How is COVID-19 affecting student learning?
Subscribe to the brown center on education policy newsletter, initial findings from fall 2020, megan kuhfeld , megan kuhfeld director of growth modeling and data analytics - nwea jim soland , jim soland assistant professor, school of education and human development - university of virginia, affiliated research fellow - nwea beth tarasawa , bt beth tarasawa executive vice president of research - nwea angela johnson , aj angela johnson research scientist - nwea erik ruzek , and er erik ruzek research assistant professor, curry school of education - university of virginia karyn lewis karyn lewis vice president of research and policy partnerships - nwea.
December 3, 2020
The COVID-19 pandemic has introduced uncertainty into major aspects of national and global society, including for schools. For example, there is uncertainty about how school closures last spring impacted student achievement, as well as how the rapid conversion of most instruction to an online platform this academic year will continue to affect achievement. Without data on how the virus impacts student learning, making informed decisions about whether and when to return to in-person instruction remains difficult. Even now, education leaders must grapple with seemingly impossible choices that balance health risks associated with in-person learning against the educational needs of children, which may be better served when kids are in their physical schools.
Amidst all this uncertainty, there is growing consensus that school closures in spring 2020 likely had negative effects on student learning. For example, in an earlier post for this blog , we presented our research forecasting the possible impact of school closures on achievement. Based on historical learning trends and prior research on how out-of-school-time affects learning, we estimated that students would potentially begin fall 2020 with roughly 70% of the learning gains in reading relative to a typical school year. In mathematics, students were predicted to show even smaller learning gains from the previous year, returning with less than 50% of typical gains. While these and other similar forecasts presented a grim portrait of the challenges facing students and educators this fall, they were nonetheless projections. The question remained: What would learning trends in actual data from the 2020-21 school year really look like?
With fall 2020 data now in hand , we can move beyond forecasting and begin to describe what did happen. While the closures last spring left most schools without assessment data from that time, thousands of schools began testing this fall, making it possible to compare learning gains in a typical, pre-COVID-19 year to those same gains during the COVID-19 pandemic. Using data from nearly 4.4 million students in grades 3-8 who took MAP ® Growth™ reading and math assessments in fall 2020, we examined two primary research questions:
- How did students perform in fall 2020 relative to a typical school year (specifically, fall 2019)?
- Have students made learning gains since schools physically closed in March 2020?
To answer these questions, we compared students’ academic achievement and growth during the COVID-19 pandemic to the achievement and growth patterns observed in 2019. We report student achievement as a percentile rank, which is a normative measure of a student’s achievement in a given grade/subject relative to the MAP Growth national norms (reflecting pre-COVID-19 achievement levels).
To make sure the students who took the tests before and after COVID-19 school closures were demographically similar, all analyses were limited to a sample of 8,000 schools that tested students in both fall 2019 and fall 2020. Compared to all public schools in the nation, schools in the sample had slightly larger total enrollment, a lower percentage of low-income students, and a higher percentage of white students. Since our sample includes both in-person and remote testers in fall 2020, we conducted an initial comparability study of remote and in-person testing in fall 2020. We found consistent psychometric characteristics and trends in test scores for remote and in-person tests for students in grades 3-8, but caution that remote testing conditions may be qualitatively different for K-2 students. For more details on the sample and methodology, please see the technical report accompanying this study.
In some cases, our results tell a more optimistic story than what we feared. In others, the results are as deeply concerning as we expected based on our projections.

Question 1: How did students perform in fall 2020 relative to a typical school year?
When comparing students’ median percentile rank for fall 2020 to those for fall 2019, there is good news to share: Students in grades 3-8 performed similarly in reading to same-grade students in fall 2019. While the reason for the stability of these achievement results cannot be easily pinned down, possible explanations are that students read more on their own, and parents are better equipped to support learning in reading compared to other subjects that require more formal instruction.
The news in math, however, is more worrying. The figure below shows the median percentile rank in math by grade level in fall 2019 and fall 2020. As the figure indicates, the math achievement of students in 2020 was about 5 to 10 percentile points lower compared to same-grade students the prior year.
Figure 1: MAP Growth Percentiles in Math by Grade Level in Fall 2019 and Fall 2020
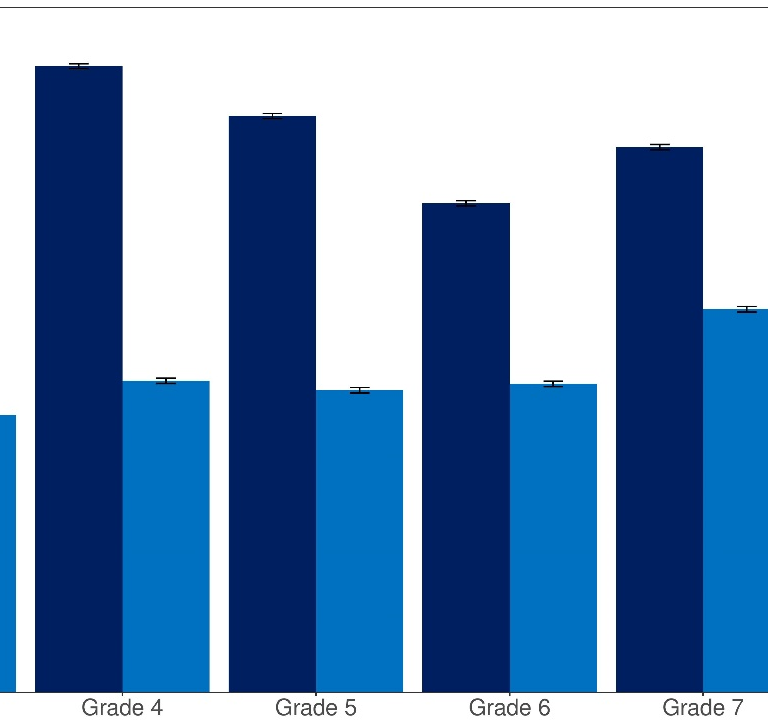
Source: Author calculations with MAP Growth data. Notes: Each bar represents the median percentile rank in a given grade/term.
Question 2: Have students made learning gains since schools physically closed, and how do these gains compare to gains in a more typical year?
