled trials or other studies through the use of phr s. Hence, they suggested that more research is needed that addresses the current lack of understanding of optimal functionality and usability of these systems, and how they can play a beneficial role in supporting patient self-management ( Archer et al., 2011 ).
9.3.4. Forms of Aggregative Reviews
Healthcare providers, practitioners, and policy-makers are nowadays overwhelmed with large volumes of information, including research-based evidence from numerous clinical trials and evaluation studies, assessing the effectiveness of health information technologies and interventions ( Ammenwerth & de Keizer, 2004 ; Deshazo et al., 2009 ). It is unrealistic to expect that all these disparate actors will have the time, skills, and necessary resources to identify the available evidence in the area of their expertise and consider it when making decisions. Systematic reviews that involve the rigorous application of scientific strategies aimed at limiting subjectivity and bias (i.e., systematic and random errors) can respond to this challenge.
Systematic reviews attempt to aggregate, appraise, and synthesize in a single source all empirical evidence that meet a set of previously specified eligibility criteria in order to answer a clearly formulated and often narrow research question on a particular topic of interest to support evidence-based practice ( Liberati et al., 2009 ). They adhere closely to explicit scientific principles ( Liberati et al., 2009 ) and rigorous methodological guidelines (Higgins & Green, 2008) aimed at reducing random and systematic errors that can lead to deviations from the truth in results or inferences. The use of explicit methods allows systematic reviews to aggregate a large body of research evidence, assess whether effects or relationships are in the same direction and of the same general magnitude, explain possible inconsistencies between study results, and determine the strength of the overall evidence for every outcome of interest based on the quality of included studies and the general consistency among them ( Cook, Mulrow, & Haynes, 1997 ). The main procedures of a systematic review involve:
- Formulating a review question and developing a search strategy based on explicit inclusion criteria for the identification of eligible studies (usually described in the context of a detailed review protocol).
- Searching for eligible studies using multiple databases and information sources, including grey literature sources, without any language restrictions.
- Selecting studies, extracting data, and assessing risk of bias in a duplicate manner using two independent reviewers to avoid random or systematic errors in the process.
- Analyzing data using quantitative or qualitative methods.
- Presenting results in summary of findings tables.
- Interpreting results and drawing conclusions.
Many systematic reviews, but not all, use statistical methods to combine the results of independent studies into a single quantitative estimate or summary effect size. Known as meta-analyses , these reviews use specific data extraction and statistical techniques (e.g., network, frequentist, or Bayesian meta-analyses) to calculate from each study by outcome of interest an effect size along with a confidence interval that reflects the degree of uncertainty behind the point estimate of effect ( Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins, & Rothstein, 2009 ; Deeks, Higgins, & Altman, 2008 ). Subsequently, they use fixed or random-effects analysis models to combine the results of the included studies, assess statistical heterogeneity, and calculate a weighted average of the effect estimates from the different studies, taking into account their sample sizes. The summary effect size is a value that reflects the average magnitude of the intervention effect for a particular outcome of interest or, more generally, the strength of a relationship between two variables across all studies included in the systematic review. By statistically combining data from multiple studies, meta-analyses can create more precise and reliable estimates of intervention effects than those derived from individual studies alone, when these are examined independently as discrete sources of information.
The review by Gurol-Urganci, de Jongh, Vodopivec-Jamsek, Atun, and Car (2013) on the effects of mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments is an illustrative example of a high-quality systematic review with meta-analysis. Missed appointments are a major cause of inefficiency in healthcare delivery with substantial monetary costs to health systems. These authors sought to assess whether mobile phone-based appointment reminders delivered through Short Message Service ( sms ) or Multimedia Messaging Service ( mms ) are effective in improving rates of patient attendance and reducing overall costs. To this end, they conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases using highly sensitive search strategies without language or publication-type restrictions to identify all rct s that are eligible for inclusion. In order to minimize the risk of omitting eligible studies not captured by the original search, they supplemented all electronic searches with manual screening of trial registers and references contained in the included studies. Study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments were performed independently by two coders using standardized methods to ensure consistency and to eliminate potential errors. Findings from eight rct s involving 6,615 participants were pooled into meta-analyses to calculate the magnitude of effects that mobile text message reminders have on the rate of attendance at healthcare appointments compared to no reminders and phone call reminders.
Meta-analyses are regarded as powerful tools for deriving meaningful conclusions. However, there are situations in which it is neither reasonable nor appropriate to pool studies together using meta-analytic methods simply because there is extensive clinical heterogeneity between the included studies or variation in measurement tools, comparisons, or outcomes of interest. In these cases, systematic reviews can use qualitative synthesis methods such as vote counting, content analysis, classification schemes and tabulations, as an alternative approach to narratively synthesize the results of the independent studies included in the review. This form of review is known as qualitative systematic review.
A rigorous example of one such review in the eHealth domain is presented by Mickan, Atherton, Roberts, Heneghan, and Tilson (2014) on the use of handheld computers by healthcare professionals and their impact on access to information and clinical decision-making. In line with the methodological guidelines for systematic reviews, these authors: (a) developed and registered with prospero ( www.crd.york.ac.uk/ prospero / ) an a priori review protocol; (b) conducted comprehensive searches for eligible studies using multiple databases and other supplementary strategies (e.g., forward searches); and (c) subsequently carried out study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments in a duplicate manner to eliminate potential errors in the review process. Heterogeneity between the included studies in terms of reported outcomes and measures precluded the use of meta-analytic methods. To this end, the authors resorted to using narrative analysis and synthesis to describe the effectiveness of handheld computers on accessing information for clinical knowledge, adherence to safety and clinical quality guidelines, and diagnostic decision-making.
In recent years, the number of systematic reviews in the field of health informatics has increased considerably. Systematic reviews with discordant findings can cause great confusion and make it difficult for decision-makers to interpret the review-level evidence ( Moher, 2013 ). Therefore, there is a growing need for appraisal and synthesis of prior systematic reviews to ensure that decision-making is constantly informed by the best available accumulated evidence. Umbrella reviews , also known as overviews of systematic reviews, are tertiary types of evidence synthesis that aim to accomplish this; that is, they aim to compare and contrast findings from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Umbrella reviews generally adhere to the same principles and rigorous methodological guidelines used in systematic reviews. However, the unit of analysis in umbrella reviews is the systematic review rather than the primary study ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Unlike systematic reviews that have a narrow focus of inquiry, umbrella reviews focus on broader research topics for which there are several potential interventions ( Smith, Devane, Begley, & Clarke, 2011 ). A recent umbrella review on the effects of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with heart failure critically appraised, compared, and synthesized evidence from 15 systematic reviews to investigate which types of home telemonitoring technologies and forms of interventions are more effective in reducing mortality and hospital admissions ( Kitsiou, Paré, & Jaana, 2015 ).
9.3.5. Realist Reviews
Realist reviews are theory-driven interpretative reviews developed to inform, enhance, or supplement conventional systematic reviews by making sense of heterogeneous evidence about complex interventions applied in diverse contexts in a way that informs policy decision-making ( Greenhalgh, Wong, Westhorp, & Pawson, 2011 ). They originated from criticisms of positivist systematic reviews which centre on their “simplistic” underlying assumptions ( Oates, 2011 ). As explained above, systematic reviews seek to identify causation. Such logic is appropriate for fields like medicine and education where findings of randomized controlled trials can be aggregated to see whether a new treatment or intervention does improve outcomes. However, many argue that it is not possible to establish such direct causal links between interventions and outcomes in fields such as social policy, management, and information systems where for any intervention there is unlikely to be a regular or consistent outcome ( Oates, 2011 ; Pawson, 2006 ; Rousseau, Manning, & Denyer, 2008 ).
To circumvent these limitations, Pawson, Greenhalgh, Harvey, and Walshe (2005) have proposed a new approach for synthesizing knowledge that seeks to unpack the mechanism of how “complex interventions” work in particular contexts. The basic research question — what works? — which is usually associated with systematic reviews changes to: what is it about this intervention that works, for whom, in what circumstances, in what respects and why? Realist reviews have no particular preference for either quantitative or qualitative evidence. As a theory-building approach, a realist review usually starts by articulating likely underlying mechanisms and then scrutinizes available evidence to find out whether and where these mechanisms are applicable ( Shepperd et al., 2009 ). Primary studies found in the extant literature are viewed as case studies which can test and modify the initial theories ( Rousseau et al., 2008 ).
The main objective pursued in the realist review conducted by Otte-Trojel, de Bont, Rundall, and van de Klundert (2014) was to examine how patient portals contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The specific goals were to investigate how outcomes are produced and, most importantly, how variations in outcomes can be explained. The research team started with an exploratory review of background documents and research studies to identify ways in which patient portals may contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The authors identified six main ways which represent “educated guesses” to be tested against the data in the evaluation studies. These studies were identified through a formal and systematic search in four databases between 2003 and 2013. Two members of the research team selected the articles using a pre-established list of inclusion and exclusion criteria and following a two-step procedure. The authors then extracted data from the selected articles and created several tables, one for each outcome category. They organized information to bring forward those mechanisms where patient portals contribute to outcomes and the variation in outcomes across different contexts.
9.3.6. Critical Reviews
Lastly, critical reviews aim to provide a critical evaluation and interpretive analysis of existing literature on a particular topic of interest to reveal strengths, weaknesses, contradictions, controversies, inconsistencies, and/or other important issues with respect to theories, hypotheses, research methods or results ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ; Kirkevold, 1997 ). Unlike other review types, critical reviews attempt to take a reflective account of the research that has been done in a particular area of interest, and assess its credibility by using appraisal instruments or critical interpretive methods. In this way, critical reviews attempt to constructively inform other scholars about the weaknesses of prior research and strengthen knowledge development by giving focus and direction to studies for further improvement ( Kirkevold, 1997 ).
Kitsiou, Paré, and Jaana (2013) provide an example of a critical review that assessed the methodological quality of prior systematic reviews of home telemonitoring studies for chronic patients. The authors conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases to identify eligible reviews and subsequently used a validated instrument to conduct an in-depth quality appraisal. Results indicate that the majority of systematic reviews in this particular area suffer from important methodological flaws and biases that impair their internal validity and limit their usefulness for clinical and decision-making purposes. To this end, they provide a number of recommendations to strengthen knowledge development towards improving the design and execution of future reviews on home telemonitoring.
9.4. Summary
Table 9.1 outlines the main types of literature reviews that were described in the previous sub-sections and summarizes the main characteristics that distinguish one review type from another. It also includes key references to methodological guidelines and useful sources that can be used by eHealth scholars and researchers for planning and developing reviews.
Typology of Literature Reviews (adapted from Paré et al., 2015).
As shown in Table 9.1 , each review type addresses different kinds of research questions or objectives, which subsequently define and dictate the methods and approaches that need to be used to achieve the overarching goal(s) of the review. For example, in the case of narrative reviews, there is greater flexibility in searching and synthesizing articles ( Green et al., 2006 ). Researchers are often relatively free to use a diversity of approaches to search, identify, and select relevant scientific articles, describe their operational characteristics, present how the individual studies fit together, and formulate conclusions. On the other hand, systematic reviews are characterized by their high level of systematicity, rigour, and use of explicit methods, based on an “a priori” review plan that aims to minimize bias in the analysis and synthesis process (Higgins & Green, 2008). Some reviews are exploratory in nature (e.g., scoping/mapping reviews), whereas others may be conducted to discover patterns (e.g., descriptive reviews) or involve a synthesis approach that may include the critical analysis of prior research ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Hence, in order to select the most appropriate type of review, it is critical to know before embarking on a review project, why the research synthesis is conducted and what type of methods are best aligned with the pursued goals.
9.5. Concluding Remarks
In light of the increased use of evidence-based practice and research generating stronger evidence ( Grady et al., 2011 ; Lyden et al., 2013 ), review articles have become essential tools for summarizing, synthesizing, integrating or critically appraising prior knowledge in the eHealth field. As mentioned earlier, when rigorously conducted review articles represent powerful information sources for eHealth scholars and practitioners looking for state-of-the-art evidence. The typology of literature reviews we used herein will allow eHealth researchers, graduate students and practitioners to gain a better understanding of the similarities and differences between review types.
