- Search the site GO Please fill out this field.
- Newsletters
- Mental Health
- Social and Public Health

What Is Gender Affirmation Surgery?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/KP-Headshot-IMG_1661-0d48c6ea46f14ab19a91e7b121b49f59.jpg)
A gender affirmation surgery allows individuals, such as those who identify as transgender or nonbinary, to change one or more of their sex characteristics. This type of procedure offers a person the opportunity to have features that align with their gender identity.
For example, this type of surgery may be a transgender surgery like a male-to-female or female-to-male surgery. Read on to learn more about what masculinizing, feminizing, and gender-nullification surgeries may involve, including potential risks and complications.
Why Is Gender Affirmation Surgery Performed?
A person may have gender affirmation surgery for different reasons. They may choose to have the surgery so their physical features and functional ability align more closely with their gender identity.
For example, one study found that 48,019 people underwent gender affirmation surgeries between 2016 and 2020. Most procedures were breast- and chest-related, while the remaining procedures concerned genital reconstruction or facial and cosmetic procedures.
In some cases, surgery may be medically necessary to treat dysphoria. Dysphoria refers to the distress that transgender people may experience when their gender identity doesn't match their sex assigned at birth. One study found that people with gender dysphoria who had gender affirmation surgeries experienced:
- Decreased antidepressant use
- Decreased anxiety, depression, and suicidal ideation
- Decreased alcohol and drug abuse
However, these surgeries are only performed if appropriate for a person's case. The appropriateness comes about as a result of consultations with mental health professionals and healthcare providers.
Transgender vs Nonbinary
Transgender and nonbinary people can get gender affirmation surgeries. However, there are some key ways that these gender identities differ.
Transgender is a term that refers to people who have gender identities that aren't the same as their assigned sex at birth. Identifying as nonbinary means that a person doesn't identify only as a man or a woman. A nonbinary individual may consider themselves to be:
- Both a man and a woman
- Neither a man nor a woman
- An identity between or beyond a man or a woman
Hormone Therapy
Gender-affirming hormone therapy uses sex hormones and hormone blockers to help align the person's physical appearance with their gender identity. For example, some people may take masculinizing hormones.
"They start growing hair, their voice deepens, they get more muscle mass," Heidi Wittenberg, MD , medical director of the Gender Institute at Saint Francis Memorial Hospital in San Francisco and director of MoZaic Care Inc., which specializes in gender-related genital, urinary, and pelvic surgeries, told Health .
Types of hormone therapy include:
- Masculinizing hormone therapy uses testosterone. This helps to suppress the menstrual cycle, grow facial and body hair, increase muscle mass, and promote other male secondary sex characteristics.
- Feminizing hormone therapy includes estrogens and testosterone blockers. These medications promote breast growth, slow the growth of body and facial hair, increase body fat, shrink the testicles, and decrease erectile function.
- Non-binary hormone therapy is typically tailored to the individual and may include female or male sex hormones and/or hormone blockers.
It can include oral or topical medications, injections, a patch you wear on your skin, or a drug implant. The therapy is also typically recommended before gender affirmation surgery unless hormone therapy is medically contraindicated or not desired by the individual.
Masculinizing Surgeries
Masculinizing surgeries can include top surgery, bottom surgery, or both. Common trans male surgeries include:
- Chest masculinization (breast tissue removal and areola and nipple repositioning/reshaping)
- Hysterectomy (uterus removal)
- Metoidioplasty (lengthening the clitoris and possibly extending the urethra)
- Oophorectomy (ovary removal)
- Phalloplasty (surgery to create a penis)
- Scrotoplasty (surgery to create a scrotum)
Top Surgery
Chest masculinization surgery, or top surgery, often involves removing breast tissue and reshaping the areola and nipple. There are two main types of chest masculinization surgeries:
- Double-incision approach : Used to remove moderate to large amounts of breast tissue, this surgery involves two horizontal incisions below the breast to remove breast tissue and accentuate the contours of pectoral muscles. The nipples and areolas are removed and, in many cases, resized, reshaped, and replaced.
- Short scar top surgery : For people with smaller breasts and firm skin, the procedure involves a small incision along the lower half of the areola to remove breast tissue. The nipple and areola may be resized before closing the incision.
Metoidioplasty
Some trans men elect to do metoidioplasty, also called a meta, which involves lengthening the clitoris to create a small penis. Both a penis and a clitoris are made of the same type of tissue and experience similar sensations.
Before metoidioplasty, testosterone therapy may be used to enlarge the clitoris. The procedure can be completed in one surgery, which may also include:
- Constructing a glans (head) to look more like a penis
- Extending the urethra (the tube urine passes through), which allows the person to urinate while standing
- Creating a scrotum (scrotoplasty) from labia majora tissue
Phalloplasty
Other trans men opt for phalloplasty to give them a phallic structure (penis) with sensation. Phalloplasty typically requires several procedures but results in a larger penis than metoidioplasty.
The first and most challenging step is to harvest tissue from another part of the body, often the forearm or back, along with an artery and vein or two, to create the phallus, Nicholas Kim, MD, assistant professor in the division of plastic and reconstructive surgery in the department of surgery at the University of Minnesota Medical School in Minneapolis, told Health .
Those structures are reconnected under an operative microscope using very fine sutures—"thinner than our hair," said Dr. Kim. That surgery alone can take six to eight hours, he added.
In a separate operation, called urethral reconstruction, the surgeons connect the urinary system to the new structure so that urine can pass through it, said Dr. Kim. Urethral reconstruction, however, has a high rate of complications, which include fistulas or strictures.
According to Dr. Kim, some trans men prefer to skip that step, especially if standing to urinate is not a priority. People who want to have penetrative sex will also need prosthesis implant surgery.
Hysterectomy and Oophorectomy
Masculinizing surgery often includes the removal of the uterus (hysterectomy) and ovaries (oophorectomy). People may want a hysterectomy to address their dysphoria, said Dr. Wittenberg, and it may be necessary if their gender-affirming surgery involves removing the vagina.
Many also opt for an oophorectomy to remove the ovaries, almond-shaped organs on either side of the uterus that contain eggs and produce female sex hormones. In this case, oocytes (eggs) can be extracted and stored for a future surrogate pregnancy, if desired. However, this is a highly personal decision, and some trans men choose to keep their uterus to preserve fertility.
Feminizing Surgeries
Surgeries are often used to feminize facial features, enhance breast size and shape, reduce the size of an Adam’s apple , and reconstruct genitals. Feminizing surgeries can include:
- Breast augmentation
- Facial feminization surgery
- Penis removal (penectomy)
- Scrotum removal (scrotectomy)
- Testicle removal (orchiectomy)
- Tracheal shave (chondrolaryngoplasty) to reduce an Adam's apple
- Vaginoplasty
- Voice feminization
Breast Augmentation
Top surgery, also known as breast augmentation or breast mammoplasty, is often used to increase breast size for a more feminine appearance. The procedure can involve placing breast implants, tissue expanders, or fat from other parts of the body under the chest tissue.
Breast augmentation can significantly improve gender dysphoria. Studies show most people who undergo top surgery are happier, more satisfied with their chest, and would undergo the surgery again.
Most surgeons recommend 12 months of feminizing hormone therapy before breast augmentation. Since hormone therapy itself can lead to breast tissue development, transgender women may or may not decide to have surgical breast augmentation.
Facial Feminization and Adam's Apple Removal
Facial feminization surgery (FFS) is a series of plastic surgery procedures that reshape the forehead, hairline, eyebrows, nose, cheeks, and jawline. Nonsurgical treatments like cosmetic fillers, botox, fat grafting, and liposuction may also be used to create a more feminine appearance.
Some trans women opt for chondrolaryngoplasty, also known as a tracheal shave. The procedure reduces the size of the Adam's apple, an area of cartilage around the larynx (voice box) that tends to be larger in people assigned male at birth.
Vulvoplasty and Vaginoplasty
As for bottom surgery, there are various feminizing procedures from which to choose. Vulvoplasty (to create external genitalia without a vagina) or vaginoplasty (to create a vulva and vaginal canal) are two of the most common procedures.
Dr. Wittenberg noted that people might undergo six to 12 months of electrolysis or laser hair removal before surgery to remove pubic hair from the skin that will be used for the vaginal lining.
Surgeons have different techniques for creating a vaginal canal. A common one is a penile inversion, where the masculine structures are emptied and inverted into a created cavity, explained Dr. Kim. Vaginoplasty may be done in one or two stages, said Dr. Wittenberg, and the initial recovery is three months—but it will be a full year until people see results.
Surgical removal of the penis or penectomy is sometimes used in feminization treatment. This can be performed along with an orchiectomy and scrotectomy.
However, a total penectomy is not commonly used in feminizing surgeries . Instead, many people opt for penile-inversion surgery, a technique that hollows out the penis and repurposes the tissue to create a vagina during vaginoplasty.
Orchiectomy and Scrotectomy
An orchiectomy is a surgery to remove the testicles —male reproductive organs that produce sperm. Scrotectomy is surgery to remove the scrotum, that sac just below the penis that holds the testicles.
However, some people opt to retain the scrotum. Scrotum skin can be used in vulvoplasty or vaginoplasty, surgeries to construct a vulva or vagina.
Other Surgical Options
Some gender non-conforming people opt for other types of surgeries. This can include:
- Gender nullification procedures
- Penile preservation vaginoplasty
- Vaginal preservation phalloplasty
Gender Nullification
People who are agender or asexual may opt for gender nullification, sometimes called nullo. This involves the removal of all sex organs. The external genitalia is removed, leaving an opening for urine to pass and creating a smooth transition from the abdomen to the groin.
Depending on the person's sex assigned at birth, nullification surgeries can include:
- Breast tissue removal
- Nipple and areola augmentation or removal
Penile Preservation Vaginoplasty
Some gender non-conforming people assigned male at birth want a vagina but also want to preserve their penis, said Dr. Wittenberg. Often, that involves taking skin from the lining of the abdomen to create a vagina with full depth.
Vaginal Preservation Phalloplasty
Alternatively, a patient assigned female at birth can undergo phalloplasty (surgery to create a penis) and retain the vaginal opening. Known as vaginal preservation phalloplasty, it is often used as a way to resolve gender dysphoria while retaining fertility.
The recovery time for a gender affirmation surgery will depend on the type of surgery performed. For example, healing for facial surgeries may last for weeks, while transmasculine bottom surgery healing may take months.
Your recovery process may also include additional treatments or therapies. Mental health support and pelvic floor physiotherapy are a few options that may be needed or desired during recovery.
Risks and Complications
The risk and complications of gender affirmation surgeries will vary depending on which surgeries you have. Common risks across procedures could include:
- Anesthesia risks
- Hematoma, which is bad bruising
- Poor incision healing
Complications from these procedures may be:
- Acute kidney injury
- Blood transfusion
- Deep vein thrombosis, which is blood clot formation
- Pulmonary embolism, blood vessel blockage for vessels going to the lung
- Rectovaginal fistula, which is a connection between two body parts—in this case, the rectum and vagina
- Surgical site infection
- Urethral stricture or stenosis, which is when the urethra narrows
- Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Wound disruption
What To Consider
It's important to note that an individual does not need surgery to transition. If the person has surgery, it is usually only one part of the transition process.
There's also psychotherapy . People may find it helpful to work through the negative mental health effects of dysphoria. Typically, people seeking gender affirmation surgery must be evaluated by a qualified mental health professional to obtain a referral.
Some people may find that living in their preferred gender is all that's needed to ease their dysphoria. Doing so for one full year prior is a prerequisite for many surgeries.
All in all, the entire transition process—living as your identified gender, obtaining mental health referrals, getting insurance approvals, taking hormones, going through hair removal, and having various surgeries—can take years, healthcare providers explained.
A Quick Review
Whether you're in the process of transitioning or supporting someone who is, it's important to be informed about gender affirmation surgeries. Gender affirmation procedures often involve multiple surgeries, which can be masculinizing, feminizing, or gender-nullifying in nature.
It is a highly personalized process that looks different for each person and can often take several months or years. The procedures also vary regarding risks and complications, so consultations with healthcare providers and mental health professionals are essential before having these procedures.
American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Gender affirmation surgeries .
Wright JD, Chen L, Suzuki Y, Matsuo K, Hershman DL. National estimates of gender-affirming surgery in the US . JAMA Netw Open . 2023;6(8):e2330348-e2330348. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.30348
Coleman E, Radix AE, Bouman WP, et al. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, version 8 . Int J Transgend Health . 2022;23(S1):S1-S260. doi:10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644
Chou J, Kilmer LH, Campbell CA, DeGeorge BR, Stranix JY. Gender-affirming surgery improves mental health outcomes and decreases anti-depressant use in patients with gender dysphoria . Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open . 2023;11(6 Suppl):1. doi:10.1097/01.GOX.0000944280.62632.8c
Human Rights Campaign. Get the facts on gender-affirming care .
Human Rights Campaign. Transgender and non-binary people FAQ .
Unger CA. Hormone therapy for transgender patients . Transl Androl Urol . 2016;5(6):877–84. doi:10.21037/tau.2016.09.04
Richards JE, Hawley RS. Chapter 8: Sex Determination: How Genes Determine a Developmental Choice . In: Richards JE, Hawley RS, eds. The Human Genome . 3rd ed. Academic Press; 2011: 273-298.
Randolph JF Jr. Gender-affirming hormone therapy for transgender females . Clin Obstet Gynecol . 2018;61(4):705-721. doi:10.1097/GRF.0000000000000396
Cocchetti C, Ristori J, Romani A, Maggi M, Fisher AD. Hormonal treatment strategies tailored to non-binary transgender individuals . J Clin Med . 2020;9(6):1609. doi:10.3390/jcm9061609
Van Boerum MS, Salibian AA, Bluebond-Langner R, Agarwal C. Chest and facial surgery for the transgender patient . Transl Androl Urol . 2019;8(3):219-227. doi:10.21037/tau.2019.06.18
Djordjevic ML, Stojanovic B, Bizic M. Metoidioplasty: techniques and outcomes . Transl Androl Urol . 2019;8(3):248–53. doi:10.21037/tau.2019.06.12
Bordas N, Stojanovic B, Bizic M, Szanto A, Djordjevic ML. Metoidioplasty: surgical options and outcomes in 813 cases . Front Endocrinol . 2021;12:760284. doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.760284
Al-Tamimi M, Pigot GL, van der Sluis WB, et al. The surgical techniques and outcomes of secondary phalloplasty after metoidioplasty in transgender men: an international, multi-center case series . The Journal of Sexual Medicine . 2019;16(11):1849-1859. doi:10.1016/j.jsxm.2019.07.027
