Manandmicrobes


33 New Medical microbiology project topics
Medical microbiology plays a crucial role in understanding and combating infectious diseases. Conducting a well-planned and meaningful project in this field is essential for advancing our knowledge and finding innovative solutions.
Choosing the right project topic is a critical first step in ensuring the success and impact of your research. In this article, we will explore various medical microbiology project topic ideas, research methodologies, project planning, data analysis, and more.
Importance of Medical Microbiology Projects
Medical microbiology projects contribute significantly to our understanding of pathogens, antimicrobial resistance, host-microbe interactions, and disease mechanisms.
By conducting research in this field, we can unravel the mysteries of infectious diseases and develop strategies for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
Significance of Choosing the Right Topic
Selecting an appropriate project topic is paramount to the success of your research. It should align with your interests, address a relevant research gap, and have practical implications .
The right topic will not only engage you throughout the project but also contribute valuable insights to the field of medical microbiology.
33 intriguing project topic ideas to consider
Here’s a non-exhaustive list of medical microbiology project topics for undergraduates and MSc students.
Topic 1: Investigating the Role of Gut Microbiota in Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases have been linked to alterations in the gut microbiota. This project aims to explore the relationship between gut microbiota composition and the development, progression, and management of autoimmune diseases.
By studying microbial diversity, immune responses, and metabolomic profiles, we can gain valuable insights into potential therapeutic interventions.
Topic 2: Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of Common Pathogens
Antibiotic resistance poses a significant global health threat. This project focuses on investigating the antibiotic resistance patterns of common pathogens, such as Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, in a local hospital setting.
By identifying the prevalent resistance mechanisms and associated risk factors, we can optimize antimicrobial therapy and develop strategies for infection control.
Topic 3: Impact of Microbial Biofilms on Chronic Wound Infections
Biofilms play a crucial role in chronic wound infections, leading to treatment challenges.
Recommended articles:
- 43 Project Topics on Food Microbiology: Latest
- 33 Microbiology Project Topics: You haven’t thought of
- 5 Best Medical Loans of 2024: Top Options
- Best Banks for Medical Practice Loans: Top Lenders…
- Loans for Medical Professionals: How to Secure…
This project aims to understand the formation, composition, and antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of biofilms associated with chronic wounds.
By elucidating the intricate interactions between biofilm communities and host factors, we can develop novel approaches to manage and prevent these infections.
4. Characterization of antibiotic resistance mechanisms in multidrug-resistant bacteria.
5. Investigation of the role of biofilms in chronic infections.
6. Exploring the impact of probiotics on gut microbiota composition and health.
7. Elucidating the molecular basis of viral-host interactions in viral infections.
8. Analysis of the microbiome in patients with autoimmune diseases.
9. Assessing the effectiveness of phage therapy against antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
10. Identification and characterization of novel antimicrobial compounds from natural sources.
11. Investigating the role of the microbiome in the development of allergies and asthma.
12. Understanding the mechanisms of horizontal gene transfer in antibiotic resistance dissemination.
13. Evaluation of the efficacy of novel disinfectants in healthcare settings.
14. Molecular epidemiology of nosocomial infections and surveillance of antibiotic-resistant pathogens.
15. Investigating the impact of climate change on the spread of vector-borne diseases.
16. Studying the role of microbiota in the development and progression of colorectal cancer.
17. Analysis of the microbial diversity in dental plaque and its association with oral health.
18. Exploring the potential of bacteriophages as alternatives to antibiotics in treating bacterial infections.
19. Investigating the impact of environmental factors on the microbiota of the skin.
20. Characterization of the role of gut microbiota in metabolic disorders, such as obesity and diabetes.
21. Understanding the mechanisms of antifungal drug resistance in Candida species.
22. Evaluation of the efficacy of different sterilization techniques in medical device manufacturing.
23. Investigation of the role of microbial communities in chronic wound infections.
24. Analysis of the impact of vaccination on the prevalence and diversity of infectious diseases.
25. Identification and characterization of novel drug targets in pathogenic bacteria.
26. Study of the interaction between the microbiome and the immune system in autoimmune disorders.
27. Exploring the microbiota composition and its association with mental health disorders.
28. Investigating the role of viral infections in the development of cancer.
29. Evaluation of the efficacy of antimicrobial coatings in preventing healthcare-associated infections.
30. Study of the genetic basis of virulence in bacterial pathogens.
31. Analysis of the impact of antimicrobial stewardship programs on antibiotic resistance patterns.
32. Investigation of the microbial diversity in respiratory tract infections.
33. Understanding the role of the microbiome in inflammatory bowel diseases.
Remember to choose a topic that aligns with your interests and research goals. These topics offer a range of exciting avenues for exploration in the field of medical microbiology.
Recommended articles
- 10 benefits of studying microbiology
- Can microbiologists work in hospitals?
- Can microbiologists make vaccines?
- Can a microbiologist work in NNPC?
- How to be a good microbiologist?
- Can microbiologists become doctors?
Project Planning and Execution
Once you have chosen a project topic , it is essential to plan and execute your research effectively.
This involves setting clear objectives and goals, designing appropriate experiments and protocols, and considering ethical aspects. Collaborating with experts in the field can enhance the quality and impact of your research.
Data Interpretation and Analysis
After collecting data, it is crucial to analyze and interpret the findings accurately. Statistical analysis and data visualization techniques can help identify trends, patterns, and statistical significance.
Ensuring the validity and reliability of your results is essential for drawing meaningful conclusions.
Discussion and Conclusion
In the discussion section, interpret the significance of your research findings in the context of existing literature.
Compare and contrast your results with previous studies, highlight limitations, and propose future directions.
Conclude your project by summarizing key findings, emphasizing their implications, and discussing potential applications in medical microbiology.
How do I choose the right medical microbiology project topic?
To choose the right project topic, consider your interests, relevance to the field, and potential impact. Research current trends and gaps in medical microbiology, consult with mentors and select a topic that aligns with your goals.
What are the ethical considerations in medical microbiology research?
Ethical considerations include obtaining informed consent, ensuring patient confidentiality, following ethical guidelines and regulations, and conducting research with integrity and transparency.
How can I ensure the validity of my research findings?
To ensure validity, employ rigorous experimental design, use appropriate controls, validate methods, replicate experiments, analyze data critically, and consider potential biases and confounding factors.
Can I collaborate with other researchers on my project?
Collaboration with other researchers is encouraged as it brings diverse expertise, resources, and perspectives to your project. Collaborative efforts can enhance the quality and impact of your research.
How can I present my project findings effectively?
To present your project findings effectively, prepare clear and concise visual aids, practice your presentation, engage with your audience, and highlight the significance and implications of your research.
Conducting a medical microbiology project provides an opportunity to contribute to scientific knowledge and make a positive impact in the field of healthcare.
By selecting a compelling topic, planning your research, analyzing data diligently, and engaging in meaningful discussions, you can successfully execute a project that advances our understanding of infectious diseases and leads to improved patient outcomes.
- Is Campylobacter Contagious?
- How to Use Bone Broth for Gut Health?
- Does Campylobacter stay in your system?
- Best greens supplement for bloating and gut health
- Is a plant-based diet good for gut health?
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Medical microbiology
- Microbiology
- Microbial pathogens
- Get an email alert for Medical microbiology
- Get the RSS feed for Medical microbiology
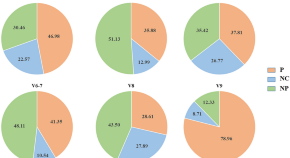
Showing 1 - 13 of 32,385
View by: Cover Page List Articles
Sort by: Recent Popular
HIV self-testing: A highly acceptable and feasible strategy for reconnecting street adolescents with HIV screening and prevention services in Togo (The STADOS study)
Arnold Junior Sadio, Harold Régis Kouanfack, [ ... ], Didier Koumavi Ekouevi
Leuconostoc mesenteroides , Lactococcus lactis ) on growth performance, immune response and gut microbiota in Nile tilapia ( Oreochromis niloticus )">The dietary effects of two strain probiotics ( Leuconostoc mesenteroides , Lactococcus lactis ) on growth performance, immune response and gut microbiota in Nile tilapia ( Oreochromis niloticus )
Assel Paritova, Akylbek Nurgaliyev, [ ... ], Kaissar Kushaliyev
Applying sigma metrics to assess quality control processes in the transfusion transmissible infection screening laboratory of a blood center
Sonu Bhatnagar, Sten Westgard, [ ... ], Nguyen Ha Thanh
A multi-site cross-sectional study on the burden of SARS-CoV-2 in healthcare workers in Madagascar
Seth Kofi Abrokwa, Lantonirina Ravaoarisoa, [ ... ], Sabrina Weiss
Facilitating the access to HIV testing at lower costs: “To the laboratory without prescription” (ALSO), a pilot intervention to expand HIV testing through medical laboratories in France
Karen Champenois, Victoire Sawras, [ ... ], the ALSO group
Impact of variable titer COVID-19 convalescent plasma and recipient SARS-CoV2-specific humoral immunity on survival in hospitalized patients
Carlo J. Iasella, Stefanie J. Hannan, [ ... ], John F. McDyer
Molecular identification and antimicrobial potential of endophytic fungi against some grapevine pathogens
Lava H. Nashat, Raed A. Haleem, Shayma H. Ali
High-risk human papillomavirus testing for cervical cancer screening in Uganda: Considering potential harms and benefits in a low-resource setting
Marat Sultanov, Jaap A. R. Koot, [ ... ], Jurjen van der Schans
Increased pathogen exposure of a marine apex predator over three decades
Karyn D. Rode, Caroline Van Hemert, [ ... ], Jitender P. Dubey
Staphylococcus giant bacteriophage S6">Examination of yield, bacteriolytic activity and cold storage of linker deletion mutants based on endolysin S6_ORF93 derived from Staphylococcus giant bacteriophage S6
Sosuke Munetomo, Jumpei Uchiyama, [ ... ], Osamu Matsushita
Dynamical behaviors of a stochastic SIVS epidemic model with the Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process and vaccination of newborns
Shenxing Li, Wenhe Li
Emergence of resistance to last-resort antimicrobials in bacteremia patients: A multicenter analysis of bloodstream pathogens in Korea
Jin Sae Yoo, Hui-Jin Yu, [ ... ], Bo-Moon Shin
Preferences for oral and injectable PrEP among qualitative sub-study participants in HPTN 084
Elizabeth E. Tolley, Agatha Bula, [ ... ], on behalf of the HPTN 084 study team
Connect with Us
- PLOS ONE on Twitter
- PLOS on Facebook
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- FEMS Microbiology Ecology
- FEMS Microbiology Letters
- FEMS Microbiology Reviews
- FEMS Yeast Research
- Pathogens and Disease
- FEMS Microbes
- Awards & Prizes
- Editor's Choice Articles
- Thematic Issues
- Virtual Special Issues
- Call for Papers
- Journal Policies
- Open Access Options
- Submit to the FEMS Journals
- Why Publish with the FEMS Journals
- About the Federation of European Microbiological Societies
- About the FEMS Journals
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Conference Reports
- Editorial Boards
- Investing in Science
- Journals Career Network
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Six Key Topics in Microbiology: 2019
Read an essential collection of papers showcasing high-quality content from across the five FEMS Journals, which together provide an overview of current research trends in microbiology. Follow the topic area links below for access to articles:
- Antimicrobial Resistance
Environmental Microbiology
Pathogenicity & virulence, biotechnology & synthetic biology, microbiomes, food microbiology, antimicrobial resistance.
Effects of sample preservation and DNA extraction on enumeration of antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater An-Dong Li, Jacob W Metch, Yulin Wang, Emily Garner, An Ni Zhang, Maria V Riquelme, Peter J Vikesland, Amy Pruden, Tong Zhang FEMS Microbilogy Ecology , DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fix189 First published online: 1 February 2018
Occurrence and abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in agricultural soil receiving dairy manure Chad W McKinney, Robert S Dungan, Amber Moore, April B Leytem FEMS Microbiology Ecology , DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fiy010; First published online: 1 March 2018
Environmental factors influencing the development and spread of antibiotic resistance Johan Bengtsson-Palme, Erik Kristiansson, D G Joakim Larsson FEMS Microbiology Reviews , DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fux053 First published online: 01 January 2018
Comparative genomic and transcriptomic analyses unveil novel features of azole resistnce and adaptation to the human host in Candida glabrata Sara Barbosa Salazar, Can Wang, Martin Münsterkötter, Michiyo Okamoto, Azusa Takahashi-Nakaguchi, Hiroji Chibana, Maria Manuel Lopes, Ulrich Güldener, Geraldine Butler, Nuno Pereira Mira FEMS Yeast Research , DOI: 10.1093/femsyr/fox079 First published online: 01 February 2018
How proteases from Enterococcus faecalis contribute to its resistance to short a-helical antimicrobial peptides Ondrej Nešuta, Miloš Budešínský, Romana Hadravová, Lenka Monincová, Jana Humpolicková, Václav Cerovský FEMS Pathogens and Disease , DOI: 10.1093/femspd/ftx091 First published online: 29 September 2017
Ice algal bloom development on the surface of the Greenland Ice Sheet C J Williamson, A M Anesio, J Cook, A Tedstone, E Poniecka, A Holland, D Fagan, M Tranter, M L Yallop FEMS Microbiology Ecology DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fiy025 First published online: 01 March 2018
Investigation of viable taxa in the deep terrestrial biosphere suggests high rates of nutrient recycling Margarita Lopez-Fernandez, Elias Broman, Stephanie Turner, Xiaofen Wu, Stefan Bertilsson, Mark Dopson FEMS Microbiology Ecology , DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fiy121 First published online: 01 August 2018
Soil Protists: a fertile frontier in soil biology research Stefan Geisen, Edward A D Mitchell, Sina Adl, Michael Bonkowski, Micah Dunthorn, Flemming Ekelund, Leonardo D Fernández, Alexandre Jousset, Valentyna Krashevska, David Singer, Frederick W Spiegel, Julia Walochnik, Enrique Lara FEMS Microbiology Reviews , DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuy006 First published online: 01 May 2018
Vector-borne diseases and climate change: a European perspective Jan C Semenza, Jonathan E Suk FEMS Microbiology Letters , DOI: 10.1093/femsle/fnx244 First published online: 01 January 2018
Beyond nitrogen metabolism: nitric oxide, cyclic-di- GMP and bacterial biofilms Serena Rinaldo, Giorgio Giardina, Federico Mantoni, Alessio Paone, Francesca Cutruzzolàr FEMS Microbiology Letters , DOI: 10.1093/femsle/fny029 First published online: 01 March 2018
Bacterial-fungal interactions: ecology, mechanisms and challenges Aurélie Deveau, Gregory Bonito, Jessie Uehling, Mathieu Paoletti, Matthias Becker, Saskia Bindschedler, Stéphane Hacquard, Vincent Hervé, Jessy Labbé, Olga A Lastovetsky, Sophie Mieszkin, Larry J Millet, Balázs Vajna, Pilar Junier, Paola Bonfante, Bastiaan P Krom, Stefan Olsson, Jan Dirk van Elsas, Lukas Y Wick FEMS Microbiology Reviews , DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuy008 First published online: 01 May 2018
The human cytomegalovirus terminase complex as an antiviral target: a close-up view G Ligat, R Cazal, S Hantz, S Alain; FEMS Microbiology Reviews , DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuy004 First published online: 01 March 2018
Molecular variability and genetic structure of white spot syndrome virus strains from northwest Mexico based on the analysis of genomes Delia Patricia Parrilla-Taylor, Norberto Vibanco-Pérez, Maria de Jesús Durán-Avelar, Bruno Gomez- Gil, Raúl Llera-Herrera, Ricardo Vázquez-Juárez FEMS Microbiology Letters , DOI: 10.1093/femsle/fny216 First published online: 01 October 2018
The first known virus isolates from Antarctic sea ice have complex infection patterns Anne-Mari Luhtanen, Eeva Eronen-Rasimus, Hanna M Oksanen, Jean-Louis Tison, Bruno Delille, Gerhard S Dieckmann, Janne-Markus Rintala, Dennis H Bamford FEMS Microbiology Ecology , DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fiy028 First published online: 1 April 2018
Host-pathogen redox dynamics modulate Mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogenesis Hayden T Pacl, Vineel P Reddy, Vikram Saini, Krishna C Chinta, Adrie J C Steyn FEMS Pathogens and Disease , DOI: 10.1093/femspd/fty036 First published online: 01 July 2018
The CRISPR-Cas system in Enterobacteriaceae Liliana Medina-Aparicio, Sonia Dávila, Javier E Rebollar-Flores, Edmundo Calva, Ismael Hernández- Lucas FEMS Pathogens and Disease , DOI: 10.1093/femspd/fty002 First published online: 01 February 2018
Mycobacterial biomaterials and resources for researchers Manzour Hernando Hazbón, Leen Rigouts, Marco Schito, Matthew Ezewudo, Takuji Kudo, Takashi Itoh, Moriya Ohkuma, Katalin Kiss, Linhuan Wu, Juncai Ma, Moriyuki Hamada, Michael Strong, Max Salfinger ,Charles L Daley, Jerry A Nick, Jung-Sook Lee, Nalin Rastogi, David Couvin, Raquel Hurtado-Ortiz, Chantal Bizet, Anita Suresh, Timothy Rodwell, Audrey Albertini, Karen A Lacourciere, Ana Deheer- Graham, Sarah Alexander, Julie E Russell, Rebecca Bradford, Marco A Riojas FEMS Pathogens and Disease , DOI: 10.1093/femspd/fty042 First published online: 01 June 2018
Yeast 2.0- connecting the dots in the construction of the world's first functional synthetic eukaryotic genome I S Pretorius, J D Boeke FEMS Yeast Research , DOI: 10.1093/femsyr/foy032 First published online: 01 June 2018
Laboratory evolution for forced glucose-xylose co-consumption enables identification of mutations that improve mixed-sugar fermentation by xylose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ioannis Papapetridis, Maarten D Verhoeven, Sanne J Wiersma, Maaike Goudriaan, Antonius J A van Maris, Jack T Pronk FEMS Yeast Research , DOI: 10.1093/femsyr/foy056 First published online:01 September 2018
