

Which program are you applying to?
Medical school personal statement examples.
Get accepted to your top choice medical school with your compelling essay.
THE TOP 10 MEDICAL SCHOOLS
HAVE AN AVERAGE ACCEPTANCE RATE OF 5.3%

A GREAT MEDICAL SCHOOL PERSONAL STATEMENT IS KEY IN THE APPLICATION PROCESS
If you want to get into the best school, you need to stand out from other applicants.
U.S. News reports the average medical school acceptance rate at the top 100 med schools at 6.35% , but our med school clients enjoy an 85% ACCEPTANCE RATE .
How can you separate yourself from the competition successfully? By creating a great personal statement.
body:nth-child(2) > div.body-wrapper > main:nth-child(3) > div:nth-child(1) > div:nth-child(1) > div:nth-child(1) > div:nth-child(1) > div.row-fluid-wrapper.row-depth-1.row-number-6 > div:nth-child(1) > div:nth-child(1) > div.row-fluid-wrapper.row-depth-1.row-number-7 > div:nth-child(1) > div:nth-child(1) > #hs_cos_wrapper_dnd_area-module-12 > #hs_cos_wrapper_dnd_area-module-12_ > h2:nth-child(2)">Medical School Sample Personal Statements and Essays
Here we present medical school personal statement examples to give you ideas for your own essay.
Pay close attention to the consistent format of these effective personal statements:
ENGAGING INTRODUCTION / UNIFYING THEME / COMPELLING CONCLUSION
Give the admissions committee readers a clear picture of you as an individual, a student, and a future medical professional. Make them want to meet you after they finish reading your essay.
Here's what you'll find on this page:
- How Sample Med School Essays Can Help You
- Before you Start Writing
- Writing Your Opening Paragraph
- Writing Your Body Paragraphs
- Writing Transitions
- Writing Your Conclusion
- Common Elements Between Personal Statements
Five Don'ts for Your Medical School Personal Statement
- Personal Statement Examples & Analysis
- Frequently Asked Questions
How can these sample med school essays help you?
You plan to become a physician, a highly respected professional who will have great responsibility over the health and well being of your future patients. How can you prove to the admissions committee that you have the intelligence, the maturity, the compassion, and the dedication needed to succeed in your goal?
The medical school personal statement examples below are all arguments in favor of top med schools accepting these applicants. And they worked. The applicants who wrote these essays were all accepted to top medical schools - most to multiple schools. They show a variety of experiences and thought processes that all led to the same outcome. However, while the paths to this decision point vary widely, these winning essays share several things in common.
As you read them, take note of how the stories are built sentence by sentence, paragraph by paragraph, adding to the evidence that the writer is worthy of acceptance. This evidence includes showing a sustained focus, mature self-reflection, and professional and educational experiences that have helped prepare the applicant to succeed.
As you write your medical school personal statement , include your most compelling, memorable and meaningful experiences that are relevant to your decision to become a doctor. Each sentence should add to the reader’s understanding of who you are, what your strengths are, and why you will make an outstanding physician. Your resulting essay will help the adcom appreciate your intellectual and psychological strengths as well as your motivations, and conclude that you are worthy of acceptance into a top medical school.
Techniques for creating successful medical school personal statements
Before you start writing your med school personal statement.
Before you start writing your medical school personal statement you will need to choose a topic that will reflect who you are and engage the reader. There are a few strong ways to proceed. Try freewriting with a few of the following topic ideas.
Why medicine? Do you have a personal experience that made you certain about being a physician? How, when, did you know this was the right career for you? Is there a doctor you know (or knew) who emulates an altruistic moral character, someone who won your deepest respect? Can you show this person in action or describe them as they model inherent qualities, those for which you will strive as a physician?
How has a clinical experience been a real growth moment for you? Can you tell that story? Sometimes a clinical experience is deeply personal, something experienced by you or by someone in your family. Sometimes a clinical experience is about a patient whose situation taught you something deeply valuable, something honestly insightful about what good care means, about humanity, about empathy, about compassion, about community, about advantage and disadvantage, about equity and inclusion.
Choose an experience outside the comfort of your own community, an experience where you were the outsider (uncertain, facing ambiguity) and this experience brought about a fresh, resonant understanding of yourself and others, an understanding that made you grow as a person, and perhaps brought about humility or joy in light of this geographical or cultural dislocation. Often this prompt includes traveling to other countries. Yet, it could work just as beautifully discovering people in close places that were previously unfamiliar to you – the shelter in the next town over, a foster home for medically unstable children, the day you witnessed food insecurity firsthand at a local church and decided to do something about disparity.
Read other successful personal statements in guides and publications. You can read sample personal statements that work here: medical school personal statement examples
The prompts above have great possibilities to be successful because they locate experiences that require better than average human understanding and insight. When we re-convey a moving human experience well, we tell a story that aims to bring us together, unite us in our common humanity. Telling powerful stories about humanity, in the end, presents your deeper attributes to others and demonstrates your capacity to feel deeply about the human condition.
Be careful how often you use the first person pronoun, though you may use it. Revise for clarity many more times than you might do in other writing moments. Choose precise vocabulary that sounds like you, and, of course, revise so that you present to your readers the most pristinely grammatical you.
Once you’ve looked at the sample medical school personal statements in the link above, try freewriting again according to one of the themes listed that applies to you. For instance, perhaps your prior freewriting aimed to describe a moment in your life that seeded your interest in medicine. Great. Save that file. Now, start again with a different topic, perhaps one from the linked page of sample personal statements. For instance, let your freewriting explore the time you traveled to another country to participate in a public health mission. What person immediately comes to mind? Hopefully this person is quite different from you in identity and culture. Make sure this comes across. Describe the scene when you first encountered this person. What happened? Tell that story. Why do you think you remember this person so vividly? Did the experience challenge you? Did you learn something deeper and perhaps more complex about humanity, about culture, about your own assumptions about humanity? Hopefully, you grew from this experience. How did you grow? What do you now understand that you did not understand before having had this experience? Hindsight may very well bring about perspective that demonstrates that you now understand the value of that human encounter.
Here is a cautionary bit of advice about writing about childhood. Yes, it is relatively common to have had a formidable experience in childhood about illness, health, healthcare, medicine or doctors. Right? Most of us have had at least one critical health issue in our own family when still a child. Sometimes it is absolutely true that a moment in childhood began your interest in healthcare.
One may have had a diagnosis as a child that turned one’s life path toward being health-aware. For instance, are you a juvenile-onset, Type I diabetic? Do you have a cognitive or physical disability? Were you raised in a home with someone who had a critical illness or disability? Did a sibling, parent or grandparent get gravely sick when you were young?
Upon writing-up any of these situations for your personal statement, there is a catch-22. For medical school application activities, the rule of thumb is “nothing from high school.” So why then is it sometimes a good idea to write about a childhood situation in a personal statement? The answer has to do with the uniqueness of your story and the quality of hindsight through which you narrate it.
Let us slow down for a moment on the issue of writing about childhood. Typically, traditional applicants to medical school are steadfastly dedicated to their academic and pre-professional aims. Science curriculum, especially pre-med curriculum, is demanding and rigorous, and it trains science students to excel in empirical thinking and assessment.
Sometimes, when asked to write a personal essay, hard core science students feel the rug pulled out from under them. Are you more confident and meticulous about action steps and future plans than you are confident about being a sage looking back on your life? Chances are your answer is “yes.”
Of course you can write; you’re a smart person and a very good student. Yet, writing a heartfelt, perceptive essay about yourself or an aspect of your life for an application to medical school is unnerving even as you understand why your application might benefit from story-telling. Yes, your application should benefit from your engaging, authorial presence in the essay. An application that lacks this is wholly at a disadvantage.
Perhaps you are gravitating to the choice to share a story about your childhood.
For instance, what if you sat down to free-write the following prompt:
Draft an essay about a childhood experience that ingrained medicine as one of your inherent interests. Do so in a manner that demonstrates the value of hindsight while telling it.
Is it hard to stay calm about this prompt right now even though this prompt is precisely what could make your personal statement successful? The idea of this prompt is what many successful applicants have written well, and you can too. Why not seek professional guidance for your personal essay? Accepted has consultants who advise applicants through this process. We advise you on the whole process of developing a successful idea for an essay, help you mine your experiences, outline your strongest ideas, and after you’ve written them up, edit your drafts. You can view these personal statement services here: Essay Package
Back to tips. The key to writing a personal statement that frames a moment in childhood well is to stand firmly in the present and stay descriptive and perceptive. Write up that experience trusting you have insight. Quite a bit of time has passed since then, and that distance has given you the opportunity to see things a little differently now.
Let’s presume you want to write about how as a child you had an older sibling with a cognitive impairment. You and your family witnessed time and again doors being shut, so to speak, on his ability to be included in school events or community events.
Free writing A: My older brother, G, had moderate cognitive impairment. He was never given field time in soccer games. When this happened, G cried. When this happened, I cried and felt hurt by how much time my parents spent trying to calm him down, eventually leaving the field, holding him close and bringing us back home, another Saturday wrecked.
Example A has no benefit of hindsight.
Free writing B (with some hindsight): My older brother, G, had moderate cognitive impairment. Most of the time, kids were kind to him. “Hey G, how are you, man?,” they would say and high-five him. Most kids greeted him, offered him snacks and a seat on the sideline blanket. It was touching to see him included and seen at soccer games.
Further hindsight: G was rarely played in the game.
Reflective comment: No harm would have been done in letting him play. It’s clear to me now how much more work we each need to do about inclusion. Community-based team sports are pretty good about extending kindness at the sidelines, but that is not the same thing as letting all kids play in the game. I am still grateful for every kindness extended to my brother, but perhaps letting him play in the game would have demonstrated to kids and parents alike a deeper message about the importance of inclusion over winning. The coaches meant no harm, but that is precisely how unconscious bias plays. Afterall, community by its very definition is about inclusion.
Standing tall on this matter brings out a maturity and vocabulary to master this kind of personal writing that Free Writing A lacks. You don’t want to go back in time and join your younger self and narrate from that perspective. The “return” to your former child typically results in replicating a childlike emotional capacity – and chances are, that’s not you anymore. You’ve seen more. You’ve grown more. You’re now formally educated. You’re more skilled at making connections between ideas and experiences. You can narrate a scene or circumstance and attach awareness of what you realize now it means – like the over-narratives of documentaries where the author sheds true insight about the meaning of past events.
Most traditional applicants to medical school are just a few years older than teenagers.
When hindsight brings great clarity and insight to the significance of an experience, we demonstrate a keener maturity and an understanding that in authoring an experience we have a responsibility to demonstrate how a personal experience becomes a valuable portal to understanding the situation of others. Hindsight done well can be a stunningly beautiful and engaging narrative skill.
Perhaps you would rather write about a clinical experience? If you write about patients, change names, change gender, change some context to assure anonymity. Nearly all healthcare workers are concerned about telling patient stories because we worry about appropriating someone else’s experience, or feel we may not have the right, literally since HIPAA set rules on patients’ privacy rights in 1996. We should be concerned about telling patients’ stories; however, how we tell them is key in honoring them. When we honor patients and convey their stories to others we demonstrate the reciprocity of the professional relationship. Physicians no longer have a prescriptive, patrician role. Physicians are no longer sole authorities. Physicians and patients establish a reciprocal relationship, a two way street wherein a physician steps into a space of illness with the patient and walks with them, with the goal of healing, curing and advocating for them. When doctors tell stories, they establish that patients matter, that these encounters matter, that doctors think about patients and often learn from them.
How we write patient stories is best done humbly, of course. We can narrate a story that becomes exemplary for its insight and empathy – after all, insight and empathy are desirable traits of a physician. Be sure to show rather than tell, most of the time. Be sure to capture the sensory detail of people and place. For instance, is the patient sitting on a blue plastic chair under ultraviolet lights in the waiting room of a free clinic? Is a woman with her gray hair twisted in a bun wearing a cotton hospital gown, waiting against a concrete wall in a tiny examination room with the door open? (Setting makes a character more real.)
Finally, your story perspective, what you see and understand, becomes another way of revealing who you are.
How to write your opening paragraph:
A strong opening paragraph for a story begins “several pages in.” A strong story begins with you, the narrator, already standing in the ocean with water splashing at your knees. This is called a hook: “D began to bleed after the second attempt to start an intravenous line.”
Then, get the basic narrative facts down, the 5 W’s, the who, what, where, when and why, so your readers will not be confused: “She was a patient in the infusion clinic in the cancer pavilion of a major Boston hospital. She came to the clinic for her first round of chemotherapy.”
What else about this moment engaged you? Did D come to her appointment alone via an Uber ride? Why wasn’t anyone with her? How did that make you feel? Did the two of you hold a conversation while you were trying to start an IV? Why do you think she started to bleed? How did she respond when she saw you were having trouble starting this IV? Why didn’t she have a Medi-port yet? Here, you are building fuller context for her story. Don’t race through the scene; rather, build it, slowing down time, using images and sensory details to “paint” with your words. Smaller details, necessary ones, help you portray D as an individual.
“Semper Fidelis was tattooed on her forearm. ‘Thank you for your service,’ I said.”
“‘This cancer thing,’ she said, ‘this is nothing.’”
“D’s comment set me back. She had triple-negative breast cancer. She had blood running down her arm to her hand, between her fingers and onto a stiff, white pillow case on which she rested her arm. Triple-negative breast cancer was much more than nothing. In fact, it was very serious.”
What questions came to mind that provide several ways of reading this moment? Write them down. For instance,
- Did D not know about the gravity of her diagnosis?
- Was she steely and tough yet informed?
- Did she live through something much worse while enlisted as a Marine?
The questions themselves may wander too much to serve your personal statement as a succinct essay, which it needs to be. However, the answers to those questions may be exactly the additional content you need to develop this story’s acumen and perception as you demonstrate how getting to know the patient is a critical skill in order to help her. And now a theme is starting to come through: a doctor treats a patient, not a diagnosis. Voilà!
Moving forward: How does a doctor reframe clinical assumptions in this instance? What does a future doctor learn from a circumstance like this?
Notice in the example above that the writing is active, uses details, and vivid language.
This writer has a palpable connection to the moment. One key to choosing one experience over another for your personal statement is how visual and vivid your recollection is. Often, moments worth mining for meaning are easy to recollect because they still have unresolved messages that need to be understood. Writing experiences helps us find their meaning, their sense.
Notice as well, the scene above captures a moment of ambiguity, a concept particularly difficult for many health science professionals to embrace because there are multiple ways of looking at and understanding something. Stories send empiricism into the wind. People are not solely empirical. There is the self that is the body, which can be understood empirically, but there’s also the self that inhabits the body, the thinking/feeling/being and perceiving self. Stories are not about right answers. Stories attend to sentience and explore humanity. Patients’ lives are rife with uncertain moments, uncertain decisions, uncertain treatments, uncertain consequences, and uncertain outcomes. How does a physician engage with health uncertainty, understand it, and navigate it through pathways of humanity rather than pathways of diagnosis?
How does health care challenge you to grow in humanistic ways?
How to write your body paragraphs:
Once you have written a compelling scene, it might be a good idea to reflect upon why you were drawn to write about this experience in particular before your proceed. How does this scene illustrate meaningfully something worth explaining about becoming a physician? For instance, D’s scene was illustrative of an unexpected shift in perception that mattered when treating a patient with a serious cancer diagnosis. This unexpected shift happened to you, not to her. D’s been living with herself aplenty. Her point of view surprised you, not her, and reveals an incongruence between her perspective on her illness and yours.
Brief moments of ambiguity like this one can make us talk to each other, make us want to do something, can bring us to explore some further niche, specialty or research. Perhaps D brought you to peruse PubMed to research “Issues in Clinical Practice when Caring for Veterans” to see if you could find articles to help you help D and other veterans. Perhaps D’s comment was so truthful that you now volunteer with a veterans’ organization to scribe their stories for a war history museum? This “call to action” is a worthy story in a personal statement. Tell D’s story and conclude it with empathy and action. (Taking action to help is a demonstration of empathy.) Mindfully showing the experience with D as a catalyst to a path of action to help those under duress -- in distress, in crisis, or adrift in inequity -- matters.
Perhaps, follow this conclusion with a brief explanation of what principles now guide your humanistic path to medical school as long as they are principles that matter to your choice schools.
Here are a few things to avoid in writing your medical school personal statement. Avoid talking about your scholastic path in preparation for medical school in your essay. The essay is not a place to reiterate scholastic achievements, for instance, a high GPA, academic honors, academic awards, publications, or MCAT scores because they’re front and center in other areas of your application.
Instead, frame your medical school personal statement around a formidable experience that directly or indirectly led you to pursue medicine. This could be a struggle that you’ve overcome that demonstrates your fortitude (the story of a sociocultural disadvantage or disability), the first time you deeply understood the ramifications of health care disparities you will not forget. Likely, this would be a personal story about yourself or a family member, a clinical story or a mission trip, or a story about a patient from some other volunteer work that you’ve done.
Additional topic ideas for your personal statement: What is a successful doctor? What does a successful life as a doctor look like? What happens to your understanding of best practices when a patient’s situation makes a best practice unrealistic, and what is the remedy? What epiphany, small or large, resides in you now since having mined a critical, clinical experience? Do you see a difference in the way you respond to patients since having had this experience? How has clinical experience matured you, deepened your awareness of living? If a patient experience became a catalyst for you to branch out or deepen your healthcare exposure opportunities, talk about that too. What opportunities? Why?
Writing effective transitions:
You are now ready to proceed to a conclusion that leaves your readers, the admissions committee, with a lasting impression of you – your life, your mind, your character -- as a 21 st century physician.
Chances are, you’ll need to transition from the previous discussion of a time in the past to squarely speak about yourself here and now or in a comment toward the future.
Can you sum up your main idea for the past experience? Consider the benefit of using a word or phrase -- thus, just as, hence, accordingly, in the same way, correspondingly -- and present your central idea again but only in a few repetitive words (called parallelism) or with synonymous words, creating internal unity in the essay.
Be careful how you do this. The phrasing should feel necessary and fluid rather than reductive or even worse, phrasing that sounds like filler.
The shift you’re making is from then to now, or from then to now and to the future as in “all this is to say.” Would you benefit from a fact, a quote, a statistic, or an informed prediction on the state of medicine, public health, or the future of medicine?
Grammar tips:
Transitional words can indicate:
- a process: first, second, next, finally…
- time: by lunch time, that evening, two weeks later…
- spatial sequences: down the block, two miles west, one bed over…
- logic sequences: likewise, however, evidently, in other words…
- meta-thought: as I say this, looking back, I have nothing left to say…
If grammar and idea flow are a concern, have a look at Accepted’s editing services: Med School Essay Package
A consultant will walk you through the inception of an essay, an outline, and editing from first through final drafts, including suggestions for idea development and transitions from one idea to another.
How to write your conclusion:
A strong conclusion for your medical school personal statement can highlight the relevance of a timely issue (for instance, the physician shortage in the U.S.), make broader inferences about something you’ve already discussed (for instance, the broader implications of a particular health care disparity), or a call to action that you now embrace (for instance, community-based work that you did during the pandemic that now has become a central interest). Altruism, or understanding another’s disadvantaged situation, should not be represented in your conclusion as “ideas alone.” Commitment to serve others is not solely aspirational (“As physicians, we must do everything we can about inequity"), but a strong conclusion puts ideals into action (“I have joined Dr. T’s research team to conduct qualitative research about how social strata paradigms impact health care inequity”). Action in the conclusion should be associated with an experience shown earlier in the essay and culminate as a demonstration that you have already begun shaping your path in medicine. You are not waiting to begin but have already begun facing the challenges and responsibilities of future physicians. This kind of conclusion shows vision, maturity, commitment and character.
If the story in the body of your personal statement is about an experience, the conclusion should show your growth since then and keep in alignment how you’ve grown with the medical school values and missions of the majority of schools on your list. So, if you’re applying to top-tier allopathic schools, your growth may be in the depth and orientation of your recent research, or in having established a tighter link between your clinical experience and research.
If you’re applying to osteopathic schools, your growth should be in keeping with the osteopathic schools’ values and missions on your list and include recent hands-on experience, something with specific tasks and responsibilities, rather than shadowing, since shadowing is often seen as passive experience. It may be that you’ve become a licensed EMT and will work as an EMT in a relevant region or state during the gap year. It may be that you’ve been certified and now work as a harm reduction specialist for a particular organization in a particular city or county.
If you’re applying to both allopathic and osteopathic schools, each personal statement should align with the academic orientation of each pathway. Using the same personal statement for both AMCAS and AACOMAS applications is rarely a good idea.
Accepted offers help with the whole application process: Primary Application Package
Other elements that each essay below have in common:
Accepted provides sample medical school personal statements with titles classifying types of narratives that have potential for success. Applicants do have some freedom of choice in what topic will serve their essay best. Why only “some” freedom in topic for this personal essay? Because this essay is one tool you will use to reach a professional goal.
Not all essays help us reach professional goals. Writers of effective essays must take into account who will read them. Think about who your audience is. In this case, it’s a medical school admissions committee – not a friend, not a parent, not a peer. How will you write an essay on the same topic, let’s say a lab experience that went from bad to revelatory? You’d tell this story quite differently to your lab mates than you would to your professor, than you would to the president of your university, than you would in a grant application.
Here’s what can happen when the “audience” isn’t considered sufficiently when writing about a passion. Let’s say you love playing soccer, and played on a Division 3 team as an undergraduate. Let’s say it didn’t matter to you that the team was Division 3 as long as it meant you could get on the field and play through your undergraduate years. It’s quite possible that one can write well about playing soccer, but one must do so in such a way that the reader really believes and understands the parallel between doing what you love and a future in medicine. Otherwise, the writer may very well convey that they love soccer. However, when written without the focus that medical school admissions committees will be readers, the essay could end up conveying that the narrator really wants to be a soccer coach, not a doctor.
So, there’s only some freedom in topic and some freedom in writing approach - and the two must make sense together in order to facilitate accomplishing your goal.
There is no “one-size-fits-all” to writing a successful medical school personal statement. There are, however, aspects to the sample essays on this site that stand out.
First, each personal statement example is authored by someone who knows exactly what story they’re telling. No matter what their first draft looked like, by the time the final draft is ready to go, all fuzzy draft moments have been made lucid and engaging. All sections of the essay should have the polish and the same goals.
- Why am I telling this in this way?
- To what ends does each scene or moment speak?
- Have I revised enough to make every sentence demonstrate strong writing skills?
Each sample personal statement emphasizes narrative control, engages with a direct voice, has conclusive things to show and say, demonstrates logical steps in idea development, and presents effective framing of the composition as a well-written form that displays strong writing skills.
Even when an essay includes a “bookend” structure (a narrative structure that begins and ends with X, with middle content about Y), the story of Y (i.e. a mission trip in Mexico) is the primary story framed by the X bookend story (i.e. the love of running) to give ballast to the context in which this writer wants us to understand the mission trip as well, as a parallel story of challenge, commitment, exhilaration, exhaustion and necessity.
The same is true for stories that contain contrasts. If you’ve traveled ten mile or ten thousand miles, it is quite possible you’ve encountered different assumptions than your own about health care, health care access, trust, understanding of middle-class or first-world beliefs about health, understanding beliefs from poor and disadvantaged communities, illness, health care in contrast with a different cultural standard than what you’re used to, different beliefs about health care access, and a lack of or cautious trust in deference to doctors. (See the “Nontraditional Applicant” and “The Traveler.”) The key to this kind of essay is first demonstrating the contrasts between the two realities (yours and the patient’s reality) and their relative assumptions. Second, demonstrate an understanding of beliefs amid the two experiences and aim to reconcile their adverse assumptions.
However you proceed with the paragraph by paragraph progression of your medical school personal statement, be sure to see how there’s deeper intuition or knowledge associated with how the ideas progress. Do not repeat yourself, or reiterate a statement or idea unless you are clearly doing so for rhetorical emphasis.
Then, kiss your draft goodnight. Let it sit for two or three days, and return to it time and again with fresh eyes – to trim, tighten, clarify, improve tone and intention, and importantly, to make sure you have direct regard for your audience, who it is, what they’re looking for, and how you are the person whom they seek, as you maintain a tone and direction consistent with your goals and what you’re seeking from an admissions committee.
Many students focus on their own or family members’ medical conditions in their personal statements. The essay sometimes reads like a medical history. Taking this approach can hurt your application for several reasons: It may alert them to conditions that could impact your ability to perform in medical school, indicate that you lack boundaries by oversharing , or suggest a lack of maturity in focusing only on yourself and family – rather than on helping others or serving the community.
Anything you share in your personal statement can be brought up in your interview. If you share details of painful events, losses, or failures that you have not yet processed or come to terms with, that disclosure could come across as an invitation for the reader to pity you. Accepting long-term changes in our lives transforms us; we are constantly evolving through our experiences. Until you have integrated this information into your identity, depending on how impactful it was, you may not be able to use the experience to shed insight on yourself quite yet. Use negative experiences that are at least a year or older depending on how long it takes you to process and reflect. Most importantly, use them to show growth and resilience , not to create pity.
- DON’T demonstrate a lack of compassion or empathy. One of the creepiest essays I’ve ever read – it still sends shivers down my spine just thinking about it – was a student’s description of how much she enjoyed anesthetizing and removing the brains of mice. Her intention was to share her love of science, research, and learning but the feverish glee with which she described these procedures lacked compassion for the creatures that lost their lives for her research project. This lack of respect for the sacredness of life made it an easy decision to reject her application. Research was probably a better path for her, especially since she wasn’t able to gauge the reaction her statements would have on her audience.
- DON’T bargain. The least fun essays to read are those that contain more promises than a politician’s speech. They include statements like, “If accepted into this program, I will….” The best predictor of future behavior is past behavior. If you really want to demonstrate what you are capable of achieving during your medical education, give examples of what you have already accomplished . This approach is far stronger than making hollow promises.
- DON’T complain. Criticizing or pointing out the failures of healthcare professionals who have treated you or whom you have observed in the past will only reflect negatively on you. Since your application will be reviewed by doctors, as well as admissions professionals, it’s critical that you do not insult those from whom you are seeking acceptance. While it is true that medical mistakes and lack of access to care have devastating consequences for patients, their families and communities, identifying ways to improve in these areas without pointing any fingers would be more effective. By demonstrating your realistic knowledge of patient needs and sharing potential solutions, you can present yourself as an asset to their team.
Be careful what you write. Create a personal statement that is honest (not bitter), reveals your personality (not your medical history), and delivers a compelling explanation for your motivations for entering medicine (not empty promises).
Do you want our expert advice on your medical school personal statement?