Waterschoot M, Hoebeke P, Verla W, et al. Urethral complications after metoidioplasty for genital gender affirming surgery . J Sex Med . 2021;18(7):1271–9. doi:10.1016/j.jsxm.2020.06.023
Nikolavsky D, Hughes M, Zhao LC. Urologic complications after phalloplasty or metoidioplasty . Clin Plast Surg . 2018;45(3):425–35. doi:10.1016/j.cps.2018.03.013
Nota NM, den Heijer M, Gooren LJ. Evaluation and treatment of gender-dysphoric/gender incongruent adults . In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, et al., eds. Endotext . MDText.com, Inc.; 2000.
Carbonnel M, Karpel L, Cordier B, Pirtea P, Ayoubi JM. The uterus in transgender men . Fertil Steril . 2021;116(4):931–5. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2021.07.005
Miller TJ, Wilson SC, Massie JP, Morrison SD, Satterwhite T. Breast augmentation in male-to-female transgender patients: Technical considerations and outcomes . JPRAS Open . 2019;21:63-74. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2019.03.003
Claes KEY, D'Arpa S, Monstrey SJ. Chest surgery for transgender and gender nonconforming individuals . Clin Plast Surg . 2018;45(3):369–80. doi:10.1016/j.cps.2018.03.010
De Boulle K, Furuyama N, Heydenrych I, et al. Considerations for the use of minimally invasive aesthetic procedures for facial remodeling in transgender individuals . Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol . 2021;14:513-525. doi:10.2147/CCID.S304032
Asokan A, Sudheendran MK. Gender affirming body contouring and physical transformation in transgender individuals . Indian J Plast Surg . 2022;55(2):179-187. doi:10.1055/s-0042-1749099
Sturm A, Chaiet SR. Chondrolaryngoplasty-thyroid cartilage reduction . Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am . 2019;27(2):267–72. doi:10.1016/j.fsc.2019.01.005
Chen ML, Reyblat P, Poh MM, Chi AC. Overview of surgical techniques in gender-affirming genital surgery . Transl Androl Urol . 2019;8(3):191-208. doi:10.21037/tau.2019.06.19
Wangjiraniran B, Selvaggi G, Chokrungvaranont P, Jindarak S, Khobunsongserm S, Tiewtranon P. Male-to-female vaginoplasty: Preecha's surgical technique . J Plast Surg Hand Surg . 2015;49(3):153-9. doi:10.3109/2000656X.2014.967253
Okoye E, Saikali SW. Orchiectomy . In: StatPearls [Internet] . Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
Salgado CJ, Yu K, Lalama MJ. Vaginal and reproductive organ preservation in trans men undergoing gender-affirming phalloplasty: technical considerations . J Surg Case Rep . 2021;2021(12):rjab553. doi:10.1093/jscr/rjab553
American Society of Plastic Surgeons. What should I expect during my recovery after facial feminization surgery?
American Society of Plastic Surgeons. What should I expect during my recovery after transmasculine bottom surgery?
de Brouwer IJ, Elaut E, Becker-Hebly I, et al. Aftercare needs following gender-affirming surgeries: findings from the ENIGI multicenter European follow-up study . The Journal of Sexual Medicine . 2021;18(11):1921-1932. doi:10.1016/j.jsxm.2021.08.005
American Society of Plastic Surgeons. What are the risks of transfeminine bottom surgery?
American Society of Plastic Surgeons. What are the risks of transmasculine top surgery?
Khusid E, Sturgis MR, Dorafshar AH, et al. Association between mental health conditions and postoperative complications after gender-affirming surgery . JAMA Surg . 2022;157(12):1159-1162. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2022.3917
Related Articles
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- COVID-19 Vaccines
- Occupational Therapy
- Healthy Aging
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
Preparation and Procedures Involved in Gender Affirmation Surgeries
If you or a loved one are considering gender affirmation surgery , you are probably wondering what steps you must go through before the surgery can be done. Let's look at what is required to be a candidate for these surgeries, the potential positive effects and side effects of hormonal therapy, and the types of surgeries that are available.
Gender affirmation surgery, also known as gender confirmation surgery, is performed to align or transition individuals with gender dysphoria to their true gender.
A transgender woman, man, or non-binary person may choose to undergo gender affirmation surgery.
The term "transexual" was previously used by the medical community to describe people who undergo gender affirmation surgery. The term is no longer accepted by many members of the trans community as it is often weaponized as a slur. While some trans people do identify as "transexual", it is best to use the term "transgender" to describe members of this community.
Transitioning
Transitioning may involve:
- Social transitioning : going by different pronouns, changing one’s style, adopting a new name, etc., to affirm one’s gender
- Medical transitioning : taking hormones and/or surgically removing or modifying genitals and reproductive organs
Transgender individuals do not need to undergo medical intervention to have valid identities.
Reasons for Undergoing Surgery
Many transgender people experience a marked incongruence between their gender and their assigned sex at birth. The American Psychiatric Association (APA) has identified this as gender dysphoria.
Gender dysphoria is the distress some trans people feel when their appearance does not reflect their gender. Dysphoria can be the cause of poor mental health or trigger mental illness in transgender people.
For these individuals, social transitioning, hormone therapy, and gender confirmation surgery permit their outside appearance to match their true gender.
Steps Required Before Surgery
In addition to a comprehensive understanding of the procedures, hormones, and other risks involved in gender-affirming surgery, there are other steps that must be accomplished before surgery is performed. These steps are one way the medical community and insurance companies limit access to gender affirmative procedures.
Steps may include:
- Mental health evaluation : A mental health evaluation is required to look for any mental health concerns that could influence an individual’s mental state, and to assess a person’s readiness to undergo the physical and emotional stresses of the transition.
- Clear and consistent documentation of gender dysphoria
- A "real life" test : The individual must take on the role of their gender in everyday activities, both socially and professionally (known as “real-life experience” or “real-life test”).
Firstly, not all transgender experience physical body dysphoria. The “real life” test is also very dangerous to execute, as trans people have to make themselves vulnerable in public to be considered for affirmative procedures. When a trans person does not pass (easily identified as their gender), they can be clocked (found out to be transgender), putting them at risk for violence and discrimination.
Requiring trans people to conduct a “real-life” test despite the ongoing violence out transgender people face is extremely dangerous, especially because some transgender people only want surgery to lower their risk of experiencing transphobic violence.
Hormone Therapy & Transitioning
Hormone therapy involves taking progesterone, estrogen, or testosterone. An individual has to have undergone hormone therapy for a year before having gender affirmation surgery.
The purpose of hormone therapy is to change the physical appearance to reflect gender identity.
Effects of Testosterone
When a trans person begins taking testosterone , changes include both a reduction in assigned female sexual characteristics and an increase in assigned male sexual characteristics.
Bodily changes can include:
- Beard and mustache growth
- Deepening of the voice
- Enlargement of the clitoris
- Increased growth of body hair
- Increased muscle mass and strength
- Increase in the number of red blood cells
- Redistribution of fat from the breasts, hips, and thighs to the abdominal area
- Development of acne, similar to male puberty
- Baldness or localized hair loss, especially at the temples and crown of the head
- Atrophy of the uterus and ovaries, resulting in an inability to have children
Behavioral changes include:
- Aggression
- Increased sex drive
Effects of Estrogen
When a trans person begins taking estrogen , changes include both a reduction in assigned male sexual characteristics and an increase in assigned female characteristics.
Changes to the body can include:
- Breast development
- Loss of erection
- Shrinkage of testicles
- Decreased acne
- Decreased facial and body hair
- Decreased muscle mass and strength
- Softer and smoother skin
- Slowing of balding
- Redistribution of fat from abdomen to the hips, thighs, and buttocks
- Decreased sex drive
- Mood swings
When Are the Hormonal Therapy Effects Noticed?
The feminizing effects of estrogen and the masculinizing effects of testosterone may appear after the first couple of doses, although it may be several years before a person is satisfied with their transition. This is especially true for breast development.
Timeline of Surgical Process
Surgery is delayed until at least one year after the start of hormone therapy and at least two years after a mental health evaluation. Once the surgical procedures begin, the amount of time until completion is variable depending on the number of procedures desired, recovery time, and more.
Transfeminine Surgeries
Transfeminine is an umbrella term inclusive of trans women and non-binary trans people who were assigned male at birth.
Most often, surgeries involved in gender affirmation surgery are broken down into those that occur above the belt (top surgery) and those below the belt (bottom surgery). Not everyone undergoes all of these surgeries, but procedures that may be considered for transfeminine individuals are listed below.
Top surgery includes:
- Breast augmentation
- Facial feminization
- Nose surgery: Rhinoplasty may be done to narrow the nose and refine the tip.
- Eyebrows: A brow lift may be done to feminize the curvature and position of the eyebrows.
- Jaw surgery: The jaw bone may be shaved down.
- Chin reduction: Chin reduction may be performed to soften the chin's angles.
- Cheekbones: Cheekbones may be enhanced, often via collagen injections as well as other plastic surgery techniques.
- Lips: A lip lift may be done.
- Alteration to hairline
- Male pattern hair removal
- Reduction of Adam’s apple
- Voice change surgery
Bottom surgery includes:
- Removal of the penis (penectomy) and scrotum (orchiectomy)
- Creation of a vagina and labia
Transmasculine Surgeries
Transmasculine is an umbrella term inclusive of trans men and non-binary trans people who were assigned female at birth.
Surgery for this group involves top surgery and bottom surgery as well.
Top surgery includes :
- Subcutaneous mastectomy/breast reduction surgery.
- Removal of the uterus and ovaries
- Creation of a penis and scrotum either through metoidioplasty and/or phalloplasty
Complications and Side Effects
Surgery is not without potential risks and complications. Estrogen therapy has been associated with an elevated risk of blood clots ( deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary emboli ) for transfeminine people. There is also the potential of increased risk of breast cancer (even without hormones, breast cancer may develop).
Testosterone use in transmasculine people has been associated with an increase in blood pressure, insulin resistance, and lipid abnormalities, though it's not certain exactly what role these changes play in the development of heart disease.
With surgery, there are surgical risks such as bleeding and infection, as well as side effects of anesthesia . Those who are considering these treatments should have a careful discussion with their doctor about potential risks related to hormone therapy as well as the surgeries.
Cost of Gender Confirmation Surgery
Surgery can be prohibitively expensive for many transgender individuals. Costs including counseling, hormones, electrolysis, and operations can amount to well over $100,000. Transfeminine procedures tend to be more expensive than transmasculine ones. Health insurance sometimes covers a portion of the expenses.
Quality of Life After Surgery
Quality of life appears to improve after gender-affirming surgery for all trans people who medically transition. One 2017 study found that surgical satisfaction ranged from 94% to 100%.
Since there are many steps and sometimes uncomfortable surgeries involved, this number supports the benefits of surgery for those who feel it is their best choice.
A Word From Verywell
Gender affirmation surgery is a lengthy process that begins with counseling and a mental health evaluation to determine if a person can be diagnosed with gender dysphoria.
After this is complete, hormonal treatment is begun with testosterone for transmasculine individuals and estrogen for transfeminine people. Some of the physical and behavioral changes associated with hormonal treatment are listed above.
After hormone therapy has been continued for at least one year, a number of surgical procedures may be considered. These are broken down into "top" procedures and "bottom" procedures.
Surgery is costly, but precise estimates are difficult due to many variables. Finding a surgeon who focuses solely on gender confirmation surgery and has performed many of these procedures is a plus. Speaking to a surgeon's past patients can be a helpful way to gain insight on the physician's practices as well.
For those who follow through with these preparation steps, hormone treatment, and surgeries, studies show quality of life appears to improve. Many people who undergo these procedures express satisfaction with their results.
Bizic MR, Jeftovic M, Pusica S, et al. Gender dysphoria: Bioethical aspects of medical treatment . Biomed Res Int . 2018;2018:9652305. doi:10.1155/2018/9652305
American Psychiatric Association. What is gender dysphoria? . 2016.
The World Professional Association for Transgender Health. Standards of care for the health of transsexual, transgender, and gender-nonconforming people . 2012.
Tomlins L. Prescribing for transgender patients . Aust Prescr . 2019;42(1): 10–13. doi:10.18773/austprescr.2019.003
T'sjoen G, Arcelus J, Gooren L, Klink DT, Tangpricha V. Endocrinology of transgender medicine . Endocr Rev . 2019;40(1):97-117. doi:10.1210/er.2018-00011
Unger CA. Hormone therapy for transgender patients . Transl Androl Urol . 2016;5(6):877-884. doi:10.21037/tau.2016.09.04
Seal LJ. A review of the physical and metabolic effects of cross-sex hormonal therapy in the treatment of gender dysphoria . Ann Clin Biochem . 2016;53(Pt 1):10-20. doi:10.1177/0004563215587763
Schechter LS. Gender confirmation surgery: An update for the primary care provider . Transgend Health . 2016;1(1):32-40. doi:10.1089/trgh.2015.0006
Altman K. Facial feminization surgery: current state of the art . Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg . 2012;41(8):885-94. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2012.04.024
Therattil PJ, Hazim NY, Cohen WA, Keith JD. Esthetic reduction of the thyroid cartilage: A systematic review of chondrolaryngoplasty . JPRAS Open. 2019;22:27-32. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2019.07.002
Top H, Balta S. Transsexual mastectomy: Selection of appropriate technique according to breast characteristics . Balkan Med J . 2017;34(2):147-155. doi:10.4274/balkanmedj.2016.0093
Chan W, Drummond A, Kelly M. Deep vein thrombosis in a transgender woman . CMAJ . 2017;189(13):E502-E504. doi:10.1503/cmaj.160408
Streed CG, Harfouch O, Marvel F, Blumenthal RS, Martin SS, Mukherjee M. Cardiovascular disease among transgender adults receiving hormone therapy: A narrative review . Ann Intern Med . 2017;167(4):256-267. doi:10.7326/M17-0577
Hashemi L, Weinreb J, Weimer AK, Weiss RL. Transgender care in the primary care setting: A review of guidelines and literature . Fed Pract . 2018;35(7):30-37.
Van de grift TC, Elaut E, Cerwenka SC, Cohen-kettenis PT, Kreukels BPC. Surgical satisfaction, quality of life, and their association after gender-affirming aurgery: A follow-up atudy . J Sex Marital Ther . 2018;44(2):138-148. doi:10.1080/0092623X.2017.1326190
American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Gender confirmation surgeries .
American Psychological Association. Transgender people, gender identity, and gender expression .
Colebunders B, Brondeel S, D'Arpa S, Hoebeke P, Monstrey S. An update on the surgical treatment for transgender patients . Sex Med Rev . 2017 Jan;5(1):103-109. doi:10.1016/j.sxmr.2016.08.001
Your browser is out-of-date!
Internet Explorer 11 has been retired by Microsoft as of June 15, 2022. To get the best experience on this website, we recommend using a modern browser, such as Safari, Chrome or Edge.
What Is Gender Confirmation Surgery?
Learn about transgender surgery: male-to-female, female-to-male.