To answer this question, we examined learning gains/losses between winter 2020 (January through early March) and fall 2020 relative to those same gains in a pre-COVID-19 period (between winter 2019 and fall 2019). We did not examine spring-to-fall changes because so few students tested in spring 2020 (after the pandemic began). In almost all grades, the majority of students made some learning gains in both reading and math since the COVID-19 pandemic started, though gains were smaller in math in 2020 relative to the gains students in the same grades made in the winter 2019-fall 2019 period.
Figure 2 shows the distribution of change in reading scores by grade for the winter 2020 to fall 2020 period (light blue) as compared to same-grade students in the pre-pandemic span of winter 2019 to fall 2019 (dark blue). The 2019 and 2020 distributions largely overlapped, suggesting similar amounts of within-student change from one grade to the next.
Figure 2: Distribution of Within-student Change from Winter 2019-Fall 2019 vs Winter 2020-Fall 2020 in Reading

Source: Author calculations with MAP Growth data. Notes: The dashed line represents zero growth (e.g., winter and fall test scores were equivalent). A positive value indicates that a student scored higher in the fall than their prior winter score; a negative value indicates a student scored lower in the fall than their prior winter score.
Meanwhile, Figure 3 shows the distribution of change for students in different grade levels for the winter 2020 to fall 2020 period in math. In contrast to reading, these results show a downward shift: A smaller proportion of students demonstrated positive math growth in the 2020 period than in the 2019 period for all grades. For example, 79% of students switching from 3 rd to 4 th grade made academic gains between winter 2019 and fall 2019, relative to 57% of students in the same grade range in 2020.
Figure 3: Distribution of Within-student Change from Winter 2019-Fall 2019 vs. Winter 2020-Fall 2020 in Math

It was widely speculated that the COVID-19 pandemic would lead to very unequal opportunities for learning depending on whether students had access to technology and parental support during the school closures, which would result in greater heterogeneity in terms of learning gains/losses in 2020. Notably, however, we do not see evidence that within-student change is more spread out this year relative to the pre-pandemic 2019 distribution.
The long-term effects of COVID-19 are still unknown
In some ways, our findings show an optimistic picture: In reading, on average, the achievement percentiles of students in fall 2020 were similar to those of same-grade students in fall 2019, and in almost all grades, most students made some learning gains since the COVID-19 pandemic started. In math, however, the results tell a less rosy story: Student achievement was lower than the pre-COVID-19 performance by same-grade students in fall 2019, and students showed lower growth in math across grades 3 to 8 relative to peers in the previous, more typical year. Schools will need clear local data to understand if these national trends are reflective of their students. Additional resources and supports should be deployed in math specifically to get students back on track.
In this study, we limited our analyses to a consistent set of schools between fall 2019 and fall 2020. However, approximately one in four students who tested within these schools in fall 2019 are no longer in our sample in fall 2020. This is a sizeable increase from the 15% attrition from fall 2018 to fall 2019. One possible explanation is that some students lacked reliable technology. A second is that they disengaged from school due to economic, health, or other factors. More coordinated efforts are required to establish communication with students who are not attending school or disengaging from instruction to get them back on track, especially our most vulnerable students.
Finally, we are only scratching the surface in quantifying the short-term and long-term academic and non-academic impacts of COVID-19. While more students are back in schools now and educators have more experience with remote instruction than when the pandemic forced schools to close in spring 2020, the collective shock we are experiencing is ongoing. We will continue to examine students’ academic progress throughout the 2020-21 school year to understand how recovery and growth unfold amid an ongoing pandemic.
Thankfully, we know much more about the impact the pandemic has had on student learning than we did even a few months ago. However, that knowledge makes clear that there is work to be done to help many students get back on track in math, and that the long-term ramifications of COVID-19 for student learning—especially among underserved communities—remain unknown.
Related Content
Jim Soland, Megan Kuhfeld, Beth Tarasawa, Angela Johnson, Erik Ruzek, Jing Liu
May 27, 2020
Amie Rapaport, Anna Saavedra, Dan Silver, Morgan Polikoff
November 18, 2020
Education Access & Equity K-12 Education
Governance Studies
Brown Center on Education Policy
Dick Startz
October 17, 2024
Mary Burns, Rebecca Winthrop, Michael Trucano, Natasha Luther
October 15, 2024
Phillip Levine

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Introduction
The global outbreak of COVID-19 has certainly taken an overwhelming toll on everyone. People have lost their jobs, their homes, and even their lives. There is no getting past the fact that the overall impact on the world has been negative, but it is important to realize that positive aspects of the pandemic have been overshadowed by the many negative ones. In an attempt to slow the spread of the disease, many governments made the decision to implement lockdowns, forcing billions to work and take classes from home, in many cases for the first times in their lives. Not only have these lockdowns altered the way that people work and go to school, but they have altered the mental health of everyone and the environmental health of the world around us.
Connection to STS Theory
The positive impacts of technology during the pandemic stems from the Modernization Theory, posing that there is a relationship between societal and technological advancements as societies shift to become updated as opposed to traditional. Technology has brought about lots of resistance to COVID that would not have been possible without the drastic advancements in science over the years. Thanks to these advancements, relationships can stay connected, students can continue to learn, jobs can stay open, and the environment can subtly improve. Our modernized world is well enough suited to take on the troubling times that COVID-19 has brought along.
Technology with School – Relates to College Students
Remote learning has allowed each of us to learn from the comfort of our homes. Working remotely has also allowed us to work from our living rooms. The perks of both are not having to wake up early to drive to work in the mornings, not having to sit at an office desk for eight hours a day, and not having to walk to class. Working remotely and remote learning has also been a time saver for many individuals.
According to Business Insider, there are a few tips that will help students be successful while being virtual. One tip is to clean your workspace. It is important to have a space, just like you would at a desk in a classroom, to ensure that you are paying attention to the professor. It is always important to engage with your professor. It is important to contact your professor outside of the class section to ensure that you are retaining the information. Another tip that the Business Insider recommends is to connect with your classmates. It is vital to build connections with your classmates that will help everyone have a comfortable environment to ask questions.