State of the art in eukaryotic nitrogenase engineering Stefan Burén, Luis M Rubio FEMS Microbiology Letters , DOI: 10.1093/femsle/fnx274 First published online: 01 January 2018
Whole-genome sequencing based characterization of antimicrobial resistance in Enterococcus Gregory H Tyson, Jonathan L Sabo, Crystal Rice-Trujillo, Jacqueline Hernandez, Patrick F McDermott FEMS Pathogens and Disease , DOI: 10.1093/femspd/fty018 First published online: 01 March 2018
Biofilm growth and control in cooling water industrial systems F Di Pippo, L Di Gregorio, R Congestri, V Tandoi, S Rossetti FEMS Microbiology Ecology , DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fiy044 First published online: 01 May 2018
Novel sequencing technologies to support industrial biotechnology Adalberto Costessi, Bartholomeus van den Bogert, Ali May, Emiel Ver Loren van Themaat, Johannes A Roubos, Marc A B Kolkman, Derek Butler, Walter Pirovano FEMS Microbiology Letters , DOI: 10.1093/femsle/fny103 First published online: 01 August 2018
Influenza A virus subtype H9N2 infection disrupts the composition of intestinal microbiota of chickens Alexander Yitbarek, J Scott Weese, Tamiru Negash Alkie, John Parkinson, Shayan Sharif FEMS Microbiology Ecology , DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fix165 First published online: 01 January 2018
Pathogens, microbiome and the host: emergence of the ecological Koch's postulates Pascale Vonaesch, Mark Anderson, Philippe J Sansonetti FEMS Microbiology Reviews , DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuy003 First published online: 09 January 2018
Talk to your gut: the oral-gut microbiome axis and its immunomodulatory role in the etiology of rheumatoid arthritis Marines du Teil Espina, Giorgio Gabarrini, Hermie J M Harmsen, Johanna Westra, Arie Jan van Winkelhoff, Jan Maarten van Dijl FEMS Microbiology Reviews , DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuy035 First published online: 01 January 2019
Shift of hindgut microbiota and microbial short chain fatty acids profiles in dairy calves from birth to pre-weaning Yang Song, Nilusha Malmuthuge, Michael A Steele, Le Luo Guan FEMS Microbiology Ecology , DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fix179 First published online: 01 March 2018
The Smallest Intestine (TSI)- a low volume in vitro model of the small intenstine with increased throughput T Cieplak, M Wiese, S Nielsen, T Van de Wiele, F van den Berg, D S Nielsen FEMS Microbiology Letters , DOI: 10.1093/femsle/fny231 First published online: 01 November 2018
Saccharomyces cerevisiae variety diastaticus friend or foe? - spoilage potential and brewing ability of different Saccharomyces cerevisiae variety diastaticus yeast isolates by genetic, phenotypic and physiological characterization Tim Meier-Dörnberg, Oliver Ingo Kory, Fritz Jacob, Maximilian Michel, Mathias Hutzler FEMS Yeast Research , DOI: 10.1093/femsyr/foy023 First published online: 01 June 2018
Trans-regulation and localization of orthologous maltose transporters in the interspecies lager yeast hybrid Virve Vidgren, Brian Gibson FEMS Yeast Research , DOI: 10.1093/femsyr/foy065 First published online: 01 September 2018
Fermentation performances and aroma production of non-conventional wine yeasts are influenced by nitrogen preferences Stéphanie Rollero, Audrey Bloem, Anne Ortiz-Julien, Carole Camarasa, Benoit Divol FEMS Yeast Research , DOI: 10.1093/femsyr/foy055 First published online: 01 August 2018
Community-led comparative genomic and phenotypic analysis of the aquaculture pathogen Pseudomonas baetica a390T sequenced by Ion semiconductor and Nanopore technologies Ainsley Beaton, Cédric Lood, Edward Cunningham-Oakes, Alison MacFadyen, Alex J Mullins, Walid El Bestawy, João Botelho, Sylvie Chevalier, Shannon Coleman, Chloe Dalzell, Stephen K Dolan, Alberto Faccenda, Maarten G K Ghequire, Steven Higgins, Alexander Kutschera, Jordan Murray, Martha Redway, Talal Salih, Ana C da Silva, Brian A Smith, Nathan Smits, Ryan Thomson, Stuart Woodcock, Martin Welch, Pierre Cornelis, Rob Lavigne, Vera van Noort, Nicholas P Tucker FEMS Microbiology Letters , DOI: 10.1093/femsle/fny069 First published online: 01 May 2018
Antibiotic resistance phenotypes and virulence-associated genes in Escherichia coli isolated from animals and animal food products in Tunisia Souhir Badi, Paola Cremonesi, Mohamed Salah Abbassi, Chourouk Ibrahim, Majdi Snoussi, Giulia Bignoli, Mario Luini, Bianca Castiglioni, Abdennaceur Hassen FEMS Microbiology Letters , DOI: 10.1093/femsle/fny088 First published online: 01 May 2018
- X (formerly Twitter)
Affiliations
- Copyright © 2024
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Revolutionizing Medical Microbiology: How Molecular and Genomic Approaches Are Changing Diagnostic Techniques
Poyasha a goyal, nandkishor j bankar, vaishnavi h mishra, sonali k borkar, jagadish g makade.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Nandkishor J. Bankar [email protected]
Corresponding author.
Received 2023 Aug 21; Accepted 2023 Oct 16; Collection date 2023 Oct.
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Molecular and genomic approaches have revolutionized medical microbiology by offering faster and more accurate diagnostic techniques for infectious diseases. Traditional methods, which include culturing microbes and biochemical testing, are time-consuming and may not detect antibiotic-resistant strains. In contrast, molecular and genomic methods, including polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based techniques and whole-genome sequencing, provide rapid and precise detection of pathogens, early-stage diseases, and antibiotic-resistant strains. These approaches have advantages such as high sensitivity and specificity, the potential for targeted therapies, and personalized medicine. However, implementing molecular and genomic techniques faces challenges related to cost, equipment, expertise, and data analysis. Ethical and legal considerations regarding patient privacy and genetic data usage also arise. Nonetheless, the future of medical microbiology lies in the widespread adoption of molecular and genomic approaches, which can lead to improved patient outcomes and the identification of antibiotic-resistant strains. Continued advancements, education, and exploration of ethical implications are necessary to fully harness the potential of molecular and genomic techniques in medical microbiology.
Keywords: revolutionizing healthcare, diagnostic tests, traditional molecular techniques, rt-pcr, molecular diagnostics
Introduction and background
The healthcare system depends heavily on the science of diagnostics because it serves as the basis for medical judgment. Diagnostic tests provide crucial data that inform personalized cancer treatments, assist in choosing the best antibiotics to treat infections, and offer insightful information on every aspect of healthcare, including disease management, prevention, detection, diagnosis, and treatment [ 1 ]. Clinical chemistry, immunology, hematology, microbiology, and molecular diagnostics are some of the primary diagnostic categories. Among these, molecular diagnostics has attracted a lot of attention recently because of its capacity to offer comprehensive insights into diagnosis as well as therapy modalities. This field has experienced significant changes, revolutionizing healthcare by deeply understanding various illness states [ 2 ]. Advanced technologies are used in molecular diagnostics to find and examine genetic and molecular changes linked to diseases. To better understand and treat a variety of medical diseases, molecular diagnostics has created new pathways for study and treatment by analyzing people's genetic makeup [ 3 ]. Specific diseases and disorders have been addressed for in-depth examination and therapy in the field of molecular diagnostics. This method has made it possible to create precise and personalized therapies based on a person's genetic profile, increasing the effectiveness and results of treatments. Particularly helpful applications of molecular diagnostics include oncology, infectious diseases, genetic abnormalities, and personalized treatment [ 4 ]. Two novel therapeutic modalities, pharmacogenomics, and nutrigenomics, have also been made possible by the science of molecular diagnostics. Pharmacogenomics entails examining a person's genetic variants to ascertain how they will react to specific pharmaceuticals, optimizing treatment regimens, and reducing negative drug reactions. Nutrigenomics, on the other hand, investigates how a person's genes and diet interact, enabling tailored nutritional recommendations that can have an impact on disease management techniques [ 5 , 6 ]. Diagnostics and healthcare have undergone a paradigm shift due to molecular diagnostics. Utilizing cutting-edge technologies and expanding our knowledge of genetic and molecular variables has changed medical research, diagnosis, and treatment methods. The potential of molecular diagnostics in creating tailored and successful disease treatment strategies is further highlighted by the development of nutrigenomics and pharmacogenomics [ 7 , 8 ]. The objective of this review is to explore molecular and genomic techniques' potential for improving medical microbiology.
Search strategy
We used the PubMed and Scopus advanced search strategy to obtain articles from PubMed and Scopus employing the following terms: (“molecular diagnostic techniques” OR “genomic diagnostic techniques” OR “traditional diagnostic techniques" or "molecular and genomic approaches” OR “traditional diagnostic techniques” OR “molecular and genomic approaches” OR “advantages of molecular and genomic approaches in medical microbiology” OR “strengths molecular and genomic approaches” OR “limitations molecular and genomic approaches”). We obtained the most pertinent research papers and used them in different arrangements using the Boolean operators “AND” and “OR.”
Search outcomes
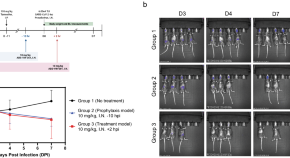
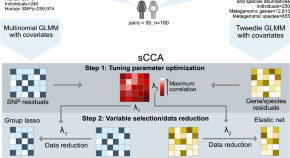
After conducting the initial search, we identified a total of 965 articles across the searched databases. We then excluded duplicates (n=400) and conducted an initial screening of titles and abstracts, which excluded a further 565 articles. After the full-text screening of the remaining 360 articles, we excluded 149 articles for not meeting the inclusion criteria; the full free text was not available and was not written in English, leaving a total of 56 articles for the final review (Figure 1 ).
Figure 1. A PRISMA flow chart of the study selection process.
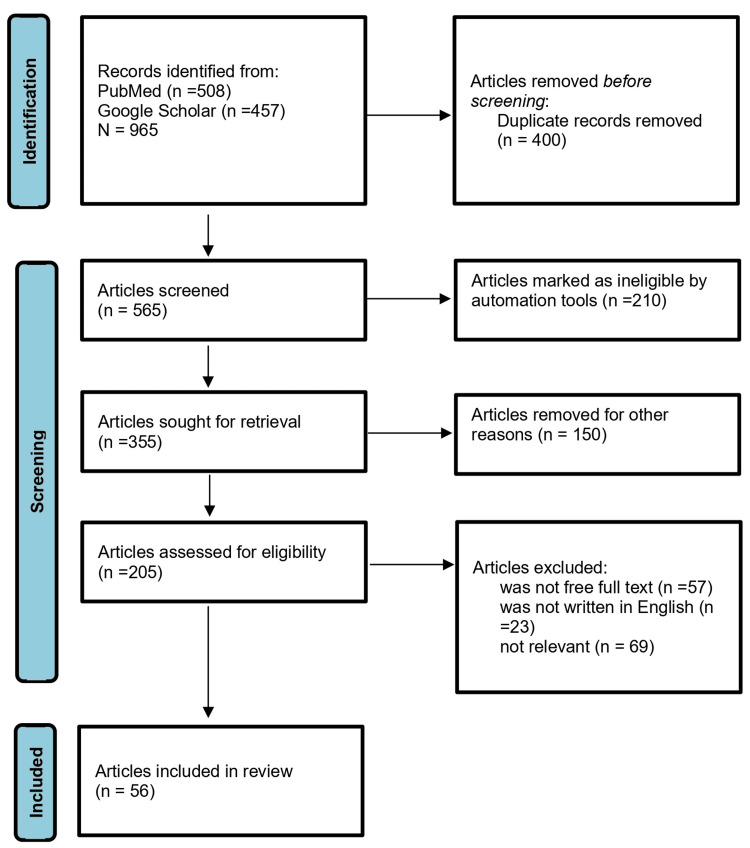
PRISMA: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses; n: number of studies
The timeline illustrates key milestones in the field of molecular diagnostics. Pauling's term "molecular disease" in 1949 linked genetics to sickle cell anemia. The 1980s saw prenatal tests using deoxyribonucleic acid-cutting enzymes. Companies like Molecular Diagnostics Inc. emerged, followed by gene discoveries and sequencing techniques in the 1990s. The Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP) was formed in 1995; the European Union (EU) allowed gene patents in 1998; and journals like The Journal of Medical Diagnostics started. Legal battles over gene patents occurred, including the 2013 United States Supreme Court ruling against patenting natural gene sequences. The history of molecular and genomic technique advancements is mentioned in Table 1 .
Table 1. Timeline representing the development of molecular diagnostic techniques.
DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid; AMP: Association for Molecular Pathology; BRCA1: BReast CAncer gene 1; BRCA2: BReast CAncer gene 2; RNA: ribonucleic acid; CRISPR: clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats
Traditional diagnostic techniques versus molecular and genomic approaches
Traditional diagnostic techniques for infectious diseases include culturing microbes on agar plates, biochemical testing, and microscopic examination of samples. These methods are slow, often taking days or weeks to yield results, and they may not be able to identify the causative agent of infection [ 12 ]. Additionally, traditional diagnostic techniques may be unable to detect antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria, which can lead to inappropriate treatment and potentially fatal outcomes [ 13 , 14 ]. Traditional methods' primary drawback is how time-consuming they are. To allow for the growth and identification of organisms, an incubation duration of several days or even weeks is necessary when cultivating bacteria on agar plates. This wait for findings can delay the start of therapy, which can be harmful, especially in cases of serious or life-threatening infections [ 15 ].
In contrast, molecular and genomic approaches offer faster and more accurate results and can detect antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria [ 16 ]. These methods entail isolating nucleic acids from a patient's sample, such as blood or tissue, and using molecular and genomic instruments to pinpoint the infection's causal culprit. These techniques include bioinformatics, whole-genome sequencing (WGS), and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) [ 17 ]. The DNA testing was significantly accelerated and made more efficient thanks to next-generation sequencing (NGS), which offered a strong alternative for identifying mutations [ 18 ].
Advantages of molecular and genomic approaches
In comparison to conventional diagnostic methods, molecular and genomic approaches have several advantages (Table 2 ).
Table 2. The strengths and limitations of traditional diagnostic techniques and molecular/genomic approaches in medical diagnostics.
These methods are quicker and more precise. While whole-genome sequencing can offer a thorough examination of all the bacteria present in a sample, PCR-based approaches can pinpoint the infection's primary cause in a matter of hours. Early and more focused treatment of infections is made possible by this speed and accuracy, which can improve patient outcomes [ 19 , 20 ]. Traditional diagnostic methods are less sensitive and specific than molecular and genomic approaches. These techniques can identify microorganisms at low concentrations that conventional techniques can miss [ 21 ]. Furthermore, molecular and genomic techniques can be used to identify particular strains of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, which can be very helpful in infectious disease epidemics [ 22 ].
Antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains can be found using molecular and genomic methods. These strains are spreading more widely, and conventional diagnostic methods might not be able to distinguish them. Antibiotic-resistant genes can be found using molecular and genomic methods, allowing for effective infection therapy [ 23 , 24 ].
Molecular and genomic techniques in the diagnosis of infectious diseases
Molecular and genomic techniques are being used in the diagnosis of a wide range of infectious diseases [ 25 ]. Polymerase chain reaction-based methods are commonly used to diagnose viral infections, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis, and influenza [ 26 ]. These methods can also be used to diagnose bacterial infections, such as tuberculosis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea [ 27 ]. Another method that is rapidly being employed in medical microbiology is whole-genome sequencing. This technique includes sequencing every piece of DNA found in a sample of microorganisms, which can produce a thorough examination of every bacterium present [ 28 ]. When infectious disease outbreaks occur, whole-genome sequencing can be very helpful in locating the outbreak origin and monitoring the disease progress [ 29 ].
Nucleic acid amplification test
The gold standard for amplification procedures in diagnostics is PCR. Since the method's initial publication in 1985 [ 30 ]. In medical microbiology, PCR-based methods are frequently employed to identify bacterial and viral illnesses. These procedures entail amplifying particular DNA sequences from a patient's sample, which can then be found using a variety of techniques, including gel electrophoresis or fluorescence. Gene analysis, the diagnosis of numerous genetic illnesses, and the detection of bacterial, viral, and fungal infections have all greatly benefited from the invention of methods for amplifying DNA segments [ 31 - 34 ]. Polymerase chain reaction-based methods are quick and accurate, and they can find small amounts of bacteria [ 35 ]. The detection of bacterial strains resistant to antibiotics is also possible using PCR-based methods. These strains frequently possess particular genes that confer antibiotic resistance, and PCR-based methods can identify the presence of these genes. This can aid in determining the most effective way to treat infections [ 36 ].
Whole-genome sequencing
A potent technique for the diagnosis of infectious disorders is WGS. This technique entails sequencing every piece of DNA found in a sample of microorganisms, which can produce a thorough examination of every bacterium present. It allows for the high-resolution characterization of bacterial pathogens in terms of traits including pathogenicity, molecular epidemiology, and antibiotic resistance [ 37 ]. When infectious disease outbreaks occur, whole-genome sequencing can be very helpful in locating the outbreak's origin and monitoring the disease's progress [ 38 , 39 ]. The identification of bacterial strains resistant to antibiotics is another application of WGS. This method involves identifying specific genes that confer antibiotic resistance, which can aid in determining the most effective way to treat infections [ 40 ]. The development of next-generation sequencing equipment has decreased the cost of WGS. However, the absence of a WGS beginner's protocol still prevents its acceptance in some contexts [ 37 ].
In bioinformatics and data analysis, molecular and genomic approaches and numerous data sets are produced by molecular and genomic techniques, and these data sets need to be evaluated and understood. Medical microbiology uses molecular and genomic techniques, while bioinformatics is the branch of science that deals with the processing and interpretation of biological data [ 41 , 42 ]. In bioinformatics, biological data are analyzed and interpreted using computational tools and algorithms. The identification of certain genes and proteins, sequence comparison, and biological molecule structure and function predictions are all possible with the use of these technologies. For the processing and interpretation of the enormous volumes of data produced by molecular and genomic techniques, bioinformatics is crucial [ 43 ].
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry
The 1980s saw the development of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF) by Hillenkamp and Karas, which is essential for analyzing biomolecule masses. It ionizes molecules using a matrix and laser to create distinctive profiles for proteomics, biomolecule analysis, and microbiological identification. Their laser-ionization and time-of-flight detection methods are used in clinical diagnostics, drug development, and quality control because they provide quick, precise molecular insights. It quickly rose to prominence in clinical microbiology, revolutionizing the identification of microorganisms based on mass spectra, "fingerprints," and proteomics, detecting and characterizing proteins [ 44 ]. It evolved, advancing sample processing, instrument design, and data analysis for use in a variety of industries, including environmental analysis, food safety, and drug discovery. Due to its great sensitivity, speed, and versatility, MALDI-TOF has become a cornerstone of mass spectrometry and is essential to modern research across many fields of science [ 45 ].