Transgender individuals feel that the sex they were assigned at birth, such as male or female, does not match the gender with which they identify. For example, a baby assigned “male” at birth may grow up with a sense of feeling they are female.
As a result of feeling that they were born in the wrong gender, some transgender individuals experience psychological distress known as “ gender dysphoria ” and take various actions to better align their gender identification with their external appearance. For some individuals, the transition process from one gender to another may include medical treatments, such as hormone therapy and gender confirmation surgery.
What is hormone therapy?
Usually the first step in the gender transition process, hormone therapy is intended to suppress the assigned sex characteristics, promote the desired characteristics, or both. For example, men who identify as women may take anti-androgens to block production of the male hormone testosterone, as well as estrogen to appear more feminine. Similarly, women who identify as men may take testosterone to develop more masculine features, such as facial hair.
What is gender confirmation surgery?
If hormone therapy does not have the desired effectiveness, gender confirmation surgery may be an option. Also called gender reassignment surgery, the goal of this procedure is to create the outward physical appearance of the gender with which the person identifies. “Top surgery” refers to surgery above the waist, while “bottom surgery” refers to surgery below the waist.
Transgender surgery is major surgery and generally not considered reversible, so many healthcare providers require transgender individuals to complete several steps before they will proceed with surgery. These may include requiring a formal diagnosis of gender dysphoria and having counseling to determine their psychological readiness for surgery.
“Gender confirmation surgery involves both physical and psychological aspects,” says Manish Champaneria, MD , a plastic surgeon at Scripps Clinic. “Scripps follows the recommendations of the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) regarding preparation for surgery, including having a referral from a mental health provider. Patients undergoing surgery are urged to live as the gender they identify as for at least 12 months before having the procedure.”
Gender confirmation surgery options
Scripps offers gender confirmation surgery procedures for both male-to-female (MTF) or transwomen patients, and female-to-male (FTM) or transmen patients.
Top surgery
Performed on the chest, top surgery is intended to create a more gender-confirming physique. Top surgery procedures include mastectomies for transmen and breast augmentation for transwomen. In most cases, top surgeries are completed in a single procedure.
MTF top surgery
MTF top surgery to augment the breasts may involve fat transfer or breast implants. In a fat transfer procedure, the surgeon removes fat from other parts of the body and injects it into the breasts. Fat transfer may be recommended for patients who wish to increase breast size without breast implants.
Patients who seek larger breasts may choose to have breast implants, which are surgically placed under the chest muscles to enhance breast size and shape. The surgeon and patient together determine the most appropriate size and type of implants.
FTM top surgery
In FTM top surgery, the surgeon removes breast tissue and manipulates the remaining tissue to create a more masculine appearance.
Facial feminization surgery
During MTF facial feminization surgery, the surgeon restructures masculine facial features to achieve a more feminine look. This involves reshaping bones and soft tissues and may be performed as a single procedure or in several stages.
Body contouring
Using various procedures, body contouring reshapes the body to create a more masculine or feminine physique. Specific procedures depend on the patient’s original body shape and desired outcomes. For example, fat transfer may be used to reduce curves in some areas and create them in others.
“We understand that gender confirmation surgery is a life-changing procedure that requires multidisciplinary medical expertise and experience, and we work very closely with our transgender patients every step of the way,” says Dr. Champaneria. “We urge anyone considering this surgery to start by talking with a trusted and physician who is experienced in transgender procedures.”
Related tags:
- Health and Wellness
- Women’s Health
- Men’s Health
How Gender Reassignment Surgery Works (Infographic)
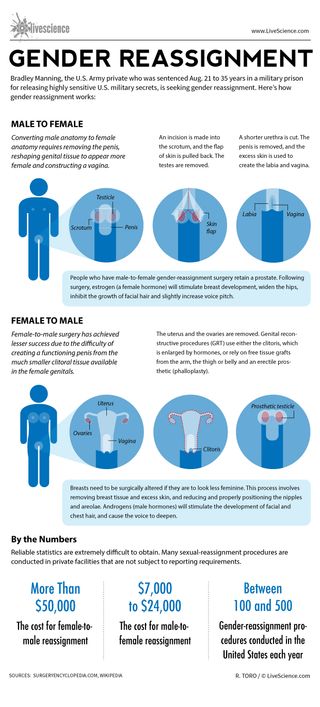
Bradley Manning, the U.S. Army private who was sentenced Aug. 21 to 35 years in a military prison for releasing highly sensitive U.S. military secrets, is seeking gender reassignment. Here’s how gender reassignment works:
Converting male anatomy to female anatomy requires removing the penis, reshaping genital tissue to appear more female and constructing a vagina.
An incision is made into the scrotum, and the flap of skin is pulled back. The testes are removed.
A shorter urethra is cut. The penis is removed, and the excess skin is used to create the labia and vagina.
People who have male-to-female gender-reassignment surgery retain a prostate. Following surgery, estrogen (a female hormone) will stimulate breast development, widen the hips, inhibit the growth of facial hair and slightly increase voice pitch.
Female-to-male surgery has achieved lesser success due to the difficulty of creating a functioning penis from the much smaller clitoral tissue available in the female genitals.
The uterus and the ovaries are removed. Genital reconstructive procedures (GRT) use either the clitoris, which is enlarged by hormones, or rely on free tissue grafts from the arm, the thigh or belly and an erectile prosthetic (phalloplasty).
Breasts need to be surgically altered if they are to look less feminine. This process involves removing breast tissue and excess skin, and reducing and properly positioning the nipples and areolae. Androgens (male hormones) will stimulate the development of facial and chest hair, and cause the voice to deepen.
Reliable statistics are extremely difficult to obtain. Many sexual-reassignment procedures are conducted in private facilities that are not subject to reporting requirements.
The cost for female-to-male reassignment can be more than $50,000. The cost for male-to-female reassignment can be $7,000 to $24,000.
Between 100 to 500 gender-reassignment procedures are conducted in the United States each year.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

Man's years of premature ejaculation had a rare cause
Viagra alternatives? Study of mouse erections hints at new ways to treat erectile dysfunction
2,000-foot-wide 'potentially hazardous' asteroid has just made its closest approach to Earth — and you can see it with a telescope
Most Popular
- 2 'Gambling with your life': Experts weigh in on dangers of the Wim Hof method
- 3 Eclipse from space: See the moon's shadow race across North America at 1,500 mph in epic satellite footage
- 4 Superfast drone fitted with new 'rotating detonation rocket engine' approaches the speed of sound
- 5 Why did Europe's hunter-gatherers disappear?
- 2 32 astonishing ancient burials, from 'vampire' decapitations to riches for the afterlife
- 3 World's fastest camera captures footage at 156 trillion frames per second
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Semin Plast Surg
- v.25(3); 2011 Aug

Aesthetic and Functional Genital and Perineal Surgery: Male
Sex reassignment surgery in the female-to-male transsexual, stan j. monstrey.
1 Department of Plastic Surgery, Ghent University Hospital, Gent, Belgium
Peter Ceulemans
Piet hoebeke.
2 Department of Urology, Ghent University Hospital, Gent, Belgium
In female-to-male transsexuals, the operative procedures are usually performed in different stages: first the subcutaneous mastectomy which is often combined with a hysterectomy-ovarectomy (endoscopically assisted). The next operative procedure consists of the genital transformation and includes a vaginectomy, a reconstruction of the horizontal part of the urethra, a scrotoplasty and a penile reconstruction usually with a radial forearm flap (or an alternative). After about one year, penile (erection) prosthesis and testicular prostheses can be implanted when sensation has returned to the tip of the penis. The authors provide a state-of-the-art overview of the different gender reassignment surgery procedures that can be performed in a female-to-male transsexual.
Transsexual patients have the absolute conviction of being born in the wrong body and this severe identity problem results in a lot of suffering from early childhood on. Although the exact etiology of transsexualism is still not fully understood, it is most probably a result of a combination of various biological and psychological factors. As to the treatment, it is universally agreed that the only real therapeutic option consists of “adjusting the body to the mind” (or gender reassignment) because trying to “adjust the mind to the body” with psychotherapy has been shown to alleviate the severe suffering of these patients. Gender reassignment usually consists of a diagnostic phase (mostly supported by a mental health professional), followed by hormonal therapy (through an endocrinologist), a real-life experience, and at the end the gender reassignment surgery itself.
As to the criteria of readiness and eligibility for these surgical interventions, it is universally recommended to adhere to the Standards of Care (SOC) of the WPATH (World Professional association of Transgender Health) 1 . It is usually advised to stop all hormonal therapy 2 to 3 weeks preoperatively.
The two major sex reassignment surgery (SRS) interventions in the female-to-male transsexual patients that will be addressed here are (1) the subcutaneous mastectomy (SCM), often combined with a hysterectomy/ ovariectomy; and (2) the actual genital transformation consisting of vaginectomy, reconstruction of the fixed part of the urethra (if isolated, metoidioplasty), scrotoplasty and phalloplasty. At a later stage, a testicular prostheses and/or erection prosthesis can be inserted.
SUBCUTANEOUS MASTECTOMY
General principles.
Because hormonal treatment has little influence on breast size, the first (and, arguably, most important) surgery performed in the female-to-male (FTM) transsexual is the creation of a male chest by means of a SCM. This procedure allows the patient to live more easily in the male role 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 and thereby facilitates the “real-life experience,” a prerequisite for genital surgery.
The goal of the SCM in a FTM transsexual patient is to create an aesthetically pleasing male chest, which includes removal of breast tissue and excess skin, reduction and proper positioning of the nipple and areola, obliteration of the inframammary fold, and minimization of chest-wall scars. 4 , 5 Many different techniques have been described to achieve these goals and most authors agree that skin excess , not breast volume, is the factor that should determine the appropriate SCM technique. 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 Recently, the importance of the skin elasticity has also been demonstrated and it is important to realize that in this patient population, poor skin quality can be exacerbated when the patient has engaged in years of “breast binding” (Fig. 1 ). 6

(A,B) Result of long-term “breast binding.”
In the largest series to date, Monstrey et al 6 described an algorithm of five different techniques to perform an aesthetically satisfactory SCM (Fig. 2 ). Preoperative parameters to be evaluated include breast volume, degree of excess skin, nipple-areola complex (NAC) size and position, and skin elasticity.

Algorithm for choosing appropriate subcutaneous mastectomy technique.
Regardless of the technique, it is extremely important to preserve all subcutaneous fat when dissecting the glandular tissue from the flaps. This ensures thick flaps that produce a pleasing contour. Liposuction is only occasionally indicated laterally, or to attain complete symmetry at the end of the procedure. Postoperatively, a circumferential elastic bandage is placed around the chest wall and maintained for a total of 4 to 6 weeks.
The semicircular technique (Fig. 3 ) is essentially the same procedure as that described by Webster in 1946 7 for gynecomastia. It is useful for individuals with smaller breasts and elastic skin. A sufficient amount of glandular tissue should be left in situ beneath the NAC to avoid a depression. The particular advantage of this technique is the small and well-concealed scar which is confined to (the lower half of) the nipple-areola complex. The major drawback is the small window through which to work, making excision of breast tissue and hemostasis more challenging.

Semicircular technique. (A) Incisions and scar; (B) preoperative; (C) postoperative.
In cases of smaller breasts with large prominent nipples, the transareolar technique (Fig. 4 ) is used. This is similar to the procedure described by Pitanguy in 1966 8 and allows for subtotal resection and immediate reduction of the nipple. The resulting scar traverses the areola horizontally and passes around the upper aspect of the nipple.

Transareolar technique. (A,B) Incisions and scar; (C) preoperative; (D) postoperative.
The concentric circular technique (Fig. 5 ) is similar to that described by Davidson in 1979. 9 It is used for breasts with a medium-sized skin envelope (B cup), or in the case of smaller breasts with poor skin elasticity. The resulting scar will be confined to the circumference of the areola. The concentric incision can be drawn as a circle or ellipse, enabling deepithelialization of a calculated amount of skin in the vertical or horizontal direction. 4 , 5 Access is gained via an incision in the inferior aspect of the outer circle leaving a wide pedicle for the NAC. A purse-string suture is placed and set to the desired areolar diameter (usually 25–30 mm). The advantage of this technique is that it allows for reduction and/or repositioning of the areola, where required, and for the removal of excess skin.