Med School Personal Statement Consultant Dr. Mary Mahoney

Med School Personal Statement Examples and Analysis
Now let’s explore what you can learn from some of these outstanding sample med school essays.
Medical school personal statement example #1: Emergency 911
“Call 911!” I shouted to my friend as I sprinted down the street. The young Caucasian male had been thrown fifteen yards from the site of impact and surprisingly was still conscious upon my arrival. “My name is Michael. Can you tell me your name?” In his late twenties, he gasped in response as his eyes searched desperately in every direction for help, for comfort, for assurance, for loved ones, for death, until his eyes met mine. “Flail chest,” I thought to myself as I unbuttoned his shirt and placed my backpack upon his right side. “Pulse 98, respiration 28 short and quick. Help is on the way. Hang in there, buddy,” I urged.
After assessing the patient, the gravity of the situation struck me into sobriety. The adrenaline was no longer running through my veins — this was real. His right leg was mangled with a compound fracture; his left leg was also obviously broken. The tow-truck that had hit him looked as though it had run into a telephone pole. Traffic had ceased on the six-lane road, and a large crowd had gathered. However, no one was by my side to help. “Get me some blankets from that motel!” I yelled to a bystander and three people immediately fled. I was in charge.
But my patient was no longer conscious; his pulse was faint and respiration was low. “Stay with me, man!” I yelled. “15 to 1, 15 to 1,” I thought as I rehearsed CPR in my mind. Suddenly he stopped breathing. Without hesitation, I removed my T-shirt and created a makeshift barrier between his mouth and mine through which I proceeded to administer two breaths. No response. And furthermore, there was no pulse. I began CPR. I continued for approximately five minutes until the paramedics arrived, but it was too late. I had lost my first patient.
Medicine. I had always imagined it as saving lives, curing ailments, alleviating pain, overall making life better for everyone. However, as I watched the paramedics pull the sheets over the victim’s head, I began to tremble. I had learned my first lesson of medicine: for all its power, medicine cannot always prevail. I had experienced one of the most disheartening and demoralizing aspects of medicine and faced it. I also demonstrated then that I know how to cope with a life-and-death emergency with confidence, a confidence instilled in me by my certification as an Emergency Medical Technician, a confidence that I had the ability to take charge of a desperate situation and help someone in critical need. This pivotal incident confirmed my decision to pursue medicine as a career.
Of course healing, curing, and saving is much more rewarding than trying and failing. As an EMT I was exposed to these satisfying aspects of medicine in a setting very new to me — urban medicine. I spent most of a summer doing ride-alongs with the Ambulance Company in Houston. Every call we received dealt with Latino patients either speaking only Spanish or very little broken English. I suddenly realized the importance of understanding a foreign culture and language in the practice of medicine, particularly when serving an underserved majority. In transporting patients from the field to the hospitals I saw the community’s reduced access to medical care due to a lack of physicians able to communicate with and understand their patients. I decided to minor in Spanish. Having almost completed my minor, I have not only expanded my academic horizons, I have gained a cultural awareness I feel is indispensable in today’s diverse society.
Throughout my undergraduate years at Berkeley I have combined my scientific interests with my passion for the Hispanic culture and language. I have even blended the two with my interests in medicine. During my sophomore year I volunteered at a medical clinic in the rural town of Chacala, Mexico. In Mexico for one month, I shadowed a doctor in the clinic and was concurrently enrolled in classes for medical Spanish. It was in Chacala, hundreds of miles away from home, that I witnessed medicine practiced as I imagined it should be. Seeing the doctor treat his patients with skill and compassion as fellow human beings rather than simply diseases to be outsmarted, I realized he was truly helping the people of Chacala in a manner unique to medicine. Fascinated by this exposure to clinical medicine, I saw medicine’s ability to make a difference in people’s lives. For me the disciplines of Spanish and science have become inseparable, and I plan to pursue a career in urban medicine that allows me to integrate them.
Having seen medicine’s different sides, I view this as a multifaceted profession. I have witnessed its power as a healing agent in rural Chacala, and I have seen its weakness when I met death face-to-face as an EMT. Inspired by the Latino community of Houston, I realize the benefits of viewing it from a holistic, culturally aware perspective. And whatever the outcome of the cry "Call 911!" I look forward as a physician to experiencing the satisfaction of saving lives, curing ailments, alleviating pain, and overall making life better for my patients.
Lessons From Med School Sample Essay #1: Emergency 911
This essay is one of our favorites. The applicant tells a story and weaves a lot of information into it about his background and interests. Note how the lead grabs one’s attention and the conclusion ties everything together.
What makes this essay work?
- A dramatic opening paragraph
This essay has an unusually long opener, but not only is it dramatic, it also lays out the high-stakes situation of the writer desperately trying to save the life of a young man. As an EMT, the writer is safe in sharing so much detail, because they establish their bona fides as medically knowledgeable. With the urgent opening sentence (“Call 911!”) and the sad final sentence (“I had lost my first patient.”), the writer bookends a particularly transformative experience, one that confirmed their goal of becoming a doctor.
- A consistent theme
The theme of a med school essay in which the applicant first deals with the inevitable reality of seeing a patient die can become hackneyed through overuse. This essay is saved from that fate because after acknowledging the pain of this reality check, the writer reports that they immediately committed to expanding his knowledge and skills to better serve the local Hispanic community. While not an extraordinary story for an EMT, the substance, self-awareness, and focus the writer brings to the topic makes it a compelling read.
- Evidence supporting the stated goal
This applicant is already a certified EMT, which serves as evidence of their serious interest in a medical career. In going on ambulance ride-alongs, the writer realized the barrier in communication between many doctors and their Spanish-speaking patients, which inspired the writer to take steps to both learn medical Spanish and shadow a doctor in a Mexican clinic. These concrete steps affirm that the applicant has serious intent.
Medical School Personal Statement Example #2: The Traveler
"On the first day that I walked into the Church Nursing Home, I was unsure of what to expect. A jumble of questions ran through my mind simultaneously: Is this the right job for me? Will I be capable of aiding the elderly residents? Will I enjoy what I do? A couple of hours later, these questions were largely forgotten as I slowly cut chicken pieces and fed them to Frau Meyer. Soon afterwards, I was strolling through the garden with Herr Schmidt, listening to him tell of his tour of duty in World War II. By the end of the day, I realized how much I enjoyed the whole experience and at the same time smiled at the irony of it all. I needed to travel to Heidelberg, Germany, to confirm my interest in clinical medicine.
Experiences like my volunteer work in the German nursing home illustrate the decisive role travel has played in my life. For instance, I had volunteered at a local hospital in New York but was not satisfied. Dreams of watching doctors in the ER or obstetricians in the maternity ward were soon replaced with the reality of carrying urine and feces samples to the lab. With virtually no patient contact, my exposure to clinical medicine in this setting was unenlightening and uninspiring. However, in Heidelberg, despite the fact that I frequently change diapers for the incontinent and deal with occasionally cantankerous elderly, I love my twice-weekly visits to the nursing home. Here, I feel that I am needed and wanted. That rewarding feeling of fulfillment attracts me to the practice of medicine.
My year abroad in Germany also enriched and diversified my experience with research. Although I had a tremendously valuable exposure to research as a summer intern investigating chemotherapeutic resistance in human carcinomas, I found disconcerting the constant cost-benefit analysis required in applied biomedical research. In contrast, my work at the University of Heidelberg gave me a broader view of basic research and demonstrated how it can expand knowledge – even without the promise of immediate profit. I am currently attempting to characterize the role of an enzyme during neural development. Even though the benefit of such research is not yet apparent, it will ultimately contribute to a vast body of information which will further medical science.
My different reactions to research and medicine just exemplify the intrinsically broadening impact of travel. For example, on a recent trip to Egypt, I visited a small village on the banks of the Nile. This impoverished hamlet boasted a large textile factory in its center where many children worked in clean, bright, and cheerful conditions weaving carpets and rugs. After a discussion with the foreman of the plant, I discovered that the children of the village learned trades at a young age to prepare them to enter the job market and to support their families. If I had just heard about this factory, I would have recoiled in horror with visions of sweatshops running through my head. However, watching the skill and precision each child displayed, in addition to his or her endless creativity, soon made me realize that it is impossible to judge this country’s attempts to deal with its poverty using American standards and experience.
Travel has not only had a formative and decisive impact on my decision to pursue a career in medicine, it has also broadened my horizons – whether in a prosperous city on the Rhine or an impoverished village on the Nile. In dealing with patients or addressing research puzzles, I intend to bring the inquiring mind fostered in school, lab, and volunteer experiences. But above all, I intend to bring the open mind formed through travel.
Lessons From Medical School Sample Essay #2: The Traveler
No boring repetition of itinerary from this seasoned traveler! This student ties their travels to their medical ambitions through the effective use of short anecdotes and vivid images. Can you sense the writer’s youthful disappointment during early clinical experiences and mature satisfaction working in the retirement home?
This applicant effectively links the expansive benefits of travel to their medical ambitions. By sharing vivid anecdotes from and reflections on these experiences, the writer enables the reader to easily imagine them as a talented physician in the future.
- An engaging opening that frames the storyline Many fine application essays open with imagery so vibrant that the writing could be mistaken for fiction. This essay is no different. We meet the writer in the setting of a nursing home overseas, where they question whether their volunteer experiences there will help them determine their career path. Notice how the first sentence reflects a worry, “I was unsure of what to expect,” but by the final sentence, the writer concludes with satisfaction, “I needed to travel to Heidelberg, Germany, to confirm my interest in clinical medicine.” With this framing, we appreciate the essay’s theme.
- Reflections on and contrasts about varied experiences in medicine The writer’s reactions to various encounters reveal a maturing mind-set: the “unenlightening and uninspiring” experience volunteering in a New York hospital versus the feeling of being “needed and wanted” in the nursing home in Heidelberg; the “disconcerting . . . constant cost-benefit analysis required in applied biomedical research” versus the “broader view of basic research and . . . how it can expand knowledge – even without the promise of immediate profit” at the University of Heidelberg. These reflections demonstrate a thoughtfulness born of experience.
- How traveling has expanded his potential as a physician Of the five tightly constructed paragraphs in this substantial essay, the final two paragraphs home in on how travel has had an “intrinsically broadening impact” and stimulated an “open mind” to people and situations. This kind of sophisticated view is a desirable trait to adcoms.
- Out-of-the-box theme Although this essay’s foundation is built on the writer’s sincere and dedicated aspirations for a medical career, they allowed themselves the space to write about the broadening intellectual benefits of travel, linking those benefits to professional potential. Even when writing about children working in a factory in Egypt, this applicant brings an expanded mind-set and greater cross-cultural understanding that will no doubt benefit them in their career.
Medical School Personal Statement Example #3: The Non-Traditional Applicant
"Modest one-room houses lay scattered across the desert landscape, their rooftops a seemingly helpless shield against the intense heat generated by the mid-July sun. The steel security bars that guarded the windows and doors of every house seemed to belie the large welcome sign at the entrance to the ABC Indian Reservation. As a young civil engineer employed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, I was far removed from my cubicle in downtown Los Angeles.
However, I felt I was well-prepared to conduct my first project proposal. The project involved a $500,000 repair of an earthen levee surrounding an active Native American burial site. A fairly inexpensive and straightforward job by federal standards, but nonetheless, I could hardly contain my excitement. Strict federal construction guidelines laden with a generous portion of technical jargon danced through my head as I stepped up to the podium to greet the twelve tribal council members. My premature confidence quickly disappeared as they confronted me with a troubled ancient gaze. Their faces revealed centuries of distrust and broken government promises.
Suddenly, from a design based solely upon abstract engineering principles, an additional human dimension emerged – one for which I had not prepared. The calculations I had crunched over the past several months and the abstract engineering principles simply no longer applied. Their potential impact on this community was clearly evident in the faces before me. With perspiration forming on my brow, I decided I would need to take a new approach to salvage this meeting. So I discarded my rehearsed speech, stepped out from behind the safety of the podium, and began to solicit the council members’ questions and concerns. By the end of the afternoon, our efforts to establish a cooperative working relationship had resulted in a distinct shift in the mood of the meeting. Although I am not saying we erased centuries of mistrust in a single day, I feel certain our steps towards improved relations and trust produced a successful project.
I found this opportunity to humanize my engineering project both personally and professionally rewarding. Unfortunately, experiences like it were not common. I realized early in my career that I needed a profession where I could more frequently incorporate human interaction and my interests in science. After two years of working as a civil engineer, I enrolled in night school to explore a medical career and test my aptitude for pre-medical classes. I found my classes fascinating and became a more effective student. Today, I am proud of the 3.7 GPA I have achieved in competitive post-baccalaureate courses such as organic chemistry, biochemistry, and genetics.
Confident of my ability to succeed in the classroom, I proceeded to volunteer in the Preceptorship Program at the Los Angeles County/University of Southern California Medical Center. I acquired an understanding of the emotional demands and time commitment required of physicians by watching them schedule their personal lives around the needs of their patients. I also soon observed that the rewards of medicine stem from serving the needs of these same patients. I too found it personally gratifying to provide individuals with emotional support by holding an elderly woman’s hand as a physician drew a blood sample or befriending frightened patients with a smile and conversation.
To test my aptitude for a medical career further, I began a research project under the supervision of Dr. John Doe from the Orthopedic Department at Big University. The focus of my study was to determine the fate of abstracts presented at the American Society for Surgery of the Hand annual meeting. As primary author, I reported the results in an article for the Journal of Hand Surgery, a peer-reviewed publication. My contribution to medicine, albeit small, gave me much satisfaction. In the future, I would like to pursue an active role in scientific research.
My preparation for a career as a medical doctor started with my work as a professional engineer. From my experiences at the ABC Indian Reservation, I realized I need more direct personal interaction than engineering offers. The rewarding experiences I have had in my research, my volunteer work at the Los Angeles County Hospital, and my post-bac studies have focused my energies and prepared me for the new challenges and responsibilities that lie ahead in medicine."
Lessons From Med School Sample Essay #3: The Non-Traditional Applicant
Here, an older applicant takes advantage of their experience and maturity. Note how this engineer demonstrates their sensitivity and addresses possible stereotypes about engineers’ lack of communications skills.
What works well in this essay?
- A compelling lead This story begins in a hot desert landscape, an unexpected and dramatic starting point. Can’t you just feel the heat and sense the loneliness of the remote Indian reservation? Equally powerful in this first paragraph is when the writer faces the need to suddenly and completely rethink their carefully planned approach to address the tribal leaders. Their excitement is dashed. Their confidence has plummeted. They are totally unprepared for the mistrust facing them and their plan, and they need to improvise –quickly. Who wouldn’t want to read on to see how they resolve this dramatic turn of events?
- Solid storytelling that leads to a satisfying conclusion This nontraditional med school applicant reinvents themself in this essay. After realizing that they want more human involvement and interaction in their work, they take this self-knowledge and show us the steps they took to achieve their new goal. The steps are logical and well thought out, so the writer’s conclusion that they are well prepared in every way for med school makes perfect sense.
- Evidence to support their theme Through taking prerequisite courses in medicine (and achieving high grades) to bedside hospital volunteering (which provides emotional satisfaction) to helping write a medical research paper (which provides a feeling that they are making a meaningful contribution), the writer offers evidence that they are well suited for their new goal of a career in medicine. Each experience shared is relevant to the writer’s story. Any reader will agree that the applicant’s future as a physician is promising.
- A thoughtful perspective From the opening paragraph, the writer shows their ability to adapt to new situations and realities with quick thinking and psychological openness. They assess each stage of their journey, testing it for intellectual value and emotional satisfaction. Journeys of reflective self-discovery are something adcoms value.
Medical School Personal Statement Example #4: The Anthropology Student
"Crayfish tails in tarragon butter, galantine of rabbit with foie gras, oxtail in red wine, and apple tartelettes. The patient had this rich meal and complained of “liver upset” (crise de foie). Why a liver ache? I always associate indigestion with a stomach ache. In studying French culture in my Evolutionary Psychology class, I learned that when experiencing discomfort after a rich meal, the French assume their liver is the culprit. Understanding and dealing with the minor – sometimes major – cultural differences is a necessity in our shrinking world and diverse American society. Anthropology has prepared me to effectively communicate with an ethnically diverse population. My science classes, research, and clinical experience have prepared me to meet the demands of medical school.
I first became aware of the valuable service that physicians provide when I observed my father, a surgeon, working in his office. I gained practical experience assisting him and his staff perform various procedures in his outpatient center. This exposure increased my admiration for the restorative, technological, and artistic aspects of surgery. I also saw that the application of medical knowledge was most effective when combined with compassion and empathy from the health care provider.
While admiring my father’s role as a head and neck surgeon helping people after severe accidents, I also found a way to help those suffering from debilitating ailments. Working as a certified physical trainer, I became aware of the powerful recuperative effects of exercise. I was able to apply this knowledge in the case of Sharon, a 43-year-old client suffering from lupus. She reported a 200% increase in her strength tests after I trained her. This meant she could once again perform simple tasks like carrying groceries into her house. Unfortunately, this glimpse of improvement was followed by a further deterioration in her condition. On one occasion, she broke down and cried about her declining health and growing fears. It was then that I learned no physical prowess or application of kinesiology would alleviate her pain. I helped reduce her anxiety with a comforting embrace. Compassion and understanding were the only remedies available, temporary though they were.
To confirm that medicine is the best way for me to help others, I assisted a research team in the Emergency Room at University Medical Center (UMC). This experience brought me in direct contact with clinical care and provided me with the opportunity to witness and participate in the “behind-the-scenes” hospital operations. Specifically, we analyzed the therapeutic effects of two new drugs – Drug A and Drug B – in patients suffering from acute ischemic stroke. The purpose of this trial was to determine the efficacy and safety of these agents in improving functional outcome in patients who had sustained an acute cerebral infarction. My duties centered around the role of patient-physician liaison, determining patients’ eligibility, monitoring their conditions, and conducting patient histories.
I continued to advance my research experience at the VA Non-Human Primate Center. During the past year, I have been conducting independent research in endocrinology and biological aspects of anthropology. For this project, I am examining the correlation between captive vervet monkeys’ adrenal and androgen levels with age, gender, and various behavioral measures across different stress-level environments. I enjoy the discipline and responsibility which research requires, and I hope to incorporate it into my career.
Anthropology is the study of humans; medicine is the science and art of dealing with the maintenance of health and the prevention, alleviation, or cure of disease in humans. From my work at UMC and my observation of my father’s practice, I know medicine will allow me to pursue an art and science that is tremendously gratifying and contributes to the welfare of those around me. My anthropology classes have taught me to appreciate cross-cultural perspectives and their relationship to pathology and its etiology. Firsthand experience with exercise therapy and nutrition has taught me the invaluable role of prevention. Medical school will now provide me with the technical knowledge to alleviate a crise de foie."
[ Click here to view an excerpt from the original draft of this essay. ]
Lessons From Medical School Sample Essay #4: The Anthropology Student
With a diverse background that includes anthropology studies, work as a certified physical trainer, and experience in clinical medical research, this applicant builds a strong case for their logical and dedicated choice of a medical career.
- An engaging opening that frames the storyline This writer cleverly uses an example from anthropology class, linking the description of a heavy, gourmet French meal to an appreciation for cross-cultural understanding that will be an asset during their medical career. Notice that the writer is not describing their own personal experience here but piggybacked on a class lesson to create a colorful, engaging opening.
- A solid variety of relevant experiences In this six-paragraph essay, the writer links their lessons from anthropology studies to a firsthand understanding based on observing how their surgeon-father related to patients, to becoming a physical trainer directly helping others, and then to two different kinds of medical research. Each experience builds logically and chronologically on what came before, adding to the substance of the applicant’s preparation for medical school.
- A powerful personal experience with a client In the third paragraph, the writer’s experience working with a patient with lupus is particularly strong and memorable. Their initial success with Sharon is followed by an almost immediate and radical decline in her condition. This is a moving anecdote that shows the applicant’s understanding of the limitations of medicine – and the power of compassion.
- An excellent summary paragraph that ties everything together The final paragraph isn’t the place to offer new information, and this one doesn’t. Instead, it reminds the reader about the strong foundation the writer built from academics to career and medical research. Readers will be persuaded that after these experiences and reflections, the applicant truly appreciates “cross-cultural perspectives and their relationship to pathology and its etiology,” as well as the “firsthand experience with exercise therapy and nutrition teaching the invaluable role of prevention.”
Don’t Write Like This!
As the time approached for me to set my personal and professional goals, I made a conscientious decision to enter a field which would provide me with a sense of achievement and, at the same time, produce a positive impact on mankind. It became apparent to me that the practice of medicine would fulfill these objectives. In retrospect, my ever-growing commitment to medicine has been crystallizing for years. My intense interest in social issues, education, and athletics seems particularly appropriate to this field and has prepared me well for such a critical choice...
I’ve been asked many times why I wish to become a physician. Upon considerable reflection, the thought of possessing the ability to help others provides me with tremendous internal gratification and offers the feeling that my life’s efforts have been focused in a positive direction. Becoming a physician is the culmination of a lifelong dream, and I am prepared to dedicate myself, as I have in the past, to achieving this goal.
Lessons from Don’t Write Like This
This is an excerpt from the original draft of the Anthropology Student’s AMCAS essay. We are not including the whole thing because you can get the idea all too rapidly from just this brief portion. Note the abundant use of generalities that apply to the overwhelming majority of medical school applicants. Observe how the colorless platitudes and pomposity hide any personality. Can you imagine reading essays like this all day long? If so, then imagine your reaction to a good essay.
More sample essays
The Dental School Applicant Sample Essay >>
The Physician Assistant Sample Application Essay >>
What's next?
You’ve just made a smart investment of time by studying these successful sample essays. Now you’re one step closer to writing essays that can lead to acceptance at a top medical school.
Why not make the next smart investment and team up with an experienced admissions expert ? We have helped thousands of qualified applicants get accepted to their dream schools and look forward to helping you too.
Get Expert Help With Your Medical School Application
Our world-class team helps you stand out from the competition and get accepted.
APPLICATION STRATEGY / PRIMARY AND SECONDARY ESSAY REVIEW / INTERVIEW PREP
Med school personal statement FAQs
1. when should i start writing my personal statement for medical school.
Typically, traditional applicants who have a goal of submitting their AMCAS or AACOMAS application in June write their personal statement after they take the MCAT in March. Starting the prewriting for the personal statement earlier than that is fine too; however, if an applicant plans to sit for the MCAT in the early spring, writing a compelling personal narrative while preparing for the MCAT can often be too much. Both require very different kinds of thinking. The intensity of studying for the MCAT, and the empirical thinking it requires, can interfere with the imaginative brainstorming needed to find your topic and develop it.
Before focusing on the personal statement, look at all the elements of the primary application. As a whole, the personal statement, activities, MMEs, MCAT, transcript, biographical information and letters, will portray you. One element alone is not enough to bring out the whole you. It might help to strategize about how (and where) to highlight different elements of your background, experience, and character in the different parts of the primary application. Then work on the personal statement knowing what aspects of you are already represented in the other sections of the application. This way, each element adds value to the application and contributes to a more complete picture of you.
It makes sense to compartmentalize completing different parts of the application. Many applicants take the time they need to focus on one application component at a time, which seems to help them be thorough.
Don’t underestimate how much time it takes to write well. Exploring ideas in writing, developing those ideas, showing rather than telling a story, staying clear, writing fluidly, surmising maturely and insightfully, takes much more time than most people anticipate. So, don’t wait until Memorial Day to write your essay and intend to submit on June 1. Give yourself the churn time writing well needs. Also, give yourself time to put a draft down for a day or two and return to it when you’re able to read it afresh. Sometimes, we revise over and over again in one sitting to the point that we can no longer hear the story or its sense because we have been rehearsing and revising a draft to beat the clock. Doing this is a risky way to go about the personal statement. Remember, this essay should be a very impressive part of your application, not merely one more part of the application to finish. At the end of the day, the medical school personal statement is a window that allows others to see you, know you as a person, know you better and beyond your achievements.
2. How do I find the perfect personal statement topic? Does one exist?
Certainly, some ideas are better than others, and one idea might work better for one person and not so well for someone else. However, there is no “perfect” topic. In fact, writing an essay with the approach of trying to out-psych this important application requirement is likely not the strongest way to find your best topic, nor is it the best way to engage your readers.
Instead, consider the following approach. What is an experience you’ve had that matters greatly in helping others understand who you are as a future physician? Why medicine, not in general, but for you, demonstrated by way of a story about an experience that directly ties to being a physician or indirectly demonstrates your sound character as it corresponds with human qualities medical schools desire. When we read what kinds of people medical schools seek, it’s easy enough to identify quite a few character traits that appeal to many schools: compassion, resiliency, adaptability, selflessness, inclusivity, and altruism among them. What experience, when written with key details and description, reveals who you really are?
3. How do you choose the right amount of personal qualities to list?
A strong medical school personal statement should not replicate other parts of the application, with the exception of it being a specific story that stems from a particular experience associated with one of your activities. Otherwise, there’s no listing in this essay. Unfortunately, some applicants do treat the personal statement as an opportunity to list awards, accolades, and experiences, paragraph by paragraph. Meanwhile, medical school admissions officers can see these awards and experiences in the Experiences section of the application. Rarely, if ever, does this kind of writing bring out voice, vision and identity. Instead, tell a true story, revised with care and precision, that shines with voice, vision and identity.
4. Are there any topics I should avoid for my medical school personal statement?
Certainly, one idea might work better for one person and not so well for someone else. So, there’s a subjectivity in what to write and what not to write. Generally, however, there are some topics to avoid. Don’t write about a time you felt cheated, inconvenienced, frustrated or angry. Sometimes, secondary essay prompts will ask you about a struggle or a mistake, and for these answers, it’s best to show how you turned the situation around or keenly learned from it. Don’t get too caught in childhood. Many applicants do write about a time when they were not yet grown; however, don’t get swallowed by it. Write the scene and then stay in the present to demonstrate your maturity and worthwhile hindsight.
Remember -- no matter what the topic, tone matters.
5. What kind of experience should I include in my personal statement?
6. can the experience i use on my med school personal statement be from outside of college.
Absolutely. It is relatively common for applicants to only portray themselves as students, and this can be a problem. Sometimes, when applicants write about themselves as excellent students the tone of such a personal statement can sound boastful or pleading. Neither quality is advantageous.
Seeing oneself in any other light can result in a stronger “snapshot” of who you are, as long as the theme or topic of your personal statement still suits the intention of the application in the first place – demonstrating who you are as an appealing candidate for medical school. When we consider the writing task for the personal statement to be much more story-driven, readers go on a descriptive journey. What journey would you like to share?
7. Should I talk about challenges I’ve faced?
If other parts of your medical school application suggest a struggle – whether a lower MCAT score or a notable weak semester on a transcript – it might be advantageous to explain what happened and how you turned that situation around. Whether writing about a challenge in the personal statement or secondaries, the key is to demonstrate resilience. Applicants with physical or cognitive disabilities may choose to write about seeking assistance -- whether a doctor, therapist or a tutor -- and how learning alternative strategies helped them figure out how to attain higher academic achievement.
Sometimes challenges are circumstantial. Sometimes families face financial hardship (did the family breadwinner become unemployed and therefore everyone else had to work more hours, including you?), emotional stress (due to an ongoing illness, Covid-19, or a divorce?) or trauma (a death of a loved one, a house fire, a veteran/sibling returning home with PTSD). Sometimes an applicant has been a caregiver for someone in the family. Sometimes an applicant has taken a leave from school because of someone else’s struggles, or the emotional fallout on the applicant from someone else’s struggle – the loss of a childhood friend, for instance. Self-care is reasonable. We might need to share a life moment in order to frame the context of a life struggle, showing it in the context of responsibility rather than recklessness or immaturity. Showing how you stepped up in a challenging time can show that you are accountable and caring, as long as the story is told to these ends, rather than suggesting resentment or self-pity. Again, neither of these tones is advantageous, nor is blame.
Occasionally applicants have been challenged by a course or by a professor, a classmate or teammate and feel unduly subjected to bias. If there’s discrimination involved, that might be a story to tell. If there’s a personality clash, that might not be a good story to tell.
Finally, as any story of challenge moves along, it’s important to demonstrate what you did, what you learned, how you adapted, or what you now value from having had this life experience that you did not understand before.
Being a doctor is rife with challenges. In the end, your readers may come to understand how you are an insightful leader with great resilience or a compassionate, problem-solver.
8. How do I focus my personal statement to show that I want to go into medicine and not another field in healthcare?
Great question. On the one hand, it’s a good idea to demonstrate your compassion for others and empathy for people suffering from illness. On the other hand, these are favorable attributes for nearly all healthcare workers -- not only doctors -- but for physician assistants, nurses, respiratory therapists, social workers and psychologists too. Since most applicants have done some shadowing of physicians, it’s not unusual for these experiences to contain moments of learning about being a physician through shadowing or through work in a clinic. However, the more clinical the story, the better especially if you’re applying to osteopathic schools of medicine. If you’re applying to allopathic schools of medicine, it’s possible you have some interest in being a researcher, so telling a story about working in a physician’s lab might demonstrate your insights into the value of research in light of disease or patient care. If you already have an affinity for a specialty, telling how you came to know this could be the way to go.
9. Do I introduce my desired field of healthcare in my personal statement?
Maybe. If you’re very committed and have demonstrated a trend in your activities from general volunteer work (older listings) to more specialized experience in a field of medicine (more recent listings), it may be a good idea to write up how you came to know one field of medicine was really your passion.
Bear in mind that announcing a deep interest in a particular field of medicine may make you “a good fit” or “not a good fit” for some schools. So, if you do write up a story about your desired field of medicine for your personal statement, be sure your list of schools corresponds with this. For instance, if you want to be an obstetrician and you convey this in your personal statement, be certain your schools have clinical exposure or better yet offer specializations in obstetrics, or a required rotation through a hospital for women, for instance.
Lastly, by no means must you announce a desired field of healthcare in your personal statement. You may be asked about your specialized interests in medicine in a secondary or in an interview, so it’s a good idea to think this through, but no, you don’t have to tackle this in the personal statement.
10. What should my character limit be?
The AMCAS and AACOMAS character limit for the personal statement is 5,300 characters with spaces. The TMDSAS character limit for the personal statement is 5,000 characters with spaces. It’s a good idea to use most if not all of this space for your personal statement. Also, try to avoid the temptation to use the same personal statement for AMCAS and AACOMAS. The osteopathic schools seek applicants who know and prefer an osteopathic orientation to medicine, so the AACOMAS personal statement should demonstrate your fit with osteopathic medicine, based on what story you choose to tell and how you tell it, or at the very least, in the conclusion.
11. How do I know when I’m ready to submit my med school personal statement?
I highly recommend getting feedback about this from a strong mentor, advisor or consultant. Accepted offers comprehensive consultation for every part of the writing process, from brainstorming, to outlining, to mentoring on ideas, and editing until a client has a solid final draft in hand, ready for submission. You can review these services here: Initial Essay Package
Generally speaking, when you’ve accomplished FAQ #2 and #3, avoided the pitfalls in #4, revised for clarity and quality of ideas, developed ideas engagingly, and meticulously revised for quality of writing, then, you may be done.
12. What if I don’t have enough space to discuss everything?
Then your topic is too large or unfocused, in which case you need to focus and narrow the scope of your essays. Or you have a bit of editing to do to eliminate wordiness, digressions, or overstatement Ultimately, you want your essay to be focused, clear, and engaging.
13. Should I personalize my personal statement to the med school I am applying to?
Only if you’re applying to one medical school. Otherwise, your personal statement will reach all schools listed in your AMCAS application or AACOMAS application. It is okay, however, to speak toward the ideals of your first choice, aspirational schools on your list. Other times, applicants choose to write toward the schools that are their safest bets.
Your secondary/supplemental essays will give you plenty of opportunity to show you belong at an individual school.
14. Can I talk about mental or physical health in my statement?
15. should i address any bad grades that i got in school.
Generally yes, as long as bad grades are truly bad grades. It’s likely that you do not need to address a rogue grade of B on a transcript. If you had a bad semester or two, the question becomes how and where to address them. The answer is an individual one dependent on the context. The one certainty: You definitely don’t want your entire application to be a rationalization of those bad grades.
See FAQ #7.

Accepted has been helping medical school applicants gain acceptance to top programs since 1994. Our staff consists of former deans, admissions directors, and experienced consultants.
Get Accepted! Sign up for a free consultation today!

Great Medical School Personal Statement Examples (2024-2025) Insider’s Guide

A physician and former medical school admissions officer teaches you how to write your medical school personal statement, step by step. Read several full-length medical school personal statement examples for inspiration.
In this article, a former medical school admissions officer explains exactly how to write a stand-out medical school personal statement!
Our goal is to empower you to write a medical school personal statement that reflects your individuality, truest aspirations and genuine motivations.
This guide also includes:
- Real life medical school personal statement examples
- Medical school personal statement inventory template and outline exercise
- AMCAS, TMDSAS, and AACOMAS personal statement prompts
- Advanced strategies to ensure you address everything admissions committees want to know
- The secret to writing a great medical school personal statement
So, if you want your medical school personal statement to earn more more medical school interviews, you will love this informative guide.
Let’s dive right in.
Table of Contents
Medical School Personal Statement Fundamentals
If you are getting ready to write your medical school personal statement for the 2024-2025 application year, you may already know that almost 60% of medical school applicants are not accepted every year . You have most likely also completed all of your medical school requirements and have scoured the internet for worthy medical school personal statement examples and guidance.
You know the medical school personal statement offers a crucial opportunity to show medical schools who you are beyond your GPA and MCAT score .
It provides an opportunity to express who you are as an individual, the major influences and background that have shaped your interests and values, what inspired you to pursue medicine, and what kind of a physician you envision yourself becoming.
However, with so much information online, you are not sure who to trust. We are happy you have found us!
Because the vast majority of people offering guidance are not former admissions officers or doctors , you must be careful when searching online.
We are real medical school admissions insiders and know what goes on behind closed doors and how to ensure your medical school personal statement has broad appeal while highlighting your most crucial accomplishments, perspectives, and insights.
With tight limits on space, it can be tough trying to decide what to include in your medical school personal statement to make sure you stand out. You must think strategically about how you want to present your personal “big picture” while showing you possess the preprofessional competencies med schools are seeking.
When a medical school admissions reviewer finishes reading your medical school personal statement, ask yourself:
- What are the most important things you want that person to remember about you?
- Does your medical school personal statement sum up your personality, interests, and talents?
- Does your medical school personal statement sound as if it’s written from the heart?
It’s pretty obvious to most admissions reviewers when applicants are trying too hard to impress them. Being authentic and upfront about who you are is the best way to be a memorable applicant.
The Biggest Medical School Personal Statement Mistakes
The most common medical school personal statement mistake we see students make is that they write about:
- What they have accomplished
- How they have accomplished it
By including details on what you have accomplished and how, you will make yourself sound like every other medical school applicant.
Most medical school applicants are involved in similar activities: research, clinical work, service, and social justice work.
To stand out, you must write from the heart making it clear you haven’t marched through your premedical years and checking boxes.
We also strongly discourage applicants from using ChatGPT or any AI bot to write their medical school personal statement. Writing in your own voice is essential and using anything automated will undermine success.
The Medical School Personal Statement Secret
MedEdits students stand out in the medical school personal statement because in their personal statements they address:
WHY they have accomplished what they have.
In other words, they write in more detail about their passions, interests, and what is genuinely important to them.
It sounds simple, we know, but by writing in a natural way, really zeroing in on WHY YOU DO WHAT YOU DO, you will appeal to a wide variety of people in a humanistic way.
MedEdits students have done extremely well in the most recent medical school admissions cycle. Many of these applicants have below average “stats” for the medical schools from which they are receiving interviews and acceptances.
Why? How is that possible? They all have a few things in common:
- They write a narrative that is authentic and distinctive to them.
- They write a medical school personal statement with broad appeal (many different types of people will be evaluating your application; most are not physicians).
- They don’t try too hard to impress; instead they write about the most impactful experiences they have had on their path to medical school.
- They demonstrate they are humble, intellectual, compassionate, and committed to a career in medicine all at the same time.
Keep reading for a step by step approach to write your medical school personal statement.
“After sitting on a medical school admissions committee for many years, I can tell you, think strategically about how you want to present your personal “big picture.” We want to know who you are as a human being.”
As physicians, former medical school faculty, and medical school admissions committee members, this article will offer a step by step guide to simplify the medical school personal statement brainstorming and writing process.
By following the proven strategies outlined in this article, you will be and to write a personal statement that will earn you more medical school interviews . This proven approach has helped hundreds of medical school applicants get in to medical school the first time they apply!
Learn the 2024-2025 Medical School Personal Statement Prompts ( AMCAS , TMDSAS , AACOMAS )
The personal statement is the major essay portion of your primary application process. In it, you should describe yourself and your background, as well as any important early exposures to medicine, how and why medicine first piqued your interest, what you have done as a pre med, your personal experiences, and how you became increasingly fascinated with it. It’s also key to explain why medicine is the right career for you, in terms of both personal and intellectual fulfillment, and to show your commitment has continued to deepen as you learned more about the field.
The personal statement also offers you the opportunity to express who you are outside of medicine. What are your other interests? Where did you grow up? What did you enjoy about college? Figuring out what aspects of your background to highlight is important since this is one of your only chances to express to the med school admissions committee before your interview what is important to you and why.
However, it is important to consider the actual personal statement prompt for each system through which you will apply, AMCAS, AACOMAS, and TMDSAS, since each is slightly different.
Getting into a medical school has never been more competitive. Let the experts at MedEdits help you with your medical school application materials. We’ve worked with more than 5,000 students and 94% have been admitted to medical school.
Need help with your Personal Statement?
Schedule a free 15 Minute Consultation with a MedEdits expert.
2024 AMCAS Personal Statement Prompt

The AMCAS personal statement instructions are as follows:
Use the Personal Comments Essay as an opportunity to distinguish yourself from other applicants. Consider and write your Personal Comments Essay carefully; many admissions committees place significant weight on the essay. Here are some questions that you may want to consider while writing the essay:
- Why have you selected the field of medicine?
- What motivates you to learn more about medicine?
- What do you want medical schools to know about you that hasn’t been disclosed in other sections of the application?
In addition, you may wish to include information such as:
- Unique hardships, challenges, or obstacles that may have influenced your educational pursuits
- Comments on significant fluctuations in your academic record that are not explained elsewhere in your application
As you can see, these prompts are not vague; there are fundamental questions that admissions committees want you to answer when writing your personal statement. While the content of your statement should be focused on medicine, answering the open ended third question is a bit trickier.
The AMCAS personal statement length is 5,300 characters with spaces maximum.
2024 TMDSAS Personal Statement Prompt

The TMDSAS personal statement is one of the most important pieces of your medical school application.
The TMDSAS personal statement prompt is as follows:
Explain your motivation to seek a career in medicine. Be sure to include the value of your experiences that prepare you to be a physician.
This TMDSAS prompt is very similar to the AMCAS personal statement prompt. The TMDSAS personal statement length is 5,000 characters with spaces whereas the AMCAS personal statement length is 5,300 characters with spaces. Most students use the same essay (with very minor modifications, if necessary) for both application systems.
You’ve been working hard on your med school application, reading medical school personal statement examples, editing, revising, editing and revising. Make sure you know where you’re sending your personal statement and application. Watch this important medical school admissions statistics video.
2024 AACOMAS Personal Statement Prompt

The AACOMAS personal statement is for osteopathic medical schools specifically. As with the AMCAS statement, you need to lay out your journey to medicine as chronologically as possible in 5,300 characters with spaces or less. So you essentially have the same story map as for an AMCAS statement. Most important, you must show you are interested in osteopathy specifically. Therefore, when trying to decide what to include or leave out, prioritize any osteopathy experiences you have had, or those that are in line with the osteopathic philosophy of the mind-body connection, the body as self-healing, and other tenets.
Medical School Application Timeline and When to Write your Personal Statement
If you’re applying to both allopathic and osteopathic schools, you can most likely use the same medical school personal statement for both AMCAS and AACOMAS. In fact, this is why AACOMAS changed the personal statement length to match the AMCAS length several years ago.
Most medical school personal statements can be used for AMCAS and AACOMAS.
Know the Required Medical School Personal Statement Length
Below are the medical schools personal statement length limits for each application system. As you can see, they are all very similar. When you start brainstorming and writing your personal statement, keep these limits in mind.
AMCAS Personal Statement Length : 5,300 characters with spaces.
As per the AAMC website : “The available space for this essay is 5,300 characters (spaces are counted as characters), or approximately one page. You will receive an error message if you exceed the available space.”
AACOMAS Personal Statement Length : 5,300 characters with spaces
TMDSAS Personal Statement Length : 5,000 characters with spaces
As per the TMDSAS Website (Page 36): “The personal essay asks you to explain your motivation to seek a career in medicine. You are asked to include the value of your experiences that prepare you to be a physician. The essay is limited to 5000 characters, including spaces.”
Demonstrate Required Preprofessional Competencies
Next, your want to be aware of the nine preprofessional core competencies as outlined by the Association of American Medical Colleges . Medical school admissions committees want to see, as evidenced by your medical school personal statement and application, that you possess these qualities and characteristics. Now, don’t worry, medical school admissions committees don’t expect you to demonstrate all of them, but, you should demonstrate some.
- Service Orientation
- Social Skills
- Cultural Competence
- Oral Communication
- Ethical Responsibility to Self and Others
- Reliability and Dependability
- Resilience and Adaptability
- Capacity for Improvement
In your personal statement, you might be able to also demonstrate the four thinking and reasoning competencies:
- Critical Thinking
- Quantitative Reasoning
- Written Communication
- Scientific Inquiry
So, let’s think about how to address the personal statement prompts in a slightly different way while ensuring you demonstrate the preprofessional competencies. When writing your personal statement, be sure it answers the four questions that follow and you will “hit” most of the core competencies listed above.
1. What have you done that supports your interest in becoming a doctor?
I always advise applicants to practice “evidence based admissions.” The reader of your essay wants to see the “evidence” that you have done what is necessary to understand the practice of medicine. This includes clinical exposure, research, and community service, among other activities.
2. Why do you want to be a doctor?
This may seem pretty basic – and it is – but admissions officers need to know WHY you want to practice medicine. Many applicants make the mistake of simply listing what they have done without offering insights about those experiences that answer the question, “Why medicine?” Your reasons for wanting to be a doctor may overlap with those of other applicants. This is okay because the experiences in which you participated, the stories you can tell about those experiences, and the wisdom you gained are completely distinct—because they are only yours.
“In admissions committee meetings we were always interested in WHY you wanted to earn a medical degree and how you would contribute to the medical school community.”
Medical school admissions committees want to know that you have explored your interest deeply and that you can reflect on the significance of these clinical experiences and volunteer work. But writing only that you “want to help people” does not support a sincere desire to become a physician; you must indicate why the medical profession in particular—rather than social work, teaching, or another “helping” profession—is your goal.
3. How have your experiences influenced you?
It is important to show how your experiences are linked and how they have influenced you. How did your experiences motivate you? How did they affect what else you did in your life? How did your experiences shape your future goals? Medical school admissions committees like to see a sensible progression of involvements. While not every activity needs to be logically “connected” with another, the evolution of your interests and how your experiences have nurtured your future goals and ambitions show that you are motivated and committed.
4. Who are you as a person? What are your values and ideals?
Medical school admissions committees want to know about you as an individual beyond your interests in medicine, too. This is where answering that third open ended question in the prompt becomes so important. What was interesting about your background, youth, and home life? What did you enjoy most about college? Do you have any distinctive passions or interests? They want to be convinced that you are a good person beyond your experiences. Write about those topics that are unlikely to appear elsewhere in your statement that will offer depth and interest to your work and illustrate the qualities and characteristics you possess.
Related Articles:
- How to Get into Stanford Medical School
- How to Get into NYU Medical School
- How To Get Into Columbia Medical School
- How To Get Into UT Southwestern Medical School
- How To Get Into Harvard Medical School
Complete Your Personal Inventory and Outline (Example Below)
The bulk of your essay should be about your most valuable experiences, personal, academic, scholarly, clinical, academic and extracurricular activities that have impacted your path to medical school and through which you have learned about the practice of medicine. The best personal statements cover several topics and are not narrow in scope. Why is this important? Many different people with a variety of backgrounds, interests, and ideas of what makes a great medical student will be reading your essay. You want to make sure you essay has broad appeal.
The following exercise will help you to determine what experiences you should highlight in your personal statement.
When composing your personal statement, keep in mind that you are writing, in effect, a “story” of how you arrived at this point in your life. But, unlike a “story” in the creative sense, yours must also offer convincing evidence for your decision to apply to medical school. Before starting your personal statement, create an experience- based personal inventory:
- Write down a list of the most important experiences in your life and your development. The list should be all inclusive and comprise those experiences that had the most impact on you. Put the list, which should consist of personal, extracurricular, and academic events, in chronological order.
- From this list, determine which experiences you consider the most important in helping you decide to pursue a career in medicine. This “experience oriented” approach will allow you to determine which experiences best illustrate the personal competencies admissions committees look for in your written documents. Remember that you must provide evidence for your interest in medicine and for most of the personal qualities and characteristics that medical school admissions committees want to see.
- After making your list, think about why each “most important” experience was influential and write that down. What did you observe? What did you learn? What insights did you gain? How did the experience influence your path and choices?
- Then think of a story or illustration for why each experience was important.
- After doing this exercise, evaluate each experience for its significance and influence and for its “story” value. Choose to write about those experiences that not only were influential but that also will provide interesting reading, keeping in mind that your goal is to weave the pertinent experiences together into a compelling story. In making your choices, think about how you will link each experience and transition from one topic to the next.
- Decide which of your listed experiences you will use for your introduction first (see below for more about your introduction). Then decide which experiences you will include in the body of your personal statement, create a general outline, and get writing!
Remember, you will also have your work and activities entries and your secondary applications to write in more detail about your experiences. Therefore, don’t feel you must pack everything in to your statement!
Craft a Compelling Personal Statement Introduction and Body
You hear conflicting advice about application essays. Some tell you not to open with a story. Others tell you to always begin with a story. Regardless of the advice you receive, be sure to do three things:
- Be true to yourself. Everyone will have an opinion regarding what you should and should not write. Follow your own instincts. Your personal statement should be a reflection of you, and only you.
- Start your personal statement with something catchy. Think about the list of potential topics above.
- Don’t rush your work. Composing thoughtful documents takes time and you don’t want your writing and ideas to be sloppy and underdeveloped.
Most important is to begin with something that engages your reader. A narrative, a “story,” an anecdote written in the first or third person, is ideal. Whatever your approach, your first paragraph must grab your reader’s attention and motivate him to want to continue reading. I encourage applicants to start their personal statement by describing an experience that was especially influential in setting them on their path to medical school. This can be a personal or scholarly experience or an extracurricular one. Remember to avoid clichés and quotes and to be honest and authentic in your writing. Don’t try to be someone who you are not by trying to imitate personal statement examples you have read online or “tell them what you think they want to hear”; consistency is key and your interviewer is going to make sure that you are who you say you are!
When deciding what experiences to include in the body of your personal statement, go back to your personal inventory and identify those experiences that have been the most influential in your personal path and your path to medical school. Keep in mind that the reader wants to have an idea of who you are as a human being so don’t write your personal statement as a glorified resume. Include some information about your background and personal experiences that can give a picture of who you are as a person outside of the classroom or laboratory.
Ideally, you should choose two or three experiences to highlight in the body of your personal statement. You don’t want to write about all of your accomplishments; that is what your application entries are for!
Write Your Personal Statement Conclusion
In your conclusion, it is customary to “go full circle” by coming back to the topic—or anecdote—you introduced in the introduction, but this is not a must. Summarize why you want to be a doctor and address what you hope to achieve and your goals for medical school. Write a conclusion that is compelling and will leave the reader wanting to meet you.
Complete Personal Statement Checklist
When reading your medical school personal statement be sure it:
Shows insight and introspection
The best medical school personal statements tell a great deal about what you have learned through your experiences and the insights you have gained.
You want to tell your story by highlighting those experiences that have been the most influential on your path to medical school and to give a clear sense of chronology. You want your statement always to be logical and never to confuse your reader.
Is interesting and engaging
The best personal statements engage the reader. This doesn’t mean you must use big words or be a literary prize winner. Write in your own language and voice, but really think about your journey to medical school and the most intriguing experiences you have had.
Gives the reader a mental image of who you are
You want the reader to be able to envision you as a caregiver and a medical professional. You want to convey that you would be a compassionate provider at the bedside – someone who could cope well with crisis and adversity.
Illustrates your passion for, and commitment to, medicine
Your reader must be convinced that you are excited about and committed to a career in medicine!
Above all, your personal statement should be about you. Explain to your reader what you have done and why you want to be a doctor with insight, compassion, and understanding.
Medical School Personal Statement Myths
Also keep in mind some common myths about personal statements that I hear quite often:
My personal statement must have a theme.
Not true. The vast majority of personal statements do not have themes. In fact, most are somewhat autobiographical and are just as interesting as those statements that are woven around a “theme.” It is only the very talented writer who can creatively write a personal statement around a theme, and this approach often backfires since the applicant fails to answer the three questions above.
My personal statement must be no longer than one page.
Not true. This advice is antiquated and dates back to the days of the written application when admissions committees flipped through pages. If your personal statement is interesting and compelling, it is fine to use the entire allotted space. The application systems have incorporated limits for exactly this reason! Many students, depending on their unique circumstances, can actually undermine their success by limiting their personal statement to a page. That said, never max out a space just for the sake of doing so. Quality writing and perspectives are preferable to quantity.
My personal statement should not describe patient encounters or my personal medical experiences.
Not true. Again, the actual topics on which you focus in your personal statement are less important than the understanding you gained from those experiences. I have successful clients who have written extremely powerful and compelling personal statements that included information about clinical encounters – both personal and professional. Write about whichever experiences were the most important on your path to medicine. It’s always best, however, to avoid spending too much space on childhood and high school activities. Focus instead on those that are more current.
In my personal statement I need to sell myself.
Not exactly true. You never want to boast in your personal statement. Let your experiences, insights, and observations speak for themselves. You want your reader to draw the conclusion – on his or her own – that you have the qualities and characteristics the medical school seeks. Never tell what qualities and characteristics you possess; let readers draw these conclusions on their own based on what you write.
Medical School Personal Statement Examples and Analysis for Inspiration
Below are examples of actual medical school personal statements. You can also likely find medical school personal statements on Reddit.