We must stress that this classification scheme does not privilege any specific type of review as being of higher quality than another ( Paré et al., 2015 ). As explained above, each type of review has its own strengths and limitations. Having said that, we realize that the methodological rigour of any review — be it qualitative, quantitative or mixed — is a critical aspect that should be considered seriously by prospective authors. In the present context, the notion of rigour refers to the reliability and validity of the review process described in section 9.2. For one thing, reliability is related to the reproducibility of the review process and steps, which is facilitated by a comprehensive documentation of the literature search process, extraction, coding and analysis performed in the review. Whether the search is comprehensive or not, whether it involves a methodical approach for data extraction and synthesis or not, it is important that the review documents in an explicit and transparent manner the steps and approach that were used in the process of its development. Next, validity characterizes the degree to which the review process was conducted appropriately. It goes beyond documentation and reflects decisions related to the selection of the sources, the search terms used, the period of time covered, the articles selected in the search, and the application of backward and forward searches ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). In short, the rigour of any review article is reflected by the explicitness of its methods (i.e., transparency) and the soundness of the approach used. We refer those interested in the concepts of rigour and quality to the work of Templier and Paré (2015) which offers a detailed set of methodological guidelines for conducting and evaluating various types of review articles.
To conclude, our main objective in this chapter was to demystify the various types of literature reviews that are central to the continuous development of the eHealth field. It is our hope that our descriptive account will serve as a valuable source for those conducting, evaluating or using reviews in this important and growing domain.
- Ammenwerth E., de Keizer N. An inventory of evaluation studies of information technology in health care. Trends in evaluation research, 1982-2002. International Journal of Medical Informatics. 2004; 44 (1):44–56. [ PubMed : 15778794 ]
- Anderson S., Allen P., Peckham S., Goodwin N. Asking the right questions: scoping studies in the commissioning of research on the organisation and delivery of health services. Health Research Policy and Systems. 2008; 6 (7):1–12. [ PMC free article : PMC2500008 ] [ PubMed : 18613961 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Archer N., Fevrier-Thomas U., Lokker C., McKibbon K. A., Straus S.E. Personal health records: a scoping review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2011; 18 (4):515–522. [ PMC free article : PMC3128401 ] [ PubMed : 21672914 ]
- Arksey H., O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology. 2005; 8 (1):19–32.
- A systematic, tool-supported method for conducting literature reviews in information systems. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 19th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2011); June 9 to 11; Helsinki, Finland. 2011.
- Baumeister R. F., Leary M.R. Writing narrative literature reviews. Review of General Psychology. 1997; 1 (3):311–320.
- Becker L. A., Oxman A.D. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Overviews of reviews; pp. 607–631.
- Borenstein M., Hedges L., Higgins J., Rothstein H. Introduction to meta-analysis. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons Inc; 2009.
- Cook D. J., Mulrow C. D., Haynes B. Systematic reviews: Synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1997; 126 (5):376–380. [ PubMed : 9054282 ]
- Cooper H., Hedges L.V. In: The handbook of research synthesis and meta-analysis. 2nd ed. Cooper H., Hedges L. V., Valentine J. C., editors. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 2009. Research synthesis as a scientific process; pp. 3–17.
- Cooper H. M. Organizing knowledge syntheses: A taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowledge in Society. 1988; 1 (1):104–126.
- Cronin P., Ryan F., Coughlan M. Undertaking a literature review: a step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing. 2008; 17 (1):38–43. [ PubMed : 18399395 ]
- Darlow S., Wen K.Y. Development testing of mobile health interventions for cancer patient self-management: A review. Health Informatics Journal. 2015 (online before print). [ PubMed : 25916831 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Daudt H. M., van Mossel C., Scott S.J. Enhancing the scoping study methodology: a large, inter-professional team’s experience with Arksey and O’Malley’s framework. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2013; 13 :48. [ PMC free article : PMC3614526 ] [ PubMed : 23522333 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Davies P. The relevance of systematic reviews to educational policy and practice. Oxford Review of Education. 2000; 26 (3-4):365–378.
- Deeks J. J., Higgins J. P. T., Altman D.G. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses; pp. 243–296.
- Deshazo J. P., Lavallie D. L., Wolf F.M. Publication trends in the medical informatics literature: 20 years of “Medical Informatics” in mesh . bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2009; 9 :7. [ PMC free article : PMC2652453 ] [ PubMed : 19159472 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dixon-Woods M., Agarwal S., Jones D., Young B., Sutton A. Synthesising qualitative and quantitative evidence: a review of possible methods. Journal of Health Services Research and Policy. 2005; 10 (1):45–53. [ PubMed : 15667704 ]
- Finfgeld-Connett D., Johnson E.D. Literature search strategies for conducting knowledge-building and theory-generating qualitative systematic reviews. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2013; 69 (1):194–204. [ PMC free article : PMC3424349 ] [ PubMed : 22591030 ]
- Grady B., Myers K. M., Nelson E. L., Belz N., Bennett L., Carnahan L. … Guidelines Working Group. Evidence-based practice for telemental health. Telemedicine Journal and E Health. 2011; 17 (2):131–148. [ PubMed : 21385026 ]
- Green B. N., Johnson C. D., Adams A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine. 2006; 5 (3):101–117. [ PMC free article : PMC2647067 ] [ PubMed : 19674681 ]
- Greenhalgh T., Wong G., Westhorp G., Pawson R. Protocol–realist and meta-narrative evidence synthesis: evolving standards ( rameses ). bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 :115. [ PMC free article : PMC3173389 ] [ PubMed : 21843376 ]
- Gurol-Urganci I., de Jongh T., Vodopivec-Jamsek V., Atun R., Car J. Mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments. Cochrane Database System Review. 2013; 12 cd 007458. [ PMC free article : PMC6485985 ] [ PubMed : 24310741 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hart C. Doing a literature review: Releasing the social science research imagination. London: SAGE Publications; 1998.
- Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: Cochrane book series. Hoboken, nj : Wiley-Blackwell; 2008.
- Jesson J., Matheson L., Lacey F.M. Doing your literature review: traditional and systematic techniques. Los Angeles & London: SAGE Publications; 2011.
- King W. R., He J. Understanding the role and methods of meta-analysis in IS research. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2005; 16 :1.
- Kirkevold M. Integrative nursing research — an important strategy to further the development of nursing science and nursing practice. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 1997; 25 (5):977–984. [ PubMed : 9147203 ]
- Kitchenham B., Charters S. ebse Technical Report Version 2.3. Keele & Durham. uk : Keele University & University of Durham; 2007. Guidelines for performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering.
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with chronic diseases: a critical assessment of their methodological quality. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2013; 15 (7):e150. [ PMC free article : PMC3785977 ] [ PubMed : 23880072 ]
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Effects of home telemonitoring interventions on patients with chronic heart failure: an overview of systematic reviews. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2015; 17 (3):e63. [ PMC free article : PMC4376138 ] [ PubMed : 25768664 ]
- Levac D., Colquhoun H., O’Brien K. K. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implementation Science. 2010; 5 (1):69. [ PMC free article : PMC2954944 ] [ PubMed : 20854677 ]
- Levy Y., Ellis T.J. A systems approach to conduct an effective literature review in support of information systems research. Informing Science. 2006; 9 :181–211.
- Liberati A., Altman D. G., Tetzlaff J., Mulrow C., Gøtzsche P. C., Ioannidis J. P. A. et al. Moher D. The prisma statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2009; 151 (4):W-65. [ PubMed : 19622512 ]
- Lyden J. R., Zickmund S. L., Bhargava T. D., Bryce C. L., Conroy M. B., Fischer G. S. et al. McTigue K. M. Implementing health information technology in a patient-centered manner: Patient experiences with an online evidence-based lifestyle intervention. Journal for Healthcare Quality. 2013; 35 (5):47–57. [ PubMed : 24004039 ]
- Mickan S., Atherton H., Roberts N. W., Heneghan C., Tilson J.K. Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: a systematic review. bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2014; 14 :56. [ PMC free article : PMC4099138 ] [ PubMed : 24998515 ]
- Moher D. The problem of duplicate systematic reviews. British Medical Journal. 2013; 347 (5040) [ PubMed : 23945367 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Montori V. M., Wilczynski N. L., Morgan D., Haynes R. B., Hedges T. Systematic reviews: a cross-sectional study of location and citation counts. bmc Medicine. 2003; 1 :2. [ PMC free article : PMC281591 ] [ PubMed : 14633274 ]
- Mulrow C. D. The medical review article: state of the science. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1987; 106 (3):485–488. [ PubMed : 3813259 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Evidence-based information systems: A decade later. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems ; 2011. Retrieved from http://aisel .aisnet.org/cgi/viewcontent .cgi?article =1221&context =ecis2011 .
- Okoli C., Schabram K. A guide to conducting a systematic literature review of information systems research. ssrn Electronic Journal. 2010
- Otte-Trojel T., de Bont A., Rundall T. G., van de Klundert J. How outcomes are achieved through patient portals: a realist review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2014; 21 (4):751–757. [ PMC free article : PMC4078283 ] [ PubMed : 24503882 ]
- Paré G., Trudel M.-C., Jaana M., Kitsiou S. Synthesizing information systems knowledge: A typology of literature reviews. Information & Management. 2015; 52 (2):183–199.
- Patsopoulos N. A., Analatos A. A., Ioannidis J.P. A. Relative citation impact of various study designs in the health sciences. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2005; 293 (19):2362–2366. [ PubMed : 15900006 ]
- Paul M. M., Greene C. M., Newton-Dame R., Thorpe L. E., Perlman S. E., McVeigh K. H., Gourevitch M.N. The state of population health surveillance using electronic health records: A narrative review. Population Health Management. 2015; 18 (3):209–216. [ PubMed : 25608033 ]
- Pawson R. Evidence-based policy: a realist perspective. London: SAGE Publications; 2006.
- Pawson R., Greenhalgh T., Harvey G., Walshe K. Realist review—a new method of systematic review designed for complex policy interventions. Journal of Health Services Research & Policy. 2005; 10 (Suppl 1):21–34. [ PubMed : 16053581 ]
- Petersen K., Vakkalanka S., Kuzniarz L. Guidelines for conducting systematic mapping studies in software engineering: An update. Information and Software Technology. 2015; 64 :1–18.
- Petticrew M., Roberts H. Systematic reviews in the social sciences: A practical guide. Malden, ma : Blackwell Publishing Co; 2006.
- Rousseau D. M., Manning J., Denyer D. Evidence in management and organizational science: Assembling the field’s full weight of scientific knowledge through syntheses. The Academy of Management Annals. 2008; 2 (1):475–515.
- Rowe F. What literature review is not: diversity, boundaries and recommendations. European Journal of Information Systems. 2014; 23 (3):241–255.
- Shea B. J., Hamel C., Wells G. A., Bouter L. M., Kristjansson E., Grimshaw J. et al. Boers M. amstar is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2009; 62 (10):1013–1020. [ PubMed : 19230606 ]
- Shepperd S., Lewin S., Straus S., Clarke M., Eccles M. P., Fitzpatrick R. et al. Sheikh A. Can we systematically review studies that evaluate complex interventions? PLoS Medicine. 2009; 6 (8):e1000086. [ PMC free article : PMC2717209 ] [ PubMed : 19668360 ]
- Silva B. M., Rodrigues J. J., de la Torre Díez I., López-Coronado M., Saleem K. Mobile-health: A review of current state in 2015. Journal of Biomedical Informatics. 2015; 56 :265–272. [ PubMed : 26071682 ]
- Smith V., Devane D., Begley C., Clarke M. Methodology in conducting a systematic review of systematic reviews of healthcare interventions. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 (1):15. [ PMC free article : PMC3039637 ] [ PubMed : 21291558 ]
- Sylvester A., Tate M., Johnstone D. Beyond synthesis: re-presenting heterogeneous research literature. Behaviour & Information Technology. 2013; 32 (12):1199–1215.