Concentric circular technique. (A) incisions; (B) preoperative; (C) postoperative.
The extended concentric circular technique (Fig. 6 ) is similar to the concentric circular technique, but includes one or two additional triangular excisions of skin and subcutaneous tissue lateral and/ or medial. This technique is useful for correcting skin excess and wrinkling produced by large differences between the inner and outer circles. The resulting scars will be around the areola, with horizontal extensions onto the breast skin, depending on the degree of excess skin.

Extended concentric circular technique. (A) Incisions and scar; (B) preoperative preoperative; (C) postoperative.
The free nipple graft technique (Fig. 7 ) has been proposed by several authors for patients with large and ptotic breasts. 2 , 3 , 10 , 11 , 12 It consists of harvesting the NAC as a full-thickness skin graft; amputating the breast; and grafting the NAC onto its new location on the chest wall. Our preference is to place the incision horizontally 1 to 2 cm above the inframammary fold, and then to move upwards laterally below the lateral border of the pectoralis major muscle. The placement of the NAC usually corresponds to the 4th or 5th intercostal space. Clinical judgment is most important, however, and we always sit the patient up intraoperatively to check final nipple position. The advantages of the free nipple graft technique are easy chest contouring, excellent exposure and more rapid resection of tissue, as well as nipple reduction, areola resizing, and repositioning. The disadvantages are the long residual scars, NAC pigmentary and sensory changes, and the possibility of incomplete graft take.

Free nipple graft technique. (A) Incisions and scar; (B) preoperative; (C) postoperative.

Complications
Postoperative complications include hematoma (most frequent, despite drains and compression bandages), (partial) nipple necrosis, and abscess formation. This underscores the importance of achieving good hemostasis intraoperatively. Smaller hematomas and seromas can be evacuated through puncture, but for larger collections surgical evacuation is required.
Another not infrequent complication consists of skin slough of the NAC, which can be left to heal by conservative means. The exceptional cases of partial or total nipple necrosis may require a secondary nipple reconstruction. Even in the patients without complications, ~25% required an additional procedure to improve the aesthetic results. The likelihood of an additional aesthetic correction should be discussed with the patient in advance. 13 Tattoo of the areola may be performed for depigmentation.
The recommendations of the authors are summarized in their algorithm (Fig. 2 ), which clearly demonstrates that a larger skin envelope and a less elastic skin will require progressively a longer-incision technique. The FTM transsexual patients are rightfully becoming a patient population that is better informed and more demanding as to the aesthetic outcomes.
Finally, it is important to note that there have been reports of breast cancer after bilateral SCM in this population 14 , 15 , 16 because in most patients the preserved NAC and the always incomplete glandular resection leave behind tissue at risk of malignant transformation.
PHALLOPLASTY
In performing a phalloplasty for a FTM transsexual, the surgeon should reconstruct an aesthetically appealing neophallus, with erogenous and tactile sensation, which enables the patient to void while standing and have sexual intercourse like a natural male, in a one-stage procedure. 17 , 18 The reconstructive procedure should also provide a normal scrotum, be predictably reproducible without functional loss in the donor area, and leave the patient with minimal scarring or disfigurement.
Despite the multitude of flaps that have been employed and described (often as Case Reports), the radial forearm is universally considered the gold standard in penile reconstruction. 17 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28
In the largest series to date (almost 300 patients), Monstrey et al 29 recently described the technical aspects of radial forearm phalloplasty and the extent to which this technique, in their hands approximates the criteria for ideal penile reconstruction.
For the genitoperineal transformation (vaginectomy, urethral reconstruction, scrotoplasty, phalloplasty), two surgical teams operate at the same time with the patient first placed in a gynecological (lithotomy) position. In the perineal area, a urologist may perform a vaginectomy, and lengthen the urethra with mucosa between the minor labiae. The vaginectomy is a mucosal colpectomy in which the mucosal lining of the vaginal cavity is removed. After excision, a pelvic floor reconstruction is always performed to prevent possible diseases such as cystocele and rectocele. This reconstruction of the fixed part of the urethra is combined with a scrotal reconstruction by means of two transposition flaps of the greater labia resulting in a very natural looking bifid scrotum.
Simultaneously, the plastic surgeon dissects the free vascularized flap of the forearm. The creation of a phallus with a tube-in-a-tube technique is performed with the flap still attached to the forearm by its vascular pedicle (Fig. 8A ). This is commonly performed on the ulnar aspect of the skin island. A small skin flap and a skin graft are used to create a corona and simulate the glans of the penis (Fig. 8B ).

(A–D) Phallic reconstruction with the radial forearm flap: creation of a tube (urethra) within a tube (penis).
Once the urethra is lengthened and the acceptor (recipient) vessels are dissected in the groin area, the patient is put into a supine position. The free flap can be transferred to the pubic area after the urethral anastomosis: the radial artery is microsurgically connected to the common femoral artery in an end-to-side fashion and the venous anastomosis is performed between the cephalic vein and the greater saphenous vein (Fig. 8C ). One forearm nerve is connected to the ilioinguinal nerve for protective sensation and the other nerve of the arm is anastomosed to one of the dorsal clitoral nerves for erogenous sensation. The clitoris is usually denuded and buried underneath the penis, thus keeping the possibility to be stimulated during sexual intercourse with the neophallus.
In the first 50 patients of this series, the defect on the forearm was covered with full-thickness skin grafts taken from the groin area. In subsequent patients, the defect was covered with split-thickness skin grafts harvested from the medial and anterior thigh (Fig. 8D ).
All patients received a suprapubic urinary diversion postoperatively.
The patients remain in bed during a one-week postoperative period, after which the transurethral catheter is removed. At that time, the suprapubic catheter was clamped, and voiding was begun. Effective voiding might not be observed for several days. Before removal of the suprapubic catheter, a cystography with voiding urethrography was performed.
The average hospital stay for the phalloplasty procedure was 2½ weeks.
Tattooing of the glans should be performed after a 2- to 3-month period, before sensation returns to the penis.
Implantation of the testicular prostheses should be performed after 6 months, but it is typically done in combination with the implantation of a penile erection prosthesis. Before these procedures are undertaken, sensation must be returned to the tip of the penis. This usually does not occur for at least a year.
The Ideal Goals of Penile Reconstruction in FTM Surgery
What can be achieved with this radial forearm flap technique as to the ideal requisites for penile reconstruction?
A ONE-STAGE PROCEDURE
In 1993, Hage 20 stated that a complete penile reconstruction with erection prosthesis never can be performed in one single operation. Monstrey et al, 29 early in their series and to reduce the number of surgeries, performed a (sort of) all-in-one procedure that included a SCM and a complete genitoperineal transformation. However, later in their series they performed the SCM first most often in combination with a total hysterectomy and ovariectomy.
The reason for this change in protocol was that lengthy operations (>8 hours) resulted in considerable blood loss and increased operative risk. 30 Moreover, an aesthetic SCM is not to be considered as an easy operation and should not be performed “quickly” before the major phalloplasty operation.
AN AESTHETIC PHALLUS
Phallic construction has become predictable enough to refine its aesthetic goals, which includes the use of a technique that can be replicated with minimal complications. In this respect, the radial forearm flap has several advantages: the flap is thin and pliable allowing the construction of a normal sized, tube-within-a-tube penis; the flap is easy to dissect and is predictably well vascularized making it safe to perform an (aesthetic) glansplasty at the distal end of the flap. The final cosmetic outcome of a radial forearm phalloplasty is a subjective determination, but the ability of most patients to shower with other men or to go to the sauna is the usual cosmetic barometer (Fig. 9A-C ).

(A–C) Late postoperative results of radial forearm phalloplasties.
The potential aesthetic drawbacks of the radial forearm flap are the need for a rigidity prosthesis and possibly some volume loss over time.
TACTILE AND EROGENOUS SENSATION
Of the various flaps used for penile reconstruction, the radial forearm flap has the greatest sensitivity. 1 Selvaggi and Monstrey et al. always connect one antebrachial nerve to the ilioinguinal nerve for protective sensation and the other forearm nerve with one dorsal clitoral nerve. The denuded clitoris was always placed directly below the phallic shaft. Later manipulation of the neophallus allows for stimulation of the still-innervated clitoris. After one year, all patients had regained tactile sensitivity in their penis, which is an absolute requirement for safe insertion of an erection prosthesis. 31
In a long-term follow-up study on postoperative sexual and physical health, more than 80% of the patients reported improvement in sexual satisfaction and greater ease in reaching orgasm (100% in practicing postoperative FTM transsexuals). 32
VOIDING WHILE STANDING
For biological males as well as for FTM transsexuals undergoing a phalloplasty, the ability to void while standing is a high priority. 33 Unfortunately, the reported incidences of urological complications, such as urethrocutaneous fistulas, stenoses, strictures, and hairy urethras are extremely high in all series of phalloplasties, as high as 80%. 34 For this reason, certain (well-intentioned) surgeons have even stopped reconstructing a complete neo-urethra. 35 , 36
In their series of radial forearm phalloplasties, Hoebeke and Monstrey still reported a urological complication rate of 41% (119/287), but the majority of these early fistulas closed spontaneously and ultimately all patients were able to void through the newly reconstructed penis. 37 Because it is unknown how the new urethra—a 16-cm skin tube—will affect bladder function in the long term, lifelong urologic follow-up was strongly recommended for all these patients.
MINIMAL MORBIDITY
Complications following phalloplasty include the general complications attendant to any surgical intervention such as minor wound healing problems in the groin area or a few patients with a (minor) pulmonary embolism despite adequate prevention (interrupting hormonal therapy, fractioned heparin subcutaneously, elastic stockings). A vaginectomy is usually considered a particularly difficult operation with a high risk of postoperative bleeding, but in their series no major bleedings were seen. 30 Two early patients displayed symptoms of nerve compression in the lower leg, but after reducing the length of the gynecological positioning to under 2 hours, this complication never occurred again. Apart from the urinary fistulas and/or stenoses, most complications of the radial forearm phalloplasty are related to the free tissue transfer. The total flap failure in their series was very low (<1%, 2/287) despite a somewhat higher anastomotic revision rate (12% or 34/287). About 7 (3%) of the patients demonstrated some degree of skin slough or partial flap necrosis. This was more often the case in smokers, in those who insisted on a large-sized penis requiring a larger flap, and also in patients having undergone anastomotic revision.
With smoking being a significant risk factor, under our current policy, we no longer operate on patients who fail to quit smoking one year prior to their surgery.
NO FUNCTIONAL LOSS AND MINIMAL SCARRING IN THE DONOR AREA
The major drawback of the radial forearm flap has always been the unattractive donor site scar on the forearm (Fig. 10 ). Selvaggi et al conducted a long-term follow-up study 38 of 125 radial forearm phalloplasties to assess the degree of functional loss and aesthetic impairment after harvesting such a large forearm flap. An increased donor site morbidity was expected, but the early and late complications did not differ from the rates reported in the literature for the smaller flaps as used in head and neck reconstruction. 38 No major or long-term problems (such as functional limitation, nerve injury, chronic pain/edema, or cold intolerance) were identified. Finally, with regard to the aesthetic outcome of the donor site, they found that the patients were very accepting of the donor site scar, viewing it as a worthwhile trade-off for the creation of a phallus (Fig. 10 ). 38 Suprafascial flap dissection, full thickness skin grafts, and the use of dermal substitutes may contribute to a better forearm scar.

(A,B) Aspect of the donor site after a phalloplasty with a radial forearm flap.
NORMAL SCROTUM
For the FTM patient, the goal of creating natural-appearing genitals also applies to the scrotum. As the labia majora are the embryological counterpart of the scrotum, many previous scrotoplasty techniques left the hair-bearing labia majora in situ, with midline closure and prosthetic implant filling, or brought the scrotum in front of the legs using a V-Y plasty. These techniques were aesthetically unappealing and reminiscent of the female genitalia. Selvaggi in 2009 reported on a novel scrotoplasty technique, which combines a V-Y plasty with a 90-degree turning of the labial flaps resulting in an anterior transposition of labial skin (Fig. 11 ). The excellent aesthetic outcome of this male-looking (anteriorly located) scrotum, the functional advantage of fewer urological complications and the easier implantation of testicular prostheses make this the technique of choice. 39

Reconstruction of a lateral looking scrotum with two transposition flaps: (A) before and (B) after implantation of testicular prostheses.
SEXUAL INTERCOURSE
In a radial forearm phalloplasty, the insertion of erection prosthesis is required to engage in sexual intercourse. In the past, attempts have been made to use bone or cartilage, but no good long-term results are described. The rigid and semirigid prostheses seem to have a high perforation rate and therefore were never used in our patients. Hoebeke, in the largest series to date on erection prostheses after penile reconstruction, only used the hydraulic systems available for impotent men. A recent long-term follow-up study showed an explantation rate of 44% in 130 patients, mainly due to malpositioning, technical failure, or infection. Still, more than 80% of the patients were able to have normal sexual intercourse with penetration. 37 In another study, it was demonstrated that patients with an erection prosthesis were more able to attain their sexual expectations than those without prosthesis (Fig. 12 ). 32

(A,B) Phalloplasty after implantation of an erection prosthesis.
A major concern regarding erectile prostheses is long-term follow-up. These devices were developed for impotent (older) men who have a shorter life expectancy and who are sexually less active than the mostly younger FTM patients.
Alternative Phalloplasty Techniques
Metaidoioplasty.
A metoidioplasty uses the (hypertrophied) clitoris to reconstruct the microphallus in a way comparable to the correction of chordee and lengthening of a urethra in cases of severe hypospadias. Eichner 40 prefers to call this intervention “the clitoris penoid.” In metoidioplasty, the clitoral hood is lifted and the suspensory ligament of the clitoris is detached from the pubic bone, allowing the clitoris to extend out further. An embryonic urethral plate is divided from the underside of the clitoris to permit outward extension and a visible erection. Then the urethra is advanced to the tip of the new penis. The technique is very similar to the reconstruction of the horizontal part of the urethra in a normal phalloplasty procedure. During the same procedure, a scrotal reconstruction, with a transposition flap of the labia majora (as previously described) is performed combined with a vaginectomy.
FTM patients interested in this procedure should be informed preoperatively that voiding while standing cannot be guaranteed, and that sexual intercourse will not be possible (Fig. 13 ).