Personal Growth
In March 2020, the COVID-19 outbreak hit the United States. College students were forced to leave their beloved campuses and go home to finish their semesters online. For some, it meant their schoolwork load was lightened and they could sleep until noon. For others, it meant their plans of graduating and having a job for the summer were in jeopardy. Regardless of their situation, one thing was likely the same for all: lots of time alone. Students found things to do to pass the time. Some learned to cook, some started exercising at home, and others had more time to do what they already loved.
Ethan, a student at the University of South Carolina, used the time to start lifting weights in his home gym. In the United States, sales of home gym equipment doubled, reaching nearly $2.4 Billion in revenue. Store shelves were entirely sold out of exercise equipment. Many students like Ethan report that exercising was one of the biggest changes they made during COVID lockdown.
Other students, such as Cam, found an opportunity to get in a better place mentally. “I learned not to take things for granted. My relationship with my family has gotten better. I’m a much stronger person,” the Clemson student reported. Grayson, an athlete at Winthrop University, reported that it made him have a more positive outlook on being by himself. A student that elected to remain anonymous was just happy they could wake up later and not have to brush their teeth as much because of masks. Whether a dentist would approve of that habit or not, an improvement in mental health is a win in anyone’s book.
A select few students decided to challenge themselves in a world where all odds are stacked against them. Dean, a freshman at the University of South Carolina, decided to start his own bracelet and T-Shirt business in a time when small businesses all over the country were facing a grave threat of going out of business. All the while, he learned to play the guitar and uploaded his songs to SoundCloud, he reported.
Whether college students decided to get a six-pack or learned how to sew, almost everyone found something constructive and positive to do with their extra free time. The college students of COVID-19 learned what it meant to make the best of an unfortunate situation. Things may have looked bleak and frightening, but they learned how to manage those feelings and make something positive out of it.
Change in Workforce
Before the pandemic, many companies did not allow employees to work from home. Also, many companies would not even allow employees to take home items, such as laptops, as a safety precaution. According to Stanford Medicine, rapid innovation and implementation of technology has allowed for the employees to navigate the challenges. It states that it is clear that technology has transformed our typical daily workflow. Technology has also made it easier to connect with the patients during the pandemic.
The Pew Research Center states “about half of new teleworkers say they have more flexibility now and that majority who are working in person worry about virus exposure.” In December 2020, 71% of the workers that were surveyed were doing their job from home all or most of the time. Of those workers, more than half said if they were given the choice that they would want to keep working from home even after the pandemic. Among those who are currently working from home, most say that it has been easy to meet deadlines and complete projects on time without interruptions.
Environmental Improvements
Before the COVID-19 outbreak, a typical day consisted of billions of people across the globe commuting to work or school, whether that be through public buses or trains, driving themselves in cars, or some other means of transportation. As all these vehicles were used, immeasurable amounts of gases and chemicals were released into the atmosphere. As infection numbers and the death toll increased, most nations began enforcing lockdown protocols, and these mandates affected almost 3 billion people (Rume & Islam, 2020). Businesses and factories shut down or people began working from home, meaning they no longer needed to drive to work. In an attempt to stunt transmission, the majority of international travel was halted, limiting tourism, which also had a great impact. Since industrialization has advanced in major cities across the globe, the amount of Greenhouse Gases that have been emitted is alarming. Cars, buses, trains, industries, factories all release harmful chemicals due to the burning of fossil fuels or other energy sources. When these pollutants enter the atmosphere, they cause a variety of issues. It decreases overall air quality and visibility, and can be dangerous to those inhali ng the m.
According to research performed by Shakeel Ahmad Bhat and a group of other scientists from India, China, and the United Kingdom, Delhi, India is one of the most polluted cities in the world (Bhat et al, 2021). The city is highly industrialized and densely populated, contributing to the elevated levels of particulate matter in the air. Particulate matter is small pollutant liquid droplets and solid particles in the air (Environmental Protection Agency, 2020). When inhaled, they can burrow deep into the lungs and even the bloodstream and cause serious damage to a person, “particularly respiratory ailments” (Bhat et al, 2021). The two types of particulate matter are PM10 and PM2.5, and their numbers correspond to the size of the particles (their diameters in units of micrometers). The smaller the particle, the more harmful they are. By National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS), the level of particulate matter in Delhi is well above the tolerable limits. In 2016 alone, the amount of deaths caused by the poor air quality in India “was approximately 4.2 million” (Bhat et al, 2021).