AMCAS Medical School Personal Statement Example and Analysis #1 with Personal Inventory
We will use Amy to illustrate the general process of writing an application to medical school, along with providing the resulting documents. Amy will first list those experiences, personal, extracurricular, and scholarly, that have been most influential in two areas: her life in general and her path to medical school. She will put this personal inventory in chronologic order for use in composing her personal statement.
She will then select those experiences that were the most significant to her and will reflect and think about why they were important. For her application entries, Amy will write about each experience, including those that she considers influential in her life but not in her choice of medicine, in her application entries. Experiences that Amy will not write about in her activity entries or her personal statement are those that she does not consider most influential in either her life or in her choice of medicine.
Amy’s personal inventory (from oldest to most recent)
- Going with my mom to work. She is a surgeon — I was very curious about what she did. I was intrigued by the relationships she had with patients and how much they valued her efforts. I also loved seeing her as “a doctor” since, to me, she was just “mom.”
- I loved biology in high school. I started to think seriously about medicine then. It was during high school that I became fascinated with biology and how the human body worked. I would say that was when I thought, “Hmm, maybe I should be a doctor.”
- Grandmother’s death, senior year of high school. My grandmother’s death was tragic. It was the first time I had ever seen someone close to me suffer. It was one of the most devastating experiences in my life.
- Global Health Trip to Guatemala my freshman year of college. I realized after going to Guatemala that I had always taken my access to health care for granted. Here I saw children who didn’t have basic health care. This made me want to become a physician so I could give more to people like those I met in Guatemala.
- Sorority involvement. Even though sorority life might seem trivial, I loved it. I learned to work with different types of people and gained some really valuable leadership experience.
- Poor grades in college science classes. I still regret that I did badly in my science classes. I think I was immature and was also too involved in other activities and didn’t have the focus I needed to do well. I had a 3.4 undergraduate GPA.
- Teaching and tutoring Jose, a child from Honduras. In a way, meeting Jose in a college tutoring program brought my Guatemala experience to my home. Jose struggled academically, and his parents were immigrants and spoke only Spanish, so they had their own challenges. I tried to help Jose as much as I could. I saw that because he lacked resources, he was at a tremendous disadvantage.
- Volunteering at Excellent Medical Center. Shadowing physicians at the medical center gave me a really broad view of medicine. I learned about different specialties, met many different patients, and saw both great and not-so-great physician role models. Counselor at Ronald McDonald House. Working with sick kids made me appreciate my health. I tried to make them happy and was so impressed with their resilience. It made me realize that good health is everything.
- Oncology research. Understanding what happens behind the scenes in research was fascinating. Not only did I gain some valuable research experience, but I learned how research is done.
- Peer health counselor. Communicating with my peers about really important medical tests gave me an idea of the tremendous responsibility that doctors have. I also learned that it is important to be sensitive, to listen, and to be open-minded when working with others.
- Clinical Summer Program. This gave me an entirely new view of medicine. I worked with the forensics department, and visiting scenes of deaths was entirely new to me. This experience added a completely new dimension to my understanding of medicine and how illness and death affect loved ones.
- Emergency department internship. Here I learned so much about how things worked in the hospital. I realized how important it was that people who worked in the clinical department were involved in creating hospital policies. This made me understand, in practical terms, how an MPH would give me the foundation to make even more change in the future.
- Master’s in public health. I decided to get an MPH for two reasons. First of all, I knew my undergraduate science GPA was an issue so I figured that graduate level courses in which I performed well would boost my record. I don’t think I will write this on my application, but I also thought the degree would give me other skills if I didn’t get into medical school, and I knew it would also give me something on which I could build during medical school and in my career since I was interested in policy work.
As you can see from Amy’s personal inventory list, she has many accomplishments that are important to her and influenced her path. The most influential personal experience that motivated her to practice medicine was her mother’s career as a practicing physician, but Amy was also motivated by watching her mother’s career evolve. Even though the death of her grandmother was devastating for Amy, she did not consider this experience especially influential in her choice to attend medical school so she didn’t write about it in her personal statement.
Amy wrote an experience-based personal statement, rich with anecdotes and detailed descriptions, to illustrate the evolution of her interest in medicine and how this motivated her to also earn a master’s in public health.
Amy’s Medical School Personal Statement Example:
She was sprawled across the floor of her apartment. Scattered trash, decaying food, alcohol bottles, medication vials, and cigarette butts covered the floor. I had just graduated from college, and this was my first day on rotation with the forensic pathology department as a Summer Scholar, one of my most valuable activities on the path to medical school. As the coroner deputy scanned the scene for clues to what caused this woman’s death, I saw her distraught husband. I did not know what to say other than “I am so sorry.” I listened intently as he repeated the same stories about his wife and his dismay that he never got to say goodbye. The next day, alongside the coroner as he performed the autopsy, I could not stop thinking about the grieving man.
Discerning a cause of death was not something I had previously associated with the practice of medicine. As a child, I often spent Saturday mornings with my mother, a surgeon, as she rounded on patients. I witnessed the results of her actions, as she provided her patients a renewed chance at life. I grew to honor and respect my mother’s profession. Witnessing the immense gratitude of her patients and their families, I quickly came to admire the impact she was able to make in the lives of her patients and their loved ones.
I knew I wanted to pursue a career in medicine as my mother had, and throughout high school and college I sought out clinical, research, and volunteer opportunities to gain a deeper understanding of medicine. After volunteering with cancer survivors at Camp Ronald McDonald, I was inspired to further understand this disease. Through my oncology research, I learned about therapeutic processes for treatment development. Further, following my experience administering HIV tests, I completed research on point-of-care HIV testing, to be instituted throughout 26 hospitals and clinics. I realized that research often served as a basis for change in policy and medical practice and sought out opportunities to learn more about both.
All of my medically related experiences demonstrated that people who were ‘behind the scenes’ and had limited or no clinical background made many of the decisions in health care. Witnessing the evolution of my mother’s career further underscored the impact of policy change on the practice of medicine. In particular, the limits legislation imposed on the care she could provide influenced my perspective and future goals. Patients whom my mother had successfully treated for more than a decade, and with whom she had long-standing, trusting relationships, were no longer able to see her, because of policy coverage changes. Some patients, frustrated by these limitations, simply stopped seeking the care they needed. As a senior in college, I wanted to understand how policy transformations came about and gain the tools I would need to help effect administrative and policy changes in the future as a physician. It was with this goal in mind that I decided to complete a master’s in public health program before applying to medical school.
As an MPH candidate, I am gaining insight into the theories and practices behind the complex interconnections of the healthcare system; I am learning about economics, operations, management, ethics, policy, finance, and technology and how these entities converge to impact delivery of care. A holistic understanding of this diverse, highly competitive, market-driven system will allow me, as a clinician, to find solutions to policy, public health, and administration issues. I believe that change can be more effective if those who actually practice medicine also decide where improvements need to be made.
For example, as the sole intern for the emergency department at County Medical Center, I worked to increase efficiency in the ED by evaluating and mapping patient flow. I tracked patients from point of entry to point of discharge and found that the discharge process took up nearly 35% of patients’ time. By analyzing the reasons for this situation, in collaboration with nurses and physicians who worked in the ED and had an intimate understanding of what took place in the clinical area, I was able to make practical recommendations to decrease throughput time. The medical center has already implemented these suggestions, resulting in decreased length of stays. This example illustrates the benefit of having clinicians who work ‘behind the scenes’ establish policies and procedures, impacting operational change and improving patient care. I will also apply what I have learned through this project as the business development intern at Another Local Medical Center this summer, where I will assist in strategic planning, financial analysis, and program reviews for various clinical departments.
Through my mother’s career and my own medical experiences, I have become aware of the need for clinician administrators and policymakers. My primary goal as a physician will be to care for patients, but with the knowledge and experience I have gained through my MPH, I also hope to effect positive public policy and administrative changes.
What’s Good About Amy’s Medical School Personal Statement:
Paragraphs 1 and 2: Amy started her personal statement by illustrating a powerful experience she had when she realized that medical caregivers often feel impotent, and how this contrasted with her understanding of medicine as a little girl going with her mother to work. Recognition of this intense contrast also highlights Amy’s maturity.
Paragraph 3: Amy then “lists” a few experiences that were important to her.
Paragraph 4: Amy describes the commonality in some of her experiences and how her observations were substantiated by watching the evolution of her mother’s practice. She then explains how this motivated her to earn an MPH so she could create change more effectively as a physician than as a layman.
Paragraph 5: Amy then explains how her graduate degree is helping her to better understand the “issues in medicine” that she observed.
Paragraph 6: Amy then describes one exceptional accomplishment she had that highlights what she has learned and how she has applied it.
Paragraph 7: Finally, Amy effectively concludes her personal statement and summarizes the major topics addressed in her essay.
As you can see, Amy’s statement has excellent flow, is captivating and unusual, and illustrates her understanding of, and commitment to, medicine. She also exhibits, throughout her application entries and statement, the personal competencies, characteristics, and qualities that medical school admissions officers are seeking. Her application also has broad appeal; reviewers who are focused on research, cultural awareness, working with the underserved, health administration and policy, teaching, or clinical medicine would all find it of interest.

med school personal statement examples
Osteopathic Medical School Personal Statement Example and Analysis #2
Medical School Personal Statement Example Background: This is a nontraditional applicant who applied to osteopathic medical schools. With a 500 and a 504 on the MCAT , he needed to showcase how his former career and what he learned through his work made him an asset. He also needed to convey why osteopathic medicine was an ideal fit for him. The student does an excellent job illustrating his commitment to medicine and explaining why and how he made the well-informed decision to leave his former career to pursue a career in osteopathic medicine.
What’s Good About It: A nontraditional student with a former career, this applicant does a great job outlining how and why he decided to pursue a career in medicine. Clearly dedicated to service, he also does a great job making it clear he is a good fit for osteopathic medical school and understands this distinctions of osteopathic practice..
Working as a police officer, one comes to expect the unexpected, but sometimes, when the unexpected happens, one can’t help but be surprised. In November 20XX, I had been a police officer for two years when my partner and I happened to be nearby when a man had a cardiac emergency in Einstein Bagels. Entering the restaurant, I was caught off guard by the lifeless figure on the floor, surrounded by spilled food. Time paused as my partner and I began performing CPR, and my heart raced as I watched color return to the man’s pale face.
Luckily, paramedics arrived within minutes to transport him to a local hospital. Later, I watched as the family thanked the doctors who gave their loved one a renewed chance at life. That day, in the “unexpected,” I confirmed that I wanted to become a physician, something that had attracted me since childhood.
I have always been enthralled by the science of medicine and eager to help those in need but, due to life events, my path to achieving this dream has been long. My journey began following high school when I joined the U.S. Army. I was immature and needed structure, and I knew the military was an opportunity to pursue my medical ambitions. I trained as a combat medic and requested work in an emergency room of an army hospital. At the hospital, I started IVs, ran EKGs, collected vital signs, and assisted with codes. I loved every minute as I was directly involved in patient care and observed physicians methodically investigating their patients’ signs and symptoms until they reached a diagnosis. Even when dealing with difficult patients, the physicians I worked with maintained composure, showing patience and understanding while educating patients about their diseases. I observed physicians not only as clinicians but also as teachers. As a medic, I learned that I loved working with patients and being part of the healthcare team, and I gained an understanding of acute care and hospital operations.
Following my discharge in 20XX, I transferred to an army reserve hospital and continued as a combat medic until 20XX. Working as a medic at several hospitals and clinics in the area, I was exposed to osteopathic medicine and the whole body approach to patient care. I was influenced by the D.O.s’ hands-on treatment and their use of manipulative medicine as a form of therapy. I learned that the body cannot function properly if there is dysfunction in the musculoskeletal system.
In 20XX, I became a police officer to support myself as I finished my undergraduate degree and premed courses. While working the streets, I continued my patient care experiences by being the first to care for victims of gunshot wounds, stab wounds, car accidents, and other medical emergencies. In addition, I investigated many unknown causes of death with the medical examiner’s office. I often found signs of drug and alcohol abuse and learned the dangers and power of addiction. In 20XX, I finished my undergraduate degree in education and in 20XX, I completed my premed courses.
Wanting to learn more about primary care medicine, in 20XX I volunteered at a community health clinic that treats underserved populations. Shadowing a family physician, I learned about the physical exam as I looked into ears and listened to the hearts and lungs of patients with her guidance. I paid close attention as she expressed the need for more PCPs and the important roles they play in preventing disease and reducing ER visits by treating and educating patients early in the disease process. This was evident as numerous patients were treated for high cholesterol, elevated blood pressure, and diabetes, all conditions that can be resolved or improved by lifestyle changes. I learned that these changes are not always easy for many in underserved populations as healthier food is often more expensive and sometimes money for prescriptions is not available. This experience opened my eyes to the challenges of being a physician in an underserved area.
The idea of disease prevention stayed with me as I thought about the man who needed CPR. Could early detection and education about heart disease have prevented his “unexpected” cardiac event? My experiences in health care and law enforcement have confirmed my desire to be an osteopathic physician and to treat the patients of the local area. I want to eliminate as many medical surprises as I can.

Texas Medical School Personal Statement Example and Analysis #3
Medical School Personal Statement Example Background: This applicant, who grew up with modest means, should be an inspiration to us all. Rather than allowing limited resources to stand in his way, he took advantage of everything that was available to him. He commuted to college from home and had a part-time job so he was stretched thin, and his initial college performance suffered. However, he worked hard and his grades improved. Most medical school admissions committees seek out applicants like this because, by overcoming adversity and succeeding with limited resources, they demonstrate exceptional perseverance, maturity, and dedication. His accomplishments are, by themselves, impressive and he does an outstanding job of detailing his path, challenges, and commitment to medicine. He received multiple acceptances to top medical schools and was offered scholarships.
What’s Good About It: This student does a great job opening his personal statement with a beautifully written introduction that immediately takes the reader to Central America. He then explains his path, why he did poorly early in college, and goes on to discuss his academic interests and pursuits. He is also clearly invested in research and articulates that he is intellectually curious, motivated, hard working, compassionate and committed to a career in medicine by explaining his experiences using interesting language and details. This is an intriguing statement that makes clear the applicant is worthy of an interview invitation. Finally, the student expresses his interest in attending medical school in Texas.
They were learning the basics of carpentry and agriculture. The air was muggy and hot, but these young boys seemed unaffected, though I and my fellow college students sweated and often complained. As time passed, I started to have a greater appreciation for the challenges these boys faced. These orphans, whom I met and trained in rural Central America as a member of The Project, had little. They dreamed of using these basic skills to earn a living wage. Abandoned by their families, they knew this was their only opportunity to re-enter society as self- sufficient individuals. I stood by them in the fields and tutored them after class. And while I tried my best to instill in them a strong work ethic, it was the boys who instilled in me a desire to help those in need. They gave me a new perspective on my decision to become a doctor.
I don’t know exactly when I decided to become a physician; I have had this goal for a long time. I grew up in the inner city of A City, in Texas and attended magnet schools. My family knew little about higher education, and I learned to seek out my own opportunities and advice. I attended The University with the goal of gaining admission to medical school. When I started college, I lacked the maturity to focus on academics and performed poorly. Then I traveled to Central America. Since I was one of the few students who spoke Spanish, many of the boys felt comfortable talking with me. They saw me as a role model.
The boys worked hard so that they could learn trades that would help them to be productive members of society. It was then I realized that my grandparents, who immigrated to the US so I would have access to greater opportunities, had done the same. I felt like I was wasting what they had sacrificed for me. When I returned to University in the fall, I made academics my priority and committed myself to learn more about medicine .

Through my major in neuroscience, I strengthened my understanding of how we perceive and experience life. In systems neurobiology, I learned the physiology of the nervous system. Teaching everything from basic neural circuits to complex sensory pathways, Professor X provided me with the knowledge necessary to conduct research in Parkinson’s disease. My research focused on the ability of antioxidants to prevent the onset of Parkinson’s, and while my project was only a pilot study at the time, Professor X encouraged me to present it at the National Research Conference. During my senior year, I developed the study into a formal research project, recruiting the help of professors of statistics and biochemistry.
Working at the School of Medicine reinforced my analytical skills. I spent my summer in the department of emergency medicine, working with the department chair, Dr. Excellent. Through Dr. Excellent’s mentorship, I participated in a retrospective study analyzing patient charts to determine the efficacy of D-dimer assays in predicting blood clots. The direct clinical relevance of my research strengthened my commitment and motivated my decision to seek out more clinical research opportunities.
A growing awareness of the role of human compassion in healing has also influenced my choice to pursue a career in medicine. It is something no animal model or cell culture can ever duplicate or rival. Working in clinical research has allowed me to see the selflessness of many physicians and patients and their mutual desire to help others. As a research study assistant in the department of surgery, I educate and enroll patients in clinical trials. One such study examines the role of pre-operative substance administration in tumor progression. Patients enrolled in this study underwent six weeks of therapy before having the affected organ surgically excised. Observing how patients were willing to participate in this research to benefit others helped me understand the resiliency of the human spirit.
Working in clinical trials has enabled me to further explore my passion for science, while helping others. Through my undergraduate coursework and participation in volunteer groups I have had many opportunities to solidify my goal to become a physician. As I am working, I sometimes think about my second summer in Central America. I recall how one day, after I had turned countless rows of soil in scorching heat, one of the boys told me that I was a trabajador verdadero—a true worker. I paused as I realized the significance of this comment. While the boy may not have been able to articulate it, he knew I could identify with him. What the boy didn’t know, however, was that had my grandparents not decided to immigrate to the US, I would not have the great privilege of seizing opportunities in this country and writing this essay today. I look forward to the next step of my education and hope to return home to Texas where I look forward to serving the communities I call home.
Final Thoughts
Above all, and as stated in this article numerous times, your personal statement should be authentic and genuine. Write about your path and and journey to this point in your life using anecdotes and observations to intrigue the reader and illustrate what is and was important to you. Good luck!
Medical School Personal Statement Help & Consulting
If all this information has you staring at your screen like a deer in the headlights, you’re not alone. Writing a superb medical school personal statement can be a daunting task, and many applicants find it difficult to get started writing, or to express everything they want to say succinctly. That’s where MedEdits can help. You don’t have to have the best writing skills to compose a stand-out statement. From personal-statement editing alone to comprehensive packages for all your medical school application needs, we offer extensive support and expertise developed from working with thousands of successful medical school applicants. We can’t promise applying to medical school will be stress-free, but most clients tell us it’s a huge relief not to have to go it alone.
MedEdits offers personal statement consulting and editing. Our goal when working with students is to draw out what makes each student distinctive. How do we do this? We will explore your background and upbringing, interests and ideals as well as your accomplishments and activities. By helping you identify the most distinguishing aspects of who you are, you will then be able to compose an authentic and genuine personal statement in your own voice to capture the admissions committee’s attention so you are invited for a medical school interview. Our unique brainstorming methodology has helped hundreds of aspiring premeds gain acceptance to medical school.

Sample Medical School Personal Statement

Example Medical School Personal Statement

- Website Disclaimer
- Terms and Conditions
- MedEdits Privacy Policy
US South Carolina
Recently viewed courses
Recently viewed.
Find Your Dream School
This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
COVID-19 Update: To help students through this crisis, The Princeton Review will continue our "Enroll with Confidence" refund policies. For full details, please click here.
Enter your email to unlock an extra $50 off any MCAT program!
By submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., 15 tips for your medical school personal statement.
Don't underestimate the power of the medical school personal statement to make a strong, positive impression on an admissions committee. Combined with your interview performance, your personal statement can account for 60% (or more) of your total admissions score!
Medical schools want to enroll bright, empathetic, communicative people. Here's how to write a compelling med school personal statement that shows schools who you are and what you're capable of.

Personal Statement Topics
Your medical school personal statement is a component of your primary application submitted via, TMDSAS (for Texas applications), or AACOMAS (NB: If you are applying to medical school in Canada, confirm the application process with your school, as not all application components may be submitted through AMCAS).
These applications offer broad topics to consider, and many essay approaches are acceptable. For example, you could write about:
- an experience that challenged or changed your perspective about medicine
- a relationship with a mentor or another inspiring individual
- a challenging personal experience
- unique hardships, challenges, or obstacles that may have influenced your educational pursuits
- your motivation to seek a career in medicine
You'll write an additional essay (or two) when you submit secondary applications to individual schools. These essays require you to respond to a specific question. Admissions committees will review your entire application, so choose subject matter that complements your original essay .
Read More: Strategies for Secondary Applications
How to Write a Personal Statement for Medical School
Follow these personal statement tips to help the admissions committee better understand you as a candidate.
1. Write, re-write, let it sit, and write again!
Allow yourself 6 months of writing and revision to get your essay in submission-ready shape. This gives you the time to take your first pass, set your draft aside (for a minimum of 24 hours), review what you’ve written, and re-work your draft.
2. Stay focused.
Your personal statement should highlight interesting aspects of your journey—not tell your entire life story. Choose a theme, stick to it, and support it with specific examples.
3. Back off the cliches.
Loving science and wanting to help people might be your sincere passions, but they are also what everyone else is writing about. Instead, be personal and specific.
4. Find your unique angle.
What can you say about yourself that no one else can? Remember, everyone has trials, successes and failures. What's important and unique is how you reacted to those incidents. Bring your own voice and perspective to your personal statement to give it a truly memorable flavor.
5. Be interesting.
Start with a “catch” that will create intrigue before launching into the story of who you are. Make the admissions committee want to read on!
6. Show don't tell.
Instead of telling the admissions committee about your unique qualities (like compassion, empathy, and organization), show them through the stories you tell about yourself. Don’t just say it—actually prove it.
7. Embrace the 5-point essay format.
Here's a trusty format that you can make your own:
- 1st paragraph: These four or five sentences should "catch" the reader's attention.
- 3-4 body paragraphs: Use these paragraphs to reveal who you are. Ideally, one of these paragraphs will reflect clinical understanding and one will reflect service.
- Concluding paragraph: The strongest conclusion reflects the beginning of your essay, gives a brief summary of you are, and ends with a challenge for the future.
8. Good writing is simple writing.
Good medical students—and good doctors—use clear, direct language. Your essays should not be a struggle to comprehend.
9. Be thoughtful about transitions.
Be sure to vary your sentence structure. You don’t want your essay to be boring! Pay attention to how your paragraphs connect to each other.
Free MCAT Practice Tests & Events
Evaluate and improve your MCAT score.
10. Stick to the rules.
Watch your word count. That’s 5,300 characters (including spaces) for AMCAS applications, 5,000 characters for TMDSAS, and 4,500 characters for AACOMAS.
11. Stay on topic.
Rambling not only uses up your precious character limit, but it also causes confusion! Think about the three to five “sound bytes” you want admissions committee to know and remember you by.
12. Don't overdo it.
Beware of being too self-congratulatory or too self-deprecating.
13. Seek multiple opinions.
Before you hit “submit,” ask several people you trust for feedback on your personal statement. The more time you have spent writing your statement, the less likely you are to spot any errors. A professor or friend whose judgment and writing skills you trust is invaluable.
Read More: 12 Smart Tips for Your AMCAS Application
14. Double-check the details.
Always check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. This goes for the rest of your application (like your activities list), too. A common oversight is referencing the wrong school in your statement! Give yourself (and your proofreaders) the time this task truly requires.
15. Consult the experts about your personal statement strategy.
Our med school admissions counselors can diagnose the “health” of your overall application, including your personal statement. Get expert help and guidance to write an effective personal statement that showcases not only your accomplishments, but your passion and your journey.
Want to get an edge over the crowd?
Our admissions experts know what it takes it get into med school. Get the customized strategy and guidance you need to help achieve your goals.
Med School Admission Counseling

Explore Graduate Programs for You
Explore our featured graduate schools & programs to find those that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Best Law Schools
Check out our complete list of 168 law schools, based on surveys of school administrators and over 17,000 students.
Search for Medical Schools
Visit our Med School Hub to explore med schools with our ‘Find Your Med School’ filtered search or visit our Med School Advice pages for info about good MCAT scores or interview question prep.

Find MBA Programs Matched to Your Interests
Explore our featured business schools to find those that are looking for students like you.
MCAT Prep Courses
510+ course, ultimate course, summer immersion, more mcat articles, free mcat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, mcat self-paced free trial.
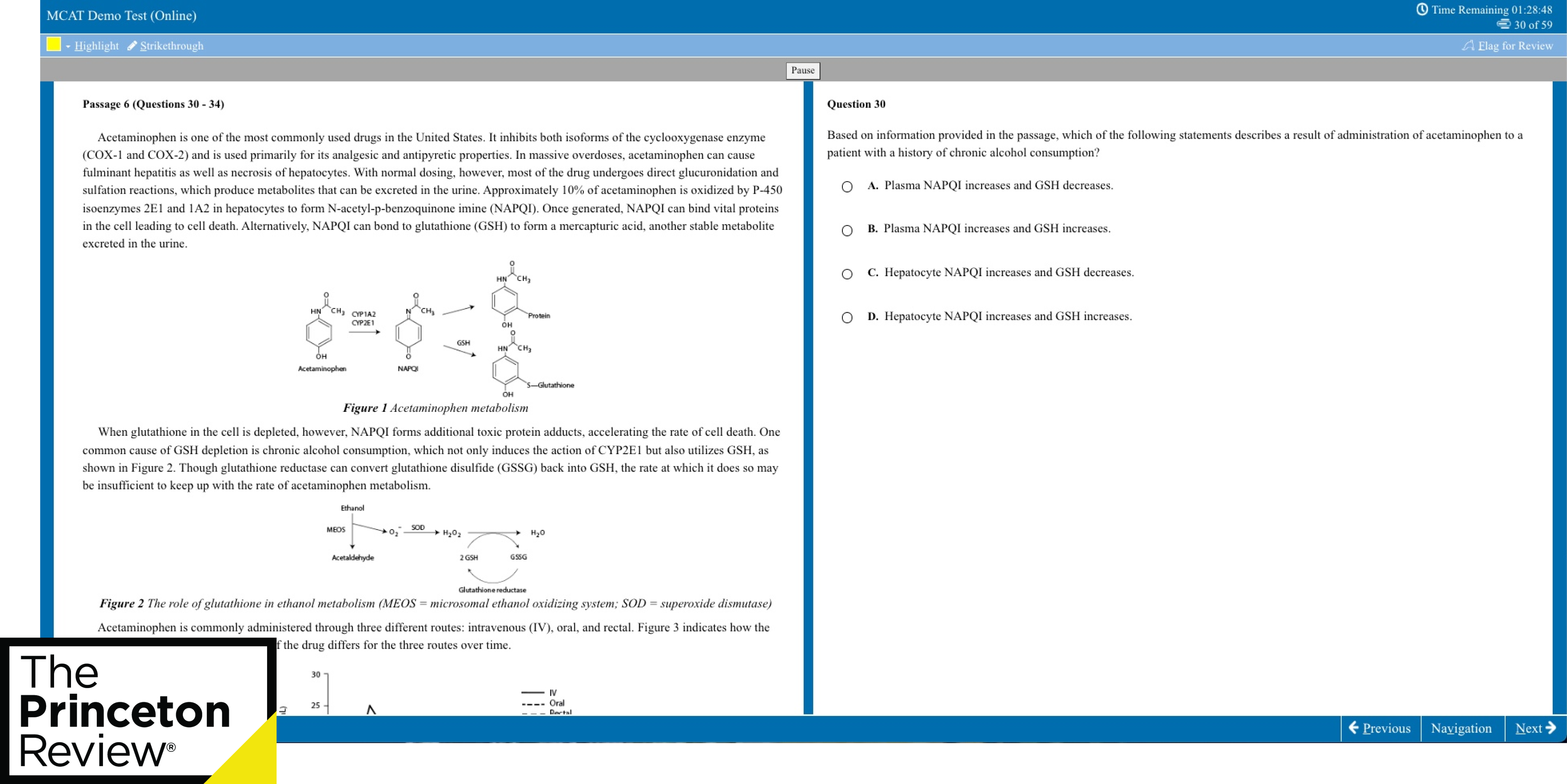
Free MCAT Practice Test
I already know my score.
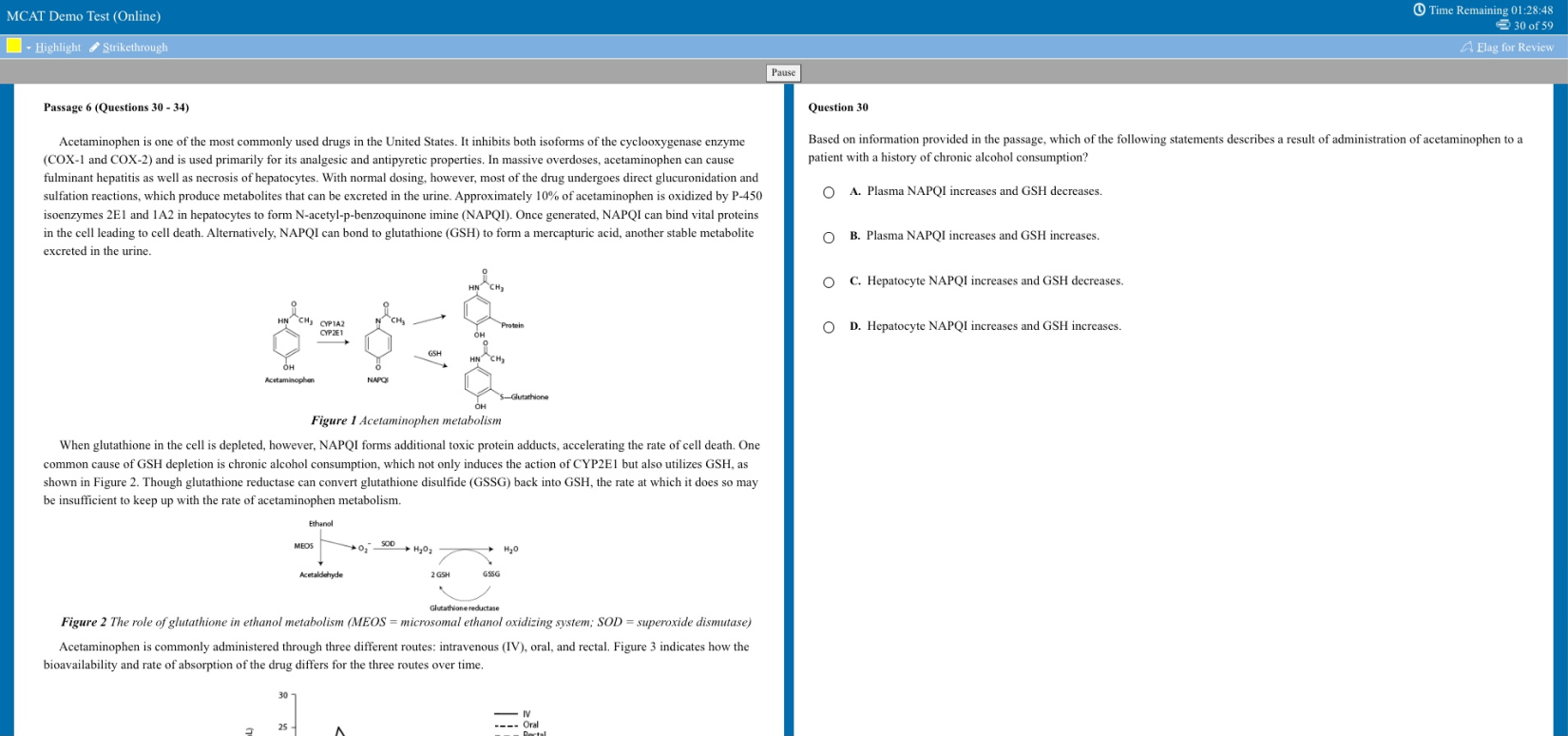
MCAT Self-Paced 14-Day Free Trial
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- Local Offices
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.
Section 8 of the AMCAS® Application: Essays
New section.
Here you will upload your Personal Comments essay.
- AMCAS® Sign In
Every applicant is required to submit a Personal Comments essay. The available space for this essay is 5,300 characters (spaces are counted as characters), or approximately one page. You will receive an error message if you exceed the available space. Click the "What information should I consider including in my personal comments?" link in the application or see Section 8 of the AMCAS Applicant Guide for suggestions of things to think about when writing this essay.
- If you're applying to an MD-PhD program, you must complete two additional essays: the MD-PhD Essay and the Significant Research Experience Essay.
- To avoid formatting issues, we recommend that you type your essay directly into the AMCAS ® application rather than copying and pasting your essay from other software.
- Alternately, you can draft your essay(s) in text-only word processing software, such as Microsoft Notepad or Mac TextEdit, then copy and paste your essay(s) into the application. Copying formatted text into the application may result in formatting issues that you will not be able to edit after your application is submitted.
- Proofread carefully! There is no “spellchecker” in the AMCAS application, and no changes will be permitted to this section after you have submitted your application.
Send us a message .
Monday-Friday, 9 a.m.-7 p.m. ET Closed Wednesday, 3-5 p.m. ET
2025 AMCAS application dates:
May 1, 2024: AMCAS application opens
May 28, 2024: Submission for AMCAS application verification begins
June 28, 2024: Application transmission to medical schools begins
Aug. 1, 2024: Early Decision Program (EDP) deadline
The 2024 AMCAS application is now open. If you wish to start medical school in Fall 2024, please complete and submit the 2024 AMCAS application.
As of April 26 AMCAS is:
Marking transcripts as "Received" that were delivered on or before:
Paper (mailed) – April 26
Parchment – April 25
National Student Clearinghouse – April 26
Processing applications that reached "Ready for Review" on April 25.
Processing Academic Change Requests submitted on April 26.
Outline of the current AMCAS application process, policies, and procedures.
This resource is designed to help you prepare your materials for the 2024 AMCAS ® application but does not replace the online application.
The application processing fee is $175 and includes one medical school designation. Additional school designations are $46 each. Tax, where applicable, will be calculated at checkout.
If approved for the Fee Assistance Program, you will receive a waiver for all AMCAS fees for one (1) application submission with up to 20 medical school designations ($1,030 value). Benefits are not retroactive.
Successful Harvard Medical School Essays | 2024
With a consistently competitive pool of applicants submitting essays to top medical schools each year, it is essential to gain a high-level understanding of what a successful application reads like. Browse through our list of successful medical school applications below from students who were accepted to elite universities and hear from expert college consultants on what made these pieces a success.
Jacqueline's Essay