Results of a metoidioplasty procedure.
The major advantage of metoidioplasty is the complete lack of scarring outside the genital area. Another advantage is that its cost is substantially lower than that of phalloplasty. Complications of this procedure also include urethral obstruction and/or urethral fistula.
It is always possible to perform a regular phalloplasty (e.g., with a radial forearm flap) at a later stage, and with substantially less risk of complications and operation time.
FIBULA FLAP
There have been several reports on penile reconstruction with the fibular flap based on the peroneal artery and the peroneal vein. 27 , 41 , 42 It consists of a piece of fibula that is vascularized by its periosteal blood supply and connected through perforating (septal) vessels to an overlying skin island at the lateral site of the lower leg. The advantage of the fibular flap is that it makes sexual intercourse possible without a penile prosthesis. The disadvantages are a pointed deformity to the distal part of the penis when the extra skin can glide around the end of fibular bone, and that a permanently erected phallus is impractical.
Many authors seem to agree that the fibular osteocutaneous flap is an optimal solution for penile reconstruction in a natal male. 42
NEW SURGICAL DEVELOPMENTS: THE PERFORATOR FLAPS
Perforator flaps are considered the ultimate form of tissue transfer. Donor site morbidity is reduced to an absolute minimum, and the usually large vascular pedicles provide an additional range of motion or an easier vascular anastomosis. At present, the most promising perforator flap for penile reconstruction is the anterolateral thigh (ALT) flap. This flap is a skin flap based on a perforator from the descending branch of the lateral circumflex femoral artery, which is a branch from the femoral artery. It can be used both as a free flap 43 and as a pedicled flap 44 then avoiding the problems related to microsurgical free flap transfer. The problem related to this flap is the (usually) thick layer of subcutaneous fat making it difficult to reconstruct the urethra as a vascularized tube within a tube. This flap might be more indicated for phallic reconstruction in the so-called boys without a penis, like in cases of vesical exstrophy (Fig. 14 ). However, in the future, this flap may become an interesting alternative to the radial forearm flap, particularly as a pedicled flap. If a solution could be found for a well-vascularized urethra, use of the ALT flap could be an attractive alternative to the radial forearm phalloplasty. The donor site is less conspicuous, and secondary corrections at that site are easier to make. Other perforator flaps include the thoracodorsal perforator artery flap (TAP) and the deep inferior epigastric perforator artery flap (DIEP). The latter might be an especially good solution for FTM patients who have been pregnant in the past. Using the perforator flap as a pedicled flap can be very attractive, both financially and technically.

Penile reconstruction with a pedicled anterolateral thigh flap. (A) Preoperative and (B) postoperative results.
The Importance of a Multidisciplinary Approach
Gender reassignment, particularly reassignment surgery, requires close cooperation between the different surgical specialties. In phalloplasty, the collaboration between the plastic surgeon, the urologist, and the gynecologist is essential. 45 The actual penile reconstruction is typically performed by the plastic and reconstructive surgeon, and the contribution of the gynecologist, who performs a hysterectomy and a BSO (preferably through a minimal endoscopic access in combination with SCM), should not be underestimated.
However, in the long term, the urologist's role may be the most important for patients who have undergone penile reconstruction, especially because the complication rate is rather high, particularly with regard to the number of urinary fistulas and urinary stenoses. The urologist also reconstructs the fixed part of the urethra. He or she is likely the best choice for implantation and follow-up of the penile and/or testicular prostheses. They must also address later sequelae, including stone formation. Moreover, the surgical complexity of adding an elongated conduit (skin-tube urethra) to a biological female bladder, and the long-term effects of evacuating urine through this skin tube, demand lifelong urological follow-up.
Therefore, professionals who unite to create a gender reassignment program should be aware of the necessity of a strong alliance between the plastic surgeon, the urologist, mental health professional and the gynecologist. In turn, the surgeons must commit to the extended care of this unique population, which, by definition, will protract well into the future.
- Meyer W J, III, Bockting W O, Cohen-Kettenis P, et al. The Standards of Care for Gender Identity Disorders, 6th Version. J Psychol Human Sex. 2002; 13 :1–30. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lindsay W RN. Creation of a male chest in female transsexuals. Ann Plast Surg. 1979; 3 (1):39–46. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eicher W. Transsexualismus. Vol. 1992. Stuttgart: Fisher Verlag; pp. 120–123. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hage J J, Bloem J J. Chest wall contouring for female-to-male transsexuals: Amsterdam experience. Ann Plast Surg. 1995; 34 (1):59–66. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hage J J, Kesteren P J van. Chest-wall contouring in female-to-male transsexuals: basic considerations and review of the literature. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1995; 96 (2):386–391. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Monstrey S, Selvaggi G, Ceulemans P, et al. Chest-wall contouring surgery in female-to-male transsexuals: a new algorithm. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008; 121 (3):849–859. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Webster J P. Mastectomy for gynecomastia through a semicircular intra-areolar incision. Ann Surg. 1946; 124 :557–575. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pitanguy I. Transareolar incision for gynecomastia. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1966; 38 (5):414–419. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Davidson B A. Concentric circle operation for massive gynecomastia to excise the redundant skin. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1979; 63 (3):350–354. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kluzák R. Sex conversion operation in female transsexualism. Acta Chir Plast. 1968; 10 (3):188–198. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hoopes J E. Surgical construction of the male external genitalia. Clin Plast Surg. 1974; 1 (2):325–334. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kenney J G, Edgerton M T. Reduction mammoplasty in gender dysphoria. Abstract presented at the 11th Symposium of the Harry Benjamin International Gender Dysphoria Association; septerber20–23, 1989; Cleveland, Ohio.
- Beer G M, Budi S, Seifert B, Morgenthaler W, Infanger M, Meyer V E. Configuration and localization of the nipple-areola complex in men. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001; 108 (7):1947–1952. discussion 1953. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Symmers W S. Carcinoma of breast in trans-sexual individuals after surgical and hormonal interference with the primary and secondary sex characteristics. BMJ. 1968; 2 (5597):83–85. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Secreto G, Toniolo P, Berrino F, et al. Increased androgenic activity and breast cancer risk in premenopausal women. Cancer Res. 1984; 44 (12 Pt 1):5902–5905. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Burcombe R J, Makris A, Pittam M, Finer N. Breast cancer after bilateral subcutaneous mastectomy in a female-to-male trans-sexual. Breast. 2003; 12 (4):290–293. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gilbert D A, Horton C E, Terzis J K, Devine C J, Jr, Winslow B H, Devine P C. New concepts in phallic reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 1987; 18 (2):128–136. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hage J J, Bouman F G, de Graaf F H, Bloem J J. Construction of the neophallus in female-to-lake transsexuals: the Amsterdam experience. J Urol. 1993; 6 :1463–1468. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chang T S, Hwang W Y. Forearm flap in one-stage reconstruction of the penis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984; 74 (2):251–258. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hage J J, De Graaf F H. Addressing the ideal requirements by free flap phalloplasty: some reflections on refinements of technique. Microsurgery. 1993; 14 (9):592–598. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fang R H, Kao Y S, Ma S, Lin J T. Phalloplasty in female-to-male transsexuals using free radial osteocutaneous flap: a series of 22 cases. Br J Plast Surg. 1999; 52 (3):217–222. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Biemer E. Penile construction by the radial arm flap. Clin Plast Surg. 1988; 15 (3):425–430. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Koshima I, Tai T, Yamasaki M. One-stage reconstruction of the penis using an innervated radial forearm osteocutaneous flap. J Reconstr Microsurg. 1986; 3 (1):19–26. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Meyer R, Daverio P J. One-stage phalloplasty without sensory deprivation in female transsexuals. World J Urol. 1987; 5 :9–13. [ Google Scholar ]
- Upton J, Mutimer K L, Loughlin K, Ritchie J. Penile reconstruction using the lateral arm flap. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1987; 32 (2):97–101. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harashina T, Inoue T, Tanaka I, Imai K, Hatoko M. Reconstruction of penis with free deltoid flap. Br J Plast Surg. 1990; 43 (2):217–222. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sadove R C, Sengezer M, McRoberts J W, Wells M D. One-stage total penile reconstruction with a free sensate osteocutaneous fibula flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993; 92 (7):1314–1323. discussion 1324–1325. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Santanelli F, Scuderi N. Neophalloplasty in female-to-male transsexuals with the island tensor fasciae latae flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000; 105 (6):1990–1996. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Monstrey S, Hoebeke P, Selvaggi G, et al. Penile reconstruction: is the radial forearm flap really the standard technique? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009; 124 (2):510–518. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weyers S, Selvaggi G, Monstrey S, et al. Two-stage versus one-stage sex reassignment surgery in female-to-male transsexual individuals. Gynecol Surg. 2006; 3 :190–194. [ Google Scholar ]
- Selvaggi G, Monstrey S, Ceulemans P, T'Sjoen G, De Cuypere G, Hoebeke P. Genital sensitivity after sex reassignment surgery in transsexual patients. Ann Plast Surg. 2007; 58 (4):427–433. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- De Cuypere G, T'Sjoen G, Beerten R, et al. Sexual and physical health after sex reassignment surgery. Arch Sex Behav. 2005; 34 (6):679–690. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hage J J, Bout C A, Bloem J J, Megens J A. Phalloplasty in female-to-male transsexuals: what do our patients ask for? Ann Plast Surg. 1993; 30 (4):323–326. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vriens J P, Acosta R, Soutar D S, Webster M H. Recovery of sensation in the radial forearm free flap in oral reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996; 98 (4):649–656. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Felici N, Felici A. A new phalloplasty technique: the free anterolateral thigh flap phalloplasty. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2006; 59 (2):153–157. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Matti B A, Matthews R N, Davies D M. Phalloplasty using the free radial forearm flap. Br J Plast Surg. 1988; 41 (2):160–164. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hoebeke P, Selvaggi G, Ceulemans P, et al. Impact of sex reassignment surgery on lower urinary tract function. Eur Urol. 2005; 47 (3):398–402. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Selvaggi G, Monstrey S, Hoebeke P, et al. Donor-site morbidity of the radial forearm free flap after 125 phalloplasties in gender identity disorder. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006; 118 (5):1171–1177. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hoebeke P, de Cuypere G, Ceulemans P, Monstrey S. Obtaining rigidity in total phalloplasty: experience with 35 patients. J Urol. 2003; 169 (1):221–223. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eicher W. Surgical Treatment of Female-to-Male Transsexuals. In: Echer W, editor. Plastic Surgery in the Sexually Handicapped. Vol. 1989. Berlin: Springer; pp. 106–112. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hage J J, Winters H A, Lieshout J Van. Fibula free flap phalloplasty: modifications and recommendations. Microsurgery. 1996; 17 (7):358–365. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sengezer M, Oztürk S, Deveci M, Odabaşi Z. Long-term follow-up of total penile reconstruction with sensate osteocutaneous free fibula flap in 18 biological male patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004; 114 (2):439–450. discussion 451–452. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Felici N. Phalloplasty with Free Anterolateral Thigh Flap. Paper presented the XIX Biennial Symposium of the Harry Benjamin International Gender Dysphoria Association (HBIGDA); April 6–9, 2005; Bologna, Italy.
- Ceulemans P. The Pedicled Anterolateral Thigh Flap (ALT) Perforator Flap: A New Technique for Phallic Reconstruction. Paper presented at the XIV Biennial Symposium of the Harry Benjamin International Gender Dysphoria Association (HBIGDA); April 6–9, 2005; Bologna, Italy.
- Monstrey S, Hoebeke P, Dhont M, et al. Surgical therapy in transsexual patients: a multi-disciplinary approach. Acta Chir Belg. 2001; 101 (5):200–209. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
What is gender reassignment surgery?
Gender reassignment surgery is any surgical procedure involved in facilitating a male-to-female (MtF) or female-to-male (FtM) transition . Gender reassignment surgery is complex and can involve a number of separate procedures, carried out over several operations.

When is gender reassignment surgery required?
Surgery is generally the last step of a person’s transition. In the UK, to receive gender reassignment surgery through the NHS you need to first spend twelve months living in a social role appropriate to your gender identity. Gender reassignment surgery also comes after any hormonal treatment you have received, whether oestrogen (for MtF transitions) or testosterone (for FtM transitions).
What does it involve?
The exact procedures involved depend on whether you are undergoing a MtF or FtM transiton:
Male-to-female transition
The procedures involved in a male-to-female transition include:
- removal of the penis and testes
- breast implants
- construction of a vagina, vulva and clitoris – usually from the skin from the penis
- surgery on the face to make it more feminine
- in some cases, the removal of the prostate gland
Female-to-male transition
The procedures involved in a female-to-male transition include:
- removal of the breasts
- removal of the womb, ovaries and fallopian tubes
- construction of a penis and testes – using vaginal tissue and skin from the forearm
- a penile implant
In both forms of surgery, the aim is to retain sexual sensation and function.
The extent of follow-up care depends on how much surgery you elect to have and where you have the procedure. It is very likely you will receive psychotherapy to help you adjust to your new body and lifestyle.
- Gender reassignment surgery
Experts available in:
Treatments / Tests / Illnesses
Popular specialties
New medical centres
New dental clinics

Tania Cubison - Plastic surgery
Created on: 02-10-2017
Updated on: 05-04-2023
Edited by: Conor Dunworth

An expert explains: what to expect from top surgery
By Tania Cubison 2024-04-15
Leading consultant plastic surgeon Miss Tania Cubison details what patients can expect from gender reassignment top surgery, including the associated risks and recovery period. See more

What should I consider before feminisation surgery?
By Mr Christopher Inglefield 2024-04-11
In his latest online article, leading London-based plastic surgeon Mr Christopher Inglefield offers some of his expert insight into feminisation surgery. He explains what potential patients need to consider, how to prioritise procedures to make the biggest impact, and how the success of these procedures is assessed. See more
Experts in Gender reassignment surgery

Miss Tina Rashid Urology

Mr Ardeshir Vahidi Plastic surgery
- Lip augmentation
- FTM top surgery
- Face Bioregeneration
- Dermal fillers
- Hyaluronic acid

Mr Alexander Armstrong Plastic surgery
- Skin cancer
- Tummy tuck (abdominoplasty)
- Breast augmentation
- Mummy makeover
- Gynaecomastia
Tania Cubison
Plastic surgery.
- Most viewed diseases, medical tests, and treatments
- Cleft palate
- Pre-eclampsia
- Women's health
- Robotic surgery
- FUE hair transplant
- Peritoneal carcinomatosis
- Medicolegal
- Endometriosis
- Cholecystitis
- Non-surgical facelift
Cookie settings
You can enable or disable according to the purposes:
Facial Feminization Surgery

Breast Augmentation
Body feminization surgery.