- Templier M., Paré G. A framework for guiding and evaluating literature reviews. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2015; 37 (6):112–137.
- Thomas J., Harden A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2008; 8 (1):45. [ PMC free article : PMC2478656 ] [ PubMed : 18616818 ]
- Reconstructing the giant: on the importance of rigour in documenting the literature search process. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2009); Verona, Italy. 2009.
- Webster J., Watson R.T. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. Management Information Systems Quarterly. 2002; 26 (2):11.
- Whitlock E. P., Lin J. S., Chou R., Shekelle P., Robinson K.A. Using existing systematic reviews in complex systematic reviews. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2008; 148 (10):776–782. [ PubMed : 18490690 ]
This publication is licensed under a Creative Commons License, Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0): see https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- Cite this Page Paré G, Kitsiou S. Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews. In: Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.
- PDF version of this title (4.5M)
- Disable Glossary Links
In this Page
- Introduction
- Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
- Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
- Concluding Remarks
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Recent Activity
- Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Ev... Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 24, Issue 2
- Five tips for developing useful literature summary tables for writing review articles
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0157-5319 Ahtisham Younas 1 , 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7839-8130 Parveen Ali 3 , 4
- 1 Memorial University of Newfoundland , St John's , Newfoundland , Canada
- 2 Swat College of Nursing , Pakistan
- 3 School of Nursing and Midwifery , University of Sheffield , Sheffield , South Yorkshire , UK
- 4 Sheffield University Interpersonal Violence Research Group , Sheffield University , Sheffield , UK
- Correspondence to Ahtisham Younas, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St John's, NL A1C 5C4, Canada; ay6133{at}mun.ca
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2021-103417
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research. 1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis in reviews, the use of literature summary tables is of utmost importance. A literature summary table provides a synopsis of an included article. It succinctly presents its purpose, methods, findings and other relevant information pertinent to the review. The aim of developing these literature summary tables is to provide the reader with the information at one glance. Since there are multiple types of reviews (eg, systematic, integrative, scoping, critical and mixed methods) with distinct purposes and techniques, 2 there could be various approaches for developing literature summary tables making it a complex task specialty for the novice researchers or reviewers. Here, we offer five tips for authors of the review articles, relevant to all types of reviews, for creating useful and relevant literature summary tables. We also provide examples from our published reviews to illustrate how useful literature summary tables can be developed and what sort of information should be provided.
Tip 1: provide detailed information about frameworks and methods
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Tabular literature summaries from a scoping review. Source: Rasheed et al . 3
The provision of information about conceptual and theoretical frameworks and methods is useful for several reasons. First, in quantitative (reviews synthesising the results of quantitative studies) and mixed reviews (reviews synthesising the results of both qualitative and quantitative studies to address a mixed review question), it allows the readers to assess the congruence of the core findings and methods with the adapted framework and tested assumptions. In qualitative reviews (reviews synthesising results of qualitative studies), this information is beneficial for readers to recognise the underlying philosophical and paradigmatic stance of the authors of the included articles. For example, imagine the authors of an article, included in a review, used phenomenological inquiry for their research. In that case, the review authors and the readers of the review need to know what kind of (transcendental or hermeneutic) philosophical stance guided the inquiry. Review authors should, therefore, include the philosophical stance in their literature summary for the particular article. Second, information about frameworks and methods enables review authors and readers to judge the quality of the research, which allows for discerning the strengths and limitations of the article. For example, if authors of an included article intended to develop a new scale and test its psychometric properties. To achieve this aim, they used a convenience sample of 150 participants and performed exploratory (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) on the same sample. Such an approach would indicate a flawed methodology because EFA and CFA should not be conducted on the same sample. The review authors must include this information in their summary table. Omitting this information from a summary could lead to the inclusion of a flawed article in the review, thereby jeopardising the review’s rigour.
Tip 2: include strengths and limitations for each article
Critical appraisal of individual articles included in a review is crucial for increasing the rigour of the review. Despite using various templates for critical appraisal, authors often do not provide detailed information about each reviewed article’s strengths and limitations. Merely noting the quality score based on standardised critical appraisal templates is not adequate because the readers should be able to identify the reasons for assigning a weak or moderate rating. Many recent critical appraisal checklists (eg, Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool) discourage review authors from assigning a quality score and recommend noting the main strengths and limitations of included studies. It is also vital that methodological and conceptual limitations and strengths of the articles included in the review are provided because not all review articles include empirical research papers. Rather some review synthesises the theoretical aspects of articles. Providing information about conceptual limitations is also important for readers to judge the quality of foundations of the research. For example, if you included a mixed-methods study in the review, reporting the methodological and conceptual limitations about ‘integration’ is critical for evaluating the study’s strength. Suppose the authors only collected qualitative and quantitative data and did not state the intent and timing of integration. In that case, the strength of the study is weak. Integration only occurred at the levels of data collection. However, integration may not have occurred at the analysis, interpretation and reporting levels.
Tip 3: write conceptual contribution of each reviewed article
While reading and evaluating review papers, we have observed that many review authors only provide core results of the article included in a review and do not explain the conceptual contribution offered by the included article. We refer to conceptual contribution as a description of how the article’s key results contribute towards the development of potential codes, themes or subthemes, or emerging patterns that are reported as the review findings. For example, the authors of a review article noted that one of the research articles included in their review demonstrated the usefulness of case studies and reflective logs as strategies for fostering compassion in nursing students. The conceptual contribution of this research article could be that experiential learning is one way to teach compassion to nursing students, as supported by case studies and reflective logs. This conceptual contribution of the article should be mentioned in the literature summary table. Delineating each reviewed article’s conceptual contribution is particularly beneficial in qualitative reviews, mixed-methods reviews, and critical reviews that often focus on developing models and describing or explaining various phenomena. Figure 2 offers an example of a literature summary table. 4
Tabular literature summaries from a critical review. Source: Younas and Maddigan. 4
Tip 4: compose potential themes from each article during summary writing
While developing literature summary tables, many authors use themes or subthemes reported in the given articles as the key results of their own review. Such an approach prevents the review authors from understanding the article’s conceptual contribution, developing rigorous synthesis and drawing reasonable interpretations of results from an individual article. Ultimately, it affects the generation of novel review findings. For example, one of the articles about women’s healthcare-seeking behaviours in developing countries reported a theme ‘social-cultural determinants of health as precursors of delays’. Instead of using this theme as one of the review findings, the reviewers should read and interpret beyond the given description in an article, compare and contrast themes, findings from one article with findings and themes from another article to find similarities and differences and to understand and explain bigger picture for their readers. Therefore, while developing literature summary tables, think twice before using the predeveloped themes. Including your themes in the summary tables (see figure 1 ) demonstrates to the readers that a robust method of data extraction and synthesis has been followed.
Tip 5: create your personalised template for literature summaries
Often templates are available for data extraction and development of literature summary tables. The available templates may be in the form of a table, chart or a structured framework that extracts some essential information about every article. The commonly used information may include authors, purpose, methods, key results and quality scores. While extracting all relevant information is important, such templates should be tailored to meet the needs of the individuals’ review. For example, for a review about the effectiveness of healthcare interventions, a literature summary table must include information about the intervention, its type, content timing, duration, setting, effectiveness, negative consequences, and receivers and implementers’ experiences of its usage. Similarly, literature summary tables for articles included in a meta-synthesis must include information about the participants’ characteristics, research context and conceptual contribution of each reviewed article so as to help the reader make an informed decision about the usefulness or lack of usefulness of the individual article in the review and the whole review.
In conclusion, narrative or systematic reviews are almost always conducted as a part of any educational project (thesis or dissertation) or academic or clinical research. Literature reviews are the foundation of research on a given topic. Robust and high-quality reviews play an instrumental role in guiding research, practice and policymaking. However, the quality of reviews is also contingent on rigorous data extraction and synthesis, which require developing literature summaries. We have outlined five tips that could enhance the quality of the data extraction and synthesis process by developing useful literature summaries.
- Aromataris E ,
- Rasheed SP ,
Twitter @Ahtisham04, @parveenazamali
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Patient consent for publication Not required.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
- Open access
- Published: 23 April 2024
Designing feedback processes in the workplace-based learning of undergraduate health professions education: a scoping review
- Javiera Fuentes-Cimma 1 , 2 ,
- Dominique Sluijsmans 3 ,
- Arnoldo Riquelme 4 ,
- Ignacio Villagran ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3130-8326 1 ,
- Lorena Isbej ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4272-8484 2 , 5 ,
- María Teresa Olivares-Labbe 6 &
- Sylvia Heeneman 7
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 440 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
130 Accesses
Metrics details
Feedback processes are crucial for learning, guiding improvement, and enhancing performance. In workplace-based learning settings, diverse teaching and assessment activities are advocated to be designed and implemented, generating feedback that students use, with proper guidance, to close the gap between current and desired performance levels. Since productive feedback processes rely on observed information regarding a student's performance, it is imperative to establish structured feedback activities within undergraduate workplace-based learning settings. However, these settings are characterized by their unpredictable nature, which can either promote learning or present challenges in offering structured learning opportunities for students. This scoping review maps literature on how feedback processes are organised in undergraduate clinical workplace-based learning settings, providing insight into the design and use of feedback.
A scoping review was conducted. Studies were identified from seven databases and ten relevant journals in medical education. The screening process was performed independently in duplicate with the support of the StArt program. Data were organized in a data chart and analyzed using thematic analysis. The feedback loop with a sociocultural perspective was used as a theoretical framework.
The search yielded 4,877 papers, and 61 were included in the review. Two themes were identified in the qualitative analysis: (1) The organization of the feedback processes in workplace-based learning settings, and (2) Sociocultural factors influencing the organization of feedback processes. The literature describes multiple teaching and assessment activities that generate feedback information. Most papers described experiences and perceptions of diverse teaching and assessment feedback activities. Few studies described how feedback processes improve performance. Sociocultural factors such as establishing a feedback culture, enabling stable and trustworthy relationships, and enhancing student feedback agency are crucial for productive feedback processes.
Conclusions
This review identified concrete ideas regarding how feedback could be organized within the clinical workplace to promote feedback processes. The feedback encounter should be organized to allow follow-up of the feedback, i.e., working on required learning and performance goals at the next occasion. The educational programs should design feedback processes by appropriately planning subsequent tasks and activities. More insight is needed in designing a full-loop feedback process, in which specific attention is needed in effective feedforward practices.
Peer Review reports
The design of effective feedback processes in higher education has been important for educators and researchers and has prompted numerous publications discussing potential mechanisms, theoretical frameworks, and best practice examples over the past few decades. Initially, research on feedback primarily focused more on teachers and feedback delivery, and students were depicted as passive feedback recipients [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. The feedback conversation has recently evolved to a more dynamic emphasis on interaction, sense-making, outcomes in actions, and engagement with learners [ 2 ]. This shift aligns with utilizing the feedback process as a form of social interaction or dialogue to enhance performance [ 4 ]. Henderson et al. (2019) defined feedback processes as "where the learner makes sense of performance-relevant information to promote their learning." (p. 17). When a student grasps the information concerning their performance in connection to the desired learning outcome and subsequently takes suitable action, a feedback loop is closed so the process can be regarded as successful [ 5 , 6 ].
Hattie and Timperley (2007) proposed a comprehensive perspective on feedback, the so-called feedback loop, to answer three key questions: “Where am I going? “How am I going?” and “Where to next?” [ 7 ]. Each question represents a key dimension of the feedback loop. The first is the feed-up, which consists of setting learning goals and sharing clear objectives of learners' performance expectations. While the concept of the feed-up might not be consistently included in the literature, it is considered to be related to principles of effective feedback and goal setting within educational contexts [ 7 , 8 ]. Goal setting allows students to focus on tasks and learning, and teachers to have clear intended learning outcomes to enable the design of aligned activities and tasks in which feedback processes can be embedded [ 9 ]. Teachers can improve the feed-up dimension by proposing clear, challenging, but achievable goals [ 7 ]. The second dimension of the feedback loop focuses on feedback and aims to answer the second question by obtaining information about students' current performance. Different teaching and assessment activities can be used to obtain feedback information, and it can be provided by a teacher or tutor, a peer, oneself, a patient, or another coworker. The last dimension of the feedback loop is the feedforward, which is specifically associated with using feedback to improve performance or change behaviors [ 10 ]. Feedforward is crucial in closing the loop because it refers to those specific actions students must take to reduce the gap between current and desired performance [ 7 ].