Next-generation sequencing
The field of genetic research has been completely changed by NGS, also known as massively parallel or deep sequencing. This technology makes it possible to quickly and affordably sequence complete genomes, opening the door for ground-breaking research in a variety of domains. Next-generation sequencing has ushered in a new era of genomics research by making it possible to sequence the human genome in just one day, enabling improvements in personalized medicine, evolutionary biology, microbiology, and other fields. This review examines the foundations, uses, and consequences of NGS, emphasizing its contribution to advancing knowledge and its potential to alter how we perceive the genetic universe [ 46 ]. Next-generation sequencing has revolutionized genomics. After a modest start in 1977 with Sanger sequencing, NGS developed in the 2000s, characterized by 454's pyro-sequencing and Illumina's parallel technology [ 47 ]. Ion Torrent's semiconductor detection, Pac Bio's real-time readings, and Oxford Nanopore's nanopore-based sequencing have all contributed to the advancement of NGS. This revolution affected genetics, medicine, agriculture, and other fields through initiatives like the Human Genome Project. Genomic profiling, cancer detection, infectious disease detection, transcriptome analysis, epigenetic, non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT), pharmacogenomics, diagnosis of rare diseases, microbiome research, and human leukocyte antigen (HLA) typing are a few of the uses of NGS. Next-generation sequencing has issues with data handling yet continues to advance molecular diagnostics and tailored treatment while providing speed, accuracy, and scalability.
Challenges in implementing molecular and genomic approaches
Although molecular and genomic approaches have several benefits over conventional diagnostic methods, there are also several practical obstacles [ 48 ]. Some medical facilities might not have the necessary tools and knowledge that these methods demand. Additionally, these methods might be pricey, which might restrict who can use them [ 49 ]. Numerous data sets are produced by molecular and genomic techniques, and these data sets need to be evaluated and understood. This calls for specific knowledge in data processing and bioinformatics, which might not be available in all medical facilities [ 50 ]. The use of molecular and genomic methods in medical microbiology has ethical and legal implications. Concerns including patient privacy, informed consent, and the ownership and usage of genetic data are among them [ 51 ].
Future of molecular and genomic approaches
Molecular and genomic methods are anticipated to influence the direction of medical microbiology in the future. With these methods, infectious illness diagnoses can be made more quickly and precisely, which can lead to better patient outcomes [ 52 , 53 ]. Additionally, in light of the increasing prevalence of antibiotic resistance, molecular and genomic techniques can be used to discover bacterial strains that are resistant to antibiotics [ 54 ].
Future developments are projected to increase the accessibility and availability of molecular and genomic methods. It will be necessary to do this by creating new technology and educating medical personnel on how to use it [ 55 ]. Additionally, continued investigation into the ethical and legal issues connected to the application of molecular and genomic techniques in medical microbiology will be necessary [ 56 ].
Conclusions
Medical microbiology is undergoing a revolution thanks to molecular and genomic techniques. Infectious disease diagnoses can now be made more quickly and precisely thanks to these methods, which can benefit patient outcomes. Additionally, molecular and genomic techniques can aid in the identification of bacterial strains that are resistant to antibiotics, which is becoming more crucial in light of the rise in antibiotic resistance. Molecular and genomic techniques are likely to be made more broadly available and accessible in the future, notwithstanding the difficulties involved in their implementation. This will necessitate continual study and development as well as instruction in the usage of these methods for medical practitioners. In the end, the application of molecular and genomic methods in medical microbiology can revolutionize how we identify and treat infectious diseases while also enhancing patient outcomes globally.
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
- 1. The growing role of precision and personalized medicine for cancer treatment. Krzyszczyk P, Acevedo A, Davidoff EJ, et al. Technology (Singap World Sci) 2018;6:79–100. doi: 10.1142/S2339547818300020. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 2. Diseases and molecular diagnostics: a step closer to precision medicine. Dwivedi S, Purohit P, Misra R, et al. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2017;32:374–398. doi: 10.1007/s12291-017-0688-8. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 3. Molecular diagnostics in clinical oncology. Sokolenko AP, Imyanitov EN. Front Mol Biosci. 2018;5:76. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2018.00076. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 4. Personalized sequencing and the future of medicine: discovery, diagnosis and defeat of disease. Esplin ED, Oei L, Snyder MP. Pharmacogenomics. 2014;15:1771–1790. doi: 10.2217/pgs.14.117. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 5. Role of pharmacogenetics in adverse drug reactions: an update towards personalized medicine. Micaglio E, Locati ET, Monasky MM, Romani F, Heilbron F, Pappone C. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:651720. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.651720. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 6. Pharmacogenetics: an important part of drug development with a focus on its application. Oates JT, Lopez D. Int J Biomed Investig. 2018;1:4745. doi: 10.31531/2581-4745.1000111. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 7. Molecular diagnostics: a healthcare perspective. Hall AG, Coulthard SA, Irving JA. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2003;3:13–16. doi: 10.1586/14737159.3.1.13. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 8. Improving health care and laboratory medicine: the past, present, and future of molecular diagnostics. Green DM. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent) 2005;18:125–129. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2005.11928050. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 9. Polymorphism of DNA sequence in the beta-globin gene region. Application to prenatal diagnosis of beta 0 thalassemia in Sardinia. Kan YW, Lee KY, Furbetta M, Angius A, Cao A. N Engl J Med. 1980;302:185–188. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001243020401. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 10. Recent advances in molecular diagnostics of fungal plant pathogens: a mini review. Hariharan G, Prasannath K. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:600234. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.600234. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 11. Recent advances in the use of molecular methods for the diagnosis of bacterial infections. Gerace E, Mancuso G, Midiri A, Poidomani S, Zummo S, Biondo C. Pathogens. 2022;11:663. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11060663. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 12. Principles of diagnosis of infectious diseases. Walker DH. Pathobiology of Human Disease. 2014:222–225. [ Google Scholar ]
- 13. Situational disease. Gannik DE. Fam Pract. 1995;12:202–206. doi: 10.1093/fampra/12.2.202. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 14. Agar pre-embedding of small skin biopsies: real-life benefits and challenges in high throughput pathology laboratories. Ridolfi M, Paudice M, Salvi S, et al. J Clin Pathol. 2019;72:448–451. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2018-205680. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 15. Current and past strategies for bacterial culture in clinical microbiology. Lagier JC, Edouard S, Pagnier I, Mediannikov O, Drancourt M, Raoult D. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015;28:208–236. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00110-14. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 16. The evolution of molecular biology. Kellenberger E. EMBO Rep. 2004;5:546–549. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400180. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 17. PCR-based detection methods for single-nucleotide polymorphism or mutation: real-time PCR and its substantial contribution toward technological refinement. Matsuda K. Adv Clin Chem. 2017;80:45–72. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2016.11.002. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 18. Next-generation sequencing of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes for rapid detection of germline mutations in hereditary breast/ovarian cancer. Nicolussi A, Belardinilli F, Mahdavian Y, et al. PeerJ. 2019;7:0. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6661. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 19. Microbiology in the post-genomic era. Medini D, Serruto D, Parkhill J, et al. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6:419–430. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1901. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 20. Integrated, automated, fast PCR system for point-of-care molecular diagnosis of bacterial infection. Lee D, Kim D, Han J, et al. Sensors (Basel) 2021;21:377. doi: 10.3390/s21020377. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 21. Advances in biosensing technologies for diagnosis of COVID-19. Alsalameh S, Alnajjar K, Makhzoum T, et al. Biosensors (Basel) 2022;12:898. doi: 10.3390/bios12100898. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 22. Species-specific genomic sequences for classification of bacteria. Paul B, Kavia Raj K, Murali TS, Satyamoorthy K. Comput Biol Med. 2020;123:103874. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103874. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 23. Prevalence, risk factors, and molecular epidemiology of intestinal carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Hu Y, Qing Y, Chen J, et al. Microbiol Spectr. 2021;9:0. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.01344-21. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 24. Fluoroquinolone resistance in Salmonella: insights by whole-genome sequencing. Cuypers WL, Jacobs J, Wong V, Klemm EJ, Deborggraeve S, Van Puyvelde S. Microb Genom. 2018;4:0. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000195. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 25. Global genomic epidemiology of Streptococcus pyogenes. Jespersen MG, Lacey JA, Tong SY, Davies MR. Infect Genet Evol. 2020;86:104609. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104609. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 26. Reacción en cadena de la polimerasa (PCR) a tiempo real (Article in Spanish) Costa J. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2004;22:299–305. doi: 10.1016/s0213-005x(04)73092-x. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 27. Applications of real-time PCR in the screening of platelet concentrates for bacterial contamination. Mohammadi T, Savelkoul PH, Pietersz RN, Reesink HW. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2006;6:865–872. doi: 10.1586/14737159.6.6.865. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 28. Potential of whole-genome sequencing-based pharmacogenetic profiling. Caspar SM, Schneider T, Stoll P, Meienberg J, Matyas G. Pharmacogenomics. 2021;22:177–190. doi: 10.2217/pgs-2020-0155. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 29. Infection prevention and control insights from a decade of pathogen whole-genome sequencing. Eyre DW. J Hosp Infect. 2022;122:180–186. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2022.01.024. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 30. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Saiki RK, Scharf S, Faloona F, Mullis KB, Horn GT, Erlich HA, Arnheim N. Science. 1985;230:1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 31. Fungal molecular diagnostics: a mini review. Atkins SD, Clark IM. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14960763/ J Appl Genet. 2004;45:3–15. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 32. Principles and applications of polymerase chain reaction in medical diagnostic fields: a review. Valones MA, Guimarães RL, Brandão LA, de Souza PR, de Albuquerque Tavares Carvalho A, Crovela S. Braz J Microbiol. 2009;40:1–11. doi: 10.1590/S1517-83822009000100001. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 33. Diagnosis of malaria aided by polymerase chain reaction in two cases with low-level parasitaemia. Speers DJ, Ryan S, Harnett G, Chidlow G. Intern Med J. 2003;33:613–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.2003.00500.x. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 34. Molecular and diagnostic clinical virology in real time. Niesters HG. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004;10:5–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2004.00699.x. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 35. Agarose gel electrophoresis to assess PCR product yield: comparison with spectrophotometry, fluorometry and qPCR. Wittmeier P, Hummel S. Biotechniques. 2022;72:155–158. doi: 10.2144/btn-2021-0094. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 36. Prevalence and characterization of Salmonella from meat in slaughterhouses in Hangzhou, China. Liu C, Yao K, Ren D, Xiao Y. Int J Food Microbiol. 2022;371:109649. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.109649. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 37. A step-by-step beginner's protocol for whole genome sequencing of human bacterial pathogens. Gautam SS, Kc R, Leong KW, Mac Aogáin M, O'Toole RF. J Biol Methods. 2019;6:0. doi: 10.14440/jbm.2019.276. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 38. Whole genome sequencing analysis of multiple Salmonella serovars provides insights into phylogenetic relatedness, antimicrobial resistance, and virulence markers across humans, food animals and agriculture environmental sources. Pornsukarom S, van Vliet AH, Thakur S. BMC Genomics. 2018;19:801. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5137-4. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 39. From theory to practice: translating whole-genome sequencing (WGS) into the clinic. Balloux F, Brønstad Brynildsrud O, van Dorp L, et al. Trends Microbiol. 2018;26:1035–1048. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2018.08.004. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 40. Sequencing-based methods and resources to study antimicrobial resistance. Boolchandani M, D'Souza AW, Dantas G. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20:356–370. doi: 10.1038/s41576-019-0108-4. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 41. A new era of virus bioinformatics. Ibrahim B, McMahon DP, Hufsky F, et al. Virus Res. 2018;251:86–90. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2018.05.009. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 42. Introduction to bioinformatics. Akalin PK. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2006;50:610–619. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200500273. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 43. A machine learning bioinformatics method to predict biological activity from biosynthetic gene clusters. Walker AS, Clardy J. J Chem Inf Model. 2021;61:2560–2571. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.0c01304. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 44. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: an emerging technology for microbial identification and diagnosis. Singhal N, Kumar M, Kanaujia PK, Virdi JS. Front Microbiol. 2015;6:791. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00791. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 45. Direct identification of urinary tract pathogens from urine samples by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. Ferreira L, Sánchez-Juanes F, González-Avila M, Cembrero-Fuciños D, Herrero-Hernández A, González-Buitrago JM, Muñoz-Bellido JL. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48:2110–2115. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02215-09. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 46. What is next generation sequencing? Behjati S, Tarpey PS. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed. 2013;98:236–238. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2013-304340. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 47. A new method for sequencing DNA. Maxam AM, Gilbert W. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977;74:560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 48. Molecular biomarkers for neuromuscular disorders - challenges and future perspectives. Mroczek M, Machoń L, Filipczyńska I. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2019;53:173–180. doi: 10.5603/PJNNS.a2019.0023. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 49. The application of radiomics in predicting gene mutations in cancer. Qi Y, Zhao T, Han M. Eur Radiol. 2022;32:4014–4024. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08520-6. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 50. Bioinformatics mentorship in a resource limited setting. Jjingo D, Mboowa G, Sserwadda I, et al. Brief Bioinform. 2022;23:0. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab399. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 51. CRISPR-Cas9: A history of its discovery and ethical considerations of its use in genome editing. Gostimskaya I. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2022;87:777–788. doi: 10.1134/S0006297922080090. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 52. Visualizing the future of molecular graphics. Olson AJ, Pique ME. SAR QSAR Environ Res. 1998;8:233–247. doi: 10.1080/10629369808039142. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 53. Genome sequencing in the clinic: the past, present, and future of genomic medicine. Prokop JW, May T, Strong K, et al. Physiol Genomics. 2018;50:563–579. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00046.2018. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 54. Improving helminth genome resources in the post-genomic era. Doyle SR. Trends Parasitol. 2022;38:831–840. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2022.06.002. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 55. Use of antibodies and immunoconjugates for the therapy of more accessible cancers. Sharkey RM, Goldenberg DM. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60:1407–1420. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2008.04.011. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 56. Ethical and legal implications of the use of molecular biology in the clinic. Alonso Bedate C. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2005;18 Suppl 1:1137–1143. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2005.18.s1.1137. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- View on publisher site
- PDF (294.1 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections

Top 50 Research Topics of Microbiology
Table of Contents
Microbiology
The microbiology sector has seen huge development over the years to what it is now. You might be well aware that our earth’s surface consists of a huge microbial diversity and these wide microbial communities are present in all nooks of the earth. They offer several services to our environment. Without microbial communities, the whole earth will be a different place to live in. This is the reason microbiological research is so vital.
Microbiology is one of the very actively researched grounds, that deal with the study of microorganisms starting from the eukaryotic fungi to single celled and various cell cluster organisms. Various courses like B.Sc., M. Sc., M. Phil and Ph.D in subjects like Microbiology , Biotechnology and Molecular Biology, students are doing projects for their thesis. Excluding these, students from other courses including B. Tech, M. Tech courses in Biotechnology , paramedical courses like Pharmacy (B. Pharm. and M. Pharm.) and even Medical are searching projects or thesis topics for microbiology. If you are thinking of starting a research or project work in microbiology, then you must be searching for a good topic. So we planned to make it somewhat simple and easy for you.
This article discusses about some of the top and current research topics on microbiology. Before coming to the lists of topics let’s have a brief discussion on some of the important and key tips that we should consider before finalizing a topic.
- We should remain more focused on our investigation which will help us in planning a very clear experiment and in getting very useful and pertinent data.
- We should choose a topic which will get easily manageable within the given time frame.
- One of the best tips is to initiate by formulating a hypothesis and then confirming it.
- The rate of success or failure depends on how well you are versed with the methodology.
We also provide Labmonk notes on some subjects on our platform. Click here to check out . If you are interested to share your notes on this platform please contact us.
Click the page numbers below to read more on this topic.
12 thoughts on “Top 50 Research Topics of Microbiology”
Thank you for sharing, fantastic blog…
I like this site its a master peace ! .
was helpful thanks
I need Bsc research titel
Yes,I interested in discussion
Yes, I interested in microbiology discussion
Can anyone suggest a topic for research in Microbiology!
It’s indeed fantastic!
Labmonk is like Alexandra Elbakyan of India… Breaking barriers for learners… More to go Monk
Hello sir Research topic for microbiology and study of microbiology
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Collection 12 March 2023
Top 100 in Microbiology - 2022
This collection highlights our most downloaded* microbiology papers published in 2022. Featuring authors from around the world, these papers showcase valuable research from an international community.
You can also view the top papers across various subject areas here .
*Data obtained from SN Insights, which is based on Digital Science's Dimensions.
mRNA vaccine-induced antibodies more effective than natural immunity in neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 and its high affinity variants
- Dominic Esposito