Gender Confirmation Surgery
What do our patients say , dr.transman, let’s start your journey from here.
Our experience, our technologically-advanced facilities and our compassionate staff are the best in the business for transgender confirmation procedures, holistic therapy and the overall patient experience.

- Patient Care & Health Information
- Tests & Procedures
- Masculinizing surgery
Masculinizing surgery, also called gender-affirming surgery or gender-confirmation surgery, involves procedures that help better align the body with a person's gender identity. Masculinizing surgery includes several options, such as top surgery to create a more male-contoured chest and bottom surgery that changes the genitals.
Not everybody chooses masculinizing surgery. These surgeries can be expensive, carry risks and complications, and involve follow-up medical care and procedures. Certain surgeries change fertility and sexual sensations. They also may change how you feel about your body.
Your health care team can talk with you about your options and help you weigh the risks and benefits.
Products & Services
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th Edition
- Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter — Digital Edition
Why it's done
Many people seek masculinizing surgery as a step in the process of treating discomfort or distress because their gender identity differs from their sex assigned at birth. The medical term for this is gender dysphoria.
For some people, having masculinizing surgery feels like a natural step. It's important to their sense of self. Others choose not to have surgery. All people relate to their bodies differently and should make individual choices that best suit their needs.
Options for masculinizing surgery include:
- Surgical removal of breast tissue. This also is referred to as top surgery or masculinizing chest surgery.
- Surgical placement of pectoral implants to create a male-contoured chest.
- Genital surgery to remove the uterus and cervix — a total hysterectomy — or to remove the fallopian tubes and ovaries — a procedure called salpingo-oophorectomy.
- Surgery to remove all or part of the vagina, called a vaginectomy, create a scrotum, called scrotoplasty, place testicular prostheses, increase the length of the clitoris, called metoidioplasty, or create a penis, called phalloplasty.
- Other procedures such liposuction, a technique to remove fat from specific areas of the body, and fat grafting.
Your health care provider might advise against these surgeries if you have:
- Significant medical conditions that haven't been addressed.
- Behavioral health conditions that haven't been addressed.
- Any condition that limits your ability to give your informed consent.
There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the information highlighted below and resubmit the form.
Stay Informed with LGBTQ+ health content.
Receive trusted health information and answers to your questions about sexual orientation, gender identity, transition, self-expression, and LGBTQ+ health topics. Click here for an email preview.
Error Email field is required
Error Include a valid email address
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Thank you for subscribing to our LGBTQ+ newsletter.
You will receive the first newsletter in your inbox shortly. This will include exclusive health content about the LGBTQ+ community from Mayo Clinic.
If you don't receive our email within 5 minutes, check your SPAM folder, then contact us at [email protected] .
Sorry something went wrong with your subscription
Please, try again in a couple of minutes
Like any major surgery, many types of masculinizing surgery pose a risk of bleeding, infection and a reaction to anesthesia. Other complications might include:
- Delayed wound healing.
- Fluid buildup beneath the skin, called seroma
- Bruising, also called hematoma
- Changes in skin sensation such as pain that doesn't go away, tingling, reduced sensation or numbness
- Damaged or dead body tissue — a condition known as tissue necrosis — such as in the nipple or in the surgically created penis
- A blood clot in a deep vein, called deep vein thrombosis, or a blood clot in the lung, a condition called pulmonary embolism
- Development of an irregular connection between two body parts, called a fistula, such as in the urinary tract
- Urinary problems, such as incontinence
- Pelvic floor problems
- Permanent scarring
- Loss of sexual pleasure or function
- Worsening of a behavioral health concern
Certain types of masculinizing surgery may limit or end fertility. If you want to have biological children, and you're having surgery that involves your reproductive organs, talk to your health care provider about your options. You may choose to freeze eggs with a procedure called mature oocyte cryopreservation, or freeze embryos using embryo cryopreservation. Another option involves having ovarian tissue surgically removed, frozen, and later thawed and reimplanted. That procedure is called ovarian tissue cryopreservation.
Egg freezing involves multiple steps, including ovulation induction, egg retrieval and freezing. If you want to freeze embryos, an additional step of having the eggs fertilized before they are frozen also is required.
How you prepare
Before surgery, you meet with your surgeon. Work with a surgeon who is board certified and experienced in the procedures you want. Your surgeon talks with you about your options and the potential results. The surgeon also may provide information on details such as the type of anesthesia that will be used during surgery and the kind of follow-up care that you may need.
Follow your health care team's directions on preparing for your procedures. This may include guidelines on eating and drinking. You may need to make changes in the medicine you take and stop using nicotine, including vaping, smoking and chewing tobacco.
Because masculinizing surgery might cause physical changes that cannot be reversed, you must give informed consent after thoroughly discussing:
- Risks and benefits
- Alternatives to surgery
- Expectations and goals
- Social and legal implications
- Potential complications
- Impact on sexual function and fertility
Evaluation for surgery
Before surgery, a health care provider evaluates your health to address any medical conditions that might prevent you from having surgery or that could affect the procedure. This evaluation may be done by a provider with expertise in transgender medicine. The evaluation might include:
- A review of your personal and family medical history
- A physical exam
- A review of your vaccinations
- Screening tests for some conditions and diseases
- Identification and management, if needed, of tobacco use, drug use, alcohol use disorder, HIV or other sexually transmitted infections
- Discussion about birth control, fertility and sexual function
You also may have a behavioral health evaluation by a health care provider with expertise in transgender health. That evaluation might assess:
- Gender identity
- Gender dysphoria
- Mental health concerns
- Sexual health concerns
- The impact of gender identity at work, at school, at home and in social settings
- The role of social transitioning and hormone therapy before surgery
- Risky behaviors, such as substance use or use of unapproved hormone therapy or supplements
- Support from family, friends and caregivers
- Your goals and expectations of treatment
- Care planning and follow-up after surgery
Other considerations
Health insurance coverage for masculinizing surgery varies widely. Before you have surgery, check with your insurance provider to see what will be covered.
Before surgery, you might consider talking to others who have had masculinizing surgery. If you don't know someone, ask your health care provider about support groups in your area or online resources you can trust. People who have gone through the process may be able to help you set your expectations and offer a point of comparison for your own goals of the surgery.
What you can expect
Chest surgery.
Top surgery, also called masculinizing chest surgery, involves the removal of breast tissue — a procedure known as subcutaneous mastectomy. There are several approaches for this surgery, including:
- Double incision mastectomy. This procedure may be recommended for people with larger breasts. During surgery, the surgeon makes cuts under and on top of each breast. Breast tissue and some chest skin is removed. The shape and location of the nipples may need to be changed. To do this, the surgeon removes the nipples and makes them smaller and more oval shaped. Then they are reattached to the chest wall. After this surgery, there is no feeling in the nipples and areolas.
- Subcutaneous mastectomy with nipple preservation. If your breasts are smaller, this approach may be an option. The surgeon makes cuts under the breasts and removes breast tissue. Usually no skin is removed. The nipples may be reshaped, but the nipples and areolas stay attached. This helps preserve feeling in the nipples.
- Periareolar mastectomy. This surgery may be used if your breasts are not large. A small cut is made around the areola of each breast and the breast tissue is removed. Usually, no skin is removed. The nipples and areolas stay attached. This helps preserve feeling in the nipples.
After surgery, you may need to stay in the hospital overnight. You might not be able to bear weight on your upper body for six weeks. Talk to your health care provider about the specific activity restrictions you need to follow.
Some breast tissue remains after surgery regardless of the surgery you have. Because of that, ask your health care provider about breast cancer screening you may need after surgery.
Genital surgery
Metoidioplasty.
Metoidioplasty is a procedure to increase the length of the clitoris without adding other tissue. During surgery, the clitoris is freed from its attachment against the body. The surgeon also can extend the urethra through the released clitoris using a graft typically taken from the lining of the mouth. This is called a urethral hookup. It makes standing urination possible.
This procedure usually results in a penis with an unstimulated length between 1 and 3 inches (3 and 8 centimeters). Typically after this surgery, you still have full sensation and the ability to have an orgasm.
It isn't necessary for the vagina to be closed or removed before metoidioplasty. But penetration and Pap tests might not be possible after it. As a result, your surgeon might suggest removing your uterus, cervix and ovaries during metoidioplasty.
After metoidioplasty, you have a tube temporarily placed in your urethra to collect urine. Recovery might take up to two weeks.
Phalloplasty
Phalloplasty, the surgical creation of a penis, involves several procedures. During phalloplasty, large amounts of skin are taken from other areas of the body. These may include the forearm, calf or lower abdomen. This can cause significant scarring. The skin is rolled into the shape of a penis and anchored into position above the clitoris. Phalloplasty also may include:
- Urethral lengthening to allow for urination through the penis
- Grafting of nerves and blood vessels to provide sensation
- Sculpting the head of the penis — a procedure called glansplasty
- Medical tattooing to create a distinct difference between the head and shaft
After phalloplasty, a tube is temporarily placed in the urethra to collect urine. You'll likely need to stay in the hospital for a few days. Phalloplasty carries a high rate of complications. It could require many follow-up surgeries. Depending on the procedure, recovery might take up to 12 weeks. The new penis will not become erect with sexual stimulation. A penile implant is needed to allow penetrative sex.
Scrotoplasty
Scrotoplasty is the surgical creation of a scrotum. During scrotoplasty, testicular implants are inserted into the labia. To prepare for the procedure, expanders are placed under the skin. The expanders are gradually filled with saline over several months. When the skin has been expanded enough, the implants are inserted. Some people find the implants uncomfortable. It is possible for the implants to wear through surrounding tissue or become infected.
Other masculinizing surgeries also are available, including surgery to place pectoral implants in the chest, as well as procedures to remove fat and fat grafting. Ask your health care provider about these options and the risks and benefits they involve.
Research has found that that gender-affirming surgery can have a positive impact on well-being and sexual function. It's important to follow your health care provider's advice for long-term care and follow-up after surgery. Continued care after surgery is associated with good outcomes for long-term health.
Before you have surgery, talk to members of your health care team about what to expect after surgery and the ongoing care you may need.
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies of tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.
Masculinizing surgery care at Mayo Clinic
- Tangpricha V, et al. Transgender men: Evaluation and management. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed July 22, 2022.
- Erickson-Schroth L, ed. Surgical transition. In: Trans Bodies, Trans Selves: A Resource by and for Transgender Communities. 2nd ed. Kindle edition. Oxford University Press; 2022. Accessed July 25, 2022.
- Coleman E, et al. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, version 8. International Journal of Transgender Health. 2022; doi:10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644.
- AskMayoExpert. Gender-affirming procedures (adult). Mayo Clinic; 2022.
- Sonmezer M, et al. Overview of fertility and reproductive hormone preservation prior to gonadotoxic therapy or surgery. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed July 25, 2022.
- Erickson-Schroth L, ed. Medical transition. In: Trans Bodies, Trans Selves: A Resource by and for Transgender Communities. 2nd ed. Kindle edition. Oxford University Press; 2022. Accessed July 25, 2022.
- Health Education & Content Services (Patient Education). Chest masculinization surgery. Mayo Clinic; 2022.
- Doctors & Departments
- Care at Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
Make twice the impact
Your gift can go twice as far to advance cancer research and care!
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Vatican Document Casts Gender Change and Fluidity as Threat to Human Dignity
The statement is likely to be embraced by conservatives and stir consternation among L.G.B.T.Q. advocates who fear it will be used as a cudgel against transgender people.