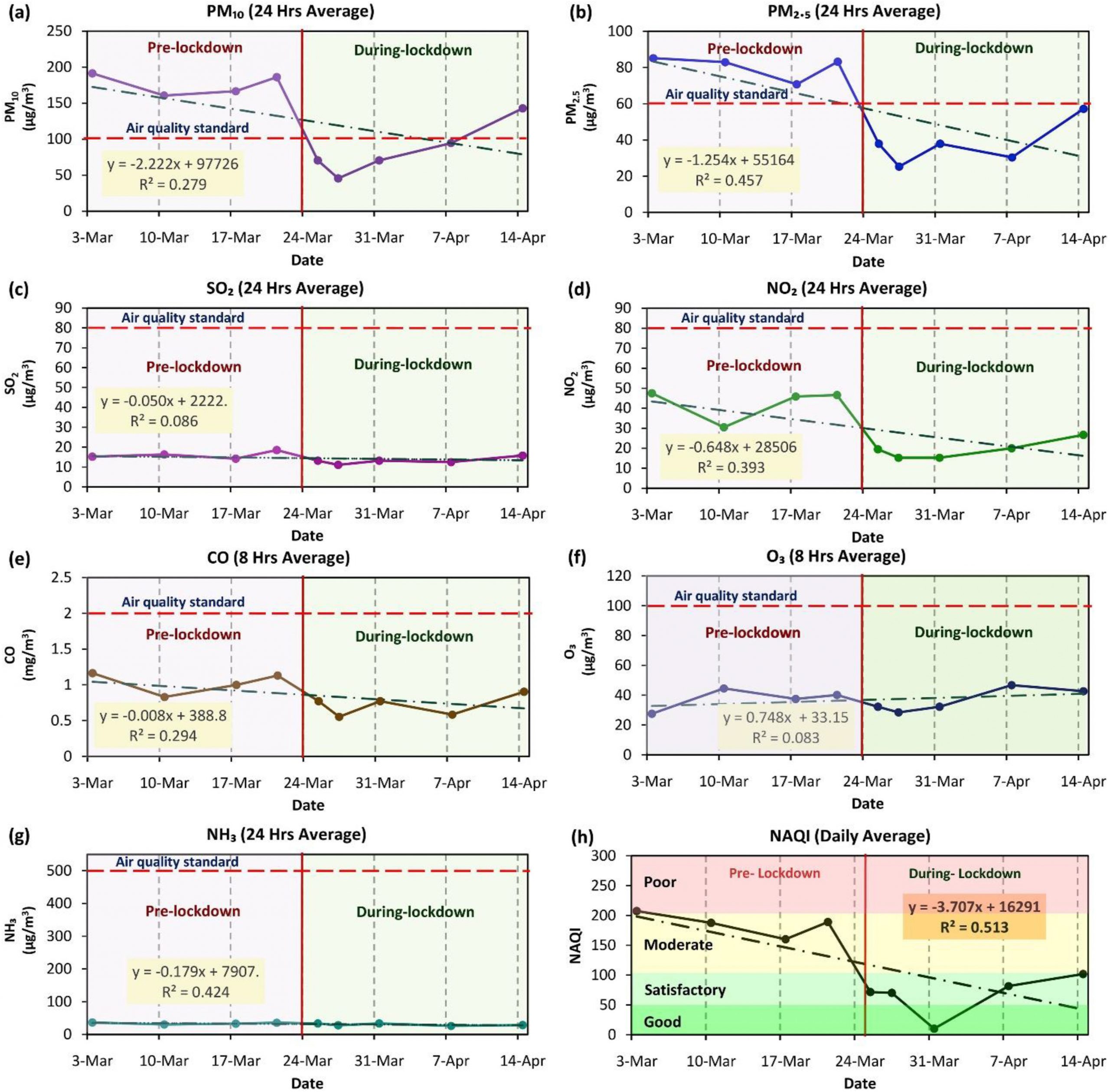
Lockdowns positively affe cted more than just the air quality around the world; additionally, water quality and beaches were a major beneficiary. Tourism for centuries has led to a significant overuse of beach resources such as fishing and leisure activities, and these in turn led to pollution of the water. If people are using jet skis and boating in lakes or oceans, the fuel and exhaust often leak into the water which can cause significant harm to the wildlife that lives in it. Restricting beach access has allowed them to recover and regain their resources, and has also decreased the pollution levels in the water. The water flowing in the Venice canals are cleaner now than they have been before (Bhat et al, 2021). pH levels, electric conductivity, dissolved oxygen levels, biochemical oxygen demand, and chemical oxygen demand have all decreased as a result of the lockdowns (Rume & Islam, 2020). These decreases all contribute to the fact that overall water quality levels have increased.
Noise pollution is an often-overlooked type of pollution that affects the world, especially in highly urbanized regions. Noise pollution is elevated levels of sound which are typically caused by human activities including transportation, machines, factories, etc. When the noise levels are elevated for extended periods of time, it negatively affects all organisms in the area. It leads to hearing loss, lack of concentration, high stress levels, interrupted sleep, and many other issues in humans. As for the wildlife, their abilities to detect and avoid predators and prey are hindered by noise pollution. It affects the invertebrates responsible for the control of many environmental processes that maintain balance in the ecosystem (Rume & Islam, 2020). When lockdowns were implemented, traveling and transportation stopped, industries shut down, flights were canceled, and people stayed home. The environment was able to recover and the people and organisms within the ecosystem enjoy a higher quality of life as a result.
Reflection Questions
- What kinds of positive experiences have you had during the pandemic?
- As stated in the chapter, there are many students who spent their time working out or picked up new hobbies. What new things were you able to focus on during the lockdowns?
Bhat, Shakeel Ahmad et al. “Impact of COVID-Related Lockdowns on Environmental and Climate Change Scenarios.” Environmental research 195 (2021): 110839–110839. Web. https://www-sciencedirect-com.libproxy.clemson.edu/science/article/pii/S001393512100133X?via%3Dihub.
DiDonato, S., Forgo, E., & Manella, H. (2020, June 5). Here’s how technology is helping residents during the COVID-19 pandemic . Scope Blog. https://scopeblog.stanford.edu/2020/06/04/how-technology-is-helping-residents-during-the-covid-19-pandemic/.
Environmental Protection Agency. (2020, October 1). Particulate Matter (PM) Basics. EPA. https://www.epa.gov/pm-pollution/particulate-matter-pm-basics.
Merkle, Steffen. “Positive Experiences During COVID-19.” Survey. 18 April 2021.
Parker, K., Horowitz, J. M., & Minkin, R. (2021, February 9). How Coronavirus Has Changed the Way Americans Work . Pew Research Center’s Social & Demographic Trends Project. https://www.pewresearch.org/social-trends/2020/12/09/how-the-coronavirus-outbreak-has-and-hasnt-changed-the-way-americans-work/.
Rume, T., & Islam, S. M. D.-U. (2020, September 17). Environmental effects of COVID-19 pandemic and potential strategies of sustainability. Heliyon. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7498239/#bib42.
Shaban, Hamza. “The Pandemic’s Home-Workout Revolution May Be Here to Stay.” The Washington Post, WP Company, 8 Jan. 2021, www.washingtonpost.com/road-to-recovery/2021/01/07/home-fitness-boom/.
Thompson, K. L. (2021, February 2). I’m a college professor who’s teaching virtually during the pandemic. Here are 7 things my most successful students do on Zoom. Business Insider. https://www.businessinsider.com/tips-for-zoom-success-as-remote-student-professor-advice-2021-2.