From a sociocultural perspective, feedback processes involve a social practice consisting of intricate relationships within a learning context [ 11 ]. The main feature of this approach is that students learn from feedback only when the feedback encounter includes generating, making sense of, and acting upon the information given [ 11 ]. In the context of workplace-based learning (WBL), actionable feedback plays a crucial role in enabling learners to leverage specific feedback to enhance their performance, skills, and conceptual understandings. The WBL environment provides students with a valuable opportunity to gain hands-on experience in authentic clinical settings, in which students work more independently on real-world tasks, allowing them to develop and exhibit their competencies [ 3 ]. However, WBL settings are characterized by their unpredictable nature, which can either promote self-directed learning or present challenges in offering structured learning opportunities for students [ 12 ]. Consequently, designing purposive feedback opportunities within WBL settings is a significant challenge for clinical teachers and faculty.
In undergraduate clinical education, feedback opportunities are often constrained due to the emphasis on clinical work and the absence of dedicated time for teaching [ 13 ]. Students are expected to perform autonomously under supervision, ideally achieved by giving them space to practice progressively and providing continuous instances of constructive feedback [ 14 ]. However, the hierarchy often present in clinical settings places undergraduate students in a dependent position, below residents and specialists [ 15 ]. Undergraduate or junior students may have different approaches to receiving and using feedback. If their priority is meeting the minimum standards given pass-fail consequences and acting merely as feedback recipients, other incentives may be needed to engage with the feedback processes because they will need more learning support [ 16 , 17 ]. Adequate supervision and feedback have been recognized as vital educational support in encouraging students to adopt a constructive learning approach [ 18 ]. Given that productive feedback processes rely on observed information regarding a student's performance, it is imperative to establish structured teaching and learning feedback activities within undergraduate WBL settings.
Despite the extensive research on feedback, a significant proportion of published studies involve residents or postgraduate students [ 19 , 20 ]. Recent reviews focusing on feedback interventions within medical education have clearly distinguished between undergraduate medical students and residents or fellows [ 21 ]. To gain a comprehensive understanding of initiatives related to actionable feedback in the WBL environment for undergraduate health professions, a scoping review of the existing literature could provide insight into how feedback processes are designed in that context. Accordingly, the present scoping review aims to answer the following research question: How are the feedback processes designed in the undergraduate health professions' workplace-based learning environments?
A scoping review was conducted using the five-step methodological framework proposed by Arksey and O'Malley (2005) [ 22 ], intertwined with the PRISMA checklist extension for scoping reviews to provide reporting guidance for this specific type of knowledge synthesis [ 23 ]. Scoping reviews allow us to study the literature without restricting the methodological quality of the studies found, systematically and comprehensively map the literature, and identify gaps [ 24 ]. Furthermore, a scoping review was used because this topic is not suitable for a systematic review due to the varied approaches described and the large difference in the methodologies used [ 21 ].
Search strategy
With the collaboration of a medical librarian, the authors used the research question to guide the search strategy. An initial meeting was held to define keywords and search resources. The proposed search strategy was reviewed by the research team, and then the study selection was conducted in two steps:
An online database search included Medline/PubMed, Web of Science, CINAHL, Cochrane Library, Embase, ERIC, and PsycINFO.
A directed search of ten relevant journals in the health sciences education field (Academic Medicine, Medical Education, Advances in Health Sciences Education, Medical Teacher, Teaching and Learning in Medicine, Journal of Surgical Education, BMC Medical Education, Medical Education Online, Perspectives on Medical Education and The Clinical Teacher) was performed.
The research team conducted a pilot or initial search before the full search to identify if the topic was susceptible to a scoping review. The full search was conducted in November 2022. One team member (MO) identified the papers in the databases. JF searched in the selected journals. Authors included studies written in English due to feasibility issues, with no time span limitation. After eliminating duplicates, two research team members (JF and IV) independently reviewed all the titles and abstracts using the exclusion and inclusion criteria described in Table 2 and with the support of the screening application StArT [ 25 ]. A third team member (AR) reviewed the titles and abstracts when the first two disagreed. The reviewer team met again at a midpoint and final stage to discuss the challenges related to study selection. Articles included for full-text review were exported to Mendeley. JF independently screened all full-text papers, and AR verified 10% for inclusion. The authors did not analyze study quality or risk of bias during study selection, which is consistent with conducting a scoping review.
The analysis of the results incorporated a descriptive summary and a thematic analysis, which was carried out to clarify and give consistency to the results' reporting [ 22 , 24 , 26 ]. Quantitative data were analyzed to report the characteristics of the studies, populations, settings, methods, and outcomes. Qualitative data were labeled, coded, and categorized into themes by three team members (JF, SH, and DS). The feedback loop framework with a sociocultural perspective was used as the theoretical framework to analyze the results.
The keywords used for the search strategies were as follows:
Clinical clerkship; feedback; formative feedback; health professions; undergraduate medical education; workplace.
Definitions of the keywords used for the present review are available in Appendix 1 .
As an example, we included the search strategy that we used in the Medline/PubMed database when conducting the full search:
("Formative Feedback"[Mesh] OR feedback) AND ("Workplace"[Mesh] OR workplace OR "Clinical Clerkship"[Mesh] OR clerkship) AND (("Education, Medical, Undergraduate"[Mesh] OR undergraduate health profession*) OR (learner* medical education)).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The following inclusion and exclusion criteria were used (Table 1 ):
Data extraction
The research group developed a data-charting form to organize the information obtained from the studies. The process was iterative, as the data chart was continuously reviewed and improved as necessary. In addition, following Levac et al.'s recommendation (2010), the three members involved in the charting process (JF, LI, and IV) independently reviewed the first five selected studies to determine whether the data extraction was consistent with the objectives of this scoping review and to ensure consistency. Then, the team met using web-conferencing software (Zoom; CA, USA) to review the results and adjust any details in the chart. The same three members extracted data independently from all the selected studies, considering two members reviewing each paper [ 26 ]. A third team member was consulted if any conflict occurred when extracting data. The data chart identified demographic patterns and facilitated the data synthesis. To organize data, we used a shared Excel spreadsheet, considering the following headings: title, author(s), year of publication, journal/source, country/origin, aim of the study, research question (if any), population/sample size, participants, discipline, setting, methodology, study design, data collection, data analysis, intervention, outcomes, outcomes measure, key findings, and relation of findings to research question.
Additionally, all the included papers were uploaded to AtlasTi v19 to facilitate the qualitative analysis. Three team members (JF, SH, and DS) independently coded the first six papers to create a list of codes to ensure consistency and rigor. The group met several times to discuss and refine the list of codes. Then, one member of the team (JF) used the code list to code all the rest of the papers. Once all papers were coded, the team organized codes into descriptive themes aligned with the research question.
Preliminary results were shared with a number of stakeholders (six clinical teachers, ten students, six medical educators) to elicit their opinions as an opportunity to build on the evidence and offer a greater level of meaning, content expertise, and perspective to the preliminary findings [ 26 ]. No quality appraisal of the studies is considered for this scoping review, which aligns with the frameworks for guiding scoping reviews [ 27 ].
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
A database search resulted in 3,597 papers, and the directed search of the most relevant journals in the health sciences education field yielded 2,096 titles. An example of the results of one database is available in Appendix 2 . Of the titles obtained, 816 duplicates were eliminated, and the team reviewed the titles and abstracts of 4,877 papers. Of these, 120 were selected for full-text review. Finally, 61 papers were included in this scoping review (Fig. 1 ), as listed in Table 2 .
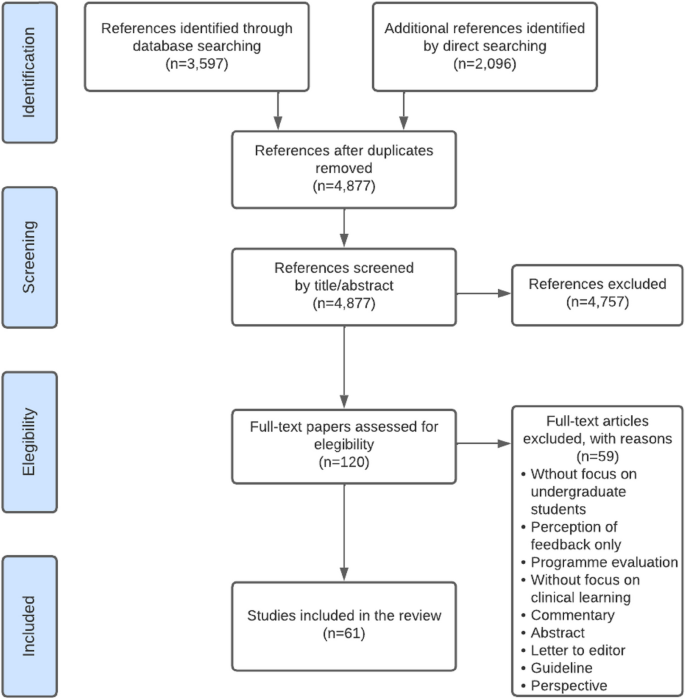
PRISMA flow diagram for included studies, incorporating records identified through the database and direct searching
The selected studies were published between 1986 and 2022, and seventy-five percent (46) were published during the last decade. Of all the articles included in this review, 13% (8) were literature reviews: one integrative review [ 28 ] and four scoping reviews [ 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 ]. Finally, fifty-three (87%) original or empirical papers were included (i.e., studies that answered a research question or achieved a research purpose through qualitative or quantitative methodologies) [ 15 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 , 79 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 ].
Table 2 summarizes the papers included in the present scoping review, and Table 3 describes the characteristics of the included studies.
The thematic analysis resulted in two themes: (1) the organization of feedback processes in WBL settings, and (2) sociocultural factors influencing the organization of feedback processes. Table 4 gives a summary of the themes and subthemes.
Organization of feedback processes in WBL settings.
Setting learning goals (i.e., feed-up dimension).
Feedback that focuses on students' learning needs and is based on known performance standards enhances student response and setting learning goals [ 30 ]. Discussing goals and agreements before starting clinical practice enhances students' feedback-seeking behavior [ 39 ] and responsiveness to feedback [ 83 ]. Farrell et al. (2017) found that teacher-learner co-constructed learning goals enhance feedback interactions and help establish educational alliances, improving the learning experience [ 50 ]. However, Kiger (2020) found that sharing individualized learning plans with teachers aligned feedback with learning goals but did not improve students' perceived use of feedback [ 64 ]
Two papers of this set pointed out the importance of goal-oriented feedback, a dynamic process that depends on discussion of goal setting between teachers and students [ 50 ] and influences how individuals experience, approach, and respond to upcoming learning activities [ 34 ]. Goal-oriented feedback should be embedded in the learning experience of the clinical workplace, as it can enhance students' engagement in safe feedback dialogues [ 50 ]. Ideally, each feedback encounter in the WBL context should conclude, in addition to setting a plan of action to achieve the desired goal, with a reflection on the next goal [ 50 ].
Feedback strategies within the WBL environment. (i.e., feedback dimension)
In undergraduate WBL environments, there are several tasks and feedback opportunities organized in the undergraduate clinical workplace that can enable feedback processes:
Questions from clinical teachers to students are a feedback strategy [ 74 ]. There are different types of questions that the teacher can use, either to clarify concepts, to reach the correct answer, or to facilitate self-correction [ 74 ]. Usually, questions can be used in conjunction with other communication strategies, such as pauses, which enable self-correction by the student [ 74 ]. Students can also ask questions to obtain feedback on their performance [ 54 ]. However, question-and-answer as a feedback strategy usually provides information on either correct or incorrect answers and fewer suggestions for improvement, rendering it less constructive as a feedback strategy [ 82 ].