Identification of ADS024, a newly characterized strain of Bacillus velezensis with direct Clostridiodes difficile killing and toxin degradation bio-activities
- Michelle M. O’Donnell
- James W. Hegarty
- Laurent Chesnel
Infections with the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant exhibit fourfold increased viral loads in the upper airways compared to Alpha or non-variants of concern
- Christian J. H. von Wintersdorff
- Jozef Dingemans
- Paul H. M. Savelkoul
Lockdown measures during the COVID-19 pandemic strongly impacted the circulation of respiratory pathogens in Southern China
- Heping Wang
- Yuejie Zheng
- Wenjian Wang
Detection of human pathogenic bacteria in rectal DNA samples from Zalophus californianus in the Gulf of California, Mexico
- Francesco Cicala
- David Ramírez-Delgado
- Alexei F. Licea-Navarro
High rates of plasmid cotransformation in E. coli overturn the clonality myth and reveal colony development
- Delia Tomoiaga
- Jaclyn Bubnell
- Paul Feinstein
Antiviral effect of cetylpyridinium chloride in mouthwash on SARS-CoV-2
- Hirofumi Sawa
Genesis of fecal floatation is causally linked to gut microbial colonization in mice
- Syed Mohammed Musheer Aalam
- Daphne Norma Crasta
- Nagarajan Kannan
Incidence of nephrotoxicity associated with intravenous colistimethate sodium administration for the treatment of multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterial infections
- Svetlana Sadyrbaeva-Dolgova
- Ricardo García-Fumero
- Carmen Hidalgo-Tenorio
A derived honey bee stock confers resistance to Varroa destructor and associated viral transmission
- Thomas A. O’Shea-Wheller
- Frank D. Rinkevich
- Kristen B. Healy
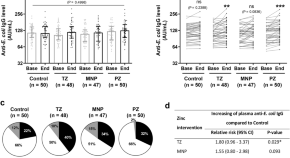
Daily preventive zinc supplementation increases the antibody response against pathogenic Escherichia coli in children with zinc insufficiency: a randomised controlled trial
- Chidchamai Kewcharoenwong
- Myint Myint Sein
- Ganjana Lertmemongkolchai
Ozone exposure upregulates the expression of host susceptibility protein TMPRSS2 to SARS-CoV-2
- Kshitiz Paudel
- Yogesh Saini
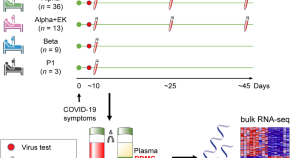
Immune transcriptome analysis of COVID-19 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 variants carrying the E484K escape mutation identifies a distinct gene module
- Hye Kyung Lee
- Ludwig Knabl
- Lothar Hennighausen