Solomon Admissions Consulting is among the largest and most diverse consulting firms in the US. Their team includes over 100 consultants, all of whom have worked in the admissions offices of elite colleges. The Solomon team boasts a combined 600+ years of admissions office experience and has reviewed over 700,000+ college applications. This extensive experience uniquely qualifies them to advise on what the most competitive colleges seek in applicants. Solomon Admissions Consulting is the only firm in the industry with college admission success rates verified by a top independent accounting firm. This verification confirms the 5.5x advantage Solomon clients have when applying to Ivy Plus schools (including all 8 Ivy League schools plus Stanford, MIT, Duke, and UChicago) compared to the national average acceptance rates at these institutions. Solomon offers admissions assistance from private/K-12 schooling through undergraduate and medical school, MBA, and post-graduate programs. Their admission consultants ensure that student essays, teacher recommendation letters, activity sheets, addendums, and interviews all support a strategic positioning narrative.
Successful Harvard Medical School Essay
Jim and I had only spoken once by phone and were now in a soundproof piano practice room in my dorm basement, after dark and out of cell phone range. My new piano student told me he lived in a sober house, was unemployed, and “had time to kill.” He wanted to learn piano and called me because he read favorable online reviews of my piano playing. I was somewhat flattered but mostly uneasy about what I was getting myself into. I have played jazz piano since age 11. My early focus was technique. I loved practicing and spent hours at the piano. Through Boston’s Berklee School of Music summer programs, I gained a solid foundation and connected with exceptional musicians. I led multiple ensembles in school and professional circles. At first, I played wherever I could, including non-paying venues, but as my music further matured, I performed at increasingly high-visibility settings. I particularly treasured playing for charitable causes such as Ronald McDonald House, Gift of Life bone marrow drive, and at Boston Children’s Hospital. During college, I taught jazz piano, helping my students navigate the complexity and nuance of jazz theory. In the last several years, a highlight of each week was playing solo jazz in Yale’s cancer center lobby. Although I could not help patients from the medical perspective, I felt that I made a small contribution when an improvisation on “Somewhere Over the Rainbow” would bring a smile to a patient’s face. To me, there are striking parallels between jazz and medicine. Jazz improvisation encourages freedom of expression and creativity within the confines of a musical structure that is unspoken but understood among performers. Medical practice emphasizes customization of care based on a patient’s unique circumstance within the boundaries of established care paths and standards. In jazz, musicians take turns at improvisation, while the rest of the band “comps” (jazz lingo for “accompanies”). A fine soloist leads without overshadowing. Effective comping highlights the soloist without drawing excessive attention. Jazz, dynamic and fluid, requires teamwork and the ability to listen. I believe jazz prepared me well for the seamless teamwork and collaboration, learning, and adaptability that are intrinsic to medicine. At Yale, I was drawn to Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry for its scientific rigors and biological applications. A major focus of my work has been laboratory research. Under the guidance of my mentor Dr. Keith Choate, a brilliant physician scientist on the Yale faculty, I identified and studied the function of a palmitoyl transferase gene responsible for a cutaneous inflammatory disorder called erythrokeratoderma variabilis. I also observed Dr. Choate in the pediatric dermatology clinic at Yale New Haven Hospital. I vividly recall a young girl with brown scaly plaques covering almost her entire arm, her tearful efforts at hiding her arm as if she felt shameful, and her mother wringing her hands in anguish. The medical team approached the girl gently, trying to put her at ease. When Dr. Choate mentioned the potential of genomic-driven medicine offering new therapies, her mother’s eyes lit up, even though the solution was not yet at hand. I had been fascinated with the gene from the molecular angle, but seeing firsthand the physical and emotional tolls from the disease strengthened my interest in developing “post-genomic” technologies. At the same time, moments like this remind me why I want to be a doctor. No doubt biomedical research is stimulating and rewarding, and I hope to continue research pursuits. But I want to work directly with patients and personally make a difference in their lives. While it is possible to make a difference through research, I find it particularly meaningful to contribute at the human-to-human level. My aspiration is to learn about the human body and its diseases and impart my knowledge and skills to patients to relieve suffering. Medicine is going through significant changes. There is hope that technologies such as high-resolution genomics may identify more biomarkers for disease diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic guidance. Refinements in DNA sequence technology and computational tools already allow higher and higher throughput at lower cost. Application of genetic analytics on a population scale will hopefully help make personalized medicine a reality. Healthcare delivery is also going through a redesign, with increased emphasis on value and teamwork. I look forward to entering medicine at such an exciting time and feel well equipped from my training in molecular biology, computer programming, bioinformatics, and jazz to make a meaningful impact. After months of piano lessons, Jim played an awesome improvisation of “Mary Had a Little Lamb.” We had become friends and shared animated dialogues about art, religion, love, biology, and of course music. Jim was delighted that I also enjoyed rap, his favorite genre. I saw a transformation from aimless addict to proud-yet fragile young man. And then . . . he got a job! Jim was gainfully employed. He told me I was his inspiration. Little did he know that through the opportunity to teach him, grow with him, and observe his remarkable transition, I was in fact inspired by him.
Professional Review by Solomon Admissions
This personal statement masterfully blends vivid imagery and a compelling narrative, outlining a journey of personal growth and aspiration. The opening metaphor of life as a mosaic sets a tone of richness and emotion, charting the applicant’s path from the Dominican Republic to medicine in the U.S., marked by resilience and cultural transition.
The applicant’s motivation for medicine, rooted in personal and familial healthcare experiences and augmented by volunteer work and global exposure, is communicated with clarity and depth. Color symbolism enriches the narrative, making the journey visually memorable and showcasing a well-rounded character defined by academic achievement, community service dedication, and adversity resilience.
Specific experiences, like confronting poverty and healthcare challenges abroad, highlight a sophisticated grasp of global health and a commitment to positive impact. However, a tighter connection between these experiences and the developed qualities essential for medical school and beyond - resilience, empathy, and leadership, for example - could amplify the statement’s impact.
In sum, this statement is remarkable and thoughtfully written, promising to make a strong impression. Its unique storytelling and clear future vision in medicine are especially striking.
Jonathan's Essay

BeMo Academic Consulting is one of the most sought-after academic consulting firms in the world, famous for helping applicants with admissions to highly competitive programs and its staunch advocacy for fair admissions.
Professional Review by BeMo Academic Consulting
The author of this personal statement has rightfully earned a spot at one of the top medical schools in the world. The introduction creates a sense of intimacy and intrigue, which entices us to uncover what happens next. This personal statement then skillfully showcases Johnathan’s passion for medicine by intertwining his experiences in music and his interest in healthcare. He seamlessly draws parallels between the improvisational nature of jazz and the adaptive nature of medicine. Not only does this illustrate his deep understanding of both pursuits, but it also demonstrates his ability to think critically and make connections across disciplines, a crucial skill for a future physician . Johnathan’s story reveals his other academic and non-academic achievements that he undoubtedly further explores in his Work and Activities section and during his medical school interview! But even here, in this succinct narrative of his research experience , he brilliantly showcases his intellectual curiosity. By demonstrating his achievements in research, Johnathan not only highlights his scholarly acumen but also his desire to alleviate patient suffering, which is a part of Harvard’s mission. At the end, Johnathan masterfully uses the introduction and conclusion as bookends to his narrative, leaving us with a profound sense of closure and a hope that we may someday be under the care of this future physician.
4 Points to Include in Every Med School Personal Statement
For a compelling essay, prospective medical school students should share their passions beyond medicine.
4 Points to Include in Med School Essays

Getty Images
You should reflect on past patient-care experiences, including any insights you gained into the medical profession.
Putting together a personal statement for medical school can be challenging, as applicants may have many ideas but are unsure which to include in their narrative.
Prospective students often ask which ideas are appropriate for the personal statement and which should be reserved for other parts of the medical school application , such as the supplemental essays. The answer is that there is no single formula for writing a good personal statement and a variety of approaches could work.
Having said that, regardless of the approach you take, consider including these four key components to ensure that your statement is compelling.
Personal narrative. As the name implies, a personal statement is meant to have a personal touch, and one of the most effective ways to give it that touch is by including a bit about who you are as a person.
Virtually every medical school essay will have something about the applicant's experiences in a hospital, service to the community, academic achievements or research involvement. Give your essay a personal touch by sharing something outside of your passion for medicine to make sure your essay stands out.
10 Reasons Not to Go to Med School
Kathleen Franco, M.D., M.S. Sept. 28, 2021

For example, where were you born? What was your upbringing like? What are some key life events that have had an impact on you? What are some of your outside interests?
Taking the time to reflect on questions like these and weaving responses into your essay will help the reader connect with you on a human level. In so doing you will come across as a multidimensional individual who is more than just a GPA, an MCAT score and a series of clinical experiences.
Reflection on patient-care experiences. Virtually all personal statements allude to the applicant's involvement in clinical care as a volunteer, scribe , shadow or medical assistant. However, not every personal statement includes careful reflection on what those experiences meant and how they helped the applicant realize that medicine is his or her calling.
After you have briefly described the nature of your clinical experiences, reflect on what insight you gained from them about the medical profession. Use this opportunity to show the reader you understand what kind of career you are embarking on. Also, draw on your clinical experiences to demonstrate in concrete terms what you saw that solidified your desire to pursue medicine.
For example, you may share a few anecdotes in which you observed a physician form trusting relationships with his or her patients. What did these anecdotes teach you about the patient-doctor relationship? How did these observations make you more excited about becoming a physician?
Reasons for pursuing medicine. Too often admissions committees read medical school personal statements that don't directly and clearly express the reasons an applicant is pursuing a career in medicine. As a result, the reader is left to read between the lines and infer from anecdotes and experiences why you want to be a physician .
You can make the reader's job much easier by summarizing your reflections on clinical experiences and stating in one sentence why you are pursuing medicine.
There is nothing wrong with having a sentence in your personal statement where you state, "I want to be a physician because I like A, B and C about the medical profession." For example, if you shadowed a surgeon and observed a variety of surgical procedures, you may cite the opportunity to perform intricate procedures as one reason why you want to be a physician.
Your strengths. Medical schools want to know what strengths you believe you can bring to your medical education and to the profession.
But it is not just about what positive attributes you possess or how many you have. It is more important to show how you acquired each positive quality. As you reflect on various personal and professional experiences, ask yourself what each experience taught you and present each as an acquired strength.
For example, your essay will sound convincing if you state that you have learned to be a good team player through your involvement in various team-based activities . Conversely, if you just state that everyone considers you a solid team player without explaining how you acquired that skill, you will have a harder time convincing your audience that this is a genuine strength.
Taking the time to plan what goes in your personal statement can make the difference between writing a strong essay and a weak one. Think about the four points above and discuss them with others to further develop each one. It may take some time to articulate these ideas, but with careful consideration, you can put together a convincing personal statement.
Should You Become a Doctor?

Tags: medical school , graduate schools , education , students
About Medical School Admissions Doctor
Need a guide through the murky medical school admissions process? Medical School Admissions Doctor offers a roundup of expert and student voices in the field to guide prospective students in their pursuit of a medical education. The blog is currently authored by Dr. Ali Loftizadeh, Dr. Azadeh Salek and Zach Grimmett at Admissions Helpers , a provider of medical school application services; Dr. Renee Marinelli at MedSchoolCoach , a premed and med school admissions consultancy; Dr. Rachel Rizal, co-founder and CEO of the Cracking Med School Admissions consultancy; Dr. Cassie Kosarec at Varsity Tutors , an advertiser with U.S. News & World Report; Dr. Kathleen Franco, a med school emeritus professor and psychiatrist; and Liana Meffert, a fourth-year medical student at the University of Iowa's Carver College of Medicine and a writer for Admissions Helpers. Got a question? Email [email protected] .
Popular Stories
Paying for Graduate School

Applying to College

Best Global Universities

Best Colleges

You May Also Like
How to win a fulbright scholarship.
Cole Claybourn and Ilana Kowarski April 26, 2024
What to Ask Law Students and Alumni
Gabriel Kuris April 22, 2024

Find a Strong Human Rights Law Program
Anayat Durrani April 18, 2024

Environmental Health in Medical School
Zach Grimmett April 16, 2024

How to Choose a Law Career Path
Gabriel Kuris April 15, 2024

Questions Women MBA Hopefuls Should Ask
Haley Bartel April 12, 2024

Law Schools With the Highest LSATs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 11, 2024

MBA Programs That Lead to Good Jobs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 10, 2024

B-Schools With Racial Diversity
Sarah Wood April 10, 2024

Law Schools That Are Hardest to Get Into
Sarah Wood April 9, 2024

Medical School Personal Statement – 2023 Guide
June 12, 2023

One of the most important parts of your medical school application is undoubtedly the personal statement. Just like writing the Common App essay when applying to college, your medical school personal statement provides the opportunity to show admissions your skills, your goals, and your relevant experiences. You may also have had to submit a similar style essay when applying to BS/MD programs or early assurance medical programs . However, there are some key differences and specific strategies in writing your personal statement. We’ve laid out the answers to the most common questions about the medical school personal statement below.
How Long is a Medical School Personal Statement?
The medical school personal statement length varies slightly among the three application portals. Specifically, you have 5,300 characters for personal statements submitted through the American College Application Service (AMCAS) and the American Association of Colleges of Osteopathic Medicine Application Service (AACOMAS). That’s about 1.5 pages single-spaced using a 12-point font. For reference, the Common App essay – which is 650 words max – would translate to about 1.3 pages single-spaced using a 12-point font. Similarly, you can use up to 5,000 characters for a personal statement submitted through Texas Medical & Dental Schools Application Services (TMDSAS).
You may be thinking one of two opposite thoughts: “Do I need to use the entire character count?” or “What if I have too much to say?” It may even feel like déjà vu with the Common App essay. Remember, writing is also revising! You should go through multiple drafts of adding and cutting before you’re satisfied with the content and length of your personal statement. You physically can’t submit a statement that’s over the character count, so you’ll eventually figure out how to be more concise with your ideas. If you’re worried about not having enough ideas, it can be helpful to read some sample statements online before you begin brainstorming from your own experiences.
What Should You Write About in a Medical School Personal Statement?
Before you start brainstorming our medical school personal statement, you must first read the prompt you’ll be responding to. Each application portal has its own unique prompt that corresponds to the character length available.
- AMCAS : “Use the space provided to explain why you want to go to medical school.”
- AACOMAS : There is no specific prompt beyond submitting a personal statement, but it is advised that you address why you want to be an osteopathic doctor.
- TMDSAS : “Explain your motivation to seek a career in medicine. Be sure to include the value of your experiences that prepare you to be a physician.”
While the three application portals have differently worded prompts, they’re all broadly asking the same two questions: Why are you applying to medical school and why are you qualified to be admitted? You have 1.5 pages single-spaced to showcase your passions, intellectual curiosity, and qualifications to ultimately answer these questions. The key, though, is leaning into your past experiences and using your best storytelling skills to show those diverse experiences.
Examples of relevant experiences may include internships, community service, lab instruction, and mentorship. However, you don’t want your personal statement to turn into an elaboration of your resume (which you’ll also be submitting in your medical school application). Instead, you should be emphasizing what strengths you’ve gained and what lessons you’ve learned from these experiences.
For instance, if could talk about your perseverance in the face of adversity, or the dedication you’ve exhibited in pursuing medical education. You could also focus on your passion for working with patients or your intellectual curiosity for medical research. In every experience you highlight in your medical school personal statement, you should be connecting it to a particular personal quality.
How Do You Start Writing a Medical School Personal Statement?
After you start reflecting on relevant experiences, organize your thoughts into a coherent essay structure. Remember the five-paragraph essay you learned to write in elementary school? Well, that’s going to come in handy now! Although your final statement may not be five paragraphs, it’s a good starting point. Putting your entire medical passion into a page-and-a-half single-spaced is no easy task. Simplifying the process will help immensely. Here’s a guide for each of your paragraphs:
Introduction
You’re definitely allowed to get a little creative with narrative storytelling in the intro! An engaging hook statement will draw the admissions officer in right away. Think about tools like scene-setting through imagery, dialogue, shocking assertions, etc. We should get a brief sense of who you are or what your goals are before diving into the body. A central theme may also be established in this paragraph.
Three Body Paragraphs
Each of your body paragraphs should highlight one experience that has impacted your desire to pursue medical school. For example, your three topics could be volunteering in a senior care home, an internship with a biomedical startup, and visiting a country with high medical needs. Beyond just describing what occurred through each experience, explain how they individually shaped you. How did you grow as a person? What did you learn? How did your perspective on medicine change? Why was this experience so impactful? What personal qualities did you develop?
Additionally, you should continue using narrative-style writing. Avoid just telling the admissions officer about each experience. Instead, show them! Put them in your shoes when you learned an important medical skill or helped make a research discovery. They’ll better understand your point of view through effective storytelling techniques.
This paragraph is your chance to reinforce everything you tried to convey throughout the personal statement. Try to tie your final thoughts back to your introduction in some way. A circular ending will help make your essay more memorable. Moreover, make sure to directly restate why you want to be a physician and what your future goals are. It’s your chance to convince the admissions officer why you’d be the best for medical school.
What Should You Avoid When Writing a Medical School Personal Statement?
In the process of writing your personal statement, it’s hard not to make the most common mistakes. When else have you written anything similar to a medical school personal statement? The closest thing would be the Common App essay, but it’s still pretty different from a creative narrative essay. So, you might not even know you’re making a mistake when you’re making it. Before you start writing, take a look at these pitfalls to avoid in your medical school personal statement.
Content to Avoid in Your Medical School Personal Statement
- Focusing on your early childhood or irrelevant experiences. It’s okay to reference something briefly from many years ago if it contributed to your passion for medicine, but your entire essay shouldn’t be based on a story about how you liked to play doctor when you were five. The more the experience, the better!
- Excusing low grades or a poor MCAT score. You only have about 1.5 pages single-spaced to put your best foot forward if other parts of your application aren’t up to the standard you’d hoped. Don’t waste the time or space trying to explain why they’re lacking. And remember, it’s impossible to have a perfect application.
- Elaborating on just one anecdote from your experiences. If you’re passionate about medicine, chances are you’ve gained worked in a variety of environments and/or communities to gain valuable experience. There may have been one internship, mentorship, etc. that was most impactful, but it’s advantageous to show a diversity in your experiences to demonstrate initiative.
Styles and Tones to Avoid in Your Medical School Personal Statement
- Bragging too much or underselling your achievements. If you’re applying seriously for medical school, chances are you have a resume full of accomplishments. Since you submit that resume in your application alongside your essay, there’s no reason to spend 5,300 characters repeating everything on that resume. On the other hand, you shouldn’t skip over meaningful experiences if they’ve actually shaped your desire to be a doctor.
- Loading up on complex medical terminology. While you may be an expert on a really niche research topic, there’s no need go overboard on vocabulary that the admissions officer may not understand without enough context. You also don’t want to come off as using terms you may not understand fully, or describe something the admission officer already knows.
- Being too conversational or informal. Although this personal statement isn’t on the same level as a dissertation in terms of formality, you shouldn’t treat it as an essay that you just throw together and submit. Phrases that you’d use when talking with a friend may not be appropriate for addressing why you’re qualified to be admitted to medical school.
When Should You Start Writing the Medical School Personal Statement?
The medical school application timeline can feel long-winded, so it’s crucial that you start earlier rather than later. You must juggle studying for the MCAT , filling out actual applications, requesting recommendation letters , preparing for interviews, and writing your personal statement in addition to school-specific supplementary essays. We know it’s a lot! To avoid getting overwhelmed and experiencing writer’s block, we recommend breaking down the writing process into more manageable steps.
Brainstorming and Drafting
In early May, you begin brainstorming your initial ideas for your medical school personal statement. Think back to the experiences in college that have meant the most to your passion for medicine. They could’ve been incredibly rewarding, taught you life-changing lessons, or even caused you to fail. Jot down key ideas about each experience and narrow down your ideas to three you’ll use in your essay. By the end of the month, try to knock out your first solid draft. Remember, it doesn’t need to be perfect! It can be a total “brain dump” or free-write that extends way beyond the character limit. It’s much easier to work with something than with nothing.
In June, you should be churning out at least 2-3 more drafts of your personal statement. Even if you were pretty happy with your first draft, there’s always room for improvement. Ask a trusted peer or advisor to read over your draft and give you pointers. Is your hook engaging enough? Are your experiences relevant enough? Did you effectively portray your passion for medicine? Where does your essay lose focus? What sentences could be more concise and punchier?
The more feedback you can get on your statement, the easier it will be to revise. There’s a famous saying in the literary world: “You must kill your darlings.” Getting outside feedback can help you review your essay more objectively. One paragraph that you think is outstanding may fall flat for everyone else that’s read it. Receiving their feedback can help you reevaluate the purpose and effectiveness of that paragraph.
Proofreading
Once you’re satisfied with the structure, content, and flow of your personal statement for medical school, it’s time to finalize and polish it. Look for lengthy sentences, incorrect grammar, informal style, etc. Essentially, keep an eye out for anything that would make an admissions officer pause as they’re reading your essay. If you’re not the strongest of writers, it might be a good idea to let a professional writer or editor read over your statement one last time. They can catch the misuse of a semi-colon from a mile away! Optimally, aim to submit your personal statement by July, so you can begin working on supplemental essays for secondary applications.
Finishing the Medical School Personal Statement – What’s Next?
Get your supplementary essays started! After you submit your primary application through one of the three portals, schools that are interested will begin sending you secondary applications to fill out. Part of these applications are school-specific essays. They may ask why you want to attend a particular medical school or what professional specialty you’re interested in. These essays all range in length from a few hundred words to another full-length personal statement. Try not to procrastinate on these essays, as you’ll probably be receiving more than one secondary application. Plus, you won’t be invited for interviews until you submit those applications!
You may also find the following College Transitions med school-related blogs to be of interest:
- Average MCAT Score & GPA for Medical Schoool
- MCAT Score Range & Percentiles
- Medical School Admissions

Emily Schmidt
Emily is currently a professional writer in the healthcare industry. As a former journalist, her work focused on climate change, health disparities, and education. She holds two bachelor's degrees in English and Spanish from Stanford University, and a master's in journalism from Arizona State University. Her first published novel debuted in 2020, and she hopes to finish her second novel by the end of this year.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High School Success
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight

“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
I am a... Student Student Parent Counselor Educator Other First Name Last Name Email Address Zip Code Area of Interest Business Computer Science Engineering Fine/Performing Arts Humanities Mathematics STEM Pre-Med Psychology Social Studies/Sciences Submit

Medical School Sample Personal Statements
These are real personal statements from successful medical school applicants (some are from students who have used our services or from our advisors ). These sample personal statements are for reference purposes only and should absolutely not be used to copy or plagiarize in any capacity. Plagiarism detection software is used when evaluating personal statements. Plagiarism is grounds for disqualification of an applicant.
Disclaimer: While these essays ultimately proved effective and led to medical school acceptances, there are multiple components that contribute to being an effective medical school applicant. These essays are not perfect, and the strengths and weaknesses have been listed where relevant.

Get 10 More Medical School Personal Statements
We'll send a PDF straight to your inbox containing 10 more stellar personal statements with expert breakdowns.
Check Your Inbox for the Next Steps!
Sample personal statements.
“I love Scriabin!” exclaimed Logan, a 19-year-old patient at the hospital, as we found a common interest in the obscure Russian composer. I knew Logan’s story because it was so similar to my own: a classically-trained pianist, he was ready to head off to college in a month, just as I had the year before. Yet it was Logan who was heading into surgery to remove a recently-discovered brain tumor. Hoping to assuage his fears of the daunting operation, I lent him my iPod full of Scriabin’s music. Though the surgery began normally, a few hours later, Logan’s blood pressure started dropping, and he became unresponsive to monitoring provided by the surgical neurophysiologist. As the nurses scrambled to stabilize him, I finally heard the neurosurgeon ask, “Did we lose him?” These four terse words immediately unnerved me. Logan was in the most critical and uncertain situation I could imagine, while the iPod I had lent him, a reminder of the conversation we had just a few hours earlier, was eerily visible on the other side of the room. While Logan, fortunately, went on to make a full recovery after a successful surgery, I was not ready to hear those four frightening words.
Perhaps I was so unnerved by those words because of my experiences with my mother’s sicknesses. My father and I try to be mentally prepared to lose her any day. With a Borderline Personality Disorder diagnosis, my mother has struggled with suicidal tendencies for most of my life. Her other illnesses, including several autoimmune disorders and severe gastrointestinal problems, certainly hinder her from experiencing the joys of life. But what is most difficult for me and my father is her anger and violence when she is in pain. My father would remind me that I had to consider the sources of her feelings, however irrational, in order to communicate with her. Though my relationship with my mother has proved challenging, I am thankful for these experiences.
In medicine, I will be able to use these experiences to understand psychological barriers to wellness and to better empathize with the patients I see in the clinic. Unique life experiences like these helped when I met Enrique, a patient presenting with an unusually painful fungal infection on one of his toenails. Though he was aware that his condition posed no lasting threat to his health, the extreme pain of the infection made him apprehensive of treatment, a soak in Povidone-iodine solution. “How can I help this man?” I asked myself, “He is about to refuse a simple treatment for a painful ailment.” Hoping to calm him, I struck up a conversation in Spanish, which I learned while living for some months in Cuernavaca, Mexico. This was not enough. As he became increasingly uneasy about the impending treatment, I remembered a line from Federico García Lorca’s “Romance de la Pena Negra”: “…wash your body with the water of the lark / and leave your heart in peace.” As Enrique calmly placed his foot into the “lark’s water,” I was relieved to see that this was the encouragement he needed. I believe that my travels have helped me appreciate the cultural backgrounds of many patients and have prepared me to be an empathetic clinician.
While I have been prepared to address patients psychologically and culturally, my training in the lab has prepared me to address patients biologically as well. Having worked extensively in two different labs studying vaccine development and microbial pathogenesis, I have developed a desire to use bench research to improve clinical care. One particularly striking manifestation of this concept came at the beginning of my day at an internist’s clinic. Walking into the office, I heard a most unsettling sound—a distinctive, screeching, painful yelp audible throughout the clinic. I instantly knew what case I would be seeing next: Whooping cough. When I saw Brody, a toddler, I was arrested by a unique commiseration, one of both pity and curiosity. I knew exactly what was happening to Brody. I had spent the last two years performing research on the bacteria that caused the disease, Bordetella pertussis . Describing elements of the microbe’s pathogenesis and explaining how our research could improve vaccine efficacy was comforting to the family, and their response was encouraging to me as I continue my work. My research experiences have engendered a passion to be at the cutting edge of medicine, seeking always to improve patient care, so that in the future, I can come to a family like Brody’s with a better prognosis.
Though I may not have been prepared to hear those frightening words during Logan’s surgery, what I can say with confidence is that I am ready to begin the journey of a physician—the journey of a lifelong learner and a committed healer. I am ready to be challenged by difficult situations in the clinic, like Logan’s, because it is through those circumstances that I will learn and grow. I want to become a physician so that I can use my liberal arts education with my personal and professional experiences to meet medicine’s unique requirement of understanding patients psychologically, culturally, and biologically. I am ready to provide the most excellent patient care, empathetically and holistically appreciating my patients’ stories in order to serve them best.
The author masterfully weaves together multiple elements of his unique experiences in medicine to tell a compelling story. This an excellent example of “show, don’t tell”, whereby the author tells stories and takes the reader on a journey rather than simply listing what he did in the past.
For example, rather than explicitly stating that he did research on Bordetella pertussis, the author tells a story of a patient with Whooping cough and interweaves his research experience there, tying together a message of the future doctor’s interest in translational (from bench to bedside) research. Similarly, rather than explicitly stating he did experience A, and learned important lesson B and C, these themes are implied more indirectly. As a result, the essay reads smoothly as a story, and grips the reader.
The author’s voice comes through, transitions are smooth, the introduction engages the reader, and the story arc neatly comes full circle. The character limit was pushed to the limit (5,299) and the author made every word count. Fantastic essay.
The main reason why I want to go into medicine is because of a promise I made to my sister when I was eight years old. My sister, who was only a few months old, was aware I had been taking care of her while our parents were working late. Caring for her gave me a feeling of responsibility I had never experienced before. When my sister woke up with a fever, I felt helpless. Her doctor was able to take care of the most important person in my life by systematically ruling out possible causes for the fever while still helping my sister feel safe, allowing me to see the beauty of medicine. I made a promise to my sister to become a medical doctor, so I can take care of her and other people who cannot take care of themselves. Later, my mother explained to me that medicine had made my life possible because I had been conceived through in vitro fertilization. This reinforced my motivation to become a physician and encourages me to this day to come full circle and give back to the field that made my life possible by helping others in need.
I continued to pursue my dream of practicing medicine by volunteering in the Intensive Care Unit at the UC San Diego Thornton Medical Center, where I gained first-hand experience interacting with patients. While collecting laboratory samples from nurses, I talked to a patient who only spoke Spanish. As the interpreter had not arrived yet, I was the only Spanish speaker in the unit, and my Spanish was basic at best. I asked the patient about her day and family, which really lifted her spirits. This interaction taught me the importance of personal connections with patients.
Shadowing allowed me to learn the characteristics of a good physician. Before surgeries, I obtained the patient’s consent to let me observe the procedure while the surgeon went over the patient’s last minute concerns. One patient needed an Aortic Valve Replacement, and when I was getting his consent he told me he was a famous Italian singer. The surgeon asked him to sing his hit song, and I was amazed. The patient’s face lit up and all his worries faded before the surgery. Even though the patient was going to be heavily sedated, the surgeon still cared about the patient’s stress about the procedure and that really drew me to the profession and showed me that there is more to being a good doctor than just the technicalities or knowledge from textbooks.
Volunteering at a veterans’ hospital exposed me to a side of medicine I have only read about in the news. People who are underserved and undereducated who refuse medical care. I would call patients who could not go to any other hospital and try to convince them to have their eyes checked for diabetes symptoms in the Teleretinal Imaging department. One veteran answered my call with a groan asking why he needs to go to the hospital when he knows he does not have diabetes. I realized I had to explain to him that symptoms can develop well before the actual disease. This inspired me to help patients in underprivileged communities because some are not educated enough to know when something is wrong with their bodies.
I know if I am given the chance to practice medicine and serve as a leader in the African American community, I can deliver the same inspiration and become a role model for those who are disadvantaged. At UC San Diego I joined the Black Student Union where I was able to reach out to those who were unsure about pursuing a higher education. Speaking to high school students about my college experiences has improved my communication skills and ability to relate to diverse populations. I spoke about how college can open many more opportunities for these students and that there are countless resources and scholarships that can help them. I will use simple and direct communication to help patients understand their disease. Through this experience, I knew I wanted to practice medicine that is personal through interaction with minority communities. After these events, it is clear to me that I cannot give up on my dreams of becoming a doctor because when I rise I will also lift those around me with the same struggle.
In elementary school, I realized there was a lack of famous African-American physicians, so I asked my parents if they knew of anyone. My father told me about my uncle, Roy Harris, who grew up in the inner city, surrounded by drugs and gangs. In order to avoid these hardships, he joined the high school track team and continued running through college while pursuing his medical degree. I began running to remind myself of his inspiring story and, like him, encourage a change in the world so one day students will have more African-American doctors to emulate. I am currently one of the top athletes in the nation, an Academic All-American, and I hope to compete at NCAA Division II nationals next year. Running has given me the discipline to maintain a balanced life, provided me the focus to succeed in medical school, and given me the drive to work toward fulfilling my dreams. Most importantly, I made a promise to my sister, creating an unshakeable foundation of endless motivation that will encourage me even through the most distressing moments of my journey to become a physician. I will never give up nor surrender because I always keep my promises.
The author uses an anecdote to start and finish the essay, which is a common and effective way to create a story arc. He calls back to multiple experiences throughout his life, from childhood to adolescence to young adulthood to bolster his resolve for pursuing medicine. His interesting background and stories, such as the promise he made to his sister, and his inspiration for picking up track, make for unique elements in this personal statement.
While the author does reflect back to multiple experiences, this comes across more as “telling” than “showing”. Compare this to the essay above to see the difference. The author has a common and repeating paragraph structure of 1) explain what the extracurricular or experience is, 2) recount a story related to said experience, and 3) draw lessons learned. While this structure gets the point across, it does not come across as engaging or compelling to the reader.
The author’s desire to give back to the African American community as well as his high aspirations are admirable.
At the beginning of the first Alternative Spring Break (ASB) meeting that I was leading in front of a group of nervous volunteers, I used an icebreaker, Two Truths and a Lie. Being a common face at my campus’s student activities, I have played this game perhaps one too many times. Unlike everyone else who had to take time to think about their interesting truths, I would say the same thing every time. “I want to be a pediatrician, I have alpacas, and I have llamas.”
I do not have llamas.
Growing up on a farm has given me great pride throughout the years and has driven my passion for service to my community, leading me to the goal of a career as a pediatrician. The farm is where I was first introduced to medicine. I would assist my father give shots to our animals, help our alpacas give birth to their crías, and talk with our family veterinarian about his treatment methods. The farm spawned in me a love for science which has shaped my career path, and my knowledge acquired through the farm has been a pleasure to share with people. My mother and I would visit the special education classrooms of different schools to show the kids presentations of the farm. We would lead demonstrations of us cleaning, spinning and crocheting the fiber to an involved and excited crowd of individuals. I have had numerous positive interactions with kids which has made me realize that there is no group I would rather work with more.
Our family farm became close with the few farms that were around us. We would help the alpaca farm 20 minutes from us shear their alpacas, and we once helped a small farm repair its fence that had been ravaged by a tornado. It felt good to be able to help people with things that not everybody has the knowledge to do. The farm helped shape my view of community into one of empathy which encompasses the spirit of being a physician. The joy I received from helping other farms led me to pursue community service opportunities at my university which I found first with ASB, a community service organization in which students dedicate their spring breaks to participate in meaningful service activities, and later as an AmeriCorps volunteer. When I signed up for my first ASB trip in my freshman year, I looked for a trip that involved helping kids. I knew I loved working with the younger population by assisting my mom at her home daycare and those presentations we gave to special education classes. The trip that caught my attention was to Pulaski, VA, which worked with a service organization called Beans and Rice. We would do fulfilling tornado recovery work in the morning, but I most looked forward to afternoons where we got to sit down and chat with kids about their days while helping them with their homework. I heard many stories from the kids about going to bed hungry or their parents being out of work. We were able to sit with whomever we wished during the kids’ lunch which I primarily spent with Chase, a boy who the other kids saw as an outcast due to his sexual orientation. My time with these kids made me realize how some people did not grow up with the strong sense of community that I knew at their age and inspired me to continue my work with their age group.
During my time in Pulaski, the director of the organization recognized my passion for working with kids and encouraged me to apply to AmeriCorps. I found a program in Lincoln, NE which allowed me to work with impoverished kids and share my passion of science with them under my given alias of T-Roy the Science Boy (not to be confused with my rival, Bill Nye the Science Guy). My relationships with the children I was working with grew fast, but one student made a significant impact on me. The second-grader was incapable of paying attention to academics yet had an amazing sense of humor. On the surface, his apparent developmental issues brought on by fetal alcohol syndrome resulted in hyperactivity and an inclination for angry outbursts. I spent time with him every day but came to the realization that, no matter how many times I was able to help him understand something, it did little to help his underlying health problems. Going to medical school will allow me to obtain the knowledge and skills I need to offer the ultimate service to people like my second-grade student—access to a healthy life.
With a strong desire to continue giving back to my community, I signed up to be a patient advocate in Baystate Medical Center’s emergency room. Here I was exposed to different health issues and many upset family members. It was my job to ensure the patients and their families were as comfortable as possible, but my job often morphed into one of a storyteller conversing with the families to get their minds off their difficult situations. Of course, the alpacas were a common topic of discussion since kids always love seeing the goofy haircuts we give them. My mother made this an easy task by uploading a video of us shearing the alpacas onto YouTube titled “Spit Happens”. A fitting name, no doubt. I have been blessed to share my farm-inspired sense of community with a broad range of different cultures from Nebraska to Virginia. I look forward to travelling to new communities as a physician while keeping my community-driven morals close, so alpaca my bags now.
This author is unique in his excellent command of humor. Note that this is a riskier approach and most applicants should avoid humor. In this setting, the humor certainly adds value to the essay, although this may be more off-putting to more traditional and conservative medical school admissions committee members. Overall, a high risk and high reward strategy, because when it lands, it makes for a compelling, unique, and entertaining read. Remember, admissions committees are reading through thousands of essays, and this comes as a breath of fresh air.
The introduction is brilliantly engaging and humorous, and entices the reader for what is to come. Clearly, this author has an interesting story to share and isn’t afraid to make you laugh.
While the essay is overall good, it could be improved in a few notable ways. First, the sentence structure and word choice can be tightened up in areas. The reader may find themself having to reread more than one sentence to understand what the writer is hoping to convey. Secondly, while the author does a great job highlighting a very unique and wide ranging background, showing more than telling would increase the effectiveness of this essay. Additionally, more emphasis and attention on “why medicine” and “why you would make a good doctor” would make this medical school personal statement more universally appealing (and less risky).
It’s not every day you help a kid become Iron Man. It happened for me during an internship at the NIH. I was responsible for designing the electronics and software for a portable robotic exoskeleton to help children expressing crouch gait due to cerebral palsy to improve their gait by retraining their muscles and neuron pathways. I saw the project as a fascinating technical problem and immersed myself in solving it.
Then I met Isaiah. Isaiah is a child with cerebral palsy expressing crouch gait with limited mobility. When Isaiah first began training on the robot, he became frustrated. As I watched him become exasperated using the device, it really hit me that I was creating a device for a real person, and the way we delivered his care was every bit as important to what we were doing as delivering an effective technical solution. As his confidence grew, I witnessed Isaiah, who could barely walk without the device, try to run. We even had to tell him to slow down! He asked if he could bring home the device because it made him feel like Iron Man. This experience crystalized for me my calling, to solve the challenging medical problems children face with love and a deep appreciation for their humanity.
I have firsthand knowledge of what it means to a child with serious medical problems to have loving physicians and nurses. When I was four, I received a heart transplant. Five years later, I fell ill with Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Throughout these difficult and uncertain times, I was fortunate to have a clinical team whose positivity and humor made me feel like a normal kid despite the fact that I was facing grave medical problems. While these experiences were difficult, they gave me a perspective that I treasure because it gives meaning to every day of my life. This perspective is where my calling originates – to become a physician-engineer completely committed to the emotional well-being of each of my patients.
The engineering problems many children face are substantial, and I am grateful for the opportunities I have been given to develop my skills in this area. As a part of the Center for Bioengineering Innovation & Design’s design team program I worked on two projects that taught me different aspects of the process of developing medical devices. The first project, NeoVate, gave me an overview of the design process of bringing medical devices to market. We developed a neonatal monitoring system for the developing world. We began with a needs assessment and then prototyped our solution to satisfy the specifications we developed. While I focused on the technical development, it was valuable to see other members create a sustainable distribution model because it helped me understand the step by step process by which an idea goes from concept to adoption in the medical field.
For the second project, TacPac, I was the team leader. On past teams I had a narrow focus on the technical development, but on TacPac I had to be knowledgeable about all aspects of the project and see the big picture in order to develop strategies to move the team forward. I learned how to create contingency plans by reaching out to our numerous advisors in many different specialties to build decision trees.
This project had an extra layer of meaning for me since we were developing an at-home monitoring system for tacrolimus, an immunosuppressant drug I have been taking for over twelve years. Currently, monitoring of this drug’s levels can only be done in a clinical setting. Our device allows patients to monitor their levels in the home, allowing for less inconvenience to patients and more data to make more informed clinical decisions.
While my engineering training developed my technical skills, the foundation of my heart and why I will pour myself into my vocation is derived from the love and care I received from my own clinical team as a child. I feel called to be of service to children with serious medical issues, just as my physicians and nurses were to me. One of my favorite volunteer experiences was when I was a camp counselor for Heart Camp, where I had previously been a camper. Heart Camp is a week-long camp for children with congenital heart defects designed to create an environment of fun, hope, and normalcy. This is one way in which I can use the difficult experiences of my childhood for good because it is easy for me to bring normalcy to these children’s lives since for me, it is normal.
Another volunteer opportunity that has had a tremendous amount of meaning for me is working with the Washington Regional Transplant Community to spread organ donation awareness by telling my story. Since I never received the chance to know my donor family, I use this volunteering as my way to say thank you.
I have enjoyed my engineering studies and my volunteering experiences have been of tremendous value to me, but I cannot wait to go to medical school. It is my desire to be a bridge between the technical engineering world and the direct delivery of care that only physicians can give. I feel it is my mission to use all of my experiences, both good and bad, to find innovative solutions to help the next Wonder Woman and Captain America thrive both physically and in every other part of their lives.
The superhero theme is unique, timely, and highly relevant to the author’s interest in pursuing a pediatric specialty. The author has a strong research background and ultimately was accepted to a highly ranked and research heavy institution, which is no surprise. While a significant portion of the body of the essay reads as “tell” more than “show”, some aspects of the personal statement use more effective story telling.
Deep interest in research, a unique background of being a lymphoma patient, and a palpable passion to help other kids who are suffering makes this applicant come across as a valuable asset to any research oriented medical school.
To further improve the impact of this essay, the author could remove one or two experiences listed in a more descriptive way and incorporate immersive stories to convey the significance and impact they had on him.