Direct observation of performance by default is needed to be able to provide information to be used as input in the feedback process [ 33 , 46 , 49 , 86 ]. In the process of observation, teachers can include clarification of objectives (i.e., feed-up dimension) and suggestions for an action plan (i.e., feedforward) [ 50 ]. Accordingly, Schopper et al. (2016) showed that students valued being observed while interviewing patients, as they received feedback that helped them become more efficient and effective as interviewers and communicators [ 33 ]. Moreover, it is widely described that direct observation improves feedback credibility [ 33 , 40 , 84 ]. Ideally, observation should be deliberate [ 33 , 83 ], informal or spontaneous [ 33 ], conducted by a (clinical) expert [ 46 , 86 ], provided immediately after the observation, and clinical teacher if possible, should schedule or be alert on follow-up observations to promote closing the gap between current and desired performance [ 46 ].
Workplace-based assessments (WBAs), by definition, entail direct observation of performance during authentic task demonstration [ 39 , 46 , 56 , 87 ]. WBAs can significantly impact behavioral change in medical students [ 55 ]. Organizing and designing formative WBAs and embedding these in a feedback dialogue is essential for effective learning [ 31 ].
Summative organization of WBAs is a well described barrier for feedback uptake in the clinical workplace [ 35 , 46 ]. If feedback is perceived as summative, or organized as a pass-fail decision, students may be less inclined to use the feedback for future learning [ 52 ]. According to Schopper et al. (2016), using a scale within a WBA makes students shift their focus during the clinical interaction and see it as an assessment with consequences [ 33 ]. Harrison et al. (2016) pointed out that an environment that only contains assessments with a summative purpose will not lead to a culture of learning and improving performance [ 56 ]. The recommendation is to separate the formative and summative WBAs, as feedback in summative instances is often not recognized as a learning opportunity or an instance to seek feedback [ 54 ]. In terms of the design, an organizational format is needed to clarify to students how formative assessments can promote learning from feedback [ 56 ]. Harrison et al. (2016) identified that enabling students to have more control over their assessments, designing authentic assessments, and facilitating long-term mentoring could improve receptivity to formative assessment feedback [ 56 ].
Multiple WBA instruments and systems are reported in the literature. Sox et al. (2014) used a detailed evaluation form to help students improve their clinical case presentation skills. They found that feedback on oral presentations provided by supervisors using a detailed evaluation form improved clerkship students’ oral presentation skills [ 78 ]. Daelmans et al. (2006) suggested that a formal in-training assessment programme composed by 19 assessments that provided structured feedback, could promote observation and verbal feedback opportunities through frequent assessments [ 43 ]. However, in this setting, limited student-staff interactions still hindered feedback follow-up [ 43 ]. Designing frequent WBA improves feedback credibility [ 28 ]. Long et al. (2021) emphasized that students' responsiveness to assessment feedback hinges on its perceived credibility, underlining the importance of credibility for students to effectively engage and improve their performance [ 31 ].
The mini-CEX is one of the most widely described WBA instruments in the literature. Students perceive that the mini-CEX allows them to be observed and encourages the development of interviewing skills [ 33 ]. The mini-CEX can provide feedback that improves students' clinical skills [ 58 , 60 ], as it incorporates a structure for discussing the student's strengths and weaknesses and the design of a written action plan [ 39 , 80 ]. When mini-CEXs are incorporated as part of a system of WBA, such as programmatic assessment, students feel confident in seeking feedback after observation, and being systematic allows for follow-up [ 39 ]. Students suggested separating grading from observation and using the mini-CEX in more informal situations [ 33 ].
Clinical encounter cards allow students to receive weekly feedback and make them request more feedback as the clerkship progresses [ 65 ]. Moreover, encounter cards stimulate that feedback is given by supervisors, and students are more satisfied with the feedback process [ 72 ]. With encounter card feedback, students are responsible for asking a supervisor for feedback before a clinical encounter, and supervisors give students written and verbal comments about their performance after the encounter [ 42 , 72 ]. Encounter cards enhance the use of feedback and add approximately one minute to the length of the clinical encounter, so they are well accepted by students and supervisors [ 72 ]. Bennett (2006) identified that Instant Feedback Cards (IFC) facilitated mid-rotation feedback [ 38 ]. Feedback encounter card comments must be discussed between students and supervisors; otherwise, students may perceive it as impersonal, static, formulaic, and incomplete [ 59 ].
Self-assessments can change students' feedback orientation, transforming them into coproducers of learning [ 68 ]. Self-assessments promote the feedback process [ 68 ]. Some articles emphasize the importance of organizing self-assessments before receiving feedback from supervisors, for example, discussing their appraisal with the supervisor [ 46 , 52 ]. In designing a feedback encounter, starting with a self-assessment as feed-up, discussing with the supervisor, and identifying areas for improvement is recommended, as part of the feedback dialogue [ 68 ].
Peer feedback as an organized activity allows students to develop strategies to observe and give feedback to other peers [ 61 ]. Students can act as the feedback provider or receiver, fostering understanding of critical comments and promoting evaluative judgment for their clinical practice [ 61 ]. Within clerkships, enabling the sharing of feedback information among peers allows for a better understanding and acceptance of feedback [ 52 ]. However, students can find it challenging to take on the peer assessor/feedback provider role, as they prefer to avoid social conflicts [ 28 , 61 ]. Moreover, it has been described that they do not trust the judgment of their peers because they are not experts, although they know the procedures, tasks, and steps well and empathize with their peer status in the learning process [ 61 ].
Bedside-teaching encounters (BTEs) provide timely feedback and are an opportunity for verbal feedback during performance [ 74 ]. Rizan et al. (2014) explored timely feedback delivered within BTEs and determined that it promotes interaction that constructively enhances learner development through various corrective strategies (e.g., question and answers, pauses, etc.). However, if the feedback given during the BTEs was general, unspecific, or open-ended, it could go unnoticed [ 74 ]. Torre et al. (2005) investigated which integrated feedback activities and clinical tasks occurred on clerkship rotations and assessed students' perceived quality in each teaching encounter [ 81 ]. The feedback activities reported were feedback on written clinical history, physical examination, differential diagnosis, oral case presentation, a daily progress note, and bedside feedback. Students considered all these feedback activities high-quality learning opportunities, but they were more likely to receive feedback when teaching was at the bedside than at other teaching locations [ 81 ].
Case presentations are an opportunity for feedback within WBL contexts [ 67 , 73 ]. However, both students and supervisors struggled to identify them as feedback moments, and they often dismissed questions and clarifications around case presentations as feedback [ 73 ]. Joshi (2017) identified case presentations as a way for students to ask for informal or spontaneous supervisor feedback [ 63 ].
Organization of follow-up feedback and action plans (i.e., feedforward dimension).
Feedback that generates use and response from students is characterized by two-way communication and embedded in a dialogue [ 30 ]. Feedback must be future-focused [ 29 ], and a feedback encounter should be followed by planning the next observation [ 46 , 87 ]. Follow-up feedback could be organized as a future self-assessment, reflective practice by the student, and/or a discussion with the supervisor or coach [ 68 ]. The literature describes that a lack of student interaction with teachers makes follow-up difficult [ 43 ]. According to Haffling et al. (2011), follow-up feedback sessions improve students' satisfaction with feedback compared to students who do not have follow-up sessions. In addition, these same authors reported that a second follow-up session allows verification of improved performances or confirmation that the skill was acquired [ 55 ].
Although feedback encounter forms are a recognized way of obtaining information about performance (i.e., feedback dimension), the literature does not provide many clear examples of how they may impact the feedforward phase. For example, Joshi et al. (2016) consider a feedback form with four fields (i.e., what did you do well, advise the student on what could be done to improve performance, indicate the level of proficiency, and personal details of the tutor). In this case, the supervisor highlighted what the student could improve but not how, which is the missing phase of the co-constructed action plan [ 63 ]. Whichever WBA instrument is used in clerkships to provide feedback, it should include a "next steps" box [ 44 ], and it is recommended to organize a long-term use of the WBA instrument so that those involved get used to it and improve interaction and feedback uptake [ 55 ]. RIME-based feedback (Reporting, Interpreting, Managing, Educating) is considered an interesting example, as it is perceived as helpful to students in knowing what they need to improve in their performance [ 44 ]. Hochberg (2017) implemented formative mid-clerkship assessments to enhance face-to-face feedback conversations and co-create an improvement plan [ 59 ]. Apps for structuring and storing feedback improve the amount of verbal and written feedback. In the study of Joshi et al. (2016), a reasonable proportion of students (64%) perceived that these app tools help them improve their performance during rotations [ 63 ].
Several studies indicate that an action plan as part of the follow-up feedback is essential for performance improvement and learning [ 46 , 55 , 60 ]. An action plan corresponds to an agreed-upon strategy for improving, confirming, or correcting performance. Bing-You et al. (2017) determined that only 12% of the articles included in their scoping review incorporated an action plan for learners [ 32 ]. Holmboe et al. (2004) reported that only 11% of the feedback sessions following a mini-CEX included an action plan [ 60 ]. Suhoyo et al. (2017) also reported that only 55% of mini-CEX encounters contained an action plan [ 80 ]. Other authors reported that action plans are not commonly offered during feedback encounters [ 77 ]. Sokol-Hessner et al. (2010) implemented feedback card comments with a space to provide written feedback and a specific action plan. In their results, 96% contained positive comments, and only 5% contained constructive comments [ 77 ]. In summary, although the recommendation is to include a “next step” box in the feedback instruments, evidence shows these items are not often used for constructive comments or action plans.
Sociocultural factors influencing the organization of feedback processes.
Multiple sociocultural factors influence interaction in feedback encounters, promoting or hampering the productivity of the feedback processes.
Clinical learning culture
Context impacts feedback processes [ 30 , 82 ], and there are barriers to incorporating actionable feedback in the clinical learning context. The clinical learning culture is partly determined by the clinical context, which can be unpredictable [ 29 , 46 , 68 ], as the available patients determine learning opportunities. Supervisors are occupied by a high workload, which results in limited time or priority for teaching [ 35 , 46 , 48 , 55 , 68 , 83 ], hindering students’ feedback-seeking behavior [ 54 ], and creating a challenge for the balance between patient care and student mentoring [ 35 ].
Clinical workplace culture does not always purposefully prioritize instances for feedback processes [ 83 , 84 ]. This often leads to limited direct observation [ 55 , 68 ] and the provision of poorly informed feedback. It is also evident that this affects trust between clinical teachers and students [ 52 ]. Supervisors consider feedback a low priority in clinical contexts [ 35 ] due to low compensation and lack of protected time [ 83 ]. In particular, lack of time appears to be the most significant and well-known barrier to frequent observation and workplace feedback [ 35 , 43 , 48 , 62 , 67 , 83 ].
The clinical environment is hierarchical [ 68 , 80 ] and can make students not consider themselves part of the team and feel like a burden to their supervisor [ 68 ]. This hierarchical learning environment can lead to unidirectional feedback, limit dialogue during feedback processes, and hinder the seeking, uptake, and use of feedback [ 67 , 68 ]. In a learning culture where feedback is not supported, learners are less likely to want to seek it and feel motivated and engaged in their learning [ 83 ]. Furthermore, it has been identified that clinical supervisors lack the motivation to teach [ 48 ] and the intention to observe or reobserve performance [ 86 ].
In summary, the clinical context and WBL culture do not fully use the potential of a feedback process aimed at closing learning gaps. However, concrete actions shown in the literature can be taken to improve the effectiveness of feedback by organizing the learning context. For example, McGinness et al. (2022) identified that students felt more receptive to feedback when working in a safe, nonjudgmental environment [ 67 ]. Moreover, supervisors and trainees identified the learning culture as key to establishing an open feedback dialogue [ 73 ]. Students who perceive culture as supportive and formative can feel more comfortable performing tasks and more willing to receive feedback [ 73 ].