By Jason Horowitz and Elisabetta Povoledo
Reporting from Rome
The Vatican on Monday issued a new document approved by Pope Francis stating that the church believes that gender fluidity and transition surgery, as well as surrogacy, amount to affronts to human dignity.
The sex a person is assigned at birth, the document argued, was an “irrevocable gift” from God and “any sex-change intervention, as a rule, risks threatening the unique dignity the person has received from the moment of conception.” People who desire “a personal self-determination, as gender theory prescribes,” risk succumbing “to the age-old temptation to make oneself God.”
Regarding surrogacy, the document unequivocally stated the Roman Catholic Church’s opposition, whether the woman carrying a baby “is coerced into it or chooses to subject herself to it freely.” Surrogacy makes the child “a mere means subservient to the arbitrary gain or desire of others,” the Vatican said in the document, which also opposed in vitro fertilization.
The document was intended as a broad statement of the church’s view on human dignity, including the exploitation of the poor, migrants, women and vulnerable people. The Vatican acknowledged that it was touching on difficult issues, but said that in a time of great tumult, it was essential, and it hoped beneficial, for the church to restate its teachings on the centrality of human dignity.
Even if the church’s teachings on culture war issues that Francis has largely avoided are not necessarily new, their consolidation now was likely to be embraced by conservatives for their hard line against liberal ideas on gender and surrogacy.
The document, five years in the making, immediately generated deep consternation among advocates for L.G.B.T.Q. rights in the church, who fear it will be used against transgender people. That was so, they said, even as the document warned of “unjust discrimination” in countries where transgender people are imprisoned or face aggression, violence and sometimes death.
“The Vatican is again supporting and propagating ideas that lead to real physical harm to transgender, nonbinary and other L.G.B.T.Q.+ people,” said Francis DeBernardo, the executive director of New Ways Ministry, a Maryland-based group that advocates for gay Catholics, adding that the Vatican’s defense of human dignity excluded “the segment of the human population who are transgender, nonbinary or gender nonconforming.”
He said it presented an outdated theology based on physical appearance alone and was blind to “the growing reality that a person’s gender includes the psychological, social and spiritual aspects naturally present in their lives.”
The document, he said, showed a “stunning lack of awareness of the actual lives of transgender and nonbinary people.” Its authors ignored the transgender people who shared their experiences with the church, Mr. DeBernardo said, “cavalierly,” and incorrectly, dismissing them as a purely Western phenomenon.
Though the document is a clear setback for L.G.B.T.Q. people and their supporters, the Vatican took pains to strike a balance between protecting personal human dignity and clearly stating church teaching, a tightrope Francis has tried to walk in his more than 11 years as pope.
Francis has made it a hallmark of his papacy to meet with gay and transgender Catholics and has made it his mission to broadcast a message for a more open, and less judgmental, church. Just months ago, Francis upset more conservative corners of his church by explicitly allowing L.G.B.T.Q. Catholics to receive blessings from priests and by allowing transgender people to be baptized and act as godparents .
But he has refused to budge on the church rules and doctrine that many gay and transgender Catholics feel have alienated them, revealing the limits of his push for inclusivity.
“In terms of pastoral consequences,” Cardinal Víctor Manuel Fernández, who leads the Vatican’s office on doctrine, said in a news conference Monday, “the principle of welcoming all is clear in the words of Pope Francis.”
Francis, he said, has repeatedly said that “all, all, all” must be welcomed. “Even those who don’t agree with what the church teaches and who make different choices from those that the church says in its doctrine, must be welcomed,” he said, including “those who think differently on these themes of sexuality.”
But Francis’ words were one thing, and church doctrine another, Cardinal Fernández made clear, drawing a distinction between the document, which he said was of high doctrinal importance, as opposed to the recent statement allowing blessings for same-sex Catholics. The church teaches that “homosexual acts are intrinsically disordered.”
In an echo of the tension between the substance of church law and Francis’ style of a papal inclusivity, Cardinal Fernández said on Monday that perhaps the “intrinsically disordered” language should be modified to better reflect that the church’s message that homosexual acts could not produce life.
“It’s a very strong expression and it requires explanation,” he said. “Maybe we could find an expression that is even clearer to understand what we want to say.”
Though receptive to gay and transgender followers, the pope has also consistently expressed concern about what he calls “ideological colonization,” the notion that wealthy nations arrogantly impose views — whether on gender or surrogacy — on people and religious traditions that do not necessarily agree with them. The document said “gender theory plays a central role” in that vision and that its “scientific coherence is the subject of considerable debate among experts.”
Using “on the one hand” and “on the other hand,” language, the Vatican’s office on teaching and doctrine wrote that “it should be denounced as contrary to human dignity the fact that, in some places, not a few people are imprisoned, tortured, and even deprived of the good of life solely because of their sexual orientation.”
“At the same time,” it continued, “the church highlights the definite critical issues present in gender theory.”
On Monday, Cardinal Fernández also struggled to reconcile the two seemingly dissonant views.
“I am shocked having read a text from some Catholics who said, ‘Bless this military government of our country that created these laws against homosexuals,’” Cardinal Fernández said on Monday. “I wanted to die reading that.”
But he went on to say that the Vatican document was itself not a call for decriminalization, but an affirmation of what the church believed. “We shall see the consequences,” he said, adding that the church would then see how to respond.
In his presentation, Cardinal Fernández described the long process of the drafting of a document on human dignity, “Infinite Dignity,” which began in March 2019, to take into account the “latest developments on the subject in academia and the ambivalent ways in which the concept is understood today.”
In 2023, Francis sent the document back with instructions to “highlight topics closely connected to the theme of dignity, such as poverty, the situation of migrants, violence against women, human trafficking, war, and other themes.” Francis signed off on the document on March 25.
The long road, Cardinal Fernández wrote, “reflects the gravity” of the process.
In the document, the Vatican embraced the “clear progress in understanding human dignity,” pointing to the “desire to eradicate racism, slavery, and the marginalization of women, children, the sick, and people with disabilities.”
But it said the church also sees “grave violations of that dignity,” including abortion, euthanasia, the death penalty, polygamy, torture, the exploitation of the poor and migrants, human trafficking and sex abuse, violence against women, capitalism’s inequality and terrorism.
The document expressed concern that eliminating sexual differences would undercut the family, and that a response “to what are at times understandable aspirations,” will become an absolute truth and ideology, and change how children are raised.
The document argued that changing sex put individualism before nature and that human dignity as a subject was often hijacked to “justify an arbitrary proliferation of new rights,” as if “the ability to express and realize every individual preference or subjective desire should be guaranteed.”
Cardinal Fernández on Monday said that a couple desperate to have a child should turn to adoption, rather than surrogacy or in vitro fertilization because those practices, he said, eroded human dignity writ large.
Individualistic thinking, the document argues, subjugates the universality of dignity to individual standards, concerned with “psycho-physical well-being” or “individual arbitrariness or social recognition.” By making dignity subjective, the Vatican argues, it becomes subject to “arbitrariness and power interests.”
Jason Horowitz is the Rome bureau chief for The Times, covering Italy, the Vatican, Greece and other parts of Southern Europe. More about Jason Horowitz
Elisabetta Povoledo is a reporter based in Rome, covering Italy, the Vatican and the culture of the region. She has been a journalist for 35 years. More about Elisabetta Povoledo
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
The Vatican says surrogacy and gender theory are 'grave threats' to human dignity

Jason DeRose

The crowd looks in direction of the window of the apostolic palace overlooking St. Peter's square during Pope Francis' prayer on April 1 in The Vatican. TizianaI Fabi/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
The crowd looks in direction of the window of the apostolic palace overlooking St. Peter's square during Pope Francis' prayer on April 1 in The Vatican.
The Vatican has released a new document calling poverty, war and the plight of migrants "threats to human dignity." But it also calls abortion, surrogacy and gender theory "grave threats" facing humanity today.
The document, titled " Infinite Dignity " says that each person's dignity comes from the love of the creator "who has imprinted the indelible features of his image on every person." This language is familiar to Christians accustomed to hearing that humans are all made in God's image.
The document goes on to say that this dignity is inalienable, beyond any circumstance or situation the person might encounter. Simply put, because a person exists, a human has intrinsic dignity.
"Infinite Dignity" details a long list of what it calls grave threats to that dignity, some of which might be expected given other Catholic teachings. It talks about the drama of poverty and how the unequal distribution of wealth denies humans their God-given dignity. It also describes war, the abuse of migrants, sexual abuse, violence against women, the marginalizing of people with disabilities, assisted suicide and abortion all as affronts to human dignity.
But then the document turns to other issues that have become more highly politicized in recent years: surrogacy, gender theory, and what it calls "sex change."

The pope wants surrogacy banned. Here's why one advocate says that's misguided
The document's framework holds that if a person is made in God's image, gender theory and gender reassignment surgery call into question why God would create a person with the wrong gender.
It says that the understanding of humanity as divided into two sexes — male and female — is biblical and deeply meaningful, especially in terms of procreation. Gender theory argues that a person's gender can be different from the sex that person was assigned at birth.
"Infinite Dignity" says the concept of human dignity can be misused to justify what it calls an "arbitrary proliferation of new rights," describing those, rather, as "individual preference" or "desire." That language is very similar to how conservatives often talk about being transgender as a choice, which is something major medical and psychological groups dispute.
The document makes a clear distinction between the issue of sexual orientation (whether a person is gay, lesbian or bisexual) and the issue of gender identity (whether a person's sex assigned at birth matches what that person understands his or her gender to be).
The document will be seen by some more conservative Catholic as a win after years of feeling embattled during Pope Francis's leadership. Just last year, the Vatican said priests could baptize transgender Catholics and allowed for priests to bless people in same-sex relationships .

Catholic Church works to explain what same-sex blessings are and are not
But many transgender Catholics and their families as well as more progressive Catholics are displeased with "Infinite Dignity."
Executive director of the LGBTQ Catholic group New Ways Ministry, Francis DeBernardo says of the document, "When it gets to the section on people who are transgender or non-binary, it doesn't apply the principles of human dignity to them."
New Ways Ministry's mission is, in part, to help pastors and religious teachers better understand gender identity and sexuality. It also fosters, "holiness and wholeness within the Catholic LGBTQ+ community."
DeBernardo argues "Infinite Dignity" does not live up to its own name. "In a sense, it's not infinite dignity," he says. "It's a very limited dignity that the church is offering."
He fears this document will be used to further persecute transgender people, and he thinks it will cause transgender Catholics and their families to leave the church.

The Vatican says priests can baptize transgender people
DeBernardo also worries the sections on gender theory and what it calls "sex change" will eclipse what he describes as the very good parts of the document on war, poverty and migrants.
The group Catholics for Choice, is also disappointed and calls into question how the document was created. "Yet again," said the group's president Jamie Manson in a written statement, "a group of all-male, celibate clergymen are telling women and gender-expansive people that their lived experiences are not real or valid."
Catholics for Choice advocates within the church on a variety of issues regarding sexual and reproductive health, including abortion rights. The group holds – and argues that Catholic teaching supports – people's individual consciences should be their guide in such decisions.
"It is clear to me that the women and trans people who continue to identify as Catholic — despite documents like this completely disregarding our experiences — only do so because of a deep love for our faith and its traditions," continues Manson in her statement. "It is devastating that our leaders do not offer the same respect and love in return."
- gender confirmation surgery
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- March Madness
- AP Top 25 Poll
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Vatican blasts gender-affirming surgery, surrogacy and gender theory as violations of human dignity
The Vatican has declared that gender-affirming surgeries and surrogacy are grave violations of human dignity. A new document from the doctrine office puts them on a par with abortion and euthanasia as practices that violate God’s plan for human life. In its most eagerly anticipated section, the Vatican flat-out rejected “gender theory” or the idea that one’s gender can be changed.

The Vatican on Monday declared gender-affirming surgery and surrogacy as grave violations of human dignity, putting them on par with abortion and euthanasia as practices that reject God’s plan for human life. The Vatican’s doctrine office issued “Infinite Dignity,” a 20-page declaration that has been in the works for five years. After substantial revision in recent months, it was approved March 25 by Pope Francis, who ordered its publication.
The prefect of the Vatican’s Dicastery for the Doctrine of the Faith, Cardinal Victor Manuel Fernandez, presents the declaration ‘Dignitas Infinita’ (Infinite Dignity) during a press conference at the Vatican, Monday, April 8, 2024. (AP Photo/Gregorio Borgia)
- Copy Link copied
A copy of the 20-page “Infinite Dignity” declaration issued by the Vatican’s doctrine office sits on a journalist desk as the prefect of the Vatican’s Dicastery for the Doctrine of the Faith, Cardinal Victor Manuel Fernandez, meets the journalists during a press conference at the Vatican, Monday, April 8, 2024. (AP Photo/Gregorio Borgia)
VATICAN CITY (AP) — The Vatican on Monday declared gender-affirming surgery and surrogacy as grave violations of human dignity , putting them on par with abortion and euthanasia as practices that it said reject God’s plan for human life.
The Vatican’s doctrine office issued “Infinite Dignity,” a 20-page declaration that has been in the works for five years. After substantial revision in recent months, it was approved March 25 by Pope Francis, who ordered its publication.
From a pope who has made outreach to the LGBTQ+ community a hallmark of his papacy, the document was received as a setback, albeit predictable, by trans Catholics. But its message was also consistent with the Argentine Jesuit’s long-standing belief that while trans people should be welcomed in the church, so-called “gender ideologies” should not.
In its most eagerly anticipated section, the Vatican repeated its rejection of “gender theory,” or the idea that one’s biological sex can change. It said God created man and woman as biologically different, separate beings, and said people must not tinker with that or try to “make oneself God.”
“It follows that any sex-change intervention, as a rule, risks threatening the unique dignity the person has received from the moment of conception,” the document said.
It distinguished between gender-affirming surgeries, which it rejected, and “genital abnormalities” that are present at birth or that develop later. Those abnormalities can be “resolved” with the help of health care professionals, it said.
Advocates for LGBTQ+ Catholics immediately criticized the document as outdated, harmful and contrary to the stated goal of recognizing the “infinite dignity” of all of God’s children. They warned it could have real-world effects on trans people, fueling anti-trans violence and discrimination.
“While it lays out a wonderful rationale for why each human being, regardless of condition in life, must be respected, honored, and loved, it does not apply this principle to gender-diverse people,” said Francis DeBernardo of New Ways Ministry, which advocates for LGBTQ+ Catholics.
“It needs to be emphasized that biological sex and the sociocultural role of sex (gender) can be distinguished but not separated”
Nicolete Burbach, lead expert in social and environmental justice at the London Jesuit Centre, said the document showed the Vatican continues to fail to engage with queer and feminist approaches to the body “which it simply dismisses as supposedly subjecting both the body and human dignity itself to human whims.”
“I think the main difficulty faced by the document is that it attempts to affirm the church’s authentic commitment to human dignity in the face of a troubling history on the part of the church itself around attacks on that dignity,” said Burbach, a trans Catholic theologian who researches transness and the Catholic Church.
The document’s existence, rumored since 2019, was confirmed in recent weeks by the new prefect of the Dicastery for the Doctrine of the Faith, Argentine Cardinal Víctor Manuel Fernández, a close Francis confidant.
Fernández had cast the document as something of a nod to conservatives after he authored a more explosive document approving blessings for same-sex couples that sparked criticism from conservative bishops around the world, especially in Africa.
And yet, in an apparent attempt at balance, the document takes pointed aim at countries — including many in Africa — that criminalize homosexuality. It echoed Francis’ assertion in a 2023 interview with The Associated Press that “being homosexual is not a crime .”
The new document denounces “as contrary to human dignity the fact that, in some places, not a few people are imprisoned, tortured, and even deprived of the good of life solely because of their sexual orientation.”
The White House said President Joe Biden, a devout Catholic, was “pleased” to see that the declaration “furthers the Vatican’s call to ensure that LGBTQ+ (individuals) are protected from violence and imprisonment around the world,” press secretary Karine Jean-Pierre said.
On the specifics involving gender theory, Jean-Pierre stressed that it was not Biden’s role to “litigate internal church policy.”
Asked how its negative take on trans people squared with Francis’ message of welcome, Fernández said the welcome remained but that the pope fervently believed that the idea that gender was fluid “rather than helping to recognize dignity, impoverishes the vision” of a man and woman coming together to create new life.
The document is something of a repackaging of previously articulated Vatican positions, read now through the prism of human dignity. It restates well-known Catholic doctrine opposing abortion and euthanasia, and adds to the list some of Francis’ main concerns as pope: the threats to human dignity posed by poverty, war, human trafficking, the death penalty and forced migration.
In a newly articulated position, it says surrogacy violates both the dignity of the surrogate mother and the child .
While much attention about surrogacy has focused on possible exploitation of poor women as surrogates, the Vatican asserts that the child “has the right to have a fully human (and not artificially induced) origin and to receive the gift of a life that manifests both the dignity of the giver and that of the receiver.”
“Considering this, the legitimate desire to have a child cannot be transformed into a ‘right to a child’ that fails to respect the dignity of that child as the recipient of the gift of life,” it said.
The Vatican had previously published its most articulated position on gender in 2019, when the Congregation for Catholic Education rejected the idea that people can choose or change their genders and insisted on the complementarity of biologically male and female sex organs to create new life.
The new document from the more authoritative Dicastery for the Doctrine of the Faith quotes from that 2019 education document, but tempers the tone. Significantly, it doesn’t repeat Vatican doctrine that homosexual people deserve to be treated with dignity and respect but that homosexual actions are “intrinsically disordered.”
In a news conference to introduce the document, Fernández acknowledged that the “intrinsically disordered” language was very strong. He suggested there might be a better way, “with other words,” to express the church’s vision of sex between husband and wife to create new life.
Francis has ministered to trans Catholics, including trans sex workers, and insisted that the Catholic Church must welcome all children of God.
But he has also denounced “gender theory” as the “worst danger” facing humanity today, an “ugly ideology” that threatens to cancel out God-given differences between man and woman. He has blasted in particular what he calls the “ideological colonization” of the West in the developing world, where development aid is sometimes conditioned on adopting Western ideas about gender.
Transgender activists immediately called the document “hurtful” and devoid of the voices and experiences of real trans people, especially in the distinction it makes between gender-affirming surgeries and surgeries on intersex people.
“The suggestion that gender-affirming health care — which has saved the lives of so many wonderful trans people and enabled them to live in harmony with their bodies, their communities and (God) — might risk or diminish trans people’s dignity is not only hurtful but dangerously ignorant,” said Mara Klein, a nonbinary, transgender activist who has participated in Germany’s church reform project.
Klein said the Vatican “hypocrisy” was furthered by the document’s approval of surgery on intersex people, “which if performed without consent especially on minors often cause immense physical and psychological harm.”
The document comes at a time of some backlash against transgender people, including in the United States where Republican-led state legislatures are considering a new round of bills restricting medical care for transgender youths — and in some cases, adults.
“On top of the rising hostility towards our communities, we are faced with a church that does not listen and refuses to see the beauty of creation that can be found in our biographies,” Klein said in an email.
AP writer Darlene Superville contributed from Air Force One.
Ohio judge blocks ban on gender-affirming care for transgender minors—for now