PET microplastics affect human gut microbiota communities during simulated gastrointestinal digestion, first evidence of plausible polymer biodegradation during human digestion
- Alba Tamargo
- Natalia Molinero
- M. Victoria Moreno-Arribas
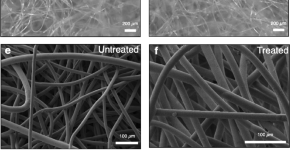
Efficacy of antimicrobial and anti-viral coated air filters to prevent the spread of airborne pathogens
- Rowan Watson
- Morwenna Oldfield
- Felicity de Cogan
Construction of SARS-CoV-2 virus-like particles in plant
- Ki-Beom Moon
- Jae-Heung Jeon
- Hyun-Soon Kim
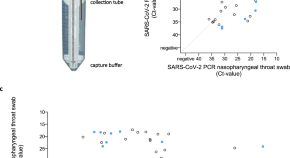
SARS-CoV-2 RNA in exhaled air of hospitalized COVID-19 patients
- Lisa Kurver
- Corné H. van den Kieboom
- Marien I. de Jonge
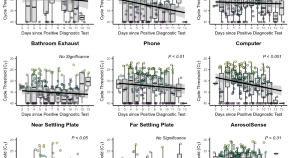
Longitudinal analysis of built environment and aerosol contamination associated with isolated COVID-19 positive individuals
- Patrick F. Horve
- Leslie G. Dietz
- Kevin G. Van Den Wymelenberg
Real-time tracking of bioluminescent influenza A virus infection in mice
- Hannah Bryant
- Jonathan O. Rayner
Survival of SARS-CoV-2 and bovine coronavirus on common surfaces of living environments
- Maiko Watanabe
- Takahiro Ohnishi
- Yukiko Hara-Kudo
Alteration of barrier properties, stratum corneum ceramides and microbiome composition in response to lotion application on cosmetic dry skin
- Barry Murphy
- Sally Grimshaw
- Andrew E. Mayes
Evaluation of microbiome enrichment and host DNA depletion in human vaginal samples using Oxford Nanopore’s adaptive sequencing
- Mike Marquet
- Janine Zöllkau
- Christian Brandt
Health improvements of type 2 diabetic patients through diet and diet plus fecal microbiota transplantation
- Zhifan Hong
- Jiayin Wang
Isolation, characterization and comparative genomics of potentially probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strains from Indian foods
- Sarvesh Surve
- Dasharath B. Shinde
- Ram Kulkarni

RT-qPCR-based tests for SARS-CoV-2 detection in pooled saliva samples for massive population screening to monitor epidemics
- Michał Różański
- Aurelia Walczak-Drzewiecka
- Jarosław Dastych
Gut microbiota and BMI throughout childhood: the role of firmicutes, bacteroidetes, and short-chain fatty acid producers
- Timothy A. Houtman
- Henrik A. Eckermann
- Carolina de Weerth
Bimodal distribution pattern associated with the PCR cycle threshold ( Ct ) and implications in COVID-19 infections
- Donna E. Hansel