Stuck on Your Personal Statement?
We can help, from brainstorming to in-depth essay editing, and everything between

Join the Insider Newsletter
Receive regular exclusive MSI content, news, and updates! No spam. One-click unsubscribe.
Customer Note Premed Preclinical Med Student Clinical Med Student

You have Successfully Subscribed!
- Medical School Application
Medical School Personal Statement Examples That Got 6 Acceptances
Featured Admissions Expert: Dr. Monica Taneja, MD

These 30 exemplary medical school personal statement examples come from our students who enrolled in one of our application review programs. Most of these examples led to multiple acceptance for our students. For instance, the first example got our student accepted into SIX medical schools. Here's what you'll find in this article: We'll first go over 30 medical school personal statement samples, then we'll provide you a step-by-step guide for composing your own outstanding statement from scratch. If you follow this strategy, you're going to have a stellar statement whether you apply to the most competitive or the easiest medical schools to get into .
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Listen to the blog!
Article Contents 36 min read
Stellar medical school personal statement examples that got multiple acceptances, medical school personal statement example #1.
I made my way to Hillary’s house after hearing about her alcoholic father’s incarceration. Seeing her tearfulness and at a loss for words, I took her hand and held it, hoping to make things more bearable. She squeezed back gently in reply, “thank you.” My silent gesture seemed to confer a soundless message of comfort, encouragement and support.
Through mentoring, I have developed meaningful relationships with individuals of all ages, including seven-year-old Hillary. Many of my mentees come from disadvantaged backgrounds; working with them has challenged me to become more understanding and compassionate. Although Hillary was not able to control her father’s alcoholism and I had no immediate solution to her problems, I felt truly fortunate to be able to comfort her with my presence. Though not always tangible, my small victories, such as the support I offered Hillary, hold great personal meaning. Similarly, medicine encompasses more than an understanding of tangible entities such as the science of disease and treatment—to be an excellent physician requires empathy, dedication, curiosity and love of problem solving. These are skills I have developed through my experiences both teaching and shadowing inspiring physicians.
Medicine encompasses more than hard science. My experience as a teaching assistant nurtured my passion for medicine; I found that helping students required more than knowledge of organic chemistry. Rather, I was only able to address their difficulties when I sought out their underlying fears and feelings. One student, Azra, struggled despite regularly attending office hours. She approached me, asking for help. As we worked together, I noticed that her frustration stemmed from how intimidated she was by problems. I helped her by listening to her as a fellow student and normalizing her struggles. “I remember doing badly on my first organic chem test, despite studying really hard,” I said to Azra while working on a problem. “Really? You’re a TA, shouldn’t you be perfect?” I looked up and explained that I had improved my grades through hard work. I could tell she instantly felt more hopeful, she said, “If you could do it, then I can too!” When she passed, receiving a B+;I felt as if I had passed too. That B+ meant so much: it was a tangible result of Azra’s hard work, but it was also symbol of our dedication to one another and the bond we forged working together.
My passion for teaching others and sharing knowledge emanates from my curiosity and love for learning. My shadowing experiences in particular have stimulated my curiosity and desire to learn more about the world around me. How does platelet rich plasma stimulate tissue growth? How does diabetes affect the proximal convoluted tubule? My questions never stopped. I wanted to know everything and it felt very satisfying to apply my knowledge to clinical problems.
Shadowing physicians further taught me that medicine not only fuels my curiosity; it also challenges my problem solving skills. I enjoy the connections found in medicine, how things learned in one area can aid in coming up with a solution in another. For instance, while shadowing Dr. Steel I was asked, “What causes varicose veins and what are the complications?” I thought to myself, what could it be? I knew that veins have valves and thought back to my shadowing experience with Dr. Smith in the operating room. She had amputated a patient’s foot due to ulcers obstructing the venous circulation. I replied, “veins have valves and valve problems could lead to ulcers.” Dr. Steel smiled, “you’re right, but it doesn’t end there!” Medicine is not disconnected; it is not about interventional cardiology or orthopedic surgery. In fact, medicine is intertwined and collaborative. The ability to gather knowledge from many specialties and put seemingly distinct concepts together to form a coherent picture truly attracts me to medicine.
It is hard to separate science from medicine; in fact, medicine is science. However, medicine is also about people—their feelings, struggles and concerns. Humans are not pre-programmed robots that all face the same problems. Humans deserve sensitive and understanding physicians. Humans deserve doctors who are infinitely curious, constantly questioning new advents in medicine. They deserve someone who loves the challenge of problem solving and coming up with innovative individualized solutions. I want to be that physician. I want to be able to approach each case as a unique entity and incorporate my strengths into providing personalized care for my patients. Until that time, I may be found Friday mornings in the operating room, peering over shoulders, dreaming about the day I get to hold the drill.
Let's take a step back to consider what this medical school personal statement example does, not just what it says. It begins with an engaging hook in the first paragraph and ends with a compelling conclusion. The introduction draws you in, making the essay almost impossible to put down, while the conclusion paints a picture of someone who is both passionate and dedicated to the profession. In between the introduction and conclusion, this student makes excellent use of personal narrative. The anecdotes chosen demonstrate this individual's response to the common question, " Why do you want to be a doctor ?" while simultaneously making them come across as compassionate, curious, and reflective. The essay articulates a number of key qualities and competencies, which go far beyond the common trope, I want to be a doctor because I want to help people.
This person is clearly a talented writer, but this was the result of several rounds of edits with one of our medical school admissions consulting team members and a lot of hard work on the student's part. If your essay is not quite there yet, or if you're just getting started, don't sweat it. Do take note that writing a good personal essay takes advanced planning and significant effort.
I was one of those kids who always wanted to be doctor. I didn’t understand the responsibilities and heartbreaks, the difficult decisions, and the years of study and training that go with the title, but I did understand that the person in the white coat stood for knowledge, professionalism, and compassion. As a child, visits to the pediatrician were important events. I’d attend to my hair and clothes, and travel to the appointment in anticipation. I loved the interaction with my doctor. I loved that whoever I was in the larger world, I could enter the safe space of the doctor’s office, and for a moment my concerns were heard and evaluated. I listened as my mother communicated with the doctor. I’d be asked questions, respectfully examined, treatments and options would be weighed, and we would be on our way. My mother had been supported in her efforts to raise a well child, and I’d had a meaningful interaction with an adult who cared for my body and development. I understood medicine as an act of service, which aligned with my values, and became a dream.
I was hospitalized for several months as a teenager and was inspired by the experience, despite the illness. In the time of diagnosis, treatment and recovery, I met truly sick children. Children who were much more ill than me. Children who wouldn’t recover. We shared a four-bed room, and we shared our medical stories. Because of the old hospital building, there was little privacy in our room, and we couldn’t help but listen-in during rounds, learning the medical details, becoming “experts” in our four distinct cases. I had more mobility than some of the patients, and when the medical team and family members were unavailable, I’d run simple errands for my roommates, liaise informally with staff, and attend to needs. To bring physical relief, a cold compress, a warmed blanket, a message to a nurse, filled me with such an intense joy and sense of purpose that I applied for a volunteer position at the hospital even before my release.
I have since been volunteering in emergency departments, out-patient clinics, and long term care facilities. While the depth of human suffering is at times shocking and the iterations of illness astounding, it is in the long-term care facility that I had the most meaningful experiences by virtue of my responsibilities and the nature of the patients’ illnesses. Charles was 55 when he died. He had early onset Parkinson’s Disease with dementia that revealed itself with a small tremor when he was in his late twenties. Charles had a wife and three daughters who visited regularly, but whom he didn’t often remember. Over four years as a volunteer, my role with the family was to fill in the spaces left by Charles’ periodic inability to project his voice as well as his growing cognitive lapses. I would tell the family of his activities between their visits, and I would remind him of their visits and their news. This was a hard experience for me. I watched as 3 daughters, around my own age, incrementally lost their father. I became angry, and then I grew even more determined.
In the summer of third year of my Health Sciences degree, I was chosen to participate in an undergraduate research fellowship in biomedical research at my university. As part of this experience, I worked alongside graduate students, postdoctoral fellows, medical students, physicians, and faculty in Alzheimer’s research into biomarkers that might predict future disease. We collaborated in teams, and by way of the principal investigator’s careful leadership, I learned wherever one falls in terms of rank, each contribution is vital to the outcome. None of the work is in isolation. For instance, I was closely mentored by Will, a graduate student who had been in my role the previous summer. He, in turn, collaborated with post docs and medical students, turning to faculty when roadblocks were met. While one person’s knowledge and skill may be deeper than another’s, individual efforts make up the whole. Working in this team, aside from developing research skills, I realized that practicing medicine is not an individual pursuit, but a collaborative commitment to excellence in scholarship and leadership, which all begins with mentorship.
Building on this experience with teamwork in the lab, I participated in a global health initiative in Nepal for four months, where I worked alongside nurses, doctors, and translators. I worked in mobile rural health camps that offered tuberculosis care, monitored the health and development of babies and children under 5, and tended to minor injuries. We worked 11-hour days helping hundreds of people in the 3 days we spent in each location. Patients would already be in line before we woke each morning. I spent each day recording basic demographic information, blood pressure, pulse, temperature, weight, height, as well as random blood sugar levels, for each patient, before they lined up to see a doctor. Each day was exhausting and satisfying. We helped so many people. But this satisfaction was quickly displaced by a developing understanding of issues in health equity.
My desire to be doctor as a young person was not misguided, but simply naïve. I’ve since learned the role of empathy and compassion through my experiences as a patient and volunteer. I’ve broadened my contextual understanding of medicine in the lab and in Nepal. My purpose hasn’t changed, but what has developed is my understanding that to be a physician is to help people live healthy, dignified lives by practicing both medicine and social justice.
28 More Medical School Personal Statement Examples That Got Accepted
What my sister went through pushed me to strengthen my knowledge in medical education, patient care, and research. These events have influenced who I am today and helped me determine my own passions. I aspire to be a doctor because I want to make miracles, like my sister, happen. Life is something to cherish; it would not be the same if I did not have one of my four sisters to spend it with. As all stories have endings, I hope that mine ends with me fulfilling my dream of being a doctor, which has been the sole focus of my life to this point. I would love nothing more than to dedicate myself to such a rewarding career, where I achieve what those doctors did for my family. Their expertise allowed my sister to get all the care she needed for her heart, eyes, lungs, and overall growth. Those physicians gave me more than just my little sister, they gave me the determination and focus needed to succeed in the medical field, and for that, I am forever grateful. ","label":"Medical School Personal Statement Example #3","title":"Medical School Personal Statement Example #3"}]" code="tab4" template="BlogArticle">
I came to America, leaving my parents and friends behind, to grasp my chance at a better future. I believe this chance is now in front of me. Medicine is the only path I truly desire because it satisfies my curiosity about the human body and it allows me to directly interact with patients. I do not want to miss this chance to further hone my skills and knowledge, in order to provide better care for my patients. ","label":"Medical School Personal Statement #4","title":"Medical School Personal Statement #4"}]" code="tab5" template="BlogArticle">
The time I have spent in various medical settings has confirmed my love for the field. Regardless of the environment, I am drawn to patients and their stories, like that scared young boy at AMC. I am aware that medicine is a constantly changing landscape; however, one thing that has remained steadfast over the years is putting the patient first, and I plan on doing this as a physician. All of my experiences have taught me a great deal about patient interaction and global health, however, I am left wanting more. I crave more knowledge to help patients and become more useful in the healthcare sector. I am certain medical school is the path that will help me reach my goal. One day, I hope to use my experiences to become an amazing doctor like the doctors that treated my sister, so I can help other children like her. ","label":"Medical School Personal Statement Example #5","title":"Medical School Personal Statement Example #5"}]" code="tab6" template="BlogArticle">
My interest in the field of medicine has developed overtime, with a common theme surrounding the importance of personal health and wellness. Through my journey in sports, travelling, and meeting some incredible individuals such as Michael, I have shifted my focus from thinking solely about the physical well-being, to understanding the importance of mental, spiritual, and social health as well. Being part of a profession that emphasizes continuous education, and application of knowledge to help people is very rewarding, and I will bring compassion, a hard work ethic and an attitude that is always focused on bettering patient outcomes. ","label":"Medical School Personal Statement Example # 7","title":"Medical School Personal Statement Example # 7"}]" code="tab8" template="BlogArticle">
Medicine embodies a hard science, but it is ultimately a profession that treats people. I have seen firsthand that medicine is not a \u201cone-treatment-fits-all\u201d practice, as an effective physician takes a holistic approach. This is the type of physician I aspire to be: one who refuses to shy away from the humanity of patients and their social context, and one who uses research and innovation to improve the human condition. So, when I rethink \u201cwhy medicine?\u201d, I know it\u2019s for me \u2013 because it is a holistic discipline, because it demands all of me, because I am ready to absorb the fascinating knowledge and science that dictates human life, and engage with humanity in a way no other profession allows for. Until the day that I dawn the coveted white coat, you can find me in inpatient units, comforting the many John\u2019s to come, or perhaps at the back of an operating room observing a mitral valve repair \u2013 dreaming of the day the puck is in my zone. ","label":"Medical School Personal Statement Example #8","title":"Medical School Personal Statement Example #8"}]" code="tab9" template="BlogArticle">
When I signed up to be a live DJ, I didn't know that the oral skills I practiced on-air would influence all aspects of my life, let alone lead me to consider a career in the art of healing. I see now, though, the importance of these key events in my life that have allowed me to develop excellent communication skills--whether that be empathic listening, reading and giving non-verbal cues, or verbal communication. I realize I have always been on a path towards medicine. Ultimately, I aim to continue to strengthen my skills as I establish my role as a medical student and leader: trusting my choices, effectively communicating, and taking action for people in need. ","label":"Medical School Personal Statement Example #9","title":"Medical School Personal Statement Example #9"}]" code="tab10" template="BlogArticle">
\u201cWhy didn\u2019t I pursue medicine sooner?\u201d Is the question that now occupies my mind. Leila made me aware of the unprofessional treatment delivered by some doctors. My subsequent activities confirmed my desire to become a doctor who cares deeply for his patients and provides the highest quality care. My passion for research fuels my scientific curiosity. I will continue to advocate for patient equality and fairness. Combining these qualities will allow me to succeed as a physician. ","label":"Medical School Personal Statement Example #10","title":"Medical School Personal Statement Example #10"}]" code="tab11" template="BlogArticle">
Medical school personal statement example: #11
Medical school personal statement example: #12, medical school personal statement example: #13, medical school personal statement example: #14, medical school personal statement example: #15, medical school personal statement example: #16, medical school personal statement example: #17, medical school personal statement example: #18, medical school personal statement example: #19, medical school personal statement example: #20, medical school personal statement example: #21, medical school personal statement example: #22, medical school personal statement example: #23, medical school personal statement example: #24, medical school personal statement example: #25, medical school personal statement example: #26, medical school personal statement example: #27, medical school personal statement example: #28, medical school personal statement example: #29, medical school personal statement example: #30.
Please note that all personal statements are the property of the students who wrote them, re-printed with permission. Names and identifying characteristics have been changed. Plagiarism detection software is used when evaluating personal statements. Plagiarism is grounds for disqualification from the application. ","label":"NOTE","title":"NOTE"}]" code="tab2" template="BlogArticle">
As one of the most important medical school requirements , the personal statement tells your story of why you decided to pursue the medical profession. Keep in mind that personal statements are one of the key factors that affect medical school acceptance rates . This is why it's important to write a stellar essay!
“Personal statements are often emphasized in your application to medical school as this singular crucial factor that distinguishes you from every other applicant. Demonstrating the uniqueness of my qualities is precisely how I found myself getting multiple interviews and offers into medical school.” – Dr. Vincent Adeyemi, MD, Emory University school of Medicine
But this is easier said than done. In fact, medical school personal statements remain one of the most challenging parts of students' journeys to medical school. Here's our student Melissa sharing her experience of working on her personal statement:
"I struggled making my personal statement personal... I couldn't incorporate my feelings, motives and life stories that inspired me to pursue medicine into my personal statement" -Melissa, BeMo Student
Our student Rishi, who is now a student at the Carver College of Medicine , learned about the importance of the medical school personal statement the hard way:
"If you're a reapplicant like me, you know we all dread it but you have to get ready to answer what has changed about your application that we should accept you this time. I had an existing personal statement that did not get me in the first time so there was definitely work to be done." - Rishi, BeMo Student, current student at the Carver College of Medicine
The importance of the medical school personal statement can actually increase if you are applying to medical school with any red flags or setbacks, as our student Kannan did:
"I got 511 on my second MCAT try... My goal was anything over median of 510 so anything over that was honestly good with me because it's just about [creating] a good personal statement at that point... I read online about how important the personal statement [is]... making sure [it's] really polished and so that's when I decided to get some professional help." - Kannan, BeMo Student, current student at the Schulich School of Medicine
As you can see from these testimonials, your medical school personal statement can really make a difference. So we are here to help you get started writing your own personal statement. Let's approach this step-by-step. Below you will see how we will outline the steps to creating your very best personal statement. And don't forget that if you need to see more examples, you can also check out our AMCAS personal statement examples, AACOMAS personal statement examples and TMDSAS personal statement examples to further inspire you!
Here's a quick run-down of what we'll cover in the article:
Now let's dive in deeper!
#1 Understanding the Qualities of a Strong Med School Personal Statement
Before discussing how to write a strong medical school personal statement, we first need to understand the qualities of a strong essay. Similar to crafting strong medical school secondary essays , writing a strong personal statement is a challenging, yet extremely important, part of your MD or MD-PhD programs applications. Your AMCAS Work and Activities section may show the reader what you have done, but the personal statement explains why. This is how Dr. Neel Mistry, MD and our admissions expert, prepared for his medical school personal statement writing:
"The personal statement is an opportunity for you to shine and really impress the committee to invite you for an interview. The personal statement is your chance to be reflective and go beyond what is stated on your CV and [activities]. In order to stand out, it is important to answer the main questions [of medical school personal statements] well: a bit about yourself and what led you to medicine, why you would make an ideal medical student and future physician, what attracts you to [medicine], and what sets you apart from the other candidates. The key here is answering the last two questions well. Most candidates simply highlight what they have done, but do not reflect on it or mention how what they have done has prepared them for a future medical career." - Dr. Neel Mistry, MD
“my essay also focused on volunteering in the local health clinic during the many summer breaks. volunteering was more than just another activity to tick off my bucket list for my medical school … i volunteered because i wanted to view medical practice through the lenses of already qualified doctors, not because i needed a reason to be a doctor. i understood that the admissions committee would be more interested in how i was motivated.” – dr. vincent adeyemi..
A personal statement should be deeply personal, giving the admissions committee insight into your passions and your ultimate decision to pursue a career in medicine. A compelling and introspective personal statement can make the difference between getting an interview and facing medical school rejection . Review our blogs to find out how to prepare for med school interviews and learn the most common medical school interview questions .
As you contemplate the task in front of you, you may be wondering what composing an essay has to do with entering the field of medicine. Many of our students were surprised to learn that medical school personal statements are so valued by med schools. The two things are more closely related than you think. A compelling personal statement demonstrates your written communication skills and highlights your accomplishments, passions, and aspirations. The ability to communicate a complex idea in a short space is an important skill as a physician. You should demonstrate your communication skills by writing a concise and meaningful statement that illustrates your best attributes. Leaving a lasting impression on your reader is what will lead to interview invitations.
A quick note: if you are applying to schools that do not require the formal medical school personal statement, such as medical schools in Canada , you should still learn how to write such essays. Many medical schools in Ontario , for example, ask for short essays for supplementary questionnaires. These are very similar to the personal statement. Knowing how to brainstorm, write, and format your answers is key to your success!!!
You want to give yourself as much time as possible to write your statement. Do not think you can do this in an evening or even in a week. Some statements take months. My best statement took almost a year to get right. Allow yourself time and start early to avoid added stress. Think of the ideas you want to include and brainstorm possible ways to highlight these ideas. Ask your friends for ideas or even brainstorm your ideas with people you trust. Get some feedback early to make sure you are headed in the right direction.
“I wrote scores of essays at my desk in those few weeks leading up to application submission. I needed it to be perfect. Do not let anyone tell you to settle. There was no moment when I had this shining light from the sky filtering into my room to motivate me. The ultimate trick is to keep writing. It is impossible to get that perfect essay on the first try, and you may not even get it on your fifteenth attempt, but the goal is to keep at it, keep making those edits, and never back down.” – Dr. Vincent Adeyemi
All personal statements for medical school, often start by explaining why medicine is awesome; the admission committee already knows that. You should explain why you want a career in medicine. What is it about the practice of medicine that resonates with who you are? Naturally, this takes a lot of reflection around who you are. Here are some additional questions you can consider as you go about brainstorming for your essay:
- What motivates you to learn more about medicine?
- What is something you want them to know about you that isn't in your application?
- Where were you born, how did you grow up, and what type of childhood did you have growing up (perhaps including interesting stories about your siblings, parents, grandparents)?
- What kinds of early exposure to the medical field left an impression on you as a child?
- Did you become familiar with and interested in the field of medicine at an early stage of your life? If so, why?
- What are your key strengths, and how have you developed these?
- What steps did you take to familiarize yourself with the medical profession?
- Did you shadow a physician? Did you volunteer or work in a clinical setting? Did you get involved in medical research?
- What challenges have you faced? Have these made an impact on what you chose to study?
- What are your favorite activities?
- What kinds of extracurriculars for medical school or volunteer work have you done, and how have these shaped who you are, your priorities, and or your perspectives on a career in medicine?
- What was your "Aha!" moment?
- When did your desire to become a doctor solidify?
- How did you make the decision to apply to medical school?
You shouldn't try to answer all of these in your essay. Try only a few main points that will carry over into the final draft. Use these to brainstorm and gather ideas. Start developing your narrative by prioritizing the most impactful responses to these prompts and the ideas that are most relevant to your own experiences and goals. The perfect personal statement not only shows the admissions committee that you have refined communication skills, but also conveys maturity and professionalism. It should also display your motivation and suitability for medical practice. Here's how our student Alison, who was a non-traditional applicant with a serious red flag in her application, used her brainstorming sessions with our admissions experts to get a theme going in her medical school personal statement and her overall application package:
"I think it was during my brainstorming session that we really started talking about... what the theme [was] going to be for my application. And I think that was really helpful in and of itself. Just [reflecting] 'Hey, what's your focus going to be like? How are we going to write this? What's the style going to be?' Just to create an element of consistency throughout..." Alison, BeMo Student, current student at Dell Medical School
After brainstorming, you should be able to clearly see a few key ideas, skills, qualities, and intersections that you want to write about. Once you've isolated the elements you want to explore in your essay (usually 2-4 key ideas), you can begin building your outline. In terms of structure, this should follow the standard academic format, with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
As you begin thinking about what to include in your personal essay, remember that you are writing for a specific audience with specific expectations. Your evaluator will be familiar with the key qualities desired by medical schools, as informed by the standards of the profession. But keep in mind that they too are human, and they respond well to well-crafted, engaging essays that tell a story. Here's what our student Alison had to share about keeping your audience in mind when writing your personal statement:
"Make it easy for the reader to be able to work [their] way through [your personal statement]. Because, at the end of the day, I think one thing that helped me a lot was being able to think about who was going to be reading this application and it's going to be these people that are sitting around a desk or sitting at a table and [go] through massive numbers of applications every single day. And the easier and more digestible that you can make it for them, gives you a little bit of a win." - Alison, BeMo student, current student at Dell Medical School
The admissions committee will be examining your essay through the lens of their particular school's mission, values, and priorities. You should think about your experiences with reference to the AAMC Core Competencies and to each school's mission statement so that you're working toward your narrative with the institution and broader discipline in mind.
Review AAMC Core Competencies : The AAMC Core Competencies are the key characteristics and skills sought by U.S. medical schools. These are separated into three general categories:
You are not expected to have mastered all of these competencies at this stage of your education. Display those that are relevant to your experiences will help demonstrate your commitment to the medical profession.
Review the school's mission statement: Educational institutions put a lot of time and care into drafting their school's vision. The mission statement will articulate the overall values and priorities of each university, giving you insight into what they might seek in candidates, and thus what you should try to display in your personal statement. Echoing the values of the university helps illustrate that you are a good fit for their intellectual culture. The mission statement may help you identify other priorities of the university, for example, whether they prioritize research-based or experiential-based education. All this research into your chosen medical schools will help you tremendously not only when you write you personal statement, but also the rest of your medical school application components, including your medical school letter of intent if you ever need to write one later.
Just like the personal statement is, in essence, a prompt without a prompt. They give you free rein to write your own prompt to tell your story. This is often difficult for students as they find it hard to get started without having a true direction. Below is a list of ideas to get your creative juices flowing. Use these prompts as a starting point for your essay. Also, they are a great way of addressing why you want to be a doctor without saying something generic.
- The moment your passion for medicine crystallized
- The events that led you toward this path
- Specific instances in which you experienced opportunities
- Challenges that helped shape your worldview
- Your compassion, resilience, or enthusiastic collaboration
- Demonstrate your commitment to others
- Your dependability
- Your leadership skills
- Your ability to problem-solve or to resolve a conflict
These are personal, impactful experiences that only you have had. Focus on the personal, and connect that to the values of your future profession. Do that and you will avoid writing the same essay as everyone else. Dr. Monica Taneja, MD and our admissions expert, shares her tip that got her accepted to the University of Maryland School of Medicine :
"I focused on my journey to medicine and opportunities that I sought out along the way. Everyone’s path and validation is unique, so walking the reader through your growth to the point of application will naturally be different, but that's what I wanted to share in my personal statement." - Dr. Monica Taneja, MD
“the essay is not about what you have been through; it's about who it made you into.” – dr. vincent adeyemi.
Admissions committees don't want your resumé in narrative form. The most boring essays are those of applicants listing their accomplishments. Remember, all that stuff is already in the activities section of the application. This is where you should discuss interesting or important life events that shaped you and your interest in medicine (a service trip to rural Guatemala, a death in the family, a personal experience as a patient). One suggestion is to have an overarching theme to your essay to tie everything together, starting with an anecdote. Alternatively, you can use one big metaphor or analogy through the essay. Dr. Jaime Cazes, MD and experienced admissions committee member of the University of Toronto Faculty of Medicine, encourages you to be creative when it comes to the theme of your personal statement:
"It is very easy to make the “cookie cutter” personal statement. To a reviewer who is reading tens of these at a time it can become quite boring. What I did was [tell] a story. Like any good novel, the stories' first lines are meant to hook the reader. This can be about anything if you can bring it back and relate it to your application. It could be about the time your friend was smashed up against the boards in hockey and you, with your limited first aid experience helped to treat him. It is important that the story be REAL." - Dr. Jaime Cazes, MD
Your personal statement must be well-organized, showing a clear, logical progression, as well as connections between ideas. It is generally best to use a chronological progression since this mirrors your progression into a mature adult and gives you the opportunity to illustrate how you learned from early mistakes later on. Carry the theme throughout the statement to achieve continuity and cohesion. Use the theme to links ideas from each paragraph to the next and to unite your piece.
Medical School Personal Statement Structure
When working toward the initial draft of your essay, it is important to keep the following in mind: The essay should read like a chronological narrative and have good structure and flow. Just like any academic essay, it will need an introduction, body content, and a conclusion. If you're wondering whether a medical school advisor can help you with your medical school application, check out our blog for the answer.
Check out our video to learn how to create a killer introduction to your medical school personal statement:
Introduction
The introductory paragraph and, even more importantly, the introductory sentence of your essay, will most certainly make or break your overall statement. Ensure that you have a creative and captivating opening sentence that draws the reader in. This is your first and only chance to make a first impression and really capture the attention of the committee. Starting with an event or an Aha! moment that inspired your decision to pursue a medical profession is one way to grab their attention. The kinds of things that inspire or motivate you can say a lot about who you are as a person.
The broader introductory paragraph itself should serve several functions. First, it must draw your reader in with an eye-catching first line and an engaging hook or anecdote. It should point toward the qualities that most effectively demonstrate your desire and suitability for becoming a physician (you will discuss these qualities further in the body paragraphs). The thesis of the introduction is that you have certain skills, experiences, and characteristics and that these skills, experiences, and characteristics will lead you to thrive in the field of medicine. Finally, it must also serve as a roadmap to the reader, allowing them to understand where the remainder of the story is headed.
That is a lot of work for a single paragraph to do. To better help you envision what this looks like in practice, here is a sample introduction that hits these main points.
I was convinced I was going to grow up to be a professional chef. This was not just another far-fetched idealistic childhood dream that many of us had growing up. There was a sense of certainty about this dream that motivated me to devote countless hours to its practice. It was mostly the wonder that it brought to others and the way they were left in awe after they tried a dish that I recall enjoying the most creating as a young chef. But, when I was 13, my grandfather was diagnosed with stage four lung cancer, and I realized that sometimes cooking is not enough, as I quickly learned about the vital role physicians play in the life of everyday people like my family and myself. Although my grandfather ended up passing away from his illness, the impact that the healthcare team had on him, my family, and I will always serve as the initial starting point of my fascination with the medical profession. Since that time, I have spent years learning more about the human sciences through my undergraduate studies and research, have developed a deeper understanding of the demands and challenges of the medical profession through my various volunteer and extra-curricular experiences, and although it has been difficult along the way, I have continued to forge a more intimate fascination with the medical field that has motivated me to apply to medical school at this juncture of my life. ","label":"Sample Introduction","title":"Sample Introduction"}]" code="tab3" template="BlogArticle">
In the body of your essay, you essentially want to elaborate on the ideas that you have introduced in your opening paragraph by drawing on your personal experiences to provide evidence. Major points from the above sample introduction could be: dedication and resilience (practicing cooking for hours, and devoting years to undergraduate studies in human sciences), passion and emotional connection (being able to create something that inspired awe in others, and personally connecting with the work of the grandfather's healthcare team), motivation and drive (being inspired by the role physicians play in their patients' lives, participating in volunteer work and extracurriculars, and an enduring fascination with the field of medicine). Depending on the details, a selection of volunteer and extra-curricular experiences might also be discussed in more detail, in order to emphasize other traits like collaboration, teamwork, perseverance, or a sense of social responsibility – all key characteristics sought by medical schools. Just like an academic essay, you will devote one paragraph to each major point, explaining this in detail, supporting your claims with experiences from your life, and reflecting on the meaning of each plot point in your personal narrative, with reference to why you want to pursue a medical career.
Your final statement should not be a simple summary of the things you have discussed. It should be insightful, captivating, and leave the reader with a lasting impression. Although you want to re-emphasize the major ideas of your essay, you should try to be creative and captivating, much like your opening paragraph. Sometimes if you can link your opening idea to your last paragraph it will really tie the whole essay together. The conclusion is just as important as the introduction. It is your last chance to express your medical aspirations. You want to impress the reader while also leaving them wanting more. In this case, more would mean getting an interview so they can learn more about who you are! Leave them thinking I have got to meet this person.
The narrative you construct should display some of your most tightly held values, principles, or ethical positions, along with key accomplishments and activities. If you see yourself as someone who is committed to community service, and you have a track record of such service, your story should feature this and provide insight into why you care about your community and what you learned from your experiences. Saying that you value community service when you've never volunteered a day in your life is pointless. Stating that your family is one where we support each other through challenge and loss (if this is indeed true), is excellent because it lays the groundwork for telling a story while showing that you are orientated towards close relationships. You would then go on to offer a brief anecdote that supports this. You are showing how you live such principles, rather than just telling your reader that you have such principles:
"Remember to use specific personal examples throughout your statement to make it more impactful and memorable for the readers. Often, painting a picture in the reader’s mind in the form of a story helps with this." - Dr. Neel Mistry, MD
A lot of students make the mistake of verbalizing their personal attributes with a bunch of adjectives, such as, "This experience taught me to be a self-reliant leader, with excellent communication skills, and empathy for others..." In reality, this does nothing to convey these qualities. It's a mistake to simply list your skills or characteristics without showing the reader an example of a time you used them to solve a problem. If you simply list your skills or characteristics (telling), without demonstrating the ways you have applied them (showing), you risk coming across as arrogant. The person reading the essay may not believe you, as you've not really given them a way to see such values in your actions. It is better to construct a narrative to show the reader that you possess the traits that medical schools are looking for, rather than explicitly stating that you are an empathetic individual or capable of deep self-reflection. Instead of listing adjectives, tell your personal story and allow the admissions committee to paint the picture for themselves. This step is very challenging for many students, but it's one of the most important strategies used in successful essays. Writing this way will absolutely make your statement stand out from the rest.
While it may be tempting to write in a high academic tone, using terminology or jargon that is often complex or discipline-specific, requiring a specialized vocabulary for comprehension. You should actually aim to write for a non-specialist audience. Remember, in the world of medicine, describing a complex, clinical condition to a patient requires using specific but clear words. This is why your personal statement should show that you can do the same thing. Using large words in unwieldy ways makes you sound like you are compensating for poor communication skills. Use words that you believe most people understand. Read your personal statement back to a 14-year-old, and then again to someone for whom English is not their first language, to see if you're on the right path.
Ultimately, fancy words do not make you a good communicator; listening and ensuring reader comprehension makes you a good communicator. Instead of using complex terminology to tell the admissions committee that you have strong communication skills, show them your communication skills through clear, accessible prose, written with non-specialists in mind. A common refrain among writing instructors is, never use a $10 word where a $2 word will suffice. If you can say it in plain, accessible language, then this is what you should do.
Display Professionalism
Professionalism may seem like a difficult quality to display when only composing a personal statement. After all, the reader can't see your mannerisms, your personal style, or any of those little qualities that allow someone to appear professional. Professionalism is about respect for the experience of others on your team or in your workplace. It is displayed when you are able to step back from your own individual position and think about what is best for your colleagues and peers, considering their needs alongside your own. If a story is relevant to why you want to be a physician and demonstrates an example of how you were professional in a workplace setting, then it is appropriate to include in your essay.
One easy way to destroy a sense of professionalism is to act in a judgmental way towards others, particularly if you perceived and ultimately resolved an error on someone else's part. Sometimes students blame another medical professional for something that went wrong with a patient.
They might say something to the effect of, "The nurse kept brushing off the patient's concerns, refusing to ask the attending to increase her pain medications. Luckily, being the empathetic individual that I am, I took the time to listen to sit with the patient, eventually bringing her concerns to the attending physician, who thanked me for letting him know."
There are a couple of things wrong with this example. It seems like this person is putting down someone else in an attempt to make themselves look better. They come across as un-empathetic and judgmental of the nurse. Maybe she was having a busy day, or maybe the attending had just seen the patient for this issue and the patient didn't really need re-assessment. Reading this kind of account in a personal statement makes the reader question the maturity of the applicant and their ability to move past blaming others and resolve problems in a meaningful way. Instead of allocating blame, identify what the problem was for the patient and then focus on what you did to resolve it and reflect on what you learned from the whole experience.
One last note on professionalism: Being professional does not mean being overly stoic, hiding your emotions, or cultivating a bland personality. A lot of students are afraid to talk about how a situation made them feel in their personal statement. They worry that discussing feelings is inappropriate and will appear unprofessional. Unfortunately for these students, emotional intelligence is hugely important to the practice of medicine. In order to be a good doctor, one must be aware of their own emotions as well as those of their patients. Good doctors are able to quickly identify their own emotions and understand how their emotional reactions may inform their actions, and the ability to deliver appropriate care, in a given situation. Someone who is incapable of identifying their emotions is also incapable of managing them effectively and will likely struggle to identify the emotions of others. So, when writing your personal statement, think about how each experience made you feel, and what you learned from those feelings and that experience.
How to Write About Discrepancies and Common Mistakes to Avoid
Part of your essay's body can include a discussion of any discrepancies or gaps in your education, or disruptions in your academic performance. If you had to take time off, or if you had a term or course with low grades, or if you had any other extenuating circumstances that impacted your education, you can take time to address these here. It is very important to address these strategically. Do not approach this section as space to plead your case. Offer a brief summary of the situation, and then emphasize what you learned from such hardships. Always focus on the positive, illustrating how such difficulties made you stronger, more resilient, or more compassionate. Connect your experiences to the qualities desired by medical schools. Here's how I student Alison address an academic discrepancy in her application:
I had an academic dishonesty during undergrad, which, at the time, ended up being this big misunderstanding. But I was going to appeal this and get it off my record. I was supposed to start nursing school two weeks after this whole ordeal had gone down and, at our university, if you try to appeal your academic dishonesty then you'd have to take an incomplete in that class and I needed this class in order to start nursing school. So I wasn't able to [appeal]. So when I talked with the people at the nursing school they were like ‘it's no big deal, it's fine’. [But] it came back and it haunted me very much. When I was applying [to medical school] I started looking online [to see] how big of a deal is it to have this ‘red flag’ on my application. I started reading all of these horror stories on Student Doctor Network and all of these other forums about how if you have an academic dishonesty you shouldn't even bother applying, that you'll never get in. Schools will blacklist you and I was [wondering] what am I going do. [My advisor suggested I use the essay to talk about my discrepancy].
First off, if anyone out there has an academic violation don't read student doctor network. don't listen to anybody. you absolutely are still a potential medical student and schools are not going to blacklist you just because of one mistake that you made. that's all lies. don't listen to them. i don't even think it came up a single time during any of my interviews. i think a lot of that came back to how i wrote that essay and the biggest advice that i can give that i got from the [bemo] team is explain what happened… just give the facts. be very objective about it. in the last two thirds [of the essay] you want to focus on what you learned from it and how it made you a better person and how it's going to make you a better physician.” – alison, bemo student, current student at dell medical school.
We hope many of you find a peace of mind when you read Alison's story. Because it shows that with the right approach to your medical school personal statement, you can overcome even red flags or setbacks that made you dread the application process. Use your personal statement to emphasize your ability to persevere through it all but do so in a positive way. Most of all, if you feel like you have to explain yourself, take accountability for the situation. State that it is unfortunate and then redirect it to what you learned and how it will make you a better doctor. Always focus on being positive and do not lament on the negative situation too much.
Additional Mistakes to Avoid in Personal Statements:
Check out this video on the top 5 errors to avoid in your personal statement!
Step 3: Writing Your First Draft
As you can see, there is a LOT of planning and consideration to be done before actually starting your first draft. Properly brainstorming, outlining, and considering the content and style of your essay prior to beginning the essay will make the writing process much smoother than it would be you to try to jump right to the draft-writing stage. Now, you're not just staring at a blank page wondering what you could possibly write to impress the admissions committee. Instead, you've researched what the school desires from its students and what the medical profession prioritizes in terms of personal characteristics, you've sketched out some key moments from your life that exemplify those traits, and you have a detailed outline that just needs filling in.
As you're getting started, focus on getting content on the page, filling in your outline and getting your ideas arranged on the page. Your essay will go through multiple drafts and re-writes, so the first step is to free write and start articulating connections between your experiences and the characteristics you're highlighting. You can worry about flow, transitions, and perfect grammar in later drafts. The first draft is always a working draft, written with the understanding that its purpose is to act as a starting point, not an ending point. Once you've completed a draft, you can begin the revising process. The next section will break down what to do once you have your first draft completed.
You can also begin looking at things like style, voice, transitions, and overall theme. The best way to do this is to read your essay aloud. This may sound strange, but it is one of the single most impactful bits of writing advice a student can receive. When we're reading in our heads (and particularly when we're reading our own words), it is easy to skip over parts that may be awkwardly worded, or where the grammar is off. As our brains process information differently, depending on whether we're taking in visual or auditory information, this can also help you understand where the connections between ideas aren't as evident as you would like. Reading the essay aloud will help you begin internalizing the narrative you've crafted, so that you can come to more easily express this both formally in writing and informally in conversation (for example, in an interview).
#1 Did You Distinguish Yourself From Others?
Does your narrative sound unique? Is it different than your peers or did you write in a generic manner? Our admissions expert Dr. Monica Taneja, MD, shares how she got the attention of the admissions committee with her personal statement:
"I also found it helpful to give schools a 'punch-line'. As in I wanted them to remember 1-2 things about me that are my differentiators and I reiterated those throughout [the personal statement]." - Dr. Monica Taneja, MD
Use your narrative to provide a compelling picture of who you are as a person, as a learner, as an advocate, and as a future medical professional. What can you offer? Remember, you will be getting a lot out of your med school experience, but the school will be getting a lot out of you, as well. You will be contributing your research efforts to your department, you will be participating in the academic community, and as you go on to become a successful medical professional you will impact the perception of your school's prestige. This is a mutually beneficial relationship, so use this opportunity to highlight what you bring to the table, and what you will contribute as a student at their institution. Let them know what it is about you that is an attribute to their program. Make them see you as a stand out from the crowd.
#2 Does My Essay Flow and is it Comprehensible?
Personal statements are a blessing and a curse for admission committees. They give them a better glimpse of who the applicant is than simple scores. Also, they are long and time-consuming to read. And often, they sound exactly alike. On occasion, a personal statement really makes an applicant shine. After reading page after page of redundant, cookie-cutter essays, an essay comes along with fluid prose and a compelling narrative, the reader snaps out of that feeling of monotony and gladly extends their enthusiastic attention.
Frankly, if the statement is pleasant to read, it will get read with more attention and appreciation. Flow is easier to craft through narrative, which is why you should root the statement in a story that demonstrates characteristics desirable to medical schools. Fluidity takes time to build, though, so your statement should be etched out through many drafts and should also be based on an outline. You need to brainstorm, then outline, then draft and re-draft, and then bring in editors and listeners for feedback (Note: You need someone to proofread your work. Bestselling authors have editors. Top scholars have editors. I need an editor. You need an editor. Everyone needs an editor). Then, check and double-check and fix anything that needs fixing. Then check again. Then submit. You want this to be a statement that captures the reader's interest by creating a fluid, comprehensible piece that leads the reader to not only read each paragraph but want to continue to the next sentence.
#3 Did You Check Your Grammar?
If you give yourself more than one night to write your statement, the chances of grammatical errors will decrease considerably. If you are pressed for time, upload your file into an online grammar website. Use the grammar checker on your word processor, but know that this, in itself, isn't enough. Use the eyes and ears of other people to check and double-check your grammar, punctuation, and syntax. Read your statement out loud to yourself and you will almost certainly find an error (and likely several errors). Use fresh eyes to review the statement several times before you actually submit it, by walking away from it for a day or so and then re-reading it. Start your essay early, so that you actually have time to do this. This step can make or break your essay. Do not waste all the effort you have put into writing, to only be discarded by the committee for using incorrect grammar and syntax.
#4 Did You Gather Feedback From Other People?
The most important tip in writing a strong application essay is this getting someone else to read your work. While the tips above are all very useful for writing a strong draft, nothing will benefit you more than getting an outside appraisal of your work. For example, it's very easy to overlook your own spelling or grammatical errors. You know your own story and you may think that your narrative and it's meaning make sense to your reader. You won't know that for sure without having someone else actually read it. This may sound obvious, but it's still an absolute necessity.
“It was very helpful for two of my mentors to review my statements before submitting my application. Ensure you trust the judgement and skills of the person to whom you would be giving your personal statement for review.” – Dr. Vincent Adeyemi
Have someone you trust to read the essay and ask them what they thought of it. What was their impression of you after reading it? Did it make sense? Was it confusing? Do they have any questions? What was the tone of the essay? Do they see the connections you're trying to make? What were their takeaways from your essay, and do these align with your intended takeaways for your reader? Ideally, this person should have some knowledge of the application process or the medical profession, so that they can say whether you were successful in demonstrating that you are a suitable candidate for medical school. However, any external reader is better than no external reader at all.
Avoid having people too close to you read your work. They may refrain from being too critical in an effort to spare your feelings. This is the time to get brutal, honest feedback. If you know someone who is an editor but do not feel that they can be objective, try and find someone else.
Want more examples? Check out our video below:
FAQs and Final Notes
Your personal statement should tell your story and highlight specific experiences or aspects of your journey that have led you to medicine. If your first exposure or interest in the medical field was sparked from your own medical struggles, then you can certainly include this in your statement. What is most important is that you write about what factors or experiences attributed to you deciding that medicine is the right career path for you.
Sometimes students shy away from including their own personal struggles and describing how they felt during difficult times but this is a great way for admissions committees to gain perspective into who you are as a person and where your motivations lie. Remember, this is your story, not someone else's, so your statement should revolve around you. If you choose to discuss a personal hardship, what's most important is that you don't cast yourself as the victim and that you discuss what the experience taught you. Also, medical schools are not allowed to discriminate against students for discussing medical issues, so it is not looked at as a red flag unless you are talking about an issue inappropriately. For example, making yourself appear as the victim or not taking responsibility.
All US medical schools require the completion of a personal statement with your AMCAS, TMDSAS or AACOMAS applications.
Medical schools in Canada on the other hand, do not require or accept personal statements. In lieu of the personal statement, a few of these schools may require you to address a prompt in the form of an essay, or allow you to submit an explanation essay to describe any extenuating circumstances, but this is not the same as the US personal statement. For example, when applying through OMSAS , the University of Toronto medical school requires applicants to complete four short, 250 words or less, personal essays.
Many students struggle with whether or not they should address an unfavorable grade in their personal statement. What one student does isn't necessarily the right decision for you.
To help you decide, think about whether or not that bad grade might reflect on your poorly. If you think it will, then it's best to address the academic misstep head-on instead of having admissions committees dwell on possible areas of concern. If you're addressing a poor evaluation, ensure that you take responsibility for your grade, discuss what you learned and how your performance will be improved in the future - then move on. It's important that you don't play the victim and you must always reflect on what lessons you've learned moving forward.
Of course not, just because you didn't wake up one morning and notice a lightbulb flashing the words medicine, doesn't mean that your experiences and journey to medicine are inferior to those who did. Students arrive to medicine in all sorts of ways, some change career paths later in life, some always knew they wanted to pursue medicine, and others slowly became interested in medicine through their life interactions and experiences. Your personal statement should address your own unique story to how you first became interested in medicine and when and how that interest turned to a concrete desire.
While your entire statement is important, the opening sentence can often make or break your statement. This is because admission committee members are reviewing hundreds, if not thousands of personal statements. If your opening sentence is not eye-catching, interesting, and memorable, you risk your statement blending in with the large pile of other statements. Have a look at our video above for tips and strategies for creating a fantastic opening sentence.
Having your statement reviewed by family and friends can be a good place to start, but unfortunately, it's near-impossible for them to provide you with unbiased feedback. Often, friends and family members are going to support us and rave about our achievements. Even if they may truly think your statement needs work, they may feel uncomfortable giving you their honest feedback at the risk of hurting your feelings.
In addition, family and friends don't know exactly what admission committee members are looking for in a personal statement, nor do they have years of experience reviewing personal statements and helping students put the best version of themselves forward. For these reasons, many students choose to seek the help of a professional medical school advisor to make sure they have the absolute best chances of acceptance to medical school the first time around.
If you have enough time set aside to write your statement without juggling multiple other commitments, it normally takes at least four weeks to write your statement. If you are working, in school, or volunteering and have other commitments, be prepared to spend 6-8 weeks.
Your conclusion should have a summary of the main points you have made in your essay, but it should not just be a summary. You should also end with something that makes the reader want to learn more about you (i.e. call you for an interview). A good way to do this is to include a call-back to your opening anecdote: how have you grown or matured since then? How are you more prepared now to begin medical school?
The goal is to show as many of them as you can in the WHOLE application: this includes your personal statement, sketch, reference letters, secondary essays, and even your GPA and MCAT (which show critical thinking and reasoning already). So, it’s not an issue to focus on only a few select experiences and competencies in the personal statement.
Yes, you can. However, if you used an experience as a most meaningful entry, pick something else to talk about in your essay. Remember, you want to highlight as many core competencies across your whole application). Or, if you do pick the same experience: pick a different specific encounter or project with a different lesson learned.
Once your essay is in good shape, it's best to submit to ensure your application is reviewed as soon as possible. Remember, with rolling admissions, as more time passes before you submit your application, your chances of acceptance decreases. Nerves are normal and wanting to tinker is also normal, but over-analyzing and constant adjustments can actually weaken your essay.
So, if you're thinking about making more changes, it's important to really reflect and think about WHY you want to change something and if it will actually make the essay stronger. If not your changes won't actually make the essay stronger or if it's a very minor change you're thinking of making, then you should likely leave it as is.
The reality is, medical school admission is an extremely competitive process. In order to have the best chance of success, every part of your application must be stellar. Also, every year some students get in whose GPAs or MCAT scores are below the median. How? Simply because they must have stood out in other parts of the application, such as the personal statement.
The ones that honestly made the most impact on you. You'll need to reflect on your whole life and think about which experiences helped you grow and pushed you to pursue medicine. Ideally, experiences that show commitment and progression are better than one-off or short-term activities, as they usually contribute more to growth.
Final Notes
This Ultimate Guide has demonstrated all the work that needs to be done to compose a successful, engaging personal statement for your medical school application. While it would be wonderful if there was an easy way to write your personal statement in a day, the reality is that this kind of composition takes a lot of work. As daunting as this may seem, this guide lays out a clear path. In summary, the following 5 steps are the basis of what you should take away from this guide. These 5 steps are your guide and sort of cheat sheet to writing your best personal statement.
5 Main Takeaways For Personal Statement Writing:
- Brainstorming
- Content and Theme
- Multiple Drafts
- Revision With Attention to Grammar
While a strong personal statement alone will not guarantee admission to medical school, it could absolutely squeeze you onto a medical school waitlist , off the waitlist, and onto the offer list, or give someone on the admissions committee a reason to go to battle for your candidacy. Use this as an opportunity to highlight the incredible skills you've worked and studied to refine, the remarkable life experiences you've had, and the key qualities you possess in your own unique way. Show the admissions committee that you are someone they want to meet. Remember, in this context, wanting to meet you means wanting to bring you in for an interview!
Dr. Lauren Prufer is an admissions expert at BeMo. Dr. Prufer is also a medical resident at McMaster University. Her medical degree is from the Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry. During her time in medical school, she developed a passion for sharing her knowledge with others through medical writing, research, and peer mentoring.
To your success,
Your friends at BeMo
BeMo Academic Consulting
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions.
Jack Weaver
I have been reading posts regarding this topic and this post is one of the most interesting and informative one I have read. Thank you for this!
Hello Jack! Thank you very much for your comment. We glad you find this helpful!
Get Started Now
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar: How To Make Your Med School Application Stand Out
(and avoid the top 5 reasons that get 90% of applicants rejected).
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee your acceptance to med school or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!
4 Medical School Personal Statement Examples
The personal statement can be one of the most challenging parts of your medical school application process. You want to show admissions committees the qualities that make you stand out while avoiding cliches. After all, a lot is riding on this essay. Don’t panic. We’ve done our homework, talked to insiders, and gathered firsthand personal statements to help you get started.
Getting Started
Before diving into the personal statement examples, here are some tips on framing your experiences to wow admissions officers.
1. Stick to your real-life experiences. While it’s great to express what you want to do in healthcare in the future, that doesn’t really set you apart. All premed students have goals for what they’ll do in the medical profession, but this often changes after time in medical school. Telling a personal story instead gives admission committee members a look at who you already are and if you have the qualities they deem desirable for med school .
Feel free to mention specialties you’re passionate about and touch on your clinical experience, but make sure the experiences you discuss are unique.
2. Build an in-depth narrative. Nobody wants to read a blanket summary of your research experience. This is your chance to get passionate and demonstrate some communication skills. Explain the driving force behind your desire to work in the medical field.
The old writing rule comes into play here: “show, don’t tell.” You will always capture your reader’s attention more by telling a story than by explaining a circumstance. Medical school admissions committees are no different. Showing them your strong work ethic — or dedication, or whatever personal quality you want — without just saying, “I have a strong work ethic” will have a greater impact.
3. Don’t include metrics. Admissions officers already have access to your GPA and MCAT scores. If they want to know how you did in biochemistry, they can find out. Don’t waste space here. If you’re concerned about those numbers, it’s much more important to nail the personal statement and secure a secondary application and eventual medical school interview.
4. Know the character limits — and try to meet them. Both AACOMAS and AMCAS applications have a character limit of 5,300. You do not necessarily need to use all 5,300 characters, but you also don’t want it to be under 3,000. You want to use as many as possible while staying on topic and being relevant. A too-short essay can look careless.
5. Get comfortable with revising . You’ll do it a lot. Expect your first draft to be just that – a first draft. This writing process will take several weeks, if not months. Once you’re confident in your essay, ask for feedback. Avoid asking family members (unless they’re experts in the field of medicine). Instead, have professors, mentors, and peers read it and offer notes.
|| Read more about capturing readers from the first paragraph with our Medical School Personal Statement Storytelling Guide . ||
6. Use coaching to craft the perfect essay. Personal statements like the ones below only come after countless hours of brainstorming and writing drafts. However, with MedSchoolCoach , you’ll work with professional writing advisors step-by-step to develop an impactful medical school personal statement.
|| Check out more Tips for Writing a Personal Statement ||
Personal Statement Example #1
Our second essay contest winner was a medical student who made their submission an AMCAS personal statement . It serves as a great and effective medical school personal statement example . We also thought it was a good read overall!
A four-letter word for “dignitary.” The combinations surge through my mind: emir? agha? tsar? or perhaps the lesser-used variant, czar? I know it’s also too early to rule out specific names – there were plenty of rulers named Omar – although the clue is suspiciously unspecific. Quickly my eyes jump two columns to the intersecting clue, 53-Across, completely ignoring the blur outside the window that indicates my train has left the Times Square station. “Nooks’ counterparts.” I am certain the answer is “crannies.” This means 49-Down must end in r, so I eliminate “agha” in my mind. Slowly, the pieces come together, the wordplay sending my brain into mental gymnastics. At the end of two hours, I find myself staring at a completed crossword puzzle, and as trivial as it is, it is one of the greatest feelings in the world.
As an avid cruciverbalist, I have a knack for problem-solving. I fell in love with another kind of puzzle in college: organic chemistry. While some of my peers struggled with its complexity, the notion of analyzing mass spectroscopy, IR spectrums, and H-NMR to identify a specific molecule invigorated me. The human body was a fantastic mystery to me in my biology classes. Intricacies such as hormonal up- and down-regulation pulled at the riddler in me; I was not satisfied until I understood the enigma of how the body worked. Graduate school at Columbia was an extension of this craving, and I chose a thesis topic to attempt to elucidate the sophisticated workings of neuro-hormonal balance peri-bariatric surgery.
In non-academic settings, I also pursued activities that would sharpen my intellect. The act of teaching is a form of problem-solving; a good teacher finds the most effective way to convey information to students. So I accepted the challenge and taught in both international and domestic settings. I assumed leadership positions in church because it forced me to think critically to resolve conflicts. In the lab, I volunteered to help write a review on the biological mechanisms of weight regain. It was precisely what I loved: isolating a specific human phenomenon and investigating how it worked.
I believe medicine and puzzles are in the same vein. After participating in health fairs, working at a clinic, and observing physicians, I understand that pinpointing a patient’s exact needs is difficult at times. In a way, disease itself can be a puzzle, and doctors sometimes detect it only one piece at a time – a cough here, lanugo there. Signs and symptoms act as clues that whittle down the possibilities until only a few remain. Then all that is left is to fill in the word and complete the puzzle. Voila!
Actually, it is more complicated than that, and inevitably the imperfect comparison falls through.
I distinctly remember a conversation I had with a psychiatric patient at Aftercare. He had just revealed his identity as Batman — but it turns out he was also Jesus. During downtime between tests, he decided to confide in me some of his dreams and aspirations. He swiftly pulled out a sketchpad and said confidently, “When I get better, I’m going back to art school.” Any doubts stemming from his earlier ramblings vanished at the sight of his charcoal-laden sheets filled with lifelike characters. “They’re… really good,” I stammered. I was looking for the right words to say, but there are times when emotions are so overwhelming that words fail. I nodded in approval and motioned that we should get back to testing.
Those next few hours of testing flew by as I ruminated on what I had experienced. After working 3 years at the clinic, I got so caught up in the routine of “figuring out” brain function that I missed the most important aspect of the job: the people. And so, just as the crossword puzzle is a 15×15 symbol of the cold New York streets, a person is the polar opposite. Our patients are breathing, fluid, and multi-dimensional. I’ve come to love both, but there is nothing I want more in the world than to see a broken person restored, a dream reignited, to see Mr. Batman regain sanity and take up art school again. The prospect of healing others brings me joy, surpassing even the most challenging crosswords in the Sunday paper.
This is why I feel called to a life in medicine. It is the one profession that allows me to restore others while thinking critically and appreciating human biology. I am passionate about people, and medicine allows me to participate in their lives in a tangible way, aligned with my interest in biology and problem-solving skill.
The New York Times prints a new puzzle daily, and so does the Washington Post, USA Today, and the list continues. The unlimited supply of puzzles mirrors the abundance of human disease and the physician’s ongoing duty to unravel the mystery, to resolve the pain. A great cruciverbalist begins with the basics of learning “crosswordese,” a nuanced language; I am prepared to do the same with health, starting with my education in medical school. Even so, I am always humbled by what little I know and am prepared to make mistakes and learn along the way. After all, I would never do a crossword puzzle in pen.
||Read Our First Essay Contest Winner: Considerations Before Applying to Medical School ||
||Read The Formula For A Good Personal Statement | |
Personal Statement Example #2
Student Accepted to Case Western SOM, Washington University SOM, University of Utah SOM, Northwestern University Feinberg SOM
With a flick and a flourish, the tongue depressor vanished, and a coin suddenly appeared behind my ear. Growing up, my pediatrician often performed magic tricks, making going to the doctor feel like literal magic. I believed all healthcare facilities were equally mystifying, especially after experiencing a different type of magic in the organized chaos of the Emergency Department. Although it was no place for a six-year-old, childcare was often a challenge, and while my dad worked extra shifts in nursing school to provide for our family, I would find myself awed by the diligence and warmth of the healthcare providers.
Though I associated the hospital with feelings of comfort and care, it sometimes became a place of fear and uncertainty. One night, my two-year-old brother, Sean, began vomiting and coughing non-stop. My dad was deployed overseas, so my mother and I had no choice but to spend the night at the hospital, watching my brother slowly recover with the help of the healthcare providers. Little did I know, it would not be long before I was in the same place. Months later, I became hospitalized with pneumonia with pleural effusions, and as I struggled to breathe, I was terrified of having fluid sucked out of my chest. But each day, physicians comforted me, asking how I was, reassuring me that I was being taken care of, and explaining any questions related to my illness and treatment. Soon, I became excited to speak with the infectious disease doctor and residents, absorbing as much as possible about different conditions.
I also came to view the magic of healing through other lenses. Growing up, Native American traditions were an important aspect of my life as my father was actively involved with native spirituality, connecting back to his Algonquin heritage. We often attended Wi-wanyang-wa-c’i-pi ceremonies or Sun Dances for healing through prayer and individuals making personal sacrifices for their community. Although I never sun danced, I spent hours in inipis chewing on osha root, finding my healing through songs.
In addition to my father’s heritage, healing came from the curanderismo traditions of Peru, my mother’s home. She came from a long line of healers using herbal remedies and ceremonies for healing the mind, body, energy, and soul. I can still see my mother preparing oils, herbs, and incense mixtures while performing healing rituals. Her compassion and care in healing paralleled the Emergency Department healthcare providers.
Through the influence of these early life experiences, I decided to pursue a career in the health sciences. Shortly after starting college, I entered a difficult time in my life as I struggled with health and personal challenges. I suddenly felt weak and tired most days, with aches all over my body. Soon, depression set in. I eventually visited a doctor, and through a series of tests, we discovered I had hypothyroidism. During this time, I also began dealing with unprocessed childhood trauma. I decided to take time off school, and with thyroid replacement hormones and therapy, I slowly began to recover. But I still had ways to go, and due to financial challenges, I decided to continue delaying my education and found work managing a donut shop. Unbeknownst to me, this experience would lead to significant personal growth by working with people from all walks of life and allowing me time for self-reflection. I continuously reflected on the hospital experiences that defined my childhood and the unmatched admiration I had for healthcare workers. With my renewed interest in medicine, I enrolled in classes to get my AEMT license and gain more medical experience.
As my health improved, I excelled in my classes, and after craving the connections of working with others, I became a medical assistant. In this position, I met “Marco,” a patient traveling from Mexico for treatment. Though I spoke Spanish while growing up, I had little experience as a medical interpreter. However, I took the opportunity to talk with him to learn his story. Afterward, he became more comfortable, and I walked him through the consultation process, interpreting the physician’s words and Marco’s questions. This moment showed me the power of connecting with others in their native language. As a result, I began volunteering at a homeless clinic to continue bridging the language barrier for patients and to help advocate for the Latinx community and those who struggle to find their voice.
My journey to becoming a doctor has been less direct than planned; however, my personal trials and tribulations have allowed me to meet and work with incredible people who have been invaluable to my recovery and personal development. Most importantly, I have seen the value of compassionate and empathetic care. Though I have not recently witnessed any sleight of hand or vanishing acts, what healthcare providers do for patients can only be described as magic.
I look forward to bringing my diverse background as a physician and expanding my abilities to help patients in their path to healing.
||Read: But I Don’t Have 15 Activities ! | Apply to Med School After 3rd or 4th Year? ||
Personal Statement Example #3
Student accepted to Weill Cornell
My path to medicine was first influenced by early adolescent experiences trying to understand my place in society. Though I was not conscious of it then, I held a delicate balance between my identity as an Indian-American and an “American-American.”
In a single day, I could be shooting hoops and eating hotdogs at school while spending the evening playing Carrom and enjoying tandoori chicken at a family get-together. When our family moved from New York to California, I had the opportunity to attend a middle school with greater diversity, so I learned Spanish to salve the loss of moving away and assimilate into my new surroundings.
As I partook in related events and cuisine, I built a mixed friend group and began understanding how culture influences our perception of those around us. While volunteering at senior centers in high school, I noticed a similar pattern to what I sometimes saw: seniors socializing in groups of shared ethnicity and culture. Moving from table to table and language to language, I also observed how each group shared different life experiences and perspectives on what constitutes health and wellness. Many seniors talked about barriers to receiving care or how their care differed from what they had envisioned. Listening to their stories on cultural experiences, healthcare disparities, and care expectations sparked my interest in becoming a physician and providing care for the whole community.
Intrigued by the science behind perception and health, I took electives during my undergraduate years to build a foundation in these domains. In particular, I was amazed by how computational approaches could help model the complexity of the human mind, so I pursued research at Cornell’s Laboratory of Rational Decision-Making. Our team used fMRI analysis to show how the framing of information affects cognitive processing and perception. Thinking back to my discussions with seniors, I often wondered if more personalized health-related messaging could positively influence their opinions. Through shadowing, I witnessed physicians engaging in honest and empathetic conversations to deliver medical information and manage patients’ expectations, but how did they navigate delicate conflicts where the patients’ perspectives diverged from their own?
My question was answered when I became a community representative for the Ethics Committee for On Lok PACE, an elderly care program. One memorable case was that of Mr. A.G, a blind 86-year-old man with radiation-induced frontal lobe injury who wanted to return home and cook despite his doctor’s expressed safety concerns. Estranged from his family, Mr. A.G. relied on cooking to find fulfillment. Recognizing the conflict between autonomy and beneficence, I joined the physicians in brainstorming and recommending ways he could cook while being supervised.
I realized that the role of a physician was to mediate between the medical care plan and the patient’s wishes to make a decision that preserves their dignity. As we considered possibilities, the physicians’ genuine concern for the patient’s emotional well-being exemplified the compassion I want to emulate as a future doctor. Our discussions emphasized the rigor of medicine — the challenge of ambiguity and the importance of working with the individual to serve their needs.
With COVID-19 ravaging our underserved communities, my desire to help others drove me towards community-based health as a contact tracer for my county’s Department of Public Health. My conversations uncovered dozens of heartbreaking stories that revealed how socioeconomic status and job security inequities left poorer families facing significantly harsher quarantines than their wealthier counterparts.
Moreover, many residents expressed fear or mistrust, such as a 7-person family who could not safely isolate in their one-bedroom and one-bath apartment. I offered to arrange free hotel accommodations but was met with a guarded response from the father: “We’ll be fine. We can maintain the 6 feet.” While initially surprised, I recognized how my government affiliation could lead to a power dynamic that made the family feel uneasy. Thinking about how to make myself more approachable, I employed motivational interviewing skills and small talk to build rapport.
When we returned to discussing the hotel, he trusted my intentions and accepted the offer. Our bond of mutual trust grew over two weeks of follow-ups, leaving me humbled yet gratified to see his family transition to a safer living situation. As a future physician, I realize I may encounter many first-time or wary patients; and I feel prepared to create a responsive environment that helps them feel comfortable about integrating into our health system.
Through my clinical and non-clinical experiences, I have witnessed the far-reaching impact of physicians, from building lasting connections with patients to being a rock of support during uncertain times. I cannot imagine a career without these dynamics—of improving the health and wellness of patients, families, and society and reducing healthcare disparities. While I know the path ahead is challenging, I am confident I want to dedicate my life to this profession.
Personal Statement Example #4
Student Accepted to UCSF SOM, Harvard Medical School
Countless visits to specialists in hope of relief left me with a slew of inconclusive test results and uncertain diagnoses. “We cannot do anything else for you.” After twelve months of waging a war against my burning back, aching neck and tingling limbs, hearing these words at first felt like a death sentence, but I continued to advocate for myself with medical professionals.
A year of combatting pain and dismissal led me to a group of compassionate and innovative physicians at the Stanford Pain Management Center (SPMC). Working alongside a diverse team including pain management specialists and my PCP, I began the long, non-linear process of uncovering the girl that had been buried in the devastating rubble of her body’s pain.
From struggling with day-to-day activities like washing my hair and sitting in class to thriving as an avid weightlifter and zealous student over the span of a year, I realized I am passionate about preventing, managing and eliminating chronic illnesses through patient-centered incremental care and medical innovation.
A few days after my pain started, I was relieved to hear that I had most likely just strained some muscles, but after an empty bottle of muscle relaxers, the stings and aches had only intensified. I went on to see 15 specialists throughout California, including neurologists, physiatrists, and rheumatologists. Neurological exams. MRIs. Blood tests. All inconclusive.
Time and time again, specialists dismissed my experience due to ambiguous test results and limited time. I spent months trying to convince doctors that I was losing my body; they thought I was losing my mind. Despite these letdowns, I did not stop fighting to regain control of my life. Armed with my medical records and a detailed journal of my symptoms, I continued scheduling appointments with the intention of finding a doctor who would dig deeper in the face of the unknown.
Between visits, I researched my symptoms and searched for others with similar experiences. One story on Stanford Medicine’s blog, “Young Woman Overcomes Multiple Misdiagnoses and Gets Her Life Back”, particularly stood out to me and was the catalyst that led me to the SPMC. After bouncing from doctor to doctor, I had finally found a team of physicians who would take the profound toll of my pain on my physical and mental well-being seriously.
Throughout my year-long journey with my care team at the SPMC, I showed up for myself even when it felt like I would lose the war against my body. I confronted daily challenges with fortitude. When lifting my arms to tie my hair into a ponytail felt agonizing, YouTube tutorials trained me to become a braiding expert. Instead of lying in bed all day when my medication to relieve nerve pain left me struggling to stay awake, I explored innovative alternative therapies with my physicians; after I was fed up with the frustration of not knowing the source of my symptoms, I became a research subject in a clinical trial aimed at identifying and characterizing pain generators in patients suffering from “mysterious” chronic pain.
At times, it felt like my efforts were only resulting in lost time. However, seeing how patient my care team was with me, offering long-term coordinated support and continually steering me towards a pain-free future, motivated me to grow stronger with every step of the process. Success was not an immediate victory, but rather a long journey of incremental steps that produced steady, life-saving progress over time.
My journey brought me relief as well as clarity with regard to how I will care for my future patients. I will advocate for them even when complex conditions, inconclusive results and stereotypes discourage them from seeking continued care; work with them to continually adapt and improve an individualized plan tailored to their needs and goals, and engage in pioneering research and medical innovations that can directly benefit them.
Reflecting on the support system that enabled me to overcome the challenges of rehabilitation, I was inspired to help others navigate life with chronic pain in a more equitable and accessible way. Not everyone has the means to work indefinitely with a comprehensive care team, but most do have a smartphone. As a result, I partnered with a team of physicians and physical therapists at the University of California San Francisco to develop a free mobile application that guides individuals dealing with chronic pain through recovery. Based on my own journey, I was able to design the app with an understanding of the mental and physical toll that pain, fear, and loss of motivation take on patients struggling with chronic pain. Having features like an exercise bank with a real-time form checker and an AI-based chatbot to motivate users, address their concerns and connect them to specific health care resources, our application helped 65 of the 100 pilot users experience a significant reduction in pain and improvement in mental health in three months.
My journey has fostered my passion for patient-centered incremental medicine and medical innovation. From barely living to thriving, I have become a trailblazing warrior with the perseverance and resilience needed to pursue these passions and help both the patients I engage with and those around the world.
Related posts:
- Why I Picked UC Denver
- Finding the Perfect Research Project
- How to Succeed on Medical School Interview Day
- How to Answer “What is the Biggest Healthcare Problem” During an Interview
Related Articles