Relationships
There is a consensus in the literature that trusting and long-term relationships improve the chances of actionable feedback. However, relationships between supervisors and students in the clinical workplace are often brief and not organized as more longitudinally [ 68 , 83 ], leaving little time to establish a trustful relationship [ 68 ]. Supervisors change continuously, resulting in short interactions that limit the creation of lasting relationships over time [ 50 , 68 , 83 ]. In some contexts, it is common for a student to have several supervisors who have their own standards in the observation of performance [ 46 , 56 , 68 , 83 ]. A lack of stable relationships results in students having little engagement in feedback [ 68 ]. Furthermore, in case of summative assessment programmes, the dual role of supervisors (i.e., assessing and giving feedback) makes feedback interactions perceived as summative and can complicate the relationship [ 83 ].
Repeatedly, the articles considered in this review describe that long-term and stable relationships enable the development of trust and respect [ 35 , 62 ] and foster feedback-seeking behavior [ 35 , 67 ] and feedback-giver behavior [ 39 ]. Moreover, constructive and positive relationships enhance students´ use of and response to feedback [ 30 ]. For example, Longitudinal Integrated Clerkships (LICs) promote stable relationships, thus enhancing the impact of feedback [ 83 ]. In a long-term trusting relationship, feedback can be straightforward and credible [ 87 ], there are more opportunities for student observation, and the likelihood of follow-up and actionable feedback improves [ 83 ]. Johnson et al. (2020) pointed out that within a clinical teacher-student relationship, the focus must be on establishing psychological safety; thus, the feedback conversations might be transformed [ 62 ].
Stable relationships enhance feedback dialogues, which offer an opportunity to co-construct learning and propose and negotiate aspects of the design of learning strategies [ 62 ].
Students as active agents in the feedback processes
The feedback response learners generate depends on the type of feedback information they receive, how credible the source of feedback information is, the relationship between the receiver and the giver, and the relevance of the information delivered [ 49 ]. Garino (2020) noted that students who are most successful in using feedback are those who do not take criticism personally, who understand what they need to improve and know they can do so, who value and feel meaning in criticism, are not surprised to receive it, and who are motivated to seek new feedback and use effective learning strategies [ 52 ]. Successful users of feedback ask others for help, are intentional about their learning, know what resources to use and when to use them, listen to and understand a message, value advice, and use effective learning strategies. They regulate their emotions, find meaning in the message, and are willing to change [ 52 ].
Student self-efficacy influences the understanding and use of feedback in the clinical workplace. McGinness et al. (2022) described various positive examples of self-efficacy regarding feedback processes: planning feedback meetings with teachers, fostering good relationships with the clinical team, demonstrating interest in assigned tasks, persisting in seeking feedback despite the patient workload, and taking advantage of opportunities for feedback, e.g., case presentations [ 67 ].
When students are encouraged to seek feedback aligned with their own learning objectives, they promote feedback information specific to what they want to learn and improve and enhance the use of feedback [ 53 ]. McGinness et al. (2022) identified that the perceived relevance of feedback information influenced the use of feedback because students were more likely to ask for feedback if they perceived that the information was useful to them. For example, if students feel part of the clinical team and participate in patient care, they are more likely to seek feedback [ 17 ].
Learning-oriented students aim to seek feedback to achieve clinical competence at the expected level [ 75 ]; they focus on improving their knowledge and skills and on professional development [ 17 ]. Performance-oriented students aim not to fail and to avoid negative feedback [ 17 , 75 ].
For effective feedback processes, including feed-up, feedback, and feedforward, the student must be feedback-oriented, i.e., active, seeking, listening to, interpreting, and acting on feedback [ 68 ]. The literature shows that feedback-oriented students are coproducers of learning [ 68 ] and are more involved in the feedback process [ 51 ]. Additionally, students who are metacognitively aware of their learning process are more likely to use feedback to reduce gaps in learning and performance [ 52 ]. For this, students must recognize feedback when it occurs and understand it when they receive it. Thus, it is important to organize training and promote feedback literacy so that students understand what feedback is, act on it, and improve the quality of feedback and their learning plans [ 68 ].
Table 5 summarizes those feedback tasks, activities, and key features of organizational aspects that enable each phase of the feedback loop based on the literature review.
The present scoping review identified 61 papers that mapped the literature on feedback processes in the WBL environments of undergraduate health professions. This review explored how feedback processes are organized in these learning contexts using the feedback loop framework. Given the specific characteristics of feedback processes in undergraduate clinical learning, three main findings were identified on how feedback processes are being conducted in the clinical environment and how these processes could be organized to support feedback processes.
First, the literature lacks a balance between the three dimensions of the feedback loop. In this regard, most of the articles in this review focused on reporting experiences or strategies for delivering feedback information (i.e., feedback dimension). Credible and objective feedback information is based on direct observation [ 46 ] and occurs within an interaction or a dialogue [ 62 , 88 ]. However, only having credible and objective information does not ensure that it will be considered, understood, used, and put into practice by the student [ 89 ].
Feedback-supporting actions aligned with goals and priorities facilitate effective feedback processes [ 89 ] because goal-oriented feedback focuses on students' learning needs [ 7 ]. In contrast, this review showed that only a minority of the studies highlighted the importance of aligning learning objectives and feedback (i.e., the feed-up dimension). To overcome this, supervisors and students must establish goals and agreements before starting clinical practice, as it allows students to measure themselves on a defined basis [ 90 , 91 ] and enhances students' feedback-seeking behavior [ 39 , 92 ] and responsiveness to feedback [ 83 ]. In addition, learning goals should be shared, and co-constructed, through a dialogue [ 50 , 88 , 90 , 92 ]. In fact, relationship-based feedback models emphasize setting shared goals and plans as part of the feedback process [ 68 ].
Many of the studies acknowledge the importance of establishing an action plan and promoting the use of feedback (i.e., feedforward). However, there is yet limited insight on how to best implement strategies that support the use of action plans, improve performance and close learning gaps. In this regard, it is described that delivering feedback without perceiving changes, results in no effect or impact on learning [ 88 ]. To determine if a feedback loop is closed, observing a change in the student's response is necessary. In other words, feedback does not work without repeating the same task [ 68 ], so teachers need to observe subsequent tasks to notice changes [ 88 ]. While feedforward is fundamental to long-term performance, it is shown that more research is needed to determine effective actions to be implemented in the WBL environment to close feedback loops.
Second, there is a need for more knowledge about designing feedback activities in the WBL environment that will generate constructive feedback for learning. WBA is the most frequently reported feedback activity in clinical workplace contexts [ 39 , 46 , 56 , 87 ]. Despite the efforts of some authors to use WBAs as a formative assessment and feedback opportunity, in several studies, a summative component of the WBA was presented as a barrier to actionable feedback [ 33 , 56 ]. Students suggest separating grading from observation and using, for example, the mini-CEX in informal situations [ 33 ]. Several authors also recommend disconnecting the summative components of WBAs to avoid generating emotions that can limit the uptake and use of feedback [ 28 , 93 ]. Other literature recommends purposefully designing a system of assessment using low-stakes data points for feedback and learning. Accordingly, programmatic assessment is a framework that combines both the learning and the decision-making function of assessment [ 94 , 95 ]. Programmatic assessment is a practical approach for implementing low-stakes as a continuum, giving opportunities to close the gap between current and desired performance and having the student as an active agent [ 96 ]. This approach enables the incorporation of low-stakes data points that target student learning [ 93 ] and provide performance-relevant information (i.e., meaningful feedback) based on direct observations during authentic professional activities [ 46 ]. Using low-stakes data points, learners make sense of information about their performance and use it to enhance the quality of their work or performance [ 96 , 97 , 98 ]. Implementing multiple instances of feedback is more effective than providing it once because it promotes closing feedback loops by giving the student opportunities to understand the feedback, make changes, and see if those changes were effective [ 89 ].
Third, the support provided by the teacher is fundamental and should be built into a reliable and long-term relationship, where the teacher must take the role of coach rather than assessor, and students should develop feedback agency and be active in seeking and using feedback to improve performance. Although it is recognized that institutional efforts over the past decades have focused on training teachers to deliver feedback, clinical supervisors' lack of teaching skills is still identified as a barrier to workplace feedback [ 99 ]. In particular, research indicates that clinical teachers lack the skills to transform the information obtained from an observation into constructive feedback [ 100 ]. Students are more likely to use feedback if they consider it credible and constructive [ 93 ] and based on stable relationships [ 93 , 99 , 101 ]. In trusting relationships, feedback can be straightforward and credible, and the likelihood of follow-up and actionable feedback improves [ 83 , 88 ]. Coaching strategies can be enhanced by teachers building an educational alliance that allows for trustworthy relationships or having supervisors with an exclusive coaching role [ 14 , 93 , 102 ].
Last, from a sociocultural perspective, individuals are the main actors in the learning process. Therefore, feedback impacts learning only if students engage and interact with it [ 11 ]. Thus, feedback design and student agency appear to be the main features of effective feedback processes. Accordingly, the present review identified that feedback design is a key feature for effective learning in complex environments such as WBL. Feedback in the workplace must ideally be organized and implemented to align learning outcomes, learning activities, and assessments, allowing learners to learn, practice, and close feedback loops [ 88 ]. To guide students toward performances that reflect long-term learning, an intensive formative learning phase is needed, in which multiple feedback processes are included that shape students´ further learning [ 103 ]. This design would promote student uptake of feedback for subsequent performance [ 1 ].
Strengths and limitations
The strengths of this study are (1) the use of an established framework, the Arksey and O'Malley's framework [ 22 ]. We included the step of socializing the results with stakeholders, which allowed the team to better understand the results from another perspective and offer a realistic look. (2) Using the feedback loop as a theoretical framework strengthened the results and gave a more thorough explanation of the literature regarding feedback processes in the WBL context. (3) our team was diverse and included researchers from different disciplines as well as a librarian.
The present scoping review has several limitations. Although we adhered to the recommended protocols and methodologies, some relevant papers may have been omitted. The research team decided to select original studies and reviews of the literature for the present scoping review. This caused some articles, such as guidelines, perspectives, and narrative papers, to be excluded from the current study.
One of the inclusion criteria was a focus on undergraduate students. However, some papers that incorporated undergraduate and postgraduate participants were included, as these supported the results of this review. Most articles involved medical students. Although the authors did not limit the search to medicine, maybe some articles involving students from other health disciplines needed to be included, considering the search in other databases or journals.
The results give insight in how feedback could be organized within the clinical workplace to promote feedback processes. On a small scale, i.e., in the feedback encounter between a supervisor and a learner, feedback should be organized to allow for follow-up feedback, thus working on required learning and performance goals. On a larger level, i.e., in the clerkship programme or a placement rotation, feedback should be organized through appropriate planning of subsequent tasks and activities.
More insight is needed in designing a closed loop feedback process, in which specific attention is needed in effective feedforward practices. The feedback that stimulates further action and learning requires a safe and trustful work and learning environment. Understanding the relationship between an individual and his or her environment is a challenge for determining the impact of feedback and must be further investigated within clinical WBL environments. Aligning the dimensions of feed-up, feedback and feedforward includes careful attention to teachers’ and students’ feedback literacy to assure that students can act on feedback in a constructive way. In this line, how to develop students' feedback agency within these learning environments needs further research.
Boud D, Molloy E. Rethinking models of feedback for learning: The challenge of design. Assess Eval High Educ. 2013;38:698–712.
Article Google Scholar
Henderson M, Ajjawi R, Boud D, Molloy E. Identifying feedback that has impact. In: The Impact of Feedback in Higher Education. Springer International Publishing: Cham; 2019. p. 15–34.
Chapter Google Scholar
Winstone N, Carless D. Designing effective feedback processes in higher education: A learning-focused approach. 1st ed. New York: Routledge; 2020.
Google Scholar
Ajjawi R, Boud D. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education Researching feedback dialogue: an interactional analysis approach. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2015.1102863 .
Carless D. Feedback loops and the longer-term: towards feedback spirals. Assess Eval High Educ. 2019;44:705–14.