To the extent possible under law, Yang Wu; Allie Messenger; Arnaut Aguilar; Ashley Bui; Ava Kramer; Ben Jablonski; Blake Busking; Blake Moore; Carrie Pohlman; Brenna Turpin; Brooke Baker; Caroline Edwards; Chris Leroux; Claudia Sisk; Clayton Trentham; Davey Crouch; Eli Packer; Elle Wagner; Eliza Nix; Ellie Vensel; Erin Kennedy; Emily Cleveland; Ethan May; Ethan Hirsch; Frances Laughlin; George Easter; Grace Arnold; Grace D'Egidio; Grace Towe; Hope Wilde; Jack Sanford; Jake Brazinski; Jason McNult; Jason Saadeh; John Fuller; John Griffen; Julia Wood; Kasey Kiser; Katie Herbolsheimer; Katrina Campos; Kerrigan Donnelly; Kierstyn Stevens; Laurence Innes; Luke Dotson; Macey Coulter; Marco Guareschi; Meg Botts; Michael Havasy; Mikel Zoeller; Mitchell Wallin; Patrick Reed; Reagan Beach; Ryan Cook; Ryan Kennedy; Spencer Dalley; Steffen Merkle; Tayler Smith; Thomas Williams; Tim Egan; Tres Key; Tyler Parker; Virginia Lundeen; Will Gosnell; William Carroll; and Zoe Sabbert have waived all copyright and related or neighboring rights to COVID 19: A Student Perspective , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Covid-19’s Impact on Students’ Academic and Mental Well-Being
The pandemic has revealed—and exacerbated—inequities that hold many students back. Here’s how teachers can help.
Your content has been saved!
The pandemic has shone a spotlight on inequality in America: School closures and social isolation have affected all students, but particularly those living in poverty. Adding to the damage to their learning, a mental health crisis is emerging as many students have lost access to services that were offered by schools.
No matter what form school takes when the new year begins—whether students and teachers are back in the school building together or still at home—teachers will face a pressing issue: How can they help students recover and stay on track throughout the year even as their lives are likely to continue to be disrupted by the pandemic?
New research provides insights about the scope of the problem—as well as potential solutions.

The Achievement Gap Is Likely to Widen
A new study suggests that the coronavirus will undo months of academic gains, leaving many students behind. The study authors project that students will start the new school year with an average of 66 percent of the learning gains in reading and 44 percent of the learning gains in math, relative to the gains for a typical school year. But the situation is worse on the reading front, as the researchers also predict that the top third of students will make gains, possibly because they’re likely to continue reading with their families while schools are closed, thus widening the achievement gap.
To make matters worse, “few school systems provide plans to support students who need accommodations or other special populations,” the researchers point out in the study, potentially impacting students with special needs and English language learners.
Of course, the idea that over the summer students forget some of what they learned in school isn’t new. But there’s a big difference between summer learning loss and pandemic-related learning loss: During the summer, formal schooling stops, and learning loss happens at roughly the same rate for all students, the researchers point out. But instruction has been uneven during the pandemic, as some students have been able to participate fully in online learning while others have faced obstacles—such as lack of internet access—that have hindered their progress.
In the study, researchers analyzed a national sample of 5 million students in grades 3–8 who took the MAP Growth test, a tool schools use to assess students’ reading and math growth throughout the school year. The researchers compared typical growth in a standard-length school year to projections based on students being out of school from mid-March on. To make those projections, they looked at research on the summer slide, weather- and disaster-related closures (such as New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina), and absenteeism.
The researchers predict that, on average, students will experience substantial drops in reading and math, losing roughly three months’ worth of gains in reading and five months’ worth of gains in math. For Megan Kuhfeld, the lead author of the study, the biggest takeaway isn’t that learning loss will happen—that’s a given by this point—but that students will come back to school having declined at vastly different rates.
“We might be facing unprecedented levels of variability come fall,” Kuhfeld told me. “Especially in school districts that serve families with lots of different needs and resources. Instead of having students reading at a grade level above or below in their classroom, teachers might have kids who slipped back a lot versus kids who have moved forward.”
Disproportionate Impact on Students Living in Poverty and Students of Color
Horace Mann once referred to schools as the “great equalizers,” yet the pandemic threatens to expose the underlying inequities of remote learning. According to a 2015 Pew Research Center analysis , 17 percent of teenagers have difficulty completing homework assignments because they do not have reliable access to a computer or internet connection. For Black students, the number spikes to 25 percent.
“There are many reasons to believe the Covid-19 impacts might be larger for children in poverty and children of color,” Kuhfeld wrote in the study. Their families suffer higher rates of infection, and the economic burden disproportionately falls on Black and Hispanic parents, who are less likely to be able to work from home during the pandemic.
Although children are less likely to become infected with Covid-19, the adult mortality rates, coupled with the devastating economic consequences of the pandemic, will likely have an indelible impact on their well-being.
Impacts on Students’ Mental Health
That impact on well-being may be magnified by another effect of school closures: Schools are “the de facto mental health system for many children and adolescents,” providing mental health services to 57 percent of adolescents who need care, according to the authors of a recent study published in JAMA Pediatrics . School closures may be especially disruptive for children from lower-income families, who are disproportionately likely to receive mental health services exclusively from schools.
“The Covid-19 pandemic may worsen existing mental health problems and lead to more cases among children and adolescents because of the unique combination of the public health crisis, social isolation, and economic recession,” write the authors of that study.
A major concern the researchers point to: Since most mental health disorders begin in childhood, it is essential that any mental health issues be identified early and treated. Left untreated, they can lead to serious health and emotional problems. In the short term, video conferencing may be an effective way to deliver mental health services to children.
Mental health and academic achievement are linked, research shows. Chronic stress changes the chemical and physical structure of the brain, impairing cognitive skills like attention, concentration, memory, and creativity. “You see deficits in your ability to regulate emotions in adaptive ways as a result of stress,” said Cara Wellman, a professor of neuroscience and psychology at Indiana University in a 2014 interview . In her research, Wellman discovered that chronic stress causes the connections between brain cells to shrink in mice, leading to cognitive deficiencies in the prefrontal cortex.
While trauma-informed practices were widely used before the pandemic, they’re likely to be even more integral as students experience economic hardships and grieve the loss of family and friends. Teachers can look to schools like Fall-Hamilton Elementary in Nashville, Tennessee, as a model for trauma-informed practices .