Associations of neurotransmitters and the gut microbiome with emotional distress in mixed type of irritable bowel syndrome
- Zahra A. Barandouzi
- Joochul Lee
- Xiaomei S. Cong
Mild chronic exposure to pesticides alters physiological markers of honey bee health without perturbing the core gut microbiota
- Hanine Almasri
- Joanito Liberti
- Luc P. Belzunces
Pathology and virology of natural highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N8 infection in wild Common buzzards ( Buteo buteo )
- Valentina Caliendo
- Lonneke Leijten
- Thijs Kuiken
First-in-class trispecific VHH-Fc based antibody with potent prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 and variants
- Allison Titong
- Sachith Gallolu Kankanamalage
Impact of long-term dietary habits on the human gut resistome in the Dutch population
- Paul B. Stege
- Joost Hordijk
- Fernanda L. Paganelli
Metagenomic sequencing for detection and identification of the boxwood blight pathogen Calonectria pseudonaviculata
- Marcela A. Johnson
- Boris A. Vinatzer
Strain-level profiling of viable microbial community by selective single-cell genome sequencing
- Masahito Hosokawa
- Taruho Endoh
- Haruko Takeyama
Collective effects of human genomic variation on microbiome function
- Felicia N. New
- Benjamin R. Baer
- Ilana L. Brito
Glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides (GBHs) induce phenotypic imipenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Balázs Kriszt
- Edit Kaszab
Apical-out airway organoids as a platform for studying viral infections and screening for antiviral drugs
- Georgios Stroulios
- Tyler Brown
- Salvatore Simmini
The human milk microbiome aligns with lactation stage and not birth mode
- Katriona E. Lyons
- Carol-Anne O.’ Shea
- Catherine Stanton
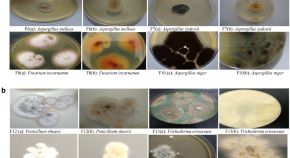
Characterization and phylogeny of fungi isolated from industrial wastewater using multiple genes
- Blessing Amaka Ezeonuegbu
- Machido Dauda Abdullahi
- Gaber El-Saber Batiha
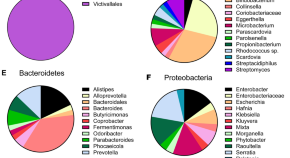
Characterizing the mucin-degrading capacity of the human gut microbiota
- Janiece S. Glover
- Taylor D. Ticer
- Melinda A. Engevik
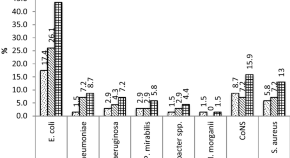
Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of urinary tract infection among pregnant women attending Hargeisa Group Hospital, Hargeisa, Somaliland
- Abdikhaliq Hussein Ali
- Dawit Yihdego Reda
- Moges Desta Ormago
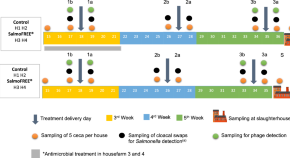
The gut microbiota of chickens in a commercial farm treated with a Salmonella phage cocktail
- Viviana Clavijo
- Tatiana Morales
- Alejandro Reyes Muñoz
Persistent Spike-specific T cell immunity despite antibody reduction after 3 months from SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2-mRNA vaccine
- Chiara Agrati
- Concetta Castilletti
- INMI COVID-19 Vaccine Study Group
Individual-based modeling reveals that the COVID-19 isolation period can be shortened by community vaccination
- Chayanin Sararat
- Jidchanok Wangkanai
- Charin Modchang
Intranasal vaccination of hamsters with a Newcastle disease virus vector expressing the S1 subunit protects animals against SARS-CoV-2 disease
- Manolo Fernández Díaz
- Katherine Calderón
- COVID-19 Working Group in Perú
Changes in the stool and oropharyngeal microbiome in obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Laura Domènech
- Jesse Willis
- Raquel Rabionet
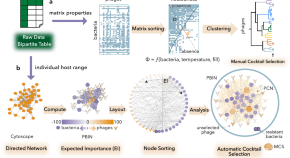
Systematic analysis of putative phage-phage interactions on minimum-sized phage cocktails
- Felipe Molina
- Manuel Menor-Flores
- Pilar García
The impact of antimicrobial stewardship program designed to shorten antibiotics use on the incidence of resistant bacterial infections and mortality
- Ling-Ju Huang
- Su-Jung Chen
- Fu-Der Wang
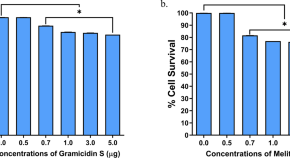
Gramicidin S and melittin: potential anti-viral therapeutic peptides to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection
- Mohammed Ghalib Enayathullah
- Yash Parekh
- Mohammed M. Idris
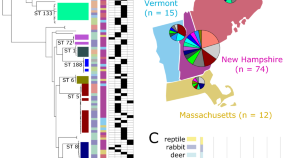
Shared antibiotic resistance and virulence genes in Staphylococcus aureus from diverse animal hosts
- Spencer A. Bruce
- Joshua T. Smith
- Cheryl P. Andam
First detection of Hedgehog coronavirus 1 in Poland
- Małgorzata Pomorska-Mól
- Jakub J. Ruszkowski
- Katarzyna Domanska-Blicharz
Vulnerability of SARS-CoV-2 and PR8 H1N1 virus to cold atmospheric plasma activated media
- Osvaldo Daniel Cortázar
- Ana Megía-Macías
- Eduardo Gómez-Casado
Excretion and viability of SARS-CoV-2 in feces and its association with the clinical outcome of COVID-19
- Cristina Cerrada-Romero
- Judith Berastegui-Cabrera
- Javier Sánchez-Céspedes
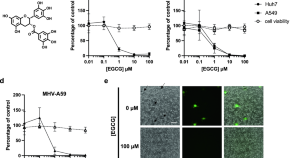
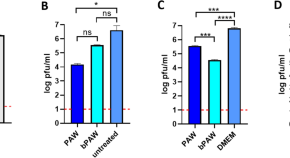
The green tea catechin EGCG provides proof-of-concept for a pan-coronavirus attachment inhibitor
- Emmanuelle V. LeBlanc
- Che C. Colpitts
The gut virome in two indigenous populations from Malaysia
- Chuen Zhang Lee
- Muhammad Zarul Hanifah Md Zoqratt
- Sadequr Rahman
High prevalence of antibiotic resistance in pathogenic foodborne bacteria isolated from bovine milk
- Sima Hassani
- Mir-Hassan Moosavy
- Zahra Barabadi
Aged related human skin microbiome and mycobiome in Korean women
- Hye-Jin Kim
- Woo Jun Sul
Potential cannabidiol (CBD) repurposing as antibacterial and promising therapy of CBD plus polymyxin B (PB) against PB-resistant gram-negative bacilli
- Nathália Abichabki
- Luísa V. Zacharias
- Leonardo N. Andrade
Systematic evaluating and modeling of SARS-CoV-2 UVC disinfection
- Sebastian Freeman
- Karen Kibler
Nasal-spraying Bacillus spores as an effective symptomatic treatment for children with acute respiratory syncytial virus infection
- Dien Minh Tran
- Tu Thanh Tran
- Anh Thi Van Nguyen
Multi-angle meta-analysis of the gut microbiome in Autism Spectrum Disorder: a step toward understanding patient subgroups
- Kiana A. West
- Xiaochen Yin
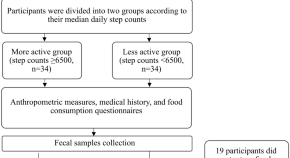
Increased physical activity improves gut microbiota composition and reduces short-chain fatty acid concentrations in older adults with insomnia
- Faiga Magzal
- Tamar Shochat
- Maayan Agmon
Characterisation and natural progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection in ferrets
- Gough G. Au
- Glenn A. Marsh
- Seshadri S. Vasan
Genomic epidemiological analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae from Portuguese hospitals reveals insights into circulating antimicrobial resistance
- Anton Spadar
- Jody Phelan
- Taane G. Clark
Human milk oligosaccharide-sharing by a consortium of infant derived Bifidobacterium species
- Clodagh Walsh
- Jonathan A. Lane
- Rita M. Hickey
Impact of urban structure on infectious disease spreading
- Javier Aguilar
- Aleix Bassolas
- Adam Sadilek
Indoor green wall affects health-associated commensal skin microbiota and enhances immune regulation: a randomized trial among urban office workers
- L. Soininen
- M. I. Roslund
- ADELE research group
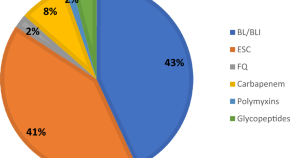
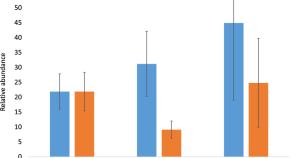
Correlation between antibiotic consumption and the occurrence of multidrug-resistant organisms in a Malaysian tertiary hospital: a 3-year observational study
- Sin Yee Tan
- Rahela Ambaras Khan
- Athirah Bakhtiar
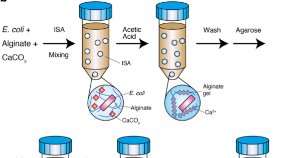
Agarose gel microcapsules enable easy-to-prepare, picolitre-scale, single-cell genomics, yielding high-coverage genome sequences
- Hiroyoshi Aoki
- Yuki Masahiro
- Yutaka Yamagata
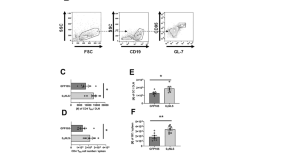
HSV-1 0∆NLS vaccine elicits a robust B lymphocyte response and preserves vision without HSV-1 glycoprotein M or thymidine kinase recognition
- Grzegorz B. Gmyrek
- Amanda N. Berube
- Daniel J. J. Carr
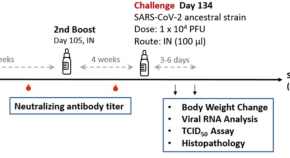
Protection of hamsters challenged with SARS-CoV-2 after two doses of MVC-COV1901 vaccine followed by a single intranasal booster with nanoemulsion adjuvanted S-2P vaccine
- Yi-Jiun Lin
- Meei-Yun Lin
- Chia-En Lien
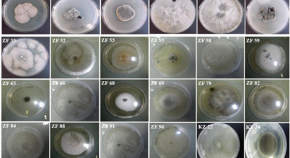
Anti- Pseudomonas aeruginosa activity of a C 16 -terpene dilactone isolated from the endophytic fungus Neofusicoccum luteum of Kigelia africana (Lam.)
- Olusola Bodede
- Mamokoena Kuali
- Roshini Govinden
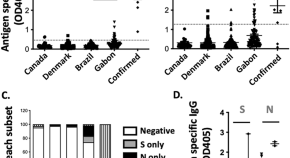
Cross-reactive immunity against SARS-CoV-2 N protein in Central and West Africa precedes the COVID-19 pandemic
- Jannie Pedersen
- Ismaël Hervé Koumakpayi
- Hugues Fausther-Bovendo
Genome sequence and characterization of Streptomyces phage Pablito, representing a new species within the genus Janusvirus
- Véronique Ongenae
- Joana Azeredo
- Dennis Claessen
Non-cytopathic herpes simplex virus type-1 isolated from acyclovir-treated patients with recurrent infections
- Subrata Roy
- Soumi Sukla
- Subhajit Biswas
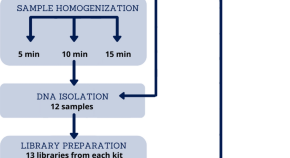
The standardisation of the approach to metagenomic human gut analysis: from sample collection to microbiome profiling
- Natalia Szóstak
- Agata Szymanek
- Anna Philips