What Are Medical Schools Looking For?

Writing the Perfect Thank You Letter After a Medical School Interview

15 Med Schools That Accept Students With Low GPAs

How Perseverance as a Nontraditional Applicant Pays Off
Medical School Examples

Craft a Winning Medical School Essay with Examples and Proven Tips
Published on: May 8, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

Share this article
Are you dreaming of becoming a doctor or a health care professional?
The first step towards achieving that goal is to get accepted into a top-tier medical school.
But with so many other qualified medical students competing for the same spot, how do you stand out from the crowd?
It all starts with your medical school essay.
Your essay is your opportunity to your unique qualities, experiences, and aspirations.
In this blog, we'll provide you with examples that will help you catch the attention of admissions committees.
From purpose to common mistakes to avoid, we'll cover everything you need to get accepted into the medical school of your dreams.
So, let's dive in!
On This Page On This Page -->
Types of Medical School Examples
Medical school essays come in many different forms, each with its own unique requirements and purpose.
In this section, we'll discuss some of the most common types of medical school essays and what you need to know to write them successfully.
Personal Statements
Personal statements are the most common type of medical school essay. They are usually a one-page essay that introduces you to the admissions officers.
It explains why you want to pursue medicine as a career. Personal statements should be engaging, and memorable, and show off your unique qualities.
An outline offers a framework to help you craft a compelling narrative that showcases your strengths and experiences.
Check out this personal statement example that can help future physicians getting into the schools of their dreams.
Medical School Personal Statement Examples pdf
Secondary Essays
Secondary essays are additional essays that some medical schools require in addition to the personal statement.
They often ask specific questions about your background, experiences, or interests. They give you an opportunity to show off your future patient care and problem-solving skills.
Here is a brief example of a secondary application medical school essay:

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Diversity Essays
Diversity essays ask you to write about your experiences with diversity and how they have influenced you to pursue a career and your interest in medicine.
These essays are becoming increasingly common in medical school applications as schools strive to build a more diverse and inclusive student body.
Good Medical School Essay Examples
Are you struggling to write a standout medical school essay? They say that the best way to learn is by example. That's especially true when it comes to public health school essays.
We'll provide you with some of the best examples to help you craft an essay that will help your career in medicine.
Medical College Essay Examples
Personal Statement Medical School Examples Pdf
Medical School Covid Essay Examples
Challenging Medical School Essay Examples
Writing a medical school essay is more than just telling a story about yourself. It's an opportunity to demonstrate your critical thinking and analytical skills.
In this section, we'll highlight some of the challenging medical school essay examples. This will give you a sense of what admissions committees are looking for. You can learn how to exceed those expectations by writing a successful medical school essay.
Greatest Challenge Medical School Essay Examples
Successful Medicine Personal Statement Examples
Medical School Scholarship Essay Examples
Medical School Essay Examples for Different Schools
Each medical school has its own unique mission, values, and admissions criteria, and your essay should reflect that.
In this section, we'll explore how to tailor your medical school essay for different schools and showcase some examples of successful essays.
Letâs explore these Stanford and Harvard medical school essay examples:
Medical School Personal Statement Examples Harvard
Medical School Personal Statement Examples Stanford
Tips on Crafting an Excellent Medical School Personal Statement
The medical school personal statement is your opportunity to showcase your unique qualities and experiences.
Here are some tips to help you craft an excellent personal statement:
Start Early
Don't wait until the last minute to start writing your personal statement. Give yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, write, and revise your essay. Starting early also allows you to get feedback from mentors, professors, or peers.
Focus on Your Story
Your personal statement should tell a story that showcases your journey to medicine. Highlight the experiences and qualities that have led you to pursue a career in medicine. Tell them how you plan to use your skills to make a difference.
Be Specific
Use specific examples to illustrate your experiences and achievements. Don't just list your accomplishments, but show how they have prepared you for a career in medicine. Use concrete details to make your essay more engaging and memorable.
Show, Don't Tell
Instead of simply stating your qualities, show them through your experiences and actions. For example, donât say you're a team player. Describe a time when you worked effectively in a team to achieve a goal.
Tailor Your Essay to the School
As mentioned earlier, each medical school has its own unique mission and values. Tailor your personal statement to each school to demonstrate your fit with their program and values.
Mistakes to Avoid in a Medical School Personal Statement
When it comes to your medical school personal statement, there are some common mistakes you should avoid:
Avoid using cliched phrases and ideas that are overused in personal statements. Admissions committees want to see your unique perspective and experiences. They do not want generic statements that could apply to anyone.
Negativity
Don't focus on negative experiences or aspects of your life in your personal statement. Instead, focus on your strengths and how you have grown from challenges.
Lack of Focus
Make sure your personal statement has a clear focus and theme. Don't try to cover too many topics or experiences in one essay. Instead, focus on one or two experiences that are meaningful to you and illustrate your journey to medicine.
Too Formal or Informal Tone
Make sure your personal statement strikes the right tone. Avoid being too formal or using overly complex language. Also, avoid being too informal or using slang.
Plagiarism
Never copy someone else's personal statement or use a template to write your own. Admissions committees can easily spot plagiarism, and it will result in an immediate rejection.
Grammatical and Spelling Errors
Proofread your personal statement thoroughly for grammatical and spelling errors. Even a few small errors can detract from the overall quality of your essay.
Lack of Authenticity
Be true to yourself in your personal statement. Don't try to present an image of yourself that is not authentic or that you think the admissions committee wants to see. Be honest and genuine in your writing.
In conclusion, crafting a winning medical school essay is a crucial step toward securing admission to the medical school of your dreams.
This blog has provided examples of essays along with tips to craft an excellent medical school personal statement. By avoiding mistakes, you can increase your chances of standing out from the crowd and impressing the admissions committee.
Struggling with your medical school essays or college papers? Look no further!
Our college paper writing service specializes in crafting exceptional papers tailored to your academic needs, including medical school essays. And for an extra boost in your writing tasks, don't forget to explore our AI essay generator .
Elevate your academic performance with our medical school essay writing service and unlock the potential of our AI essay tools.
Get started today!
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
What is the ideal med school personal statement word limit.
There is no set length for a medical school personal statement, but most schools typically require a personal statement of 500-800 words.
How do I choose a topic for my medical school essay?
Choose a topic that showcases your unique perspective and experiences, and illustrates your journey to medicine. Consider what makes you stand out and what you are passionate about.
Should I mention my grades and test scores in my medical school essay?
It is not necessary to mention your grades and test scores in your medical school essay as they are already included in your application. Instead, focus on showcasing your unique qualities, experiences, and perspective.
Can I get help with writing my medical school essay?
Yes, there are various resources available to help you with writing your medical school essay. Consider seeking help from a writing tutor, career services office, or professional writing service like ours.
Nova A. (Literature, Marketing)
As a Digital Content Strategist, Nova Allison has eight years of experience in writing both technical and scientific content. With a focus on developing online content plans that engage audiences, Nova strives to write pieces that are not only informative but captivating as well.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Don't have an Account?
Register Now!