3 Ways Teachers Can Prepare
When schools reopen, many students may be behind, compared to a typical school year, so teachers will need to be very methodical about checking in on their students—not just academically but also emotionally. Some may feel prepared to tackle the new school year head-on, but others will still be recovering from the pandemic and may still be reeling from trauma, grief, and anxiety.
Here are a few strategies teachers can prioritize when the new school year begins:
- Focus on relationships first. Fear and anxiety about the pandemic—coupled with uncertainty about the future—can be disruptive to a student’s ability to come to school ready to learn. Teachers can act as a powerful buffer against the adverse effects of trauma by helping to establish a safe and supportive environment for learning. From morning meetings to regular check-ins with students, strategies that center around relationship-building will be needed in the fall.
- Strengthen diagnostic testing. Educators should prepare for a greater range of variability in student learning than they would expect in a typical school year. Low-stakes assessments such as exit tickets and quizzes can help teachers gauge how much extra support students will need, how much time should be spent reviewing last year’s material, and what new topics can be covered.
- Differentiate instruction—particularly for vulnerable students. For the vast majority of schools, the abrupt transition to online learning left little time to plan a strategy that could adequately meet every student’s needs—in a recent survey by the Education Trust, only 24 percent of parents said that their child’s school was providing materials and other resources to support students with disabilities, and a quarter of non-English-speaking students were unable to obtain materials in their own language. Teachers can work to ensure that the students on the margins get the support they need by taking stock of students’ knowledge and skills, and differentiating instruction by giving them choices, connecting the curriculum to their interests, and providing them multiple opportunities to demonstrate their learning.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
current events conversation
What Students Are Saying About Living Through a Pandemic
Teenage comments in response to our recent writing prompts, and an invitation to join the ongoing conversation.

By The Learning Network
The rapidly-developing coronavirus crisis is dominating global headlines and altering life as we know it. Many schools worldwide have closed. In the United States alone, 55 million students are rapidly adjusting to learning and socializing remotely, spending more time with family, and sacrificing comfort and convenience for the greater good.
For this week’s roundup of student comments on our writing prompts , it was only fitting to ask teenagers to react to various dimensions of this unprecedented situation: how the coronavirus outbreak is affecting their daily lives, how we can all help one another during the crisis and what thoughts or stories the term “social distancing” conjures for them.
Every week, we shout out new schools who have commented on our writing prompts. This week, perhaps because of many districts’ move to remote online learning, we had nearly 90 new classes join us from around the world. Welcome to the conversation to students from:
Academy of St. Elizabeth; Abilene, Tex.; Alabama; Anna High School, Tex.; Arlington, Va.; Austria-Hungary; Baltimore, Md.; Bellingham, Wash.; Ben Lippen School; Bloomington, Ind.; Branham High School, San Jose, Calif.; Boston; Buffalo High School, Wyo.; Camdenton, Mo.; Cincinnati, Ohio; Collierville, Tenn.; Dawson High School, Tex.; Denmark; Desert Vista High School; Doylestown, Penn.; Dublin, Calif.; Dunkirk, N.Y. ; Eleanor Murray Fallon Middle School; Elmhurst, Ill.; Fairfax, Va.; Framingham, Mass.; Frederick, Md.; Hartford, Conn.; Jefferson, N.J.; Kantonschule Uster, Switzerland; Laconia, N.H.; Las Vegas; Lashon Academy; Lebanon, N.H.; Ledyard High School; Leuzinger High School; Livonia, Mich.; Manistee Middle School; Miami, Fla.; Melrose High School; Milton Hershey School, Hershey, Penn.; Milwaukee; Montreal; Naguabo, Puerto Rico; Nebraska; Nessacus Regional Middle School; New Rochelle, N.Y.; Newport, Ky.; Newton, Mass.; North Stanly High School; Oakland, Calif.; Papillion Middle School; Polaris Expeditionary Learning School; Pomona, Calif.; Portsmouth, N.H.; Pueblo, Colo.; Reading, Mass.; Redmond Wash.; Richland, Wash.; Richmond Hill Ontario; Ridgeley, W.Va.; Rockford, Mich.; Rovereto, Italy; Salem, Mass.; Scottsdale, Ariz.; Seattle, Wash.; Sequoyah School Pasadena; Shackelford Junior High, Arlington, Tex.; South El Monte High School; Sugar Grove, Ill.; St. Louis, Mo.; Timberview High School; Topsfield, Mass.; Valley Stream North High School; Vienna, Va.; Waupun, Wis.; Wauwatosa, Wis.; Wenatchee, Wash.; Westborough Mass.; White Oak Middle School, Ohio; and Winter Park High School.
We’re so glad to have you here! Now, on to this week’s comments.
Please note: Student comments have been lightly edited for length, but otherwise appear as they were originally submitted.
How Is the Coronavirus Outbreak Affecting Your Life?
The coronavirus has changed how we work, play and learn : Schools are closing, sports leagues have been canceled, and many people have been asked to work from home.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Writing about COVID-19 in a college admission essay
by: Venkates Swaminathan | Updated: September 14, 2020
Print article

For students applying to college using the CommonApp, there are several different places where students and counselors can address the pandemic’s impact. The different sections have differing goals. You must understand how to use each section for its appropriate use.
The CommonApp COVID-19 question
First, the CommonApp this year has an additional question specifically about COVID-19 :
Community disruptions such as COVID-19 and natural disasters can have deep and long-lasting impacts. If you need it, this space is yours to describe those impacts. Colleges care about the effects on your health and well-being, safety, family circumstances, future plans, and education, including access to reliable technology and quiet study spaces. Please use this space to describe how these events have impacted you.
This question seeks to understand the adversity that students may have had to face due to the pandemic, the move to online education, or the shelter-in-place rules. You don’t have to answer this question if the impact on you wasn’t particularly severe. Some examples of things students should discuss include:
- The student or a family member had COVID-19 or suffered other illnesses due to confinement during the pandemic.
- The candidate had to deal with personal or family issues, such as abusive living situations or other safety concerns
- The student suffered from a lack of internet access and other online learning challenges.
- Students who dealt with problems registering for or taking standardized tests and AP exams.