Sadler DR. Formative assessment and the design of instructional systems. Instr Sci. 1989;18:119–44.
Hattie J, Timperley H. The Power of Feedback The Meaning of Feedback. Rev Educ Res. 2007;77:81–112.
Zarrinabadi N, Rezazadeh M. Why only feedback? Including feed up and feed forward improves nonlinguistic aspects of L2 writing. Language Teaching Research. 2023;27(3):575–92.
Fisher D, Frey N. Feed up, back, forward. Educ Leadersh. 2009;67:20–5.
Reimann A, Sadler I, Sambell K. What’s in a word? Practices associated with ‘feedforward’ in higher education. Assessment evaluation in higher education. 2019;44:1279–90.
Esterhazy R. Re-conceptualizing Feedback Through a Sociocultural Lens. In: Henderson M, Ajjawi R, Boud D, Molloy E, editors. The Impact of Feedback in Higher Education. Cham: Palgrave Macmillan; 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-25112-3_5 .
Bransen D, Govaerts MJB, Sluijsmans DMA, Driessen EW. Beyond the self: The role of co-regulation in medical students’ self-regulated learning. Med Educ. 2020;54:234–41.
Ramani S, Könings KD, Ginsburg S, Van Der Vleuten CP. Feedback Redefined: Principles and Practice. J Gen Intern Med. 2019;34:744–53.
Atkinson A, Watling CJ, Brand PL. Feedback and coaching. Eur J Pediatr. 2022;181(2):441–6.
Suhoyo Y, Schonrock-Adema J, Emilia O, Kuks JBM, Cohen-Schotanus JA. Clinical workplace learning: perceived learning value of individual and group feedback in a collectivistic culture. BMC Med Educ. 2018;18:79.
Bowen L, Marshall M, Murdoch-Eaton D. Medical Student Perceptions of Feedback and Feedback Behaviors Within the Context of the “Educational Alliance.” Acad Med. 2017;92:1303–12.
Bok HGJ, Teunissen PW, Spruijt A, Fokkema JPI, van Beukelen P, Jaarsma DADC, et al. Clarifying students’ feedback-seeking behaviour in clinical clerkships. Med Educ. 2013;47:282–91.
Al-Kadri HM, Al-Kadi MT, Van Der Vleuten CPM. Workplace-based assessment and students’ approaches to learning: A qualitative inquiry. Med Teach. 2013;35(SUPPL):1.
Dennis AA, Foy MJ, Monrouxe LV, Rees CE. Exploring trainer and trainee emotional talk in narratives about workplace-based feedback processes. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2018;23:75–93.
Watling C, LaDonna KA, Lingard L, Voyer S, Hatala R. ‘Sometimes the work just needs to be done’: socio-cultural influences on direct observation in medical training. Med Educ. 2016;50:1054–64.
Bing-You R, Hayes V, Varaklis K, Trowbridge R, Kemp H, McKelvy D. Feedback for Learners in Medical Education: What is Known? A Scoping Review Academic Medicine. 2017;92:1346–54.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8:19–32.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169:467–73.
Colquhoun HL, Levac D, O’brien KK, Straus S, Tricco AC, Perrier L, et al. Scoping reviews: time for clarity in definition methods and reporting. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014;67:1291–4.
StArt - State of Art through Systematic Review. 2013.
Levac D, Colquhoun H, O’Brien KK. Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implementation Science. 2010;5:1–9.
Peters MDJ, BPharm CMGHK, Parker PMD, Soares CB. Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2015;13:141–6.
Bing-You R, Varaklis K, Hayes V, Trowbridge R, Kemp H, McKelvy D, et al. The Feedback Tango: An Integrative Review and Analysis of the Content of the Teacher-Learner Feedback Exchange. Acad Med. 2018;93:657–63.
Ossenberg C, Henderson A, Mitchell M. What attributes guide best practice for effective feedback? A scoping review. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2019;24:383–401.
Spooner M, Duane C, Uygur J, Smyth E, Marron B, Murphy PJ, et al. Self -regulatory learning theory as a lens on how undergraduate and postgraduate learners respond to feedback: A BEME scoping review: BEME Guide No. 66. Med Teach. 2022;44:3–18.
Long S, Rodriguez C, St-Onge C, Tellier PP, Torabi N, Young M. Factors affecting perceived credibility of assessment in medical education: A scoping review. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2022;27:229–62.
Bing-You R, Hayes V, Varaklis K, Trowbridge R, Kemp H, McKelvy D. Feedback for Learners in Medical Education: What is Known? A Scoping Review: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2017.
Schopper H, Rosenbaum M, Axelson R. “I wish someone watched me interview:” medical student insight into observation and feedback as a method for teaching communication skills during the clinical years. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:286.
Crommelinck M, Anseel F. Understanding and encouraging feedback-seeking behaviour: a literature review. Med Educ. 2013;47:232–41.
Adamson E, Kinga L, Foy L, McLeodb M, Traynor J, Watson W, et al. Feedback in clinical practice: Enhancing the students’ experience through action research. Nurse Educ Pract. 2018;31:48–53.
Al-Mously N, Nabil NM, Al-Babtain SA, et al. Undergraduate medical students’ perceptions on the quality of feedback received during clinical rotations. Med Teach. 2014;36(Supplement 1):S17-23.
Bates J, Konkin J, Suddards C, Dobson S, Pratt D. Student perceptions of assessment and feedback in longitudinal integrated clerkships. Med Educ. 2013;47:362–74.
Bennett AJ, Goldenhar LM, Stanford K. Utilization of a Formative Evaluation Card in a Psychiatry Clerkship. Acad Psychiatry. 2006;30:319–24.
Bok HG, Jaarsma DA, Spruijt A, Van Beukelen P, Van Der Vleuten CP, Teunissen PW, et al. Feedback-giving behaviour in performance evaluations during clinical clerkships. Med Teach. 2016;38:88–95.
Bok HG, Teunissen PW, Spruijt A, Fokkema JP, van Beukelen P, Jaarsma DA, et al. Clarifying students’ feedback-seeking behaviour in clinical clerkships. Med Educ. 2013;47:282–91.
Calleja P, Harvey T, Fox A, Carmichael M, et al. Feedback and clinical practice improvement: A tool to assist workplace supervisors and students. Nurse Educ Pract. 2016;17:167–73.
Carey EG, Wu C, Hur ES, Hasday SJ, Rosculet NP, Kemp MT, et al. Evaluation of Feedback Systems for the Third-Year Surgical Clerkship. J Surg Educ. 2017;74:787–93.
Daelmans HE, Overmeer RM, Van der Hem-Stokroos HH, Scherpbier AJ, Stehouwer CD, van der Vleuten CP. In-training assessment: qualitative study of effects on supervision and feedback in an undergraduate clinical rotation. Medical education. 2006;40(1):51–8.
DeWitt D, Carline J, Paauw D, Pangaro L. Pilot study of a ’RIME’-based tool for giving feedback in a multi-specialty longitudinal clerkship. Med Educ. 2008;42:1205–9.
Dolan BM, O’Brien CL, Green MM. Including Entrustment Language in an Assessment Form May Improve Constructive Feedback for Student Clinical Skills. Med Sci Educ. 2017;27:461–4.
Duijn CC, Welink LS, Mandoki M, Ten Cate OT, Kremer WD, Bok HG. Am I ready for it? Students’ perceptions of meaningful feedback on entrustable professional activities. Perspectives on medical education. 2017;6:256–64.
Elnicki DM, Zalenski D. Integrating medical students’ goals, self-assessment and preceptor feedback in an ambulatory clerkship. Teach Learn Med. 2013;25:285–91.
Embo MP, Driessen EW, Valcke M, Van der Vleuten CP. Assessment and feedback to facilitate self-directed learning in clinical practice of Midwifery students. Medical teacher. 2010;32(7):e263-9.
Eva KW, Armson H, Holmboe E, Lockyer J, Loney E, Mann K, et al. Factors influencing responsiveness to feedback: On the interplay between fear, confidence, and reasoning processes. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2012;17:15–26.
Farrell L, Bourgeois-Law G, Ajjawi R, Regehr G. An autoethnographic exploration of the use of goal oriented feedback to enhance brief clinical teaching encounters. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2017;22:91–104.
Fernando N, Cleland J, McKenzie H, Cassar K. Identifying the factors that determine feedback given to undergraduate medical students following formative mini-CEX assessments. Med Educ. 2008;42:89–95.
Garino A. Ready, willing and able: a model to explain successful use of feedback. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2020;25:337–61.
Garner MS, Gusberg RJ, Kim AW. The positive effect of immediate feedback on medical student education during the surgical clerkship. J Surg Educ. 2014;71:391–7.
Bing-You R, Hayes V, Palka T, Ford M, Trowbridge R. The Art (and Artifice) of Seeking Feedback: Clerkship Students’ Approaches to Asking for Feedback. Acad Med. 2018;93:1218–26.
Haffling AC, Beckman A, Edgren G. Structured feedback to undergraduate medical students: 3 years’ experience of an assessment tool. Medical teacher. 2011;33(7):e349-57.
Harrison CJ, Könings KD, Dannefer EF, Schuwirth LWTT, Wass V, van der Vleuten CPMM. Factors influencing students’ receptivity to formative feedback emerging from different assessment cultures. Perspect Med Educ. 2016;5:276–84.
Harrison CJ, Könings KD, Schuwirth LW, Wass V, Van der Vleuten CP, Konings KD, et al. Changing the culture of assessment: the dominance of the summative assessment paradigm. BMC medical education. 2017;17:1–4.
Harvey P, Radomski N, O’Connor D. Written feedback and continuity of learning in a geographically distributed medical education program. Medical teacher. 2013;35(12):1009–13.
Hochberg M, Berman R, Ogilvie J, Yingling S, Lee S, Pusic M, et al. Midclerkship feedback in the surgical clerkship: the “Professionalism, Reporting, Interpreting, Managing, Educating, and Procedural Skills” application utilizing learner self-assessment. Am J Surg. 2017;213:212–6.
Holmboe ES, Yepes M, Williams F, Huot SJ. Feedback and the mini clinical evaluation exercise. Journal of general internal medicine. 2004;19(5):558–61.
Tai JHM, Canny BJ, Haines TP, Molloy EK. The role of peer-assisted learning in building evaluative judgement: opportunities in clinical medical education. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2016;21:659–76.
Johnson CE, Keating JL, Molloy EK. Psychological safety in feedback: What does it look like and how can educators work with learners to foster it? Med Educ. 2020;54:559–70.
Joshi A, Generalla J, Thompson B, Haidet P. Facilitating the Feedback Process on a Clinical Clerkship Using a Smartphone Application. Acad Psychiatry. 2017;41:651–5.
Kiger ME, Riley C, Stolfi A, Morrison S, Burke A, Lockspeiser T. Use of Individualized Learning Plans to Facilitate Feedback Among Medical Students. Teach Learn Med. 2020;32:399–409.
Kogan J, Shea J. Implementing feedback cards in core clerkships. Med Educ. 2008;42:1071–9.
Lefroy J, Walters B, Molyneux A, Smithson S. Can learning from workplace feedback be enhanced by reflective writing? A realist evaluation in UK undergraduate medical education. Educ Prim Care. 2021;32:326–35.
McGinness HT, Caldwell PHY, Gunasekera H, Scott KM. ‘Every Human Interaction Requires a Bit of Give and Take’: Medical Students’ Approaches to Pursuing Feedback in the Clinical Setting. Teach Learn Med. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1080/10401334.2022.2084401 .
Noble C, Billett S, Armit L, Collier L, Hilder J, Sly C, et al. ``It’s yours to take{’’}: generating learner feedback literacy in the workplace. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2020;25:55–74.
Ogburn T, Espey E. The R-I-M-E method for evaluation of medical students on an obstetrics and gynecology clerkship. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;189:666–9.
Po O, Reznik M, Greenberg L. Improving a medical student feedback with a clinical encounter card. Ambul Pediatr. 2007;7:449–52.