- International Student
- Essay Writing Center
- Sample Essays
Sample Medical School Essays
Applying to medical school is an exciting decision, but the application process is very competitive. This means when it comes to your application you need to ensure you’ve put your best foot forward and done everything you can to stand out from other applicants. One great way to provide additional information on why you have decided to pursue a career in medicine and why you’re qualified, is your medical school essay. Read these samples to get a good idea on how you can write your own top-notch essay.
This section contains five sample medical school essays
- Medical School Sample Essay One
- Medical School Sample Essay Two
- Medical School Sample Essay Three
- Medical School Sample Essay Four
- Medical School Sample Essay Five
Medical School Essay One
When I was twelve years old, a drunk driver hit the car my mother was driving while I was in the backseat. I have very few memories of the accident, but I do faintly recall a serious but calming face as I was gently lifted out of the car. The paramedic held my hand as we traveled to the hospital. I was in the hospital for several weeks and that same paramedic came to visit me almost every day. During my stay, I also got to know the various doctors and nurses in the hospital on a personal level. I remember feeling anxiety about my condition, but not sadness or even fear. It seemed to me that those around me, particularly my family, were more fearful of what might happen to me than I was. I don’t believe it was innocence or ignorance, but rather a trust in the abilities of my doctors. It was as if my doctors and I had a silent bond. Now that I’m older I fear death and sickness in a more intense way than I remember experiencing it as a child. My experience as a child sparked a keen interest in how we approach pediatric care, especially as it relates to our psychological and emotional support of children facing serious medical conditions. It was here that I experienced first-hand the power and compassion of medicine, not only in healing but also in bringing unlikely individuals together, such as adults and children, in uncommon yet profound ways. And it was here that I began to take seriously the possibility of becoming a pediatric surgeon.
My interest was sparked even more when, as an undergraduate, I was asked to assist in a study one of my professors was conducting on how children experience and process fear and the prospect of death. This professor was not in the medical field; rather, her background is in cultural anthropology. I was very honored to be part of this project at such an early stage of my career. During the study, we discovered that children face death in extremely different ways than adults do. We found that children facing fatal illnesses are very aware of their condition, even when it hasn’t been fully explained to them, and on the whole were willing to fight their illnesses, but were also more accepting of their potential fate than many adults facing similar diagnoses. We concluded our study by asking whether and to what extent this discovery should impact the type of care given to children in contrast to adults. I am eager to continue this sort of research as I pursue my medical career. The intersection of medicine, psychology, and socialization or culture (in this case, the social variables differentiating adults from children) is quite fascinating and is a field that is in need of better research.
Although much headway has been made in this area in the past twenty or so years, I feel there is a still a tendency in medicine to treat diseases the same way no matter who the patient is. We are slowly learning that procedures and drugs are not always universally effective. Not only must we alter our care of patients depending upon these cultural and social factors, we may also need to alter our entire emotional and psychological approach to them as well.
It is for this reason that I’m applying to the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, as it has one of the top programs for pediatric surgery in the country, as well as several renowned researchers delving into the social, generational, and cultural questions in which I’m interested. My approach to medicine will be multidisciplinary, which is evidenced by the fact that I’m already double-majoring in early childhood psychology and pre-med, with a minor in cultural anthropology. This is the type of extraordinary care that I received as a child—care that seemed to approach my injuries with a much larger and deeper picture than that which pure medicine cannot offer—and it is this sort of care I want to provide my future patients. I turned what might have been a debilitating event in my life—a devastating car accident—into the inspiration that has shaped my life since. I am driven and passionate. And while I know that the pediatric surgery program at Johns Hopkins will likely be the second biggest challenge I will face in my life, I know that I am up for it. I am ready to be challenged and prove to myself what I’ve been telling myself since that fateful car accident: I will be a doctor.
Tips for a Successful Medical School Essay
- If you’re applying through AMCAS, remember to keep your essay more general rather than tailored to a specific medical school, because your essay will be seen by multiple schools.
- AMCAS essays are limited to 5300 characters—not words! This includes spaces.
- Make sure the information you include in your essay doesn't conflict with the information in your other application materials.
- In general, provide additional information that isn’t found in your other application materials. Look at the essay as an opportunity to tell your story rather than a burden.
- Keep the interview in mind as you write. You will most likely be asked questions regarding your essay during the interview, so think about the experiences you want to talk about.
- When you are copying and pasting from a word processor to the AMCAS application online, formatting and font will be lost. Don’t waste your time making it look nice. Be sure to look through the essay once you’ve copied it into AMCAS and edit appropriately for any odd characters that result from pasting.
- Avoid overly controversial topics. While it is fine to take a position and back up your position with evidence, you don’t want to sound narrow-minded.
- Revise, revise, revise. Have multiple readers look at your essay and make suggestions. Go over your essay yourself many times and rewrite it several times until you feel that it communicates your message effectively and creatively.
- Make the opening sentence memorable. Admissions officers will read dozens of personal statements in a day. You must say something at the very beginning to catch their attention, encourage them to read the essay in detail, and make yourself stand out from the crowd.
- Character traits to portray in your essay include: maturity, intellect, critical thinking skills, leadership, tolerance, perseverance, and sincerity.
Medical School Essay Two
If you had told me ten years ago that I would be writing this essay and planning for yet another ten years into the future, part of me would have been surprised. I am a planner and a maker of to-do lists, and it has always been my plan to follow in the steps of my father and become a physician. This plan was derailed when I was called to active duty to serve in Iraq as part of the War on Terror.
I joined the National Guard before graduating high school and continued my service when I began college. My goal was to receive training that would be valuable for my future medical career, as I was working in the field of emergency health care. It was also a way to help me pay for college. When I was called to active duty in Iraq for my first deployment, I was forced to withdraw from school, and my deployment was subsequently extended. I spent a total of 24 months deployed overseas, where I provided in-the-field medical support to our combat troops. While the experience was invaluable not only in terms of my future medical career but also in terms of developing leadership and creative thinking skills, it put my undergraduate studies on hold for over two years. Consequently, my carefully-planned journey towards medical school and a medical career was thrown off course. Thus, while ten-year plans are valuable, I have learned from experience how easily such plans can dissolve in situations that are beyond one’s control, as well as the value of perseverance and flexibility.
Eventually, I returned to school. Despite my best efforts to graduate within two years, it took me another three years, as I suffered greatly from post-traumatic stress disorder following my time in Iraq. I considered abandoning my dream of becoming a physician altogether, since I was several years behind my peers with whom I had taken biology and chemistry classes before my deployment. Thanks to the unceasing encouragement of my academic advisor, who even stayed in contact with me when I was overseas, I gathered my strength and courage and began studying for the MCAT. To my surprise, my score was beyond satisfactory and while I am several years behind my original ten-year plan, I am now applying to Brown University’s School of Medicine.
I can describe my new ten-year plan, but I will do so with both optimism and also caution, knowing that I will inevitably face unforeseen complications and will need to adapt appropriately. One of the many insights I gained as a member of the National Guard and by serving in war-time was the incredible creativity medical specialists in the Armed Forces employ to deliver health care services to our wounded soldiers on the ground. I was part of a team that was saving lives under incredibly difficult circumstances—sometimes while under heavy fire and with only the most basic of resources. I am now interested in how I can use these skills to deliver health care in similar circumstances where basic medical infrastructure is lacking. While there is seemingly little in common between the deserts of Fallujah and rural Wyoming, where I’m currently working as a volunteer first responder in a small town located more than 60 miles from the nearest hospital, I see a lot of potential uses for the skills that I gained as a National Guardsman. As I learned from my father, who worked with Doctors Without Borders for a number of years, there is quite a bit in common between my field of knowledge from the military and working in post-conflict zones. I feel I have a unique experience from which to draw as I embark on my medical school journey, experiences that can be applied both here and abroad.
In ten years’ time, I hope to be trained in the field of emergency medicine, which, surprisingly, is a specialization that is actually lacking here in the United States as compared to similarly developed countries. I hope to conduct research in the field of health care infrastructure and work with government agencies and legislators to find creative solutions to improving access to emergency facilities in currently underserved areas of the United States, with an aim towards providing comprehensive policy reports and recommendations on how the US can once again be the world leader in health outcomes. While the problems inherent in our health care system are not one-dimensional and require a dynamic approach, one of the solutions as I see it is to think less in terms of state-of-the-art facilities and more in terms of access to primary care. Much of the care that I provide as a first responder and volunteer is extremely effective and also relatively cheap. More money is always helpful when facing a complex social and political problem, but we must think of solutions above and beyond more money and more taxes. In ten years I want to be a key player in the health care debate in this country and offering innovative solutions to delivering high quality and cost-effective health care to all our nation’s citizens, especially to those in rural and otherwise underserved areas.
Of course, my policy interests do not replace my passion for helping others and delivering emergency medicine. As a doctor, I hope to continue serving in areas of the country that, for one reason or another, are lagging behind in basic health care infrastructure. Eventually, I would also like to take my knowledge and talents abroad and serve in the Peace Corps or Doctors Without Borders.
In short, I see the role of physicians in society as multifunctional: they are not only doctors who heal, they are also leaders, innovators, social scientists, and patriots. Although my path to medical school has not always been the most direct, my varied and circuitous journey has given me a set of skills and experiences that many otherwise qualified applicants lack. I have no doubt that the next ten years will be similarly unpredictable, but I can assure you that no matter what obstacles I face, my goal will remain the same. I sincerely hope to begin the next phase of my journey at Brown University. Thank you for your kind attention.
Additional Tips for a Successful Medical School Essay
- Regardless of the prompt, you should always address the question of why you want to go to medical school in your essay.
- Try to always give concrete examples rather than make general statements. If you say that you have perseverance, describe an event in your life that demonstrates perseverance.
- There should be an overall message or theme in your essay. In the example above, the theme is overcoming unexpected obstacles.
- Make sure you check and recheck for spelling and grammar!
- Unless you’re very sure you can pull it off, it is usually not a good idea to use humor or to employ the skills you learned in creative writing class in your personal statement. While you want to paint a picture, you don’t want to be too poetic or literary.
- Turn potential weaknesses into positives. As in the example above, address any potential weaknesses in your application and make them strengths, if possible. If you have low MCAT scores or something else that can’t be easily explained or turned into a positive, simply don’t mention it.
Medical School Essay Three
The roots of my desire to become a physician are, thankfully, not around the bedside of a sick family member or in a hospital, but rather on a 10-acre plot of land outside of a small town in Northwest Arkansas. I loved raising and exhibiting cattle, so every morning before the bus arrived at 7 a.m. I was in the barn feeding, checking cattle for any health issues and washing the show heifers. These early mornings and my experiences on a farm not only taught me the value of hard work, but ignited my interest in the body, albeit bovine at the time. It was by a working chute that I learned the functions of reproductive hormones as we utilized them for assisted reproduction and artificial insemination; it was by giving vaccinations to prevent infection that I learned about bacteria and the germ theory of disease; it was beside a stillborn calf before the sun had risen that I was exposed to the frailty of life.
Facing the realities of disease and death daily from an early age, I developed a strong sense of pragmatism out of necessity. There is no place for abstractions or euphemisms about life and death when treating a calf’s pneumonia in the pouring rain during winter. Witnessing the sometimes harsh realities of life on a farm did not instill within me an attitude of jaded inevitability of death. Instead, it germinated a responsibility to protect life to the best of my abilities, cure what ailments I can and alleviate as much suffering as possible while recognizing that sometimes nothing can be done.
I first approached human health at the age of nine through beef nutrition and food safety. Learning the roles of nutrients such as zinc, iron, protein and B-vitamins in the human body as well as the dangers of food-borne illness through the Beef Ambassador program shifted my interest in the body to a new species. Talking with consumers about every facet of the origins of food, I realized that the topics that most interested me were those that pertained to human health. In college, while I connected with people over samples of beef and answered their questions, I also realized that it is not enough simply to have adequate knowledge. Ultimately knowledge is of little use if it is not digestible to those who receive it. So my goal as a future clinical physician is not only to illuminate the source of an affliction and provide treatment for patients, but take care to ensure the need for understanding by both patient and family is met.
I saw this combination of care and understanding while volunteering in an emergency room, where I was also exposed to other aspects and players in the medical field. While assisting a nurse perform a bladder scan and witnessing technicians carry out an echocardiogram or CT scan, I learned the important roles that other professionals who do not wear white coats have in today’s medical field. Medicine is a team sport, and coordinating the efforts of each of these players is crucial for the successful execution of patient care. It is my goal to serve as the leader of this healthcare unit and unify a team of professionals to provide the highest quality care for patients. Perhaps most importantly my time at the VA showed me the power a smile and an open ear can have with people. On the long walk to radiology, talking with patients about their military service and families always seemed to take their mind off the reason for their visit, if only for a few minutes. This served as a reminder that we are helping people with pasts and dreams, rather than simply remedying patients’ symptoms.
Growing up in a small town, I never held aspirations of world travel when I was young. But my time abroad revealed to me the state of healthcare in developing countries and fostered a previously unknown interest in global health. During my first trip abroad to Ghana, my roommate became ill with a severe case of traveler’s diarrhea. In the rural north of the country near the Sahara, the options for healthcare were limited; he told me how our professor was forced to bribe employees to bypass long lines and even recounted how doctors took a bag of saline off the line of another patient to give to him. During a service trip to a rural community in Nicaragua, I encountered patients with preventable and easily treatable diseases that, due to poverty and lack of access, were left untreated for months or years at a time. I was discouraged by the state of healthcare in these countries and wondered what could be done to help. I plan to continue to help provide access to healthcare in rural parts of developing countries, and hopefully as a physician with an agricultural background I can approach public health and food security issues in a multifaceted and holistic manner.
My time on a cattle farm taught me how to work hard to pursue my interests, but also fueled my appetite for knowledge about the body and instilled within me a firm sense of practicality. Whether in a clinic, operating room or pursuing public and global health projects, I plan to bring this work ethic and pragmatism to all of my endeavors. My agricultural upbringing has produced a foundation of skills and values that I am confident will readily transplant into my chosen career. Farming is my early passion, but medicine is my future.
Medical School Essay Four
I am a white, cisgender, and heterosexual female who has been afforded many privileges: I was raised by parents with significant financial resources, I have traveled the world, and I received top-quality high school and college educations. I do not wish to be addressed or recognized in any special way; all I ask is to be treated with respect.
As for my geographic origin, I was born and raised in the rural state of Maine. Since graduating from college, I have been living in my home state, working and giving back to the community that has given me so much. I could not be happier here; I love the down-to-earth people, the unhurried pace of life, and the easy access to the outdoors. While I am certainly excited to move elsewhere in the country for medical school and continue to explore new places, I will always self-identify as a Mainer as being from Maine is something I take great pride in. I am proud of my family ties to the state (which date back to the 1890’s), I am proud of the state’s commitment to preserving its natural beauty, and I am particularly proud of my slight Maine accent (we don’t pronounce our r’s). From the rocky coastline and rugged ski mountains to the locally-grown food and great restaurants, it is no wonder Maine is nicknamed, "Vacationland.” Yet, Maine is so much more than just a tourist destination. The state is dotted with wonderful communities in which to live, communities like the one where I grew up.
Perhaps not surprisingly, I plan to return to Maine after residency. I want to raise a family and establish my medical practice here. We certainly could use more doctors! Even though Maine is a terrific place to live, the state is facing a significant doctor shortage. Today, we are meeting less than half of our need for primary care providers. To make matters worse, many of our physicians are close to retirement age. Yet, according to the AAMC, only 53 Maine residents matriculated into medical school last year! Undoubtedly, Maine is in need of young doctors who are committed to working long term in underserved areas. As my primary career goal is to return to my much adored home state and do my part to help fill this need, I have a vested interest in learning more about rural medicine during medical school.
I was raised in Cumberland, Maine, a coastal town of 7,000 just north of Portland. With its single stoplight and general store (where it would be unusual to visit without running into someone you know), Cumberland is the epitome of a small New England town. It truly was the perfect place to grow up. According to the most recent census, nearly a third of the town’s population is under 18 and more than 75% of households contain children, two statistics which speak to the family-centric nature of Cumberland’s community. Recently rated Maine's safest town, Cumberland is the type of place where you allow your kindergartener to bike alone to school, leave your house unlocked while at work, and bring home-cooked food to your sick neighbors and their children. Growing up in such a safe, close-knit, and supportive community instilled in me the core values of compassion, trustworthiness, and citizenship. These three values guide me every day and will continue to guide me through medical school and my career in medicine.
As a medical student and eventual physician, my compassion will guide me to become a provider who cares for more than just the physical well-being of my patients. I will also commit myself to my patients’ emotional, spiritual, and social well-being and make it a priority to take into account the unique values and beliefs of each patient. By also demonstrating my trustworthiness during every encounter, I will develop strong interpersonal relationships with those whom I serve. As a doctor once wisely said, “A patient does not care how much you know until he knows how much you care.”
My citizenship will guide me to serve my community and to encourage my classmates and colleagues to do the same. We will be taught in medical school to be healers, scientists, and educators. I believe that, in addition, as students and as physicians, we have the responsibility to use our medical knowledge, research skills, and teaching abilities to benefit more than just our patients. We must also commit ourselves to improving the health and wellness of those living in our communities by participating in public events (i.e by donating our medical services), lobbying for better access to healthcare for the underprivileged, and promoting wellness campaigns. As a medical student and eventual physician, my compassion, trustworthiness, and citizenship will drive me to improve the lives of as many individuals as I can.
Cumberland instilled in me important core values and afforded me a wonderful childhood. However, I recognize that my hometown is not perfect. For one, the population is shockingly homogenous, at least as far as demographics go. As of the 2010 census, 97.2% of the residents of Cumberland were white. Only 4.1% of residents speak a language other than English at home and even fewer were born in another country. Essentially everybody who identified with a religion identified as some denomination of Christian. My family was one of maybe five Jewish families in the town. Additionally, nearly all the town’s residents graduated from high school (98.1%), are free of disability (93.8%), and live above the poverty line (95.8%). Efforts to attract diverse families to Cumberland is one improvement that I believe would make the community a better place in which to live. Diversity in background (and in thought) is desirable in any community as living, learning, and working alongside diverse individuals helps us develop new perspectives, enhances our social development, provides us with a larger frame of reference, and improves our understanding of our place in society.
Medical School Essay Five
“How many of you received the flu vaccine this year?” I asked my Bricks 4 Kidz class, where I volunteer to teach elementary students introductory science and math principles using Lego blocks. “What’s a flu vaccine?” they asked in confusion. Surprised, I briefly explained the influenza vaccine and its purpose for protection. My connection to children and their health extends to medical offices, clinics and communities where I have gained experience and insight into medicine, confirming my goal of becoming a physician.
My motivation to pursue a career in medicine developed when my mother, who was diagnosed with Lupus, underwent a kidney transplant surgery and suffered multiple complications. I recall the fear and anxiety I felt as a child because I misunderstood her chronic disease. This prompted me to learn more about the science of medicine. In high school, I observed patients plagued with acute and chronic kidney disease while briefly exploring various fields of medicine through a Mentorship in Medicine summer program at my local hospital. In addition to shadowing nephrologists in a hospital and clinical setting, I scrubbed into the operating room, viewed the radiology department, celebrated the miracle of birth in the delivery room, and quietly observed a partial autopsy in pathology. I saw many patients confused about their diagnoses. I was impressed by the compassion of the physicians and the time they took to reassure and educate their patients.
Further experiences in medicine throughout and after college shaped a desire to practice in underserved areas. While coloring and reading with children in the patient area at a Family Health Center, I witnessed family medicine physicians diligently serve patients from low-income communities. On a medical/dental mission trip to the Philippines, I partnered with local doctors to serve and distribute medical supplies to rural schools and communities. At one impoverished village, I held a malnourished two-year old boy suffering from cerebral palsy and cardiorespiratory disease. His family could not afford to take him to the nearest pediatrician, a few hours away by car, for treatment. Overwhelmed, I cried as we left the village. Many people were suffering through pain and disease due to limited access to medicine. But this is not rare; there are many people suffering due to inadequate access/accessibility around the world, even in my hometown. One physician may not be able to change the status of underserved communities, however, one can alleviate some of the suffering.
Dr. X, my mentor and supervisor, taught me that the practice of medicine is both a science and an art. As a medical assistant in a pediatric office, I am learning about the patient-physician relationship and the meaningful connection with people that medicine provides. I interact with patients and their families daily. Newborn twins were one of the first patients I helped, and I look forward to seeing their development at successive visits. A young boy who endured a major cardiac surgery was another patient I connected with, seeing his smiling face in the office often as he transitioned from the hospital to his home. I also helped many excited, college-bound teenagers with requests for medical records in order to matriculate. This is the art of medicine – the ability to build relationships with patients and have an important and influential role in their lives, from birth to adulthood and beyond.
In addition, medicine encompasses patient-centered care, such as considering and addressing concerns. While taking patient vitals, I grew discouraged when parents refused the influenza vaccine and could not understand their choices. With my experience in scientific research, I conducted an informal yet insightful study. Over one hundred families were surveyed about their specific reasons for refusing the flu vaccine. I sought feedback on patients’ level of understanding about vaccinations and its interactions with the human immune system. Through this project, I learned the importance of understanding patient’s concerns in order to reassure them through medicine. I also learned the value of communicating with patients, such as explaining the purpose of a recommended vaccine. I hope to further this by attending medical school to become a physician focused on patient-centered care, learning from and teaching my community.
Children have been a common thread in my pursuit of medicine, from perceiving medicine through child-like eyes to interacting daily with children in a medical office. My diverse experiences in patient interaction and the practice of medicine inspire me to become a physician, a path that requires perseverance and passion. Physicians are life-long learners and teachers, educating others whether it is on vaccinations or various diseases. This vocation also requires preparation, and I eagerly look forward to continually learning and growing in medical school and beyond.
To learn more about what to expect from the study of medicine, check out our Study Medicine in the US section.
Related Content:
Get the international student newsletter.
- Open access
- Published: 26 April 2024
Why are medical students so motivated to learn ultrasound skills? A qualitative study
- Anina Pless 1 na1 ,
- Roman Hari 1 na1 &
- Michael Harris 1 , 2
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 458 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
41 Accesses
Metrics details
The introduction of ultrasound (US) courses into medical undergraduate courses is usually met with a particularly high level of student motivation. The reasons for this are unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the factors that contribute to undergraduate medical students’ motivation to learn US skills. Understanding what motivates students to learn US will inform the efforts of faculty to foster students’ motivation to learn.
We carried out in-depth semi-structured one-to-one interviews with medical students participating in an optional US course at two Swiss universities. The interview guide consisted of 10 main questions. The content was informed by experts in the field of medical education and US, as well as by a literature review of motivation theories for learning, in particular by self-determination theory (SDT). SDT was used to guide the development of the interview guide and to reflect on the resulting themes in the discussion section. The interview guide was piloted with two medical students. The interviews lasted an average of 45 min and were audio recorded and transcribed. Thematic analysis was used to analyse the data.
Fourteen undergraduate medical students in their preclinical (year 3) and clinical studies (years 4 and 5) elaborated on a wide range of reasons for their high motivation to learn US. They were motivated for US training because of the positive nimbus of the US modality, emphasising the advantages of visualisation. Students acknowledged the potential professional benefits of learning US and described it as a fun, exciting group activity.
Conclusions
The four themes we found in our analysis can all be related to the three universal needs described in SDT. The strong focus on the visual aspect and the positive nimbus of the modality goes beyond that and reflects the visuo-centric Zeitgeist, which claims the superiority of visual information over other data. Educators should be aware that motivation to learn is affected by the Zeitgeist and ensuing preconceptions, such as the perception of the positive nimbus surrounding a topic. Other key elements that can be implemented to motivate students are just-in-time feedback, enabling group experiences and creating awareness of the clinical relevance of learning content.
Peer Review reports
The introduction of mandatory ultrasound (US) courses at our University was greeted with a standing ovation. This is not the usual reaction to the implementation of new courses and is worth exploring. We hope to understand factors that contribute to students’ motivation for learning to foster such factors when teaching.
High levels of motivation correlate with better grades throughout medical studies [ 1 , 2 ]. Kusurkar et al. examined “the effect of quality of motivation on performance” and found that motivation stemming from personal interest positively affects academic performance [ 3 ]. There is a positive correlation between motivation from personal interest and the intention to continue ones studies [ 1 ]. Motivation seems also to be correlated with learners’ well-being [ 4 ].
Several theories try to explain why students are motivated to learn. According to Self-determination theory (SDT), developed by Deci and Ryan, motivation varies not only in quantity but also in quality [ 5 ]. A central idea of the theory is that there is a distinction between autonomous motivation and controlled motivation. Autonomous motivation can be defined as engaging in an activity because one finds it interesting: doing something of one’s own free will. Controlled motivation is the norm, especially after early childhood, when social demands and roles require individuals to take responsibility for non-intrinsically interesting tasks. Students’ motivation to learn ultrasound, as perceived in our experience and as described in the literature, would mainly be classified as “autonomous” motivation in SDT, as they are engaging in an activity that they find interesting [ 6 , 7 , 8 ]. Three universal psychological needs add to the autonomous motivation: autonomy (being free to choose whatever one considers useful to do), competence (the desire to master a task and to feel effective) and relatedness (the feeling of wanting to connect with others and have a sense of belonging) [ 8 , 9 ]. Figure 1 depicts states of motivated behaviour and its relation to autonomy, competence and relatedness. At one end of the continuum is amotivation, the state of lacking an intention to act. When amotivated, people either do not act at all or they act without purpose. Amotivation results from not appreciating an activity, not feeling competent to do it, or not expecting it to achieve a desired outcome. Intrinsic motivation is placed at the other end of the continuum, emphasising that it is the essential form of self-determined activity, based solely on an internal desire to act. Extrinsically motivated behaviours cover the states between amotivation and intrinsic motivation, varying in the extent to which their regulation is autonomous [ 7 ].
The Self-Determination Continuum, adapted from Ryan and Deci, 2000, Cook and Artino, 2016 and ten Cate et al., 2011
Our observation of students’ reception of the implementation of US teaching is in line with recent evidence [ 10 ]. Evaluations of US training programmes report positive feedback from over 95% of students, approval rates rarely seen in other fields of medical education [ 11 , 12 ]. In a USA study, 97% of students agreed that it was important for them to learn basic US skills during medical school [ 13 ]. A German questionnaire study of medical students found a similar number (98.2%) reporting a high or very high interest in curricular US in medical education, with the large majority (94.4%) of respondents agreeing or strongly agreeing that US education should be a mandatory part of their curriculum [ 14 ]. In another study, a large majority of teachers (97%) felt that the students were interested in the course [ 15 ]. Another development that underlines the attractiveness of US education for students is the introduction of extracurricular, student-led peer-tutoring initiatives [ 16 ].
The scarce evidence on why students are motivated to learn US skills, suggests that they believe that US education helps them to be prepared for clinical practice before and after graduation [ 14 , 17 ]. They also describe educational benefits beyond the mastering of US skills, for example learning physical examination skills or improving their understanding of anatomy and physiology [ 11 , 13 , 14 , 18 ]. In a recent study, Wang et al. explored why pre-clinical medical students wanted to learn US by applying Existence, Relatedness and Growth Theory, a model with three categories often used for analysing employee work performance. Students gave reasons related to all three categories, foremost existence needs (e.g. future work requirement) and growth needs (e.g. improving diagnostic skills), with relatedness needs being mentioned less often [ 19 ]. Given SDT’s three basic psychological needs of autonomy, competence and relatedness, the spectrum of reasons is likely to be broader than this.
The aim of this study was to investigate the factors that contribute to undergraduate medical students’ motivation to learn US skills, using SDT as a conceptual framework.
Study design
This was a qualitative study following a constructivist paradigm. We used semi-structured one-to-one interviews to allow the exploration of sensitive topics and motivators. We used thematic analysis to analyse the data [ 20 , 21 ]. We adhered to the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research Checklist (COREQ) in the reporting of this study (for full COREQ checklist see supplementary Appendix 1) [ 22 ].
Study setting and participants
We interviewed 14 medical students from two different Swiss medical schools (University of Bern, University of Zurich) between 2019 and 2022. Both Universities had developed identical, optional medical student courses in abdominal US education that used volunteer peer-tutors. The blended learning programme was available to all Swiss medical students. The ultrasound course curriculum for the students consisted of five modules, with five hours of e-learning and 16 hours of peer-led tutoring. After completing a summative practical assessment, participants could obtain an internationally recognised course certificate in abdominal ultrasound [ 23 ]. Approximately 20% of medical students participated in these courses.
Recruitment and sampling method
We used purposive sampling. We contacted all the students that were enrolled in a voluntary, extracurricular US course ( n = 95). Potential participants were invited by an email forwarded to them by the course organisers and were also approached directly at US courses. While we had aimed to stratify participants with regards to gender, University site and age, recruitment was difficult during the COVID-19 pandemic, so we interviewed all the students willing to participate. All the students who agreed to take part had already participated in at least two tutored sessions and gave written, informed consent. After initial contact had been made, none of the participants declined to take part in the study or dropped out of it.
Ethical considerations
The study was submitted to the regional ethics committee which stated that the study does not fall under the Swiss Human Research Act (BASEC-Nr. Req-2018-00059).
All participants gave written informed consent. To ensure participant anonymity, each participant was identified only by a code after interview transcription.
Development of the interview guide
The semi-structured interview guide was informed by a literature review of motivation theories for learning, in particular by SDT, and discussions with faculty who are involved in US education, including medical educators, clinicians and US experts. Based on this information the research team discussed how to phrase questions that would be broad enough to encompass a variety of factors which can contribute to motivation according to SDT [ 7 , 9 ]. The interview guide consisted of 10 main questions which focussed on participants’ reasons to learn US and the perceived benefits (see Appendix 2). Each main question had probes to get more in-depth information. The interview guide was piloted with two students, and changes were made where necessary.
Data collection
All 14 interviews were carried out by the lead researcher AP, who had no prior relationship with the participants and was not affiliated with the US course. The interviewees were told that AP had an interest in their views of learning US skills. The risk of respondent bias, in this case the tendency to give socially desirable answers, was minimised by careful question design. The interviewer was not much older than the participants, preventing a feeling of hierarchy. Only the interviewee and AP were present during the interviews, which lasted an average of 45 min and were audio-recorded. Short field notes were made after each interview, commenting on the mood of the interview and reflecting the interviewer’s role and potential influence. The interviews were conducted at a location of the participants’ choice, most often at a public venue or at the University. Interviews were conducted in Swiss German and transcribed verbatim using High German diction. The transcriptions were done by AP as well as BB and KL, two medical students, all of whom are native Swiss German speakers. We wrote and used a transcription manual to ensure that transcripts were consistent. No repeat interviews were carried out and interview transcripts were not returned to the participants. Analysis was conducted using the High German transcripts.
Data analysis
AP, a medical doctor as well as a medical educator, did the primary analysis. She and MH, an experienced medical doctor, medical educator and qualitative researcher, independently coded three of the transcripts and compared their results to look for inconsistencies. Throughout the process, data was read and reread, using constant comparison with earlier data. Themes which derived from the data were labelled using a process of open coding to identify and later categorise phenomena in the data [ 24 ]. The interviews and analysis of the data were carried out in iterative cycles, going back and forth between the data gathering and analysis, allowing for new insights to inform changes to the interview guide [ 20 , 25 ]. Both coders regularly revised and refined the codes. No software was used.
After 14 interviews, the question of data saturation was discussed among the research team (AP, MH, RH, BB). As no new themes were arising, it was agreed that data saturation had been achieved [ 26 ].
The research team reviewed the findings individually then met to discuss the thematic structure. Each member of the team first presented their initial thoughts as to the themes. The team identified and continuously reviewed the themes until there was consensus [ 21 ]. For the sake of clarity and focus, the analysis focused on ultrasound-related factors and excluded themes related to course design in general.
We sent an overview of the key themes to four of the participants and asked for their comments. No changes needed to be made as a result of this.
14 students participated in the interviews. Table 1 shows participants’ characteristics.
We identified four US-specific themes that contribute to high levels of motivation to learn US skills. Table 2 shows the themes and subthemes.
The themes and subthemes are described in more detail below, with quotations identified by participant number.
Perception of professional benefits
All participants expressed that learning US would be an advantage professionally. This could be during their studies, or as practicing physicians. Learning US as early as possible was seen as adding to this benefit.
Benefits as a medical student
Some participants wanted to understand US images shown in lectures: Now, if we now have an US image in a lecture, I think “yes, ok, I can follow now”. (Participant(P)6)
For most participants, revising and deepening their knowledge of anatomy, as well as applying that knowledge to the patient’s body, were key benefits and motivators. Many participants felt learning US improved their spatial thinking: US gives you a different feeling of the relationships between the organs in the body. And uh, somehow you really know where the kidneys are or where the liver is. (P9)
One participant appreciated that US also put into perspective what was clinically relevant for their future career: And it was always reassuring for me that “yes, what is really relevant, I know” and if I no longer have the twenty-seventh branch of this artery in my head (…) so I was able to put in perspective the anatomical knowledge. For my future medical career. (P9)
Benefits as a physician
All participants stated that having US skills could be relevant to their future as physicians. They thought it was important to understand the indications and be able to interpret US images. Many participants were certain US would be part of their clinical life. One participant stated: Yes, it is also an examination method that is actually used in many disciplines. That means that sooner or later I will be asked to perform it on a patient. (P2) Several participants felt that they needed to be well prepared for their transition from student to resident: And that that’s my goal more or less, things that you can already acquire now, that I have them ready at hand. That at least that will work. (P2) There was also the notion that having US skills would help (…) avoid and reduce unnecessary imaging procedures and refer less patients to specialists. (P6)
The “exciting experience” component
For many participants, the motivation was connected to the feeling of experiencing something inherently fun and exciting: So, yes, it’s also a fascinating, so it’s still a “wow”. A “wow moment”. (laughs) (P3). Participants were intrinsically fascinated with the topic of US and the aspect of visualisation added to this: What I really find interesting is that my fascination still doesn’t let up (…) well, I just found it fascinating to somehow see my own organs for once (laughs). (P9)
The social aspects of learning US
Interpersonal factors played an important role, to learn and interact in small groups with other participants was described as similar to engaging in a new hobby, as well as a way of escaping everyday student life: Um, and what did I always enjoy the most? I think it was simply the interaction with the others. It’s just something that we don’t have much of in our studies. (P9)
While most participants said that the social aspect did not influence the decision to apply for the course, it was important for their positive perception of, and continuing engagement in, the course. They noted that the course gave them the opportunity to meet new people or do something with friends.
A practical skill
Many participants enjoyed doing something practical, as opposed to simply learning theory: Yes, and that’s actually kind of cool. Yeah, not exactly like a surgeon, but still a little bit hands-on. Yes. (P3)
They found learning US also enabled them to put their learning into a clinical perspective, giving them an insight into what they were working towards. One participant described how their US skills helped her become an active member of a clinical team during the practical year: I was allowed to scan a child because I said I had done this course. And afterwards I felt like one of them, not just like a trainee standing at the back, but that I had been fully interactive. (P12)
Learning US as a challenge
Participants found learning US to be a positive challenge: If you just get it or, also with the kidney, if you get it and then you recognize everything, that’s a pleasure. (P11)
Most participants performing US was not a natural gift but something they had to learn, requiring practice, diligence, and effort: Sure, there’s a mega process behind it until it’s intuitive, and it’s not the case with me at all yet, but I can imagine that, that it’s, um, doable with practice. Like the driving test, maybe. (P13)
The positive nimbus of US
Many participants said that they believed US to be an up-and-coming modality in medicine, with many advantages. We summarise these recurrent themes under the concept of the “positive nimbus” of US, referring to its positive image in public and medical discourse.
US as a modern tool
Many participants stated that US was the diagnostic tool of the future, which would become part of every physician’s basic equipment. This was often something that they had heard from others (peers, lecturers, physicians): (…) there was a doctor who said it was super important that you can do it and I should definitely take every opportunity. (P5)
Participants had a positive impression of US as a tool, ascribing many favourable attributes to it, principally that it was fast and easy. The participants found US to be versatile in terms of when and where it could be used (which body part, but also which geographical location), and for which indications to use it. They commented that they were fascinated by the breadth of what can be done with US: Yes, what I find interesting about US is that it can really be used in many different areas. (P7)
Advantages for patients
US as a tool was also described as having advantages for patients because it did not entail radiation, was non-invasive, and not painful. Another benefit for patients was that they could watch the examination “live”: You can show an image directly and that you can say to the patient “there it is and that’s how it is now. It’s good the way it is.” (P7) .
The power of visualisation
One key theme was the appeal of visualising things with US, and this contributed to the positive nimbus of US. For some participants, visualising organs was helpful because it matched their learning style: Well, personally, I’m just very much a visual person. (P8)
Most participants found it impressive to see inside the body and thereby gather a lot of information. It gave them a sense of security and the feeling that US was more objective and precise than other forms of examination: So yes, it seems to me that US is a bit more objective. (P5)
With the help of US, participants were easily able to confirm or exclude pathologies, which they found fascinating. Being able to capture an image was thought to be helpful too: some participants stated that it allowed them to show the image to others if they had any uncertainties, and to check that they had done it correctly: Something that you can see can perhaps be better discussed with other people afterwards. (P8)
Principal findings
In this qualitative interview study, medical students gave a range of reasons for their high motivation to learn US: the positive image surrounding the modality in general, with an emphasis on the advantages of visualisation; they perceived potential professional benefits; and they described it as a fun, exciting activity and a way to interact positively with other learners.
Interpretation of the results
The four themes we identified can be related to the three universal needs of autonomy, competence and relatedness described in SDT.
Mastering US skills contributed to a feeling of competence and autonomy. At the same time, feeling competent in performing US supported students in preparing for their transition from student to resident, giving them confidence in clinical situations and in interactions with patients, thus providing a professional advantage.
Learning US was described as an exciting and fun group activity. This perception aligns with the need for relatedness as described in SDT. The feeling that US was a practical alternation to their theoretical student life and a positive challenge map across to the need for competence.
The idea of learning to use a “modern”, technical tool, gave a feeling of autonomy and competence. Additionally, the fact that US is a mobile device compared to other imaging modalities was seen to offer a high degree of autonomy when deciding when and where to use it.
The visual aspect of US allows for just-in-time feedback and the immediate feeling of success when getting the right image, thus meeting the need for competence.
Whereas all four themes can be linked to the universal needs of SDT, the visual aspect of US and the positive nimbus surrounding US are more related to the “Zeitgeist”. In our study, participants’ comments suggested that they associated US with positive attributes and thought it would become increasingly important in the future. The sense that being able to visualise something was superior to other ways of examining– another subtheme we found– was central to this notion.
Comparison with existing literature
Other studies confirm that students believe learning US is an advantage in their medical studies [ 11 , 13 , 14 ]. A cross-sectional survey of graduates confirms that early US training yields physicians who are better prepared to integrate it into clinical practice [ 27 ]. While the transition from medical school to residency differs depending on the national context, it has been described as stressful and challenging in studies from different countries [ 28 , 29 ]. Early exposure to clinical environments in undergraduate years may help reduce the stress of this transition [ 29 ]. Integrating theoretical knowledge into practice in medical education has been an important issue in medical education for over a decade and remains so today. US teaching in undergraduate studies can aid professional identity formation [ 30 ]. Our results correspond with Wang et al.’s findings, that students are motivated to learn ultrasound because they believe it to be a necessity and/or advantage in their future work or current studies and because they want to learn out of interest. Wang et al. point out that relatedness played less of a role for students’ motivation, while in our study relatedness played an important role in the theme of “fun and exciting activity”. One possible explanation for this discrepancy could be that a distinction between motivation to initiate behaviour (e.g. sign up for a course) and to maintain motivation (e.g. stay motivated during the course) is seldom made. Participants in Wang et al’s study were questioned on motivation to initiate US learning, while in our study, participants had already begun or finished the US course and relatedness contributed to continuing motivation during the course but was seldom discussed as a reason for initial interest [ 19 ].
Our participants felt that visualisation enhanced the objectivity and reliability of an examination, providing a feeling of security, corresponding with Feilchenfeld et al.’s statement that “US’s visual evidence is viewed as truth, more accurate (truthful) than clinical information provided via other senses” [ 31 ]. This “Zeitgeist”, the “visuo-centric discourse” which claims the superiority of visual information over other data, may be common among medical students: a paper on body pedagogics states that “oculocentrism” (a perception of superiority of vision over other senses) is typical in Western society, especially in the medical profession [ 32 ]. The current discourse in our (medical) society that seeing is superior to, and more legitimate than, perceiving with other senses and is thus also beneficial for patient care seems to add to the “positive nimbus” of US and has an effect on students’ high motivation to learn the skill [ 26 , 28 ].
This is the first qualitative study designed to study medical students’ motivation for US education. The design of the interview guide and the interpretation of the results were guided by a consistent theoretical framework (SDT). We interviewed participants from two different medical schools. We piloted the interview guides carefully, achieved data saturation and member-checked the findings.
Limitations
Our participants were from a population taking part in a course with no curricular accreditation, making it likely that they had a high degree of motivation. The participants were students who volunteered to take part in the study, resulting in a risk of self-selection bias. We assumed that the students participating in a voluntary course and voluntarily taking part in the study would be especially highly motivated. Because our aim was to explore high levels of motivation for ultrasound, we hypothesise that the sample was in line with our research question. The factors motivating these students may not apply to other students, for example students with low motivation to learn ultrasound. Including a more varied sample might have given us other insights. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, we could not stratify participants as intended, as US courses were put on hold for some time. Many students were busy with volunteer work at health facilities and may have been less willing to meet face-to-face. However, there was an equal number of participants from both Universities, and the gender distribution approximately reflects the gender distribution in Swiss medical studies. Also, the participants came from a homogenous group, which makes it more likely that the sample was adequate [ 33 ].
Implications for research and practice
Understanding the mechanisms of motivation in medical education helps to create a supportive learning environment and to nurture autonomous motivation. While some of our findings were specific to the modality of US, some can also be applied to other teaching areas:
Visualisation aids learning, providing immediate feedback, a sense of competence and of autonomy, adding to the motivation. For areas where visualisation is not an option, educators should consider using alternative ways to give immediate feedback, when planning educational programmes. This could mean verbally providing immediate and constructive feedback, or using a portfolio to visually track learners’ progress.
Participants found learning US fun and exciting. Not all areas of learning allow for the hands-on experience of US education, but reflecting on where practical aspects can be integrated into teaching and how to challenge students optimally– making tasks not too easy nor too difficult– could enhance students’ motivation. One example is the “gameification” of learning content, which may add to the fun factor. Educators should enable group experiences and interaction when possible. This could be supported by encouraging students to actively participate in group work, giving a structure to educational units, while also providing enough room to learn in a self-directed way as a group. Facilitators to this can be a setting of mutual trust and open dialogue, and adjusting the learning environment, for example by considering seating arrangements.
Students are motivated to learn things that will benefit them professionally, making awareness of the clinical relevance of learning content essential. Explicitly addressing concerns about transitioning from medical school to residency and providing information on how a specific skill will help for this transition could increase students’ motivation to learn. Pointing out the relevance of the subject to medical practice could help less enthusiastic students see the importance of it and result in a more autonomous– rather than controlled– choice to learn something [ 34 ].
Educators should be aware that learning happens in the context and discourse of society, and that this can affect both educators’ and learners’ perspectives and motivation. While educators cannot influence the discourse directly, it is important to understand its existence, to modify barriers and facilitate motivation. The mechanisms of such discourses and their possible impact on students’ views require more research.
Future quantitative studies could explore to which extent a more general medical student population relates to the identified themes in order to validate them. Including students with low motivation for ultrasound or students with high motivation in other areas as participants and comparing and contrasting these results with those of this study could also provide a more comprehensive view of motivational factors and be an interesting area for further research. Factors which initially sparked participants’ interest and motivation to sign up for the course may be different to those which maintained and increased their motivation during the course. Longitudinal studies would enable a deeper understanding of such nuances and other changes in motivation over time.
We found four themes that have not yet been described in the literature: US was perceived as helpful in contextualising and exemplifying other learning content and supporting the transition into professional identity and, ultimately, clinical practice; the group setting with just-in-time feedback provides a fun and positive learning experience; participants reported being motivated to learn US because it was the tool of the future, and being able to visualise something trumped other forms of examination, reflecting the visuo-centric Zeitgeist. Knowledge and understanding of these themes may be relevant to other areas of medical education.
Data availability
The datasets used and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
participant
Sobral DT. What kind of motivation drives medical students’ learning quests? Medical Education [Internet]. 2004 [cited 2019 Apr 16];38(9):950–7. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2929.2004.01913.x .
Moulaert V, Verwijnen MGM, Rikers R, Scherpbier AJJA. The effects of deliberate practice in undergraduate medical education. Med Educ [Internet]. 2004 Oct [cited 2020 May 27];38(10):1044–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2929.2004.01954.x .
Kusurkar RA, Ten Cate TJ, Vos CMP, Westers P, Croiset G. How motivation affects academic performance: a structural equation modelling analysis. Advances in Health Sciences Education [Internet]. 2013 Mar [cited 2020 May 4];18(1):57–69. http://link.springer.com/ https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-012-9354-3 .
Babenko O, Daniels L, Ross S, White J, Oswald A. Medical student well-being and lifelong learning: A motivational perspective. Educ Health [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2023 Jul 11];32(1):25. https://journals.lww.com/ https://doi.org/10.4103/efh.EfH_237_17 .
Ryan RM, Deci EL. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivations: Classic Definitions and New Directions. Contemporary Educational Psychology [Internet]. 2000 Jan [cited 2019 Jul 4];25(1):54–67. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0361476X99910202 .
Kusurkar RA. Autonomous motivation in medical education. Medical Teacher [Internet]. 2019 Sep 2 [cited 2023 Jul 11];41(9):1083–4. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/0142159X.2018.1545087 .
Ryan RM, Deci EL. Self-Determination Theory and the Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development, and Well-Being. American Psychologist. 2000;11.
Cook DA, Artino AR. Motivation to learn: an overview of contemporary theories. Medical Education [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2019 Apr 10];50(10):997–1014. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/medu.13074 .
ten Cate OTJ, Kusurkar RA, Williams GC. How self-determination theory can assist our understanding of the teaching and learning processes in medical education. AMEE Guide No. 59. Medical Teacher [Internet]. 2011 Dec [cited 2020 Sep 5];33(12):961–73. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/ https://doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2011.595435 .
Birrane J, Misran H, Creaney M, Shorten G, Nix CM. A Scoping Review of Ultrasound Teaching in Undergraduate Medical Education. MedSciEduc [Internet]. 2018 Mar [cited 2019 Jul 3];28(1):45–56. http://link.springer.com/ https://doi.org/10.1007/s40670-017-0491-4 .
Hammoudi N, Arangalage D, Boubrit L, Renaud MC, Isnard R, Collet JP et al. Ultrasound-based teaching of cardiac anatomy and physiology to undergraduate medical students. Archives of Cardiovascular Diseases [Internet]. 2013 Oct [cited 2020 May 5];106(10):487–91. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1875213613001976 .
Limchareon S, Asawaworarit N, Klinwichit W, Dinchuthai P. Development of the ultrasonography learning model for undergraduate medical students: A case study of the Faculty of Medicine, Burapha University. Journal of the Chinese Medical Association [Internet]. 2016 Aug [cited 2020 May 5];79(8):445–9. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1726490116300077 .
Rempell JS, Saldana F, DiSalvo D, Kumar N, Stone MB, Chan W et al. Pilot Point-of-Care Ultrasound Curriculum at Harvard Medical School: Early Experience. West J Emerg Med [Internet]. 2016 Nov [cited 2019 Jul 3];17(6):734–40. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5102600/ .
Recker F, Barth G, Lo H, Haverkamp N, Nürnberg D, Kravchenko D et al. Students’ Perspectives on Curricular Ultrasound Education at German Medical Schools. Front Med [Internet]. 2021 Nov 25 [cited 2024 Mar 5];8:758255. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/ https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.758255/full .
Dietrich CF, Hoffmann B, Abramowicz J, Badea R, Braden B, Cantisani V et al. Medical Student Ultrasound Education: A WFUMB Position Paper, Part I. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology [Internet]. 2019 Feb [cited 2023 Jul 11];45(2):271–81. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0301562918304174 .
Jahns J, Recker F, Thiessen V, Rüenauver K, Bailer B. Sono4Students– sonographische Lehre nach dem Peer-teaching Prinzip. Ultraschall in der Medizin - European Journal of Ultrasound [Internet]. 2014 Sep 24 [cited 2020 May 5];35(S 01). http://www.thieme-connect.de/DOI/DOI?10.1055/s-0034-1389403 .
Hoppmann RA, Rao VV, Bell F, Poston MB, Howe DB, Riffle S et al. The evolution of an integrated ultrasound curriculum (iUSC) for medical students: 9-year experience. Crit Ultrasound J [Internet]. 2015 Dec [cited 2020 Aug 26];7(1):18. https://theultrasoundjournal.springeropen.com/articles/ https://doi.org/10.1186/s13089-015-0035-3 .
Kefala-Karli P, Sassis L, Sassi M, Zervides C. Introduction of ultrasound-based living anatomy into the medical curriculum: a survey on medical students’ perceptions. Ultrasound J [Internet]. 2021 Dec [cited 2023 Jul 11];13(1):47. https://theultrasoundjournal.springeropen.com/articles/ https://doi.org/10.1186/s13089-021-00247-1 .
Wang TC, Chen WT, Kang YN, Lin CW, Cheng CY, Suk FM et al. Why do pre-clinical medical students learn ultrasound? Exploring learning motivation through ERG theory. BMC Med Educ [Internet]. 2021 Dec [cited 2024 Mar 5];21(1):438. https://bmcmededuc.biomedcentral.com/articles/ https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-021-02869-4 .
Ng SL, Baker L, Cristancho S, Kennedy TJ, Lingard L. Qualitative Research in Medical Education: Methodologies and Methods. In: Swanwick T, Forrest K, O’Brien BC, editors. Understanding Medical Education [Internet]. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2018 [cited 2020 May 5]. pp. 427–41. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119373780.ch29 .
Castleberry A, Nolen A. Thematic analysis of qualitative research data: Is it as easy as it sounds? Currents in Pharmacy Teaching and Learning [Internet]. 2018 Jun [cited 2020 May 5];10(6):807–15. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1877129717300606 .
Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. International Journal for Quality in Health Care [Internet]. 2007 Sep 16 [cited 2024 Apr 7];19(6):349–57. https://academic.oup.com/intqhc/article-lookup/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzm042 .
Räschle N, Hari R. «Blended Learning»-Basiskurs Sonografie: Im Peer-Tutoring zu einem SGUM-akkreditierten Ultraschall-Kurs. Praxis [Internet]. 2018 Nov [cited 2024 Mar 13];107(23):1255–9. https://econtent.hogrefe.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1024/1661-8157/a003116 .
Charmaz K. Constructing grounded theory. 2nd edition. London; Thousand Oaks, Calif: Sage; 2014. 388 p. (Introducing qualitative methods).
Cristancho S, Goldszmidt M, Lingard L, Watling C. Qualitative research essentials for medical education. Singapore Medical Journal [Internet]. 2018 Dec [cited 2020 May 5];59(12):622–7. http://www.smj.org.sg/article/qualitative-research-essentials-medical-education .
Morse JM. The Significance of Saturation. Qualitative Health Research [Internet]. 1995 May [cited 2020 May 5];5(2):147–9. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/104973239500500201 .
Prats MI, Royall NA, Panchal AR, Way DP, Bahner DP. Outcomes of an Advanced Ultrasound Elective: Preparing Medical Students for Residency and Practice. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine [Internet]. 2016 May [cited 2023 Jul 11];35(5):975–82. https://doi.org/10.7863/ultra.15.06060 .
Chang LY, Eliasz KL, Cacciatore DT, Winkel AF. The Transition From Medical Student to Resident: A Qualitative Study of New Residents’ Perspectives. Academic Medicine [Internet]. 2020 Sep [cited 2020 Sep 7];95(9):1421–7. https://journals.lww.com/ https://doi.org/10.1097/ACM.0000000000003474 .
Brennan N, Corrigan O, Allard J, Archer J, Barnes R, Bleakley A et al. The transition from medical student to junior doctor: today’s experiences of Tomorrow’s Doctors. Medical Education [Internet]. 2010 May [cited 2020 Sep 8];44(5):449–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2923.2009.03604.x .
Darici D, Missler M, Schober A, Masthoff M, Schnittler H, Schmitz M. Fun slipping into the doctor’s role—The relationship between sonoanatomy teaching and professional identity formation before and during the Covid-19 pandemic. Anatomical Sciences Ed [Internet]. 2022 May [cited 2023 Jul 11];15(3):447–63. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.2178 .
Feilchenfeld Z, Kuper A, Whitehead C. Stethoscope of the 21st century: dominant discourses of ultrasound in medical education. Medical Education [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2019 Jul 3];52(12):1271–87. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.1111/medu.13714 .
Kelly M, Ellaway R, Scherpbier A, King N, Dornan T. Body pedagogics: embodied learning for the health professions. Med Educ [Internet]. 2019 Oct [cited 2020 Aug 11];53(10):967–77. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.1111/medu.13916 .
Guest G, Bunce A, Johnson L. How Many Interviews Are Enough? An Experiment with Data Saturation and Variability. Field Methods [Internet]. 2006 Feb [cited 2020 Sep 5];18(1):59–82. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1177/1525822X05279903 .
Kusurkar RA, Croiset G, Ten Cate OTJ. Twelve tips to stimulate intrinsic motivation in students through autonomy-supportive classroom teaching derived from Self-Determination Theory. Medical Teacher [Internet]. 2011 Dec [cited 2024 Mar 4];33(12):978–82. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/ https://doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2011.599896 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank Benjamin Bulling for his literature review of motivation theories and for the transcription of interviews. We thank Katharina Lüscher for the interview transcription.
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Anina Pless, Roman Hari contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Institute of Primary Health Care (BIHAM), University of Bern, Mittelstrasse 43, 3012, Bern, Switzerland
Anina Pless, Roman Hari & Michael Harris
College of Medicine & Health, University of Exeter Medical School, Exeter, UK
Michael Harris
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
AP and RH contributed to the conception of the work. AP, RH and MH contributed to the design of the work. AP did the acquisition and primary analysis. AP, MH and RH interpreted the data. AP wrote the main manuscript and MH and RH substantively revised it. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Anina Pless .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was submitted to the regional ethics committee (Kantonale Ehtikkommission für die Forschung, Gesundheits- und Fürsorgedirektion des Kantons Bern). A waiver was issued, stating that the study does not fall under the Swiss Human Research Act (BASEC-Nr. Req-2018-00059).
Consent for publication
Additional information, publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Pless, A., Hari, R. & Harris, M. Why are medical students so motivated to learn ultrasound skills? A qualitative study. BMC Med Educ 24 , 458 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05420-3
Download citation
Received : 08 February 2024
Accepted : 12 April 2024
Published : 26 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05420-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Medical education
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- National Security
- Matthew Continetti
- Men of the Year
- Men Of The Year
UCLA Med School Launches Review Of ‘Health Equity’ Course But Warns That Whistleblowers Could Be Disciplined
Columbia Student Protesters Demand an Apology From President Shafik: 'We Believe That It's on the Table'
Watch: joe biden's senior moment of the week (vol. 91), biden’s pier gets pummeled—along with his foreign policy, biden walks with aides to hide 'halting and stiff gait': report, guest column: help the anti-semitic freak leading protests at columbia is holding me captive as his 'emotional support' slave, ‘pedagogical malpractice’: inside ucla medical school’s mandatory ‘health equity’ class, top physicians, including former harvard dean, say required course is riddled with dangerous falsehoods.
Students in their first year of medical school typically learn what a healthy body looks like and how to keep it that way. At the University of California, Los Angeles, they learn that "fatphobia is medicine’s status quo" and that weight loss is a "hopeless endeavor."
Those are two of the more moderate claims made by Marquisele Mercedes, a self-described "fat liberationist," in an essay assigned to all first-year students in UCLA medical school’s mandatory "Structural Racism and Health Equity" class. Launched in the wake of George Floyd’s death, the course is required for all first-year medical students.
The Washington Free Beacon has obtained the entire syllabus for the course, along with slide decks and lecture prep from some of its most explosive sessions. The materials offer the fullest picture to date of what students at the elite medical school are learning and have dismayed prominent physicians—including those sympathetic to the goals of the class—who say UCLA has traded medicine for Marxism.
Jeffrey Flier, the former dean of Harvard Medical School and one of the world’s foremost experts on obesity, said the curriculum "promotes extensive and dangerous misinformation."
UCLA "has centered this required course on a socialist/Marxist ideology that is totally inappropriate," said Flier, who reviewed the full syllabus and several of the assigned readings. "As a longstanding medical educator, I found this course truly shocking."
One required reading lists "anti-capitalist politics" as a principle of "disability justice" and attacks the evils of "ableist heteropatriarchal capitalism." Others decry "racial capitalism," attack "growth-centered economic theories," and call for "moving beyond capitalism for our health."
The essay by Mercedes "describes how weight came to be pathologized and medicalized in racialized terms" and offers guidance on "resisting entrenched fat oppression," according to the course syllabus. Mercedes claims that "ob*sity" is a slur "used to exact violence on fat people"—particularly "Black, disabled, trans, poor fat people"—and offers a "fat ode to care" that students are instructed to analyze, taking note of which sections "most resonate with you."
"This is a profoundly misguided view of obesity, a complex medical disorder with major adverse health consequences for all racial and ethnic groups," Flier told the Free Beacon . "Promotion of these ignorant ideas to medical students without counterbalancing input from medical experts in the area is nothing less than pedagogical malpractice."
Nicholas Christakis, a sociologist and physician at Yale University, who has spent decades providing medical care to underserved communities, including in the South Side of Chicago, called the curriculum "nonsensical."
The relationship between health and social forces "should indeed be taught at medical school," Christakis wrote in an email, "but to have a mandatory course like this—so tendentious, sloganeering, incurious, and nonsensical—strikes me as embarrassing to UCLA."
UCLA did not respond to requests for comment.
Snapshots of the course have been leaking for months and left the school doing damage control as members of UCLA’s own faculty have spoken out against the curriculum. The most recent embarrassment came when a guest lecturer, Lisa Gray-Garcia, led students in chants of "Free, Free Palestine" after instructing them to kneel on the floor and pray to "Mama Earth." Lessons on " decolonization " and climate activism , as well as a classroom exercise that separated students by race, have also stirred controversy.
"There are areas where medicine and public health intersect with politics, and these require discussion and debate of conflicting viewpoints," Flier said. "That is distinct from education designed to ideologically indoctrinate physician-activists."
The mandatory class is part of a nationwide push by medical schools to integrate DEI content into their curricula—for residents as well as students— both by adding required courses and by changing the way traditional subjects are taught.
Stanford Medical School sprinkles lessons on "microaggressions," "structural racism," and "privilege" throughout its curriculum. Residents at Yale Medical School must complete an "Advocacy and Equity" sequence focused on "becoming physician advocates for health justice," while those in the infectious disease program must complete additional lessons on "Diversity, Equity, and Antiracism."
Columbia Medical School promotes an "Anti-bias and Inclusive" curriculum by encouraging educators to use "precise, accurate language." Instead of "women," guidelines for the curriculum state, faculty should refer to "people with uteruses."
The changes have been driven partly by the Association of American Medical Colleges—one of two groups that oversees the accrediting body for all U.S. medical schools—which in 2022 released a set of DEI "competencies" to guide curricula. Schools should teach students how to identify "systems of power, privilege, and oppression," the competencies state, and how to incorporate "knowledge of intersectionality" into clinical decision-making. Students should also be able to describe "public policy that promotes social justice" and demonstrate "moral courage" when faced with "microaggression."
The course at UCLA, which predates those accreditation standards, offers a preview of how DEI mandates could reshape medical education. It is littered with the lingo of progressive activism—"intersectionality" is a core value of the class, according to slides from the first session —and states outright that it is training doctors to become activists.
Students will "build critical consciousness" and move toward a "liberatory practice of medicine" by "focusing on praxis," according to the slides.
A section called "Our Hxstories" adds that "[h]ealth and medical practice are deeply impacted by racism and other intersectional structures of power, hierarchy, and oppression—all of which require humility, space and patience to understand, deconstruct, and eventually rectify."
That jargon reflects a worldview with clinical implications. In a unit on "abolitionist" health, which explores "alternatives to carceral systems in LA," students are assigned a paper that argues police should be removed from emergency rooms, where 55 percent of doctors say they’ve been assaulted—mostly by patients—and threats of violence are common, according to a 2022 survey from American College of Emergency Physicians. Other units discuss the "sickness of policing" and link "Queer liberation to liberation from the carceral state."
Flier said the syllabus was so bad it called for an investigation—and that anyone who signed off on it was unfit to make curricular decisions.
"Assuming the school’s dean," Steven Dubinett, a pulmonologist, "does not himself support this course as presented, it is his responsibility to review the course and the curriculum committee that approved it," Flier said. "If that body judged the course as appropriate, he should change its leadership and membership."
Dubinett did not respond to a request for comment.
One of the leaders of the course is Shamsher Samra, a professor of emergency medicine who in December signed an open letter endorsing "Palestinians’ right to return" and linking "health equity" to divestment from Israel.
"To authentically engage in antiracism health scholarship and practice is to explicitly name injustices tied to white supremacy and maintain an unapologetic commitment to antiracism praxis that transcends US borders," the letter reads. "As such, we, the undersigned,* unequivocally support a free Palestine and Palestinians’ right to return."
Samra, who in 2021 published a paper on "infrastructural violence and the health of border abolition," did not respond to a request for comment.
To the extent the course addresses actual medical debates, it frames contested treatments as settled science, omitting evidence that cuts against its activist narrative. A unit on "Queerness/Gender," for example, assigns readings on "gender self-determination" and "DIY transition," but does not include any of the research from Europe—such as the newly released Cass Report —that has led England and other countries to restrict hormone therapies for children.
"UCLA School of Medicine has decided to shield its students from the ongoing scientific debates playing out in Europe and even in the U.S.," said Leor Sapir, a fellow at the Manhattan Institute who researches gender medicine. "This is fundamentally unserious, and a stain on the school’s reputation."
The omission of inconvenient facts extends to a unit on Los Angeles's King/Drew hospital—nicknamed "Killer King" for its high rates of medical error—which the course promotes as an example of "community health."
Founded in 1972 as a response to the Watts riots, the hospital was majority black, had a documented policy of racial preferences, and was hit with several civil rights complaints by non-black doctors alleging discrimination in hiring and promotion.
It closed in 2007 after a Pulitzer Prize-winning investigation by the Los Angeles Times found numerous cases in which patients had been killed or injured by clinical mistakes, such as overdosing a child with sedatives and giving cancer drugs to a meningitis patient. Efforts to reform the hospital stalled, according to the Times , because its board of supervisors feared coming across as racially insensitive.
The assigned readings on King/Drew do not include any of this history. Lecture slides instead praise the hospital for "suturing racial divides," but suggest that it may not have gone far enough. A focus on "producing highly talented and skilled physicians," one slide reads, "forced" King/Drew to hire doctors who were, "in some cases, not Black."
The curriculum is a "compilation of ideologic and anecdotal assertions that represent a warped view of medicine," said Stanley Goldfarb, the founder of the medical advocacy group Do No Harm and the father of Free Beacon chairman Michael Goldfarb. "American medical education needs to purge itself of this nonsense and treat every patient as an individual."
The slides suggest that "lived experiences," "historical memory," and "other knowledges" can constitute medical expertise.
Biomedical knowledge, after all, is "just one way of knowing, understanding, and experiencing health in the world."
Published under: DEI , Higher Education , Medical Ethics , UCLA
latest in US News