Jeff Schiffman of the Tulane University admissions office has a blog about this section. He recommends students ask themselves several questions as they go about answering this section:
- Are my experiences different from others’?
- Are there noticeable changes on my transcript?
- Am I aware of my privilege?
- Am I specific? Am I explaining rather than complaining?
- Is this information being included elsewhere on my application?
If you do answer this section, be brief and to-the-point.
Counselor recommendations and school profiles
Second, counselors will, in their counselor forms and school profiles on the CommonApp, address how the school handled the pandemic and how it might have affected students, specifically as it relates to:
- Grading scales and policies
- Graduation requirements
- Instructional methods
- Schedules and course offerings
- Testing requirements
- Your academic calendar
- Other extenuating circumstances
Students don’t have to mention these matters in their application unless something unusual happened.
Writing about COVID-19 in your main essay
Write about your experiences during the pandemic in your main college essay if your experience is personal, relevant, and the most important thing to discuss in your college admission essay. That you had to stay home and study online isn’t sufficient, as millions of other students faced the same situation. But sometimes, it can be appropriate and helpful to write about something related to the pandemic in your essay. For example:
- One student developed a website for a local comic book store. The store might not have survived without the ability for people to order comic books online. The student had a long-standing relationship with the store, and it was an institution that created a community for students who otherwise felt left out.
- One student started a YouTube channel to help other students with academic subjects he was very familiar with and began tutoring others.
- Some students used their extra time that was the result of the stay-at-home orders to take online courses pursuing topics they are genuinely interested in or developing new interests, like a foreign language or music.
Experiences like this can be good topics for the CommonApp essay as long as they reflect something genuinely important about the student. For many students whose lives have been shaped by this pandemic, it can be a critical part of their college application.
Want more? Read 6 ways to improve a college essay , What the &%$! should I write about in my college essay , and Just how important is a college admissions essay? .

Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

How our schools are (and aren't) addressing race

The truth about homework in America

What should I write my college essay about?
What the #%@!& should I write about in my college essay?
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience
I Thought We’d Learned Nothing From the Pandemic. I Wasn’t Seeing the Full Picture

M y first home had a back door that opened to a concrete patio with a giant crack down the middle. When my sister and I played, I made sure to stay on the same side of the divide as her, just in case. The 1988 film The Land Before Time was one of the first movies I ever saw, and the image of the earth splintering into pieces planted its roots in my brain. I believed that, even in my own backyard, I could easily become the tiny Triceratops separated from her family, on the other side of the chasm, as everything crumbled into chaos.
Some 30 years later, I marvel at the eerie, unexpected ways that cartoonish nightmare came to life – not just for me and my family, but for all of us. The landscape was already covered in fissures well before COVID-19 made its way across the planet, but the pandemic applied pressure, and the cracks broke wide open, separating us from each other physically and ideologically. Under the weight of the crisis, we scattered and landed on such different patches of earth we could barely see each other’s faces, even when we squinted. We disagreed viciously with each other, about how to respond, but also about what was true.
Recently, someone asked me if we’ve learned anything from the pandemic, and my first thought was a flat no. Nothing. There was a time when I thought it would be the very thing to draw us together and catapult us – as a capital “S” Society – into a kinder future. It’s surreal to remember those early days when people rallied together, sewing masks for health care workers during critical shortages and gathering on balconies in cities from Dallas to New York City to clap and sing songs like “Yellow Submarine.” It felt like a giant lightning bolt shot across the sky, and for one breath, we all saw something that had been hidden in the dark – the inherent vulnerability in being human or maybe our inescapable connectedness .
More from TIME
Read More: The Family Time the Pandemic Stole
But it turns out, it was just a flash. The goodwill vanished as quickly as it appeared. A couple of years later, people feel lied to, abandoned, and all on their own. I’ve felt my own curiosity shrinking, my willingness to reach out waning , my ability to keep my hands open dwindling. I look out across the landscape and see selfishness and rage, burnt earth and so many dead bodies. Game over. We lost. And if we’ve already lost, why try?
Still, the question kept nagging me. I wondered, am I seeing the full picture? What happens when we focus not on the collective society but at one face, one story at a time? I’m not asking for a bow to minimize the suffering – a pretty flourish to put on top and make the whole thing “worth it.” Yuck. That’s not what we need. But I wondered about deep, quiet growth. The kind we feel in our bodies, relationships, homes, places of work, neighborhoods.
Like a walkie-talkie message sent to my allies on the ground, I posted a call on my Instagram. What do you see? What do you hear? What feels possible? Is there life out here? Sprouting up among the rubble? I heard human voices calling back – reports of life, personal and specific. I heard one story at a time – stories of grief and distrust, fury and disappointment. Also gratitude. Discovery. Determination.
Among the most prevalent were the stories of self-revelation. Almost as if machines were given the chance to live as humans, people described blossoming into fuller selves. They listened to their bodies’ cues, recognized their desires and comforts, tuned into their gut instincts, and honored the intuition they hadn’t realized belonged to them. Alex, a writer and fellow disabled parent, found the freedom to explore a fuller version of herself in the privacy the pandemic provided. “The way I dress, the way I love, and the way I carry myself have both shrunk and expanded,” she shared. “I don’t love myself very well with an audience.” Without the daily ritual of trying to pass as “normal” in public, Tamar, a queer mom in the Netherlands, realized she’s autistic. “I think the pandemic helped me to recognize the mask,” she wrote. “Not that unmasking is easy now. But at least I know it’s there.” In a time of widespread suffering that none of us could solve on our own, many tended to our internal wounds and misalignments, large and small, and found clarity.
Read More: A Tool for Staying Grounded in This Era of Constant Uncertainty
I wonder if this flourishing of self-awareness is at least partially responsible for the life alterations people pursued. The pandemic broke open our personal notions of work and pushed us to reevaluate things like time and money. Lucy, a disabled writer in the U.K., made the hard decision to leave her job as a journalist covering Westminster to write freelance about her beloved disability community. “This work feels important in a way nothing else has ever felt,” she wrote. “I don’t think I’d have realized this was what I should be doing without the pandemic.” And she wasn’t alone – many people changed jobs , moved, learned new skills and hobbies, became politically engaged.