Transmission of B.1.617.2 Delta variant between vaccinated healthcare workers
- Steven A. Kemp
- Mark T. K. Cheng
- Ravindra K. Gupta
Mobile phones are hazardous microbial platforms warranting robust public health and biosecurity protocols
- Matthew Olsen
- Rania Nassar
- Lotti Tajouri

Synthesis of new series of quinoline derivatives with insecticidal effects on larval vectors of malaria and dengue diseases
- Kadarkarai Murugan
- Chellasamy Panneerselvam
- Jiang-Shiou Hwang
Prevalence and characterisation of antimicrobial resistance genes and class 1 and 2 integrons in multiresistant Escherichia coli isolated from poultry production
- Przemysław Racewicz
- Michał Majewski
- Zofia E. Madeja
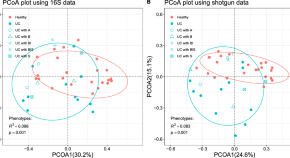
16S rRNA and metagenomic shotgun sequencing data revealed consistent patterns of gut microbiome signature in pediatric ulcerative colitis
- Wenxuan Zuo
- Beibei Wang
- Fengzhu Sun

Genomic and functional characterization of bacteriocinogenic lactic acid bacteria isolated from Boza, a traditional cereal-based beverage
- Luciano Lopes Queiroz
- Christian Hoffmann
- Svetoslav Dimitrov Todorov
Natural and after colon washing fecal samples: the two sides of the coin for investigating the human gut microbiome
- Elisabetta Piancone
- Bruno Fosso
- Graziano Pesole

Assessment of the frequency of coughing and sneezing triggered by nasopharyngeal swabbing in the pandemic setting
- Cosmin Andrei Cismaru
- Sergiu Chira
- Ioana Berindan-Neagoe
Risk of Plasmodium falciparum infection in south-west Burkina Faso: potential impact of expanding eligibility for seasonal malaria chemoprevention
- Jean Baptiste Yaro
- Alfred B. Tiono
- Anne L. Wilson
Understanding the dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in Ontario, Canada: a modeling study
- Anita T. Layton
- Mehrshad Sadria
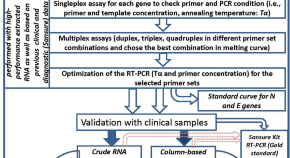
Development and validation of cost-effective one-step multiplex RT-PCR assay for detecting the SARS-CoV-2 infection using SYBR Green melting curve analysis
- Shovon Lal Sarkar
- A. S. M. Rubayet Ul Alam
- M. Anwar Hossain
Prediction of dengue fever outbreaks using climate variability and Markov chain Monte Carlo techniques in a stochastic susceptible-infected-removed model
- Tarun Kumar Martheswaran
- Hamida Hamdi
- Biswadeep Das
Lasiodiplodia theobromae as a causal pathogen of leaf blight, stem canker, and pod rot of Theobroma cacao in Malaysia
- Abd Rahim Huda-Shakirah
- Nik Mohd Izham Mohamed Nor
- Masratul Hawa Mohd

Transatlantic spread of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 by wild birds from Europe to North America in 2021
- V. Caliendo
- N. S. Lewis

Strain-specific interspecies interactions between co-isolated pairs of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa from patients with tracheobronchitis or bronchial colonization
- Meissiner Gomes-Fernandes
- Andromeda-Celeste Gomez
- Daniel Yero

Genomic epidemiology and emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in the United Arab Emirates
- Habiba Alsafar
- Mohammed Albreiki
- Andreas Henschel
Bioprocess development for bacterial cellulose biosynthesis by novel Lactiplantibacillus plantarum isolate along with characterization and antimicrobial assessment of fabricated membrane
- Ahmed K. Saleh
- Hamada El-Gendi
- Yasser R. Abdel-Fattah
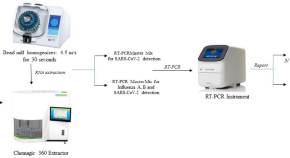
Clinical validation of a multiplex PCR-based detection assay using saliva or nasopharyngeal samples for SARS-Cov-2, influenza A and B
- Nikhil S. Sahajpal
- Ashis K. Mondal
- Ravindra Kolhe
Optimized production and fluorescent labeling of SARS-CoV-2 virus-like particles
- Manon Gourdelier
- Jitendriya Swain
- Delphine Muriaux
Agr Quorum Sensing influences the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway in Clostridium autoethanogenum
- Pawel Piatek
- Christopher Humphreys
- Klaus Winzer
Enhanced antibacterial effect of a novel Friunavirus phage vWU2001 in combination with colistin against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
- Phitchayapak Wintachai
- Narumon Phaonakrop
- Duncan R. Smith
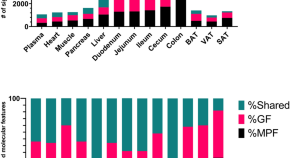
Tissue-wide metabolomics reveals wide impact of gut microbiota on mice metabolite composition
- Ville M. Koistinen
- Kati Hanhineva

Gut microbiota analysis of Blenniidae fishes including an algae-eating fish and clear boundary formation among isolated Vibrio strains
- Masa-aki Yoshida
- Takuma Tanabe
- Makoto Kawamukai
Gut dysbiosis is associated with acceleration of lupus nephritis
- Giancarlo R. Valiente
- Armin Munir
- Wael N. Jarjour
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

COMMENTS
This collection from the FEMS journals presents the latest high-quality research in six key topic areas of microbiology that have an impact across the world. All of the FEMS journals aim to serve the microbiology community with timely and authoritative research and reviews, and by investing back into the science community.
Research Open Access 23 Oct 2024 npj Biofilms and Microbiomes Volume: 10, P: 112 Molecular mechanisms of re-emerging chloramphenicol susceptibility in extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing ...
Remember to choose a topic that aligns with your interests and research goals. These topics offer a range of exciting avenues for exploration in the field of medical microbiology. Recommended articles. 10 benefits of studying microbiology; 43 Project Topics on Food Microbiology: Latest; 33 Microbiology Project Topics: You haven't thought of
Important notice: this title will transition to a Subscribe to Open (S2O) model from 2025. With sufficient institutional subscriptions, content published from 15th February 2025 will be Open Access. For more information on how this may affect your submission, see our FAQs.Journal of Medical Microbiology is the go-to interdisciplinary journal for medical, dental and veterinary microbiology, at ...
Microbiology is the study of microscopic organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, archaea, fungi and protozoa. This discipline includes fundamental research on the biochemistry, physiology, cell ...
The most cited microbiology journal which advances our understanding of the role microbes play in addressing global challenges such as healthcare, food security, and climate change. ... 1,810 Research Topics Guest edit your own article collection Suggest a topic. Submission. null. Submission
Read an essential collection of papers showcasing high-quality content from across the five FEMS Journals, which together provide an overview of current research trends in microbiology. Follow the topic area links below for access to articles: Antimicrobial Resistance; Environmental Microbiology; Pathogenicity and Virulence
Infections Part 1 of 3. Peter A. Riley, in Medicine, 2013 Introduction. Diagnostic medical microbiology is undergoing a rapid change as advances in molecular technology and automated techniques are becoming available in most laboratories. However, the backbone of most diagnostic work still relies on the older techniques of microscopy, culture and serology, which are efficient and comparatively ...
A pilot study examining periodontally healthy middle-aged humans and monkeys display different levels of alveolar bone resorption, gingival inflammatory infiltrate, and salivary microbiota profile
Raoult and colleagues review recent developments in clinical microbiology, including the development of mass spectrometry-based diagnostics and point-of-care tests, which might change clinical ...
Reviews and Research in Medical Microbiology is a quarterly review journal which provides a balanced coverage of the whole field of medical microbiology. The Journal publishes state-of-the art reviews, mini-reviews, case presentations and original research from on-going research of the latest developments and techniques in medical microbiology, virology, mycology, parasitology, clinical ...
Medical microbiology is a subset of microbiology that deals with microorganisms (including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites) colonizing or infecting humans. Through examination of their phenotypic features (e.g., shape, structure, reproduction, physiology, and metabolism, etc.), medical microbiology aims to identify microorganisms of interest, diagnose associated infectious diseases ...
This page lists various research-topics about microbiology to help researchers find relevant research articles. ... The objective of this Research Topic is to highlight the growing knowledge of these beneficial plant interactions and their direct impact on plant and ecosystem performance, as well as open questions and challenges. ...
The most cited microbiology journal which advances our understanding of the role microbes play in addressing global challenges such as healthcare, food security, and climate change. ... Research Topics See all (1,809) Learn more about Research Topics. Footer. Guidelines. Author guidelines; Editor guidelines; Policies and publication ethics ...
Read an essential collection of papers showcasing high-quality content from across the five FEMS Journals, which together provide an overview of current research trends in microbiology. Follow the topic area links below for access to articles: Antimicrobial Resistance; Environmental Microbiology; Pathogenicity & Virulence; Biotechnology ...
GMT-containing genomic islands in Vibrio parahaemolyticus and other diverse bacteria serve as a stockpile of immune and anti-phage defence systems, antibiotic-resistance genes and offensive tools ...
Additionally, continued investigation into the ethical and legal issues connected to the application of molecular and genomic techniques in medical microbiology will be necessary . Conclusions. Medical microbiology is undergoing a revolution thanks to molecular and genomic techniques.
Advances vaccine development and drug discovery by exploring bacterial pathogenesis, immune response, and microbial resistance to help improve global health and provide equitable treatment
Excluding these, students from other courses including B. Tech, M. Tech courses in Biotechnology, paramedical courses like Pharmacy (B. Pharm. and M. Pharm.) and even Medical are searching projects or thesis topics for microbiology. If you are thinking of starting a research or project work in microbiology, then you must be searching for a good ...
This collection highlights our most downloaded* microbiology papers published in 2022. Featuring authors from around the world, these papers showcase valuable research from an international community.