Mom of Kansas City Chiefs fan found frozen speaks out during...

Ex-gov says Jewish protesters marched with MLK — and they...

Louisiana sicko agrees to be surgically castrated after raping,...

Dan Rather returns to CBS for the first time 18 years after his...

Eric Trump warns Biden could be hit with charges for White House...

'Hunter got high:' Biden son's drug, laptop troubles spoofed in...

Concerns grow as builder 'desperate' for apartments at toxic site...

I lost 80 pounds and became a fitness instructor — thanks to...
Breaking news, mandatory ucla medical school ‘structural racism and health equity’ course says weight loss is ‘useless’.
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
First-year medical students are required to learn that weight has little to do with health, according to a new report.
The Washington Free Beacon obtained a syllabus from the “Structural Racism and Health Equity” course at The David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. The document includes required reading lists to prepare for classes regarding topics like “The Sickness of Policing & Incarceration,” “Anti-Settler Colonialism/Indigenous Health” and “Environmental Racism & Justice.”
Among the materials for the “Disability Justice” session include an article by Marquisele Mercedes, titled “No Health, No Care: The Big Fat Loophole in the Hippocratic Oath,” which says “fatphobia is medicine’s status quo.”
“It is proven that weight loss is a useless, hopeless endeavor. You are unlikely to lose weight in any permanent way and highly likely to open yourself to the myriad risks associated with weight cycling. The relationship between weight and health is also muddy,” the essay reads.

Fox News Digital reached out to The David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA for a comment but has yet to receive a response.
UCLA’s medical school has come under fire in the last few months over its “Health Equity” class for its assignments and controversial events.
Earlier this month, the UCLA Jewish Faculty Resilience Group spoke to several witnesses who testified that an invited lecturer “instructed students to touch the floor, ‘mama earth with a fist’ while she made a ‘non-secular’ prayer to ‘mama earth’ and our ‘ancestors.'”
Keep up with today's most important news
Stay up on the very latest with Evening Update.
Thanks for signing up!
Please provide a valid email address.
By clicking above you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Never miss a story.
The speaker also allegedly “instructed students to get out of their seats and stand upright with her for a closing prayer, once again to ‘mama earth’ and the ‘ancestors.’ Of those gathered, a handful of students who were visibly uncomfortable declined to participate, remaining seated throughout.”
In January, the school was forced to cancel a class exercise that divided students into racial groups following a civil rights complaint.

“[R]ecognizing the imperfect and problematic nature of our socially constructed racial categories, we ask that you identify the group in which you feel you are most perceived as in clinical spaces,” the exercise reportedly said.
The “Structural Racism and Health Equity” class was established in 2020 as part of the school’s “anti-racist” curriculum shift in the wake of George Floyd’s death.
Share this article:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Jude's essay provides a very matter-of-fact account of their experience as a pre-medical student. However, they deepen this narrative by merging two distinct cultures through some common ground ...
Med School Personal Statement Consultant Dr. Mary Mahoney. T his med school essay advice is written by Dr. Mary Mahoney, Ph.D. who has over 20 years of experience as an advisor and essay reviewer for med school applicants. She is a tenured English Professor with an MFA in Creative Writing from Sarah Lawrence College and a PhD in Literature and Writing from the University of Houston.
Medical School Personal Statement Fundamentals. If you are getting ready to write your medical school personal statement for the 2024-2025 application year, you may already know that almost 60% of medical school applicants are not accepted every year. You have most likely also completed all of your medical school requirements and have scoured the internet for worthy medical school personal ...
Part 3: The medical school adversity essay Example adversity essay prompts. Example 1: "Share with us a difficult or challenging situation you have encountered and how you dealt with it.In your response, identify both the coping skills you called upon to resolve the dilemma, and the support person(s) from whom you sought advice." (University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine)
This is precisely why we included the numerous sample medical school personal statement essays at the end of this guide. We also don't believe that reviewing your CV or thinking through your personal experiences to identify the "most unique" topic ideas is a valuable approach to brainstorming your personal statement. This "resume-first ...
A compelling medical school admissions essay can address nearly any topic the applicant is interested in, as long as it conveys the applicant's personality, according to Dr. Barbara Kazmierczak ...
Example 3 — Beyond the Diagnosis: The Importance of Individualized Care in Medicine. The applicant who wrote this personal statement was accepted into Touro College of Osteopathic Medicine and Nova Southeastern University College Of Osteopathic Medicine. Dr. Haywood sighs and shakes her head upon opening the chart.
Concluding paragraph: The strongest conclusion reflects the beginning of your essay, gives a brief summary of you are, and ends with a challenge for the future. 8. Good writing is simple writing. Good medical students—and good doctors—use clear, direct language. Your essays should not be a struggle to comprehend. 9. Be thoughtful about ...
Describe how the experience influenced your decision to pursue medicine. The best personal statements tell a story about who you are. "Show, don't tell," what you've experienced — immerse the reader in your narrative, and you'll have a higher chance of being accepted to medical school. 6. Create an engaging conclusion.
This equals about 1 1/2 pages of writing, single-spaced. Make sure your essay is interesting, follows a logical and orderly flow, relates to your reasons for choosing medicine, and describes why you believe you will be successful as a physician. Don't be afraid of the editing process. Be sure to write more than one draft and make edits to ...
link in the application or see Section 8 of the AMCAS Applicant Guide for suggestions of things to think about when writing this essay. If you're applying to an MD-PhD program, you must complete two additional essays: the MD-PhD Essay and the Significant Research Experience Essay. To avoid formatting issues, we recommend that you type your ...
A refreshingly honest essay describing rejection from medical school during your first application cycle, and your continued commitment to the long road ahead - including how you have worked to ...
Successful Harvard Medical School Essay. Jim and I had only spoken once by phone and were now in a soundproof piano practice room in my dorm basement, after dark and out of cell phone range. My ...
4 Points to Include in Every Med School Personal Statement. For a compelling essay, prospective medical school students should share their passions beyond medicine. You should reflect on past ...
An essay prompt is the question you are asked to answer within your essay. For the AMCAS medical school personal statement, your essay prompt is: "Use the space provided to explain why you want to go to medical school.". The essay prompt varies slightly depending on the application service you're using. For TMDSAS, the essay prompt is ...
June 12, 2023. One of the most important parts of your medical school application is undoubtedly the personal statement. Just like writing the Common App essay when applying to college, your medical school personal statement provides the opportunity to show admissions your skills, your goals, and your relevant experiences.
11 | Invest in Essay Editing Services. Your medical school personal statement is arguably the most important piece of your application. While an excellent essay can lock-in your interview offer, a poorly-written personal statement can ruin your chances—even with stellar grades, impressive academic awards, and a notable list of extracurriculars.
In this setting, the humor certainly adds value to the essay, although this may be more off-putting to more traditional and conservative medical school admissions committee members. Overall, a high risk and high reward strategy, because when it lands, it makes for a compelling, unique, and entertaining read.
Similar to crafting strong medical school secondary essays, writing a strong personal statement is a challenging, yet extremely important, part of your MD or MD-PhD programs applications. Your AMCAS Work and Activities section may show the reader what you have done, but the personal statement explains why. This is how Dr. Neel Mistry, MD and ...
Personal Statement Example #3. Student accepted to Weill Cornell. My path to medicine was first influenced by early adolescent experiences trying to understand my place in society. Though I was not conscious of it then, I held a delicate balance between my identity as an Indian-American and an "American-American.".
B. Final thoughts on why you are a strong candidate for medical school. C. Call-to-action or next steps. (Note: This is just one example of a potential outline for a medical school personal statement. The specific content and structure may vary based on individual experiences and preferences.)
Medical School Essay Four. Prompt: Tell us more about who you are. I am a white, cisgender, and heterosexual female who has been afforded many privileges: I was raised by parents with significant financial resources, I have traveled the world, and I received top-quality high school and college educations.
MD Student Essays. Nora Abo-Sido. Class of 2018. The Promise of Peace: Cultivating health to heal communities. Wilfredo García Beltrán. Class of 2018. The Promise of Hope: Believing in the power of medicine's miracles. Andrew Kim. Class of 2018.
Some medical school applicants are already focused on pursuing a particular career pathway in medicine. While many students will change from this pathway during medical school, knowing of your potential interests does help us to assign interviewers. Your choice below does not influence how the Admissions Committee selects students to interview.
The introduction of ultrasound (US) courses into medical undergraduate courses is usually met with a particularly high level of student motivation. The reasons for this are unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the factors that contribute to undergraduate medical students' motivation to learn US skills. Understanding what motivates students to learn US will inform the efforts of ...
For a 2023 study published in the Archives of Women's Mental Health, researchers examined how being a parent during medical school can affect specialty choice.In the study of 59 parents and 478 nonparents, the three factors most predictive of specialty choice were the same for each group—passion for the field, culture of the specialty and quality of life.
Last month, nearly 40,000 medical students were accepted into residency programs on "Match Day." Surrounded by family and friends, these soon-to-be-physicians opened envelopes revealing where ...
First Opinion essays on free medical school tuition, site-neutral-payments, and other topics prompted readers to respond.
Those are two of the more moderate claims made by Marquisele Mercedes, a self-described "fat liberationist," in an essay assigned to all first-year students in UCLA medical school's mandatory ...
The relationship between weight and health is also muddy," the essay reads. UCLA medical school students learn that "fatphobia is medicine's status quo." Getty Images.