An Ohio judge on Tuesday temporarily blocked an impending law that would restrict medical care for transgender minors in the Buckeye State.
The decision came weeks after the American Civil Liberties Union filed a lawsuit challenging the state on behalf of two transgender girls and their families. The measure prevents doctors from prescribing hormones, puberty blockers, or gender reassignment surgery before patients turn 18.
Attorneys contend the law violates the state Constitution , which gives Ohioans the right to choose their health care.
“Today’s ruling is a victory for transgender Ohioans and their families,” said Harper Seldin, staff attorney for the ACLU. “Ohio’s ban is an openly discriminatory breach of the rights of transgender youth and their parents alike and presents a real danger to the same young people it claims to protect.”
The legislation was set to take effect on April 24 after House and Senate Republicans voted to override Gov. Mike DeWine’s veto. Proponents of the bill contend it will protect children, but critics say decisions about transition care should be left to families and their medical providers.
Prep for the polls: See who is running for president and compare where they stand on key issues in our Voter Guide
The suit in Ohio mirrors efforts in other states to challenge laws that restrict gender-affirming care for minors. A federal judge struck down a similar policy in Arkansas , arguing it violates the constitutional rights of transgender youth and their families. The state is appealing that decision.
“We protect children with various restrictions that do not apply to adults − from signing legal contracts to buying alcohol and tobacco and more,” Attorney General Dave Yost posted on X , formerly known as Twitter, after the lawsuit was filed. “As I promised during the veto override, my office will defend this constitutional statute.”
What does the Ohio bill do?
The bill allows Ohioans younger than 18 who are already receiving hormones or puberty blockers to continue as long as doctors determine stopping the prescription would cause harm. Critics say that’s not enough to protect current patients because health care providers could be wary of legal consequences.
The legislation does not ban talk therapy, but it requires mental health providers to get permission from at least one parent or guardian to diagnose and treat gender dysphoria.
More: 6 jurors selected to serve in Donald Trump's hush money trial: Latest Trump trial news
The bill also bans transgender girls and women from playing on female sports teams in high school and college. It doesn’t specify how schools would verify an athlete’s gender if it’s called into question. Players and their families can sue if they believe they lost an opportunity because of a transgender athlete.
The lawsuit doesn’t specifically challenge the athlete ban. But it argues the legislation flouts the constitution’s single-subject rule, which requires legislation to address only one topic. House Republicans introduced separate bills on gender-affirming care and transgender athletes before combining them into one .
In Tuesday’s decision, Franklin County Judge Michael Holbrook indicated that the law could be tossed out because of a single-subject violation.
“It is not lost upon this Court that the General Assembly was unable to pass the (Saving Ohio Adolescents from Experimentation) portion of the Act separately, and it was only upon logrolling in the Saving Women’s Sports provisions that it was able to pass,” Holbrook wrote.
Panel clears ban on gender reassignment surgery for minors
Tuesday’s decision came one day after a legislative panel cleared the way for an administrative rule that will ban gender reassignment surgery for minors. Ohio health care providers say they do not perform that procedure on patients under 18.
The rule will take effect May 3.
More: Supreme Court, in an emergency order, lets Idaho enforce ban on transgender care
The measure was among several that DeWine proposed to regulate gender-affirming care after he vetoed the legislation. In testimony for Monday’s meeting, opponents argued that the rules overstep the administration’s authority and conflict with federal law.
“The proposed administrative rule changes are based on biased definitions, ignore well-established best practices, and restrict countless patients’ access to gender-affirming care,” said Mallory Golski, civic engagement and advocacy manager for Kaleidoscope Youth Center.
DeWine’s other proposals are still working their way through the rulemaking process. That includes a requirement for transgender minors to undergo at least six months of counseling before further treatment occurs. Another rule would require providers to report non-identifying data on gender dysphoria diagnoses and treatment.
Haley BeMiller is a reporter for the USA TODAY Network Ohio Bureau, which serves the Columbus Dispatch, Cincinnati Enquirer, Akron Beacon Journal and 18 other affiliated news organizations across Ohio.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Surgery may also involve constructing labia (labiaplasty) and a clitoris (clitoroplasty). ... What's the difference between gender affirmation surgery and gender (sex) reassignment surgery? Gender reassignment is an outdated term for gender affirmation surgery. The new language, "gender affirmation," is more accurate in terms of what the ...
Female-to-male surgery is a type of gender-affirmation or gender-affirming surgery. There are multiple forms of gender-affirming surgery, including altering the genital region, known as "bottom ...
Gender-affirming surgery for male-to-female transgender women or transfeminine non-binary people describes a variety of surgical procedures that alter the body to provide physical traits more comfortable and affirming to an individual's gender identity and overall functioning.. Often used to refer to vaginoplasty, sex reassignment surgery can also more broadly refer to other gender-affirming ...
A gender affirmation surgery allows individuals, such as those who identify as transgender or nonbinary, to change one or more of their sex characteristics. This type of procedure offers a person ...
Gender affirming surgery can be used to create a vulva and vagina. It involves removing the penis, testicles and scrotum. During a vaginoplasty procedure, tissue in the genital area is rearranged to create a vaginal canal (or opening) and vulva (external genitalia), including the labia. A version of vaginoplasty called vulvoplasty can create a ...
The cost of transitioning can often exceed $100,000 in the United States, depending upon the procedures needed. A typical genitoplasty alone averages about $18,000. Rhinoplasty, or a nose job, averaged $5,409 in 2019. Insurance Coverage for Sex Reassignment Surgery.
Gender affirmation surgery, also known as gender confirmation surgery, is performed to align or transition individuals with gender dysphoria to their true gender. A transgender woman, man, or non-binary person may choose to undergo gender affirmation surgery. The term "transexual" was previously used by the medical community to describe people ...
Overview. Feminizing surgery, also called gender-affirming surgery or gender-confirmation surgery, involves procedures that help better align the body with a person's gender identity. Feminizing surgery includes several options, such as top surgery to increase the size of the breasts. That procedure also is called breast augmentation.
Gender-affirming surgery is a surgical procedure, or series of procedures, that alters a person's physical appearance and sexual characteristics to resemble those associated with their identified gender.The phrase is most often associated with transgender health care and intersex medical interventions, although many such treatments are also pursued by cisgender and non-intersex individuals.
Top surgery is surgery that removes or augments breast tissue and reshapes the chest to create a more masculine or feminine appearance for transgender and nonbinary people. Facial gender surgery: While hormone replacement therapy can help achieve gender affirming changes to the face, surgery may help. Facial gender surgery can include a variety ...
Gender-affirming surgery for female-to-male transgender people includes a variety of surgical procedures that alter anatomical traits to provide physical traits more comfortable to the trans man's male identity and functioning.. Often used to refer to phalloplasty, metoidoplasty, or vaginectomy, sex reassignment surgery can also more broadly refer to many procedures an individual may have ...
Breast augmentation is often performed as an outpatient procedure but some patients may require one night stay in the hospital. 1 of 7. See before and after photos of patients who have undergone gender-affirming surgeries at Cleveland Clinic, including breast augmentations, facial feminizations, mastectomies and vaginoplasty.
410-955-5000 Maryland. 855-695-4872 Outside of Maryland. +1-410-502-7683 International. To help provide guidance for those considering gender affirmation surgery, two experts from the Johns Hopkins Center for Transgender Health answer questions about what to expect before and after your surgery.
A trans person can choose from multiple procedures to make their appearance match their self-identified gender identity. Doctors refer to this as gender "affirmation" surgery. Trans people might ...
Also called gender reassignment surgery, the goal of this procedure is to create the outward physical appearance of the gender with which the person identifies. "Top surgery" refers to surgery above the waist, while "bottom surgery" refers to surgery below the waist. Transgender surgery is major surgery and generally not considered ...
Here's how gender reassignment works: Converting male anatomy to female anatomy requires removing the penis, reshaping genital tissue to appear more female and constructing a vagina. An incision ...
Gender dysphoria, earlier known as gender identity disorder, describes a heterogeneous group of individuals having the desire to possess secondary sexual characteristics of the opposite sex and possessing varying degrees of dissatisfaction regarding their anatomical gender . Gender reassignment surgery (GRS) has proven to be a revolutionary ...
The two major sex reassignment surgery (SRS) interventions in the female-to-male transsexual patients that will be addressed here are (1) the subcutaneous mastectomy (SCM), often combined with a hysterectomy/ ovariectomy; and (2) the actual genital transformation consisting of vaginectomy, reconstruction of the fixed part of the urethra (if ...
Female-to-male transition. The procedures involved in a female-to-male transition include: removal of the breasts. removal of the womb, ovaries and fallopian tubes. construction of a penis and testes - using vaginal tissue and skin from the forearm. a penile implant. In both forms of surgery, the aim is to retain sexual sensation and function.
We are proud to offer all of our services in a respectful, welcoming environment at our world-class surgical center in Dallas, Texas. We look forward to assisting you in achieving the very best possible results for all of your gender transition procedures. Contact us today to schedule a consultation at (972) 543-2477.
Sex and sexual health tips for transgender women after gender-affirming surgery. Sex after surgery. Achieving orgasm. Libido. Vaginal depth and lubrication. Aftercare. Contraceptions and STIs ...
Overview. Masculinizing surgery, also called gender-affirming surgery or gender-confirmation surgery, involves procedures that help better align the body with a person's gender identity. Masculinizing surgery includes several options, such as top surgery to create a more male-contoured chest and bottom surgery that changes the genitals.
The Vatican has issued a strong warning against "gender theory" and said that any gender-affirming surgery risks threatening "the unique dignity" of a person, in a new document signed off ...
Ettore Ferrari/EPA, via Shutterstock. The Vatican on Monday issued a new document approved by Pope Francis stating that the church believes that gender fluidity and transition surgery, as well as ...
The document's framework holds that if a person is made in God's image, gender theory and gender reassignment surgery call into question why God would create a person with the wrong gender.
VATICAN CITY (AP) — The Vatican on Monday declared gender-affirming surgery and surrogacy as grave violations of human dignity, putting them on par with abortion and euthanasia as practices that it said reject God's plan for human life. The Vatican's doctrine office issued "Infinite Dignity," a 20-page declaration that has been in the ...
The measure prevents doctors from prescribing hormones, puberty blockers, or gender reassignment surgery before patients turn 18. Attorneys contend the law violates the state Constitution, ...
While other gender-affirming treatments — including hormone therapy, fertility preservation and hair removal — are covered by the VA, the department has effectively banned transgender veterans from accessing surgery since 2013, when a department directive stated that the VA "does not provide sex reassignment surgery."