Parkes J, Abercrombie S, McCarty T, Parkes J, Abercrombie S, McCarty T. Feedback sandwiches affect perceptions but not performance. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2013;18:397–407.
Paukert JL, Richards ML, Olney C. An encounter card system for increasing feedback to students. Am J Surg. 2002;183:300–4.
Rassos J, Melvin LJ, Panisko D, Kulasegaram K, Kuper A. Unearthing Faculty and Trainee Perspectives of Feedback in Internal Medicine: the Oral Case Presentation as a Model. J Gen Intern Med. 2019;34:2107–13.
Rizan C, Elsey C, Lemon T, Grant A, Monrouxe L. Feedback in action within bedside teaching encounters: a video ethnographic study. Med Educ. 2014;48:902–20.
Robertson AC, Fowler LC. Medical student perceptions of learner-initiated feedback using a mobile web application. Journal of medical education and curricular development. 2017;4:2382120517746384.
Scheidt PC, Lazoritz S, Ebbeling WL, Figelman AR, Moessner HF, Singer JE. Evaluation of system providing feedback to students on videotaped patient encounters. J Med Educ. 1986;61(7):585–90.
Sokol-Hessner L, Shea J, Kogan J. The open-ended comment space for action plans on core clerkship students’ encounter cards: what gets written? Acad Med. 2010;85:S110–4.
Sox CM, Dell M, Phillipi CA, Cabral HJ, Vargas G, Lewin LO. Feedback on oral presentations during pediatric clerkships: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2014;134:965–71.
Spickard A, Gigante J, Stein G, Denny JC. Automatic capture of student notes to augment mentor feedback and student performance on patient write-ups. J Gen Intern Med. 2008;23:979–84.
Suhoyo Y, Van Hell EA, Kerdijk W, Emilia O, Schönrock-Adema J, Kuks JB, et al. nfluence of feedback characteristics on perceived learning value of feedback in clerkships: does culture matter? BMC medical education. 2017;17:1–7.
Torre DM, Simpson D, Sebastian JL, Elnicki DM. Learning/feedback activities and high-quality teaching: perceptions of third-year medical students during an inpatient rotation. Acad Med. 2005;80:950–4.
Urquhart LM, Ker JS, Rees CE. Exploring the influence of context on feedback at medical school: a video-ethnography study. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2018;23:159–86.
Watling C, Driessen E, van der Vleuten C, Lingard L. Learning culture and feedback: an international study of medical athletes and musicians. Med Educ. 2014;48:713–23.
Watling C, Driessen E, van der Vleuten C, Vanstone M, Lingard L. Beyond individualism: Professional culture and its influence on feedback. Med Educ. 2013;47:585–94.
Soemantri D, Dodds A, Mccoll G. Examining the nature of feedback within the Mini Clinical Evaluation Exercise (Mini-CEX): an analysis of 1427 Mini-CEX assessment forms. GMS J Med Educ. 2018;35:Doc47.
Van De Ridder JMMM, Stokking KM, McGaghie WC, ten Cate OTJ, van der Ridder JM, Stokking KM, et al. What is feedback in clinical education? Med Educ. 2008;42:189–97.
van de Ridder JMMM, McGaghie WC, Stokking KM, ten Cate OTJJ. Variables that affect the process and outcome of feedback, relevant for medical training: a meta-review. Med Educ. 2015;49:658–73.
Boud D. Feedback: ensuring that it leads to enhanced learning. Clin Teach. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1111/tct.12345 .
Brehaut J, Colquhoun H, Eva K, Carrol K, Sales A, Michie S, et al. Practice feedback interventions: 15 suggestions for optimizing effectiveness. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164:435–41.
Ende J. Feedback in clinical medical education. J Am Med Assoc. 1983;250:777–81.
Cantillon P, Sargeant J. Giving feedback in clinical settings. Br Med J. 2008;337(7681):1292–4.
Norcini J, Burch V. Workplace-based assessment as an educational tool: AMEE Guide No. 31. Med Teach. 2007;29:855–71.
Watling CJ, Ginsburg S. Assessment, feedback and the alchemy of learning. Med Educ. 2019;53:76–85.
van der Vleuten CPM, Schuwirth LWT, Driessen EW, Dijkstra J, Tigelaar D, Baartman LKJ, et al. A model for programmatic assessment fit for purpose. Med Teach. 2012;34:205–14.
Schuwirth LWT, der Vleuten CPM. Programmatic assessment: from assessment of learning to assessment for learning. Med Teach. 2011;33:478–85.
Schut S, Driessen E, van Tartwijk J, van der Vleuten C, Heeneman S. Stakes in the eye of the beholder: an international study of learners’ perceptions within programmatic assessment. Med Educ. 2018;52:654–63.
Henderson M, Boud D, Molloy E, Dawson P, Phillips M, Ryan T, Mahoney MP. Feedback for learning. Closing the assessment loop. Framework for effective learning. Canberra, Australia: Australian Government, Department for Education and Training; 2018.
Heeneman S, Pool AO, Schuwirth LWT, van der Vleuten CPM, Driessen EW, Oudkerk A, et al. The impact of programmatic assessment on student learning: theory versus practice. Med Educ. 2015;49:487–98.
Lefroy J, Watling C, Teunissen P, Brand P, Watling C. Guidelines: the do’s, don’ts and don’t knows of feedback for clinical education. Perspect Med Educ. 2015;4:284–99.
Ramani S, Krackov SK. Twelve tips for giving feedback effectively in the clinical environment. Med Teach. 2012;34:787–91.
Telio S, Ajjawi R, Regehr G. The, “Educational Alliance” as a Framework for Reconceptualizing Feedback in Medical Education. Acad Med. 2015;90:609–14.
Lockyer J, Armson H, Könings KD, Lee-Krueger RC, des Ordons AR, Ramani S, et al. In-the-Moment Feedback and Coaching: Improving R2C2 for a New Context. J Grad Med Educ. 2020;12:27–35.
Black P, Wiliam D. Developing the theory of formative assessment. Educ Assess Eval Account. 2009;21:5–31.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Health Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Avenida Vicuña Mackenna 4860, Macul, Santiago, Chile
Javiera Fuentes-Cimma & Ignacio Villagran
School of Health Professions Education, Maastricht University, Maastricht, Netherlands
Javiera Fuentes-Cimma & Lorena Isbej
Rotterdam University of Applied Sciences, Rotterdam, Netherlands
Dominique Sluijsmans
Centre for Medical and Health Profession Education, Department of Gastroenterology, Faculty of Medicine, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
Arnoldo Riquelme
School of Dentistry, Faculty of Medicine, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
Lorena Isbej
Sistema de Bibliotecas UC (SIBUC), Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
María Teresa Olivares-Labbe
Department of Pathology, Faculty of Health, Medicine and Health Sciences, Maastricht University, Maastricht, Netherlands
Sylvia Heeneman
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
J.F-C, D.S, and S.H. made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the work. M.O-L contributed to the identification of studies. J.F-C, I.V, A.R, and L.I. made substantial contributions to the screening, reliability, and data analysis. J.F-C. wrote th e main manuscript text. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Javiera Fuentes-Cimma .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1, supplementary material 2., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Fuentes-Cimma, J., Sluijsmans, D., Riquelme, A. et al. Designing feedback processes in the workplace-based learning of undergraduate health professions education: a scoping review. BMC Med Educ 24 , 440 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05439-6
Download citation
Received : 25 September 2023
Accepted : 17 April 2024
Published : 23 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05439-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Clinical clerkship
- Feedback processes
- Feedforward
- Formative feedback
- Health professions
- Undergraduate medical education
- Undergraduate healthcare education
- Workplace learning
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye. Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently ...
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
Writing a literature review is often the most daunting part of writing an article, book, thesis, or dissertation. "The literature" seems (and often is) massive. I have found it helpful to be as systematic as possible when completing this gargantuan task.
A formal literature review is an evidence-based, in-depth analysis of a subject. There are many reasons for writing one and these will influence the length and style of your review, but in essence a literature review is a critical appraisal of the current collective knowledge on a subject. Rather than just being an exhaustive list of all that ...
A literature review is a collection of selected articles, books and other sources about a specific subject. The purpose is to summarize the existing research that has been done on the subject in order to put your research in context and to highlight what your research will add to the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews are typically ...
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A review is a required part of grant and research proposals and often a chapter in theses and dissertations. Generally, the purpose of a review is to analyze critically a segment of a published body of knowledge through summary, classification, and comparison of prior research studies, reviews of literature, and theoretical articles.
The nature of the literature review depends on the academic discipline. If in doubt, please check with your supervisors before starting the review. ... Producing a literature review is a complex task requiring a range of skills, from collecting material to writing a professional discussion of what you have found
literature review process. While reference is made to diflFerent types of literature reviews, the focus is on the traditional or narrative review that is undertaken, usually either as an academic assignment or part of the research process. Key words: Aneilysis and synthesis • Literature review • Literature searching • Writing a review T
make the task any easier, and indeed for many, writing a literature review is one of the most challenging aspects of their academic writing. In this study guide, I will begin by clearing up some misconceptions about what a literature review is and what it is not. Then, I will break the process down into a series of simple steps, looking at
INTRODUCTION. Writing the literature review (LR) is often viewed as a difficult task that can be a point of writer's block and procrastination in postgraduate life.Disagreements on the definitions or classifications of LRs may confuse students about their purpose and scope, as well as how to perform an LR.Interestingly, at many universities, the LR is still an important element in any ...
Literature review is an essential feature of academic research. Fundamentally, knowledge advancement must be built on prior existing work. To push the knowledge frontier, we must know where the frontier is. By reviewing relevant literature, we understand the breadth and depth of the existing body of work and identify gaps to explore.
Literature Review; Write and Cite. This guide offers information on writing resources, citation style guides, and academic writing expectations and best practices, as well as information on resources related to copyright, fair use, permissions, and open access. Table of Contents .
As mentioned previously, there are a number of existing guidelines for literature reviews. Depending on the methodology needed to achieve the purpose of the review, all types can be helpful and appropriate to reach a specific goal (for examples, please see Table 1).These approaches can be qualitative, quantitative, or have a mixed design depending on the phase of the review.
A literature review is a research task that finds, evaluates and discusses information on a particular topic. You need to analyse multiple texts, and discuss key ideas that you find in the reading. A literature review may also identify gaps for further research. It is not a process of summarising texts separately - that is done in an ...
task design strategies, the most recent compre-hensive review of this literature is nearly ten years old. In 1968, the literature relating to task design spanning three and a half decades was reviewed by Hulin and Blood (31). Their main conclusion was that the task design-individual response linkage is not the universally direct re-
Literature reviews play a critical role in scholarship because science remains, first and foremost, a cumulative endeavour (vom Brocke et al., 2009). As in any academic discipline, rigorous knowledge syntheses are becoming indispensable in keeping up with an exponentially growing eHealth literature, assisting practitioners, academics, and graduate students in finding, evaluating, and ...
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research.1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis ...
The literature review process involves both creative and mechanical tasks, which creates exciting opportunities for advanced AI-based tools 1 to reduce prospective authors' efforts for time-consuming and repetitive tasks and to dedicate more time to the creative tasks that require human interpretation, intuition, and expertise (Tsafnat et al ...
In Skehan`s (1998) features of tasks: Meaning is primary; There are some sort of relationship to comparable real word activities; Task completion has some priorities; The assessment of the task is in terms of outcome. The task primary perspective is focused on meaning. As for the authenticity, it should include read-world tasks.
The post-Hulin and Blood task design literature is reviewed, and several observations are made Individual differences (especially growth need strength) and organization variables moderate, affective responses (especially satisfaction with work) are most predictable, objective measures are needed; dimensionality is variable; optimal combinatory models are not widely accepted; and methodological ...
A scoping review was conducted using the five-step methodological framework proposed by Arksey and O'Malley (2005) [], intertwined with the PRISMA checklist extension for scoping reviews to provide reporting guidance for this specific type of knowledge synthesis [].Scoping reviews allow us to study the literature without restricting the methodological quality of the studies found ...