Perhaps more than any other shifts, people described a significant reassessment of their relationships. They set boundaries, said no, had challenging conversations. They also reconnected, fell in love, and learned to trust. Jeanne, a quilter in Indiana, got to know relatives she wouldn’t have connected with if lockdowns hadn’t prompted weekly family Zooms. “We are all over the map as regards to our belief systems,” she emphasized, “but it is possible to love people you don’t see eye to eye with on every issue.” Anna, an anti-violence advocate in Maine, learned she could trust her new marriage: “Life was not a honeymoon. But we still chose to turn to each other with kindness and curiosity.” So many bonds forged and broken, strengthened and strained.
Instead of relying on default relationships or institutional structures, widespread recalibrations allowed for going off script and fortifying smaller communities. Mara from Idyllwild, Calif., described the tangible plan for care enacted in her town. “We started a mutual-aid group at the beginning of the pandemic,” she wrote, “and it grew so quickly before we knew it we were feeding 400 of the 4000 residents.” She didn’t pretend the conditions were ideal. In fact, she expressed immense frustration with our collective response to the pandemic. Even so, the local group rallied and continues to offer assistance to their community with help from donations and volunteers (many of whom were originally on the receiving end of support). “I’ve learned that people thrive when they feel their connection to others,” she wrote. Clare, a teacher from the U.K., voiced similar conviction as she described a giant scarf she’s woven out of ribbons, each representing a single person. The scarf is “a collection of stories, moments and wisdom we are sharing with each other,” she wrote. It now stretches well over 1,000 feet.
A few hours into reading the comments, I lay back on my bed, phone held against my chest. The room was quiet, but my internal world was lighting up with firefly flickers. What felt different? Surely part of it was receiving personal accounts of deep-rooted growth. And also, there was something to the mere act of asking and listening. Maybe it connected me to humans before battle cries. Maybe it was the chance to be in conversation with others who were also trying to understand – what is happening to us? Underneath it all, an undeniable thread remained; I saw people peering into the mess and narrating their findings onto the shared frequency. Every comment was like a flare into the sky. I’m here! And if the sky is full of flares, we aren’t alone.
I recognized my own pandemic discoveries – some minor, others massive. Like washing off thick eyeliner and mascara every night is more effort than it’s worth; I can transform the mundane into the magical with a bedsheet, a movie projector, and twinkle lights; my paralyzed body can mother an infant in ways I’d never seen modeled for me. I remembered disappointing, bewildering conversations within my own family of origin and our imperfect attempts to remain close while also seeing things so differently. I realized that every time I get the weekly invite to my virtual “Find the Mumsies” call, with a tiny group of moms living hundreds of miles apart, I’m being welcomed into a pocket of unexpected community. Even though we’ve never been in one room all together, I’ve felt an uncommon kind of solace in their now-familiar faces.
Hope is a slippery thing. I desperately want to hold onto it, but everywhere I look there are real, weighty reasons to despair. The pandemic marks a stretch on the timeline that tangles with a teetering democracy, a deteriorating planet , the loss of human rights that once felt unshakable . When the world is falling apart Land Before Time style, it can feel trite, sniffing out the beauty – useless, firing off flares to anyone looking for signs of life. But, while I’m under no delusions that if we just keep trudging forward we’ll find our own oasis of waterfalls and grassy meadows glistening in the sunshine beneath a heavenly chorus, I wonder if trivializing small acts of beauty, connection, and hope actually cuts us off from resources essential to our survival. The group of abandoned dinosaurs were keeping each other alive and making each other laugh well before they made it to their fantasy ending.
Read More: How Ice Cream Became My Own Personal Act of Resistance
After the monarch butterfly went on the endangered-species list, my friend and fellow writer Hannah Soyer sent me wildflower seeds to plant in my yard. A simple act of big hope – that I will actually plant them, that they will grow, that a monarch butterfly will receive nourishment from whatever blossoms are able to push their way through the dirt. There are so many ways that could fail. But maybe the outcome wasn’t exactly the point. Maybe hope is the dogged insistence – the stubborn defiance – to continue cultivating moments of beauty regardless. There is value in the planting apart from the harvest.
I can’t point out a single collective lesson from the pandemic. It’s hard to see any great “we.” Still, I see the faces in my moms’ group, making pancakes for their kids and popping on between strings of meetings while we try to figure out how to raise these small people in this chaotic world. I think of my friends on Instagram tending to the selves they discovered when no one was watching and the scarf of ribbons stretching the length of more than three football fields. I remember my family of three, holding hands on the way up the ramp to the library. These bits of growth and rings of support might not be loud or right on the surface, but that’s not the same thing as nothing. If we only cared about the bottom-line defeats or sweeping successes of the big picture, we’d never plant flowers at all.
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Nicola Coughlan Bet on Herself—And Won
- What Kind of President Would Kamala Harris Be?
- Is Adrenal Fatigue Real?
- Why It's So Hard to Quit Vaping
- Our Guide to Voting in the 2024 Election
- The 10 Races That Will Determine Control of the Senate
- Column: How My Shame Became My Strength
- Meet TIME's Newest Class of Next Generation Leaders
Contact us at [email protected]

IMAGES
COMMENTS
How to Write About Coronavirus in a College Essay. Students can share how they navigated life during the coronavirus pandemic in a full-length essay or an optional supplement. By Josh Moody.
This paper attempts to shed light on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on college students. First, we describe and quantify the causal e ects of the COVID-19 outbreak on a wide set of students’ out-
As we outline in our new research study released in January, the cumulative impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on students’ academic achievement has been large. We tracked changes in math and...
To answer these questions, we compared students’ academic achievement and growth during the COVID-19 pandemic to the achievement and growth patterns observed in 2019.
Thanks to these advancements, relationships can stay connected, students can continue to learn, jobs can stay open, and the environment can subtly improve. Our modernized world is well enough suited to take on the troubling times that COVID-19 has brought along.
Fear and anxiety about the pandemic—coupled with uncertainty about the future—can be disruptive to a student’s ability to come to school ready to learn. Teachers can act as a powerful buffer against the adverse effects of trauma by helping to establish a safe and supportive environment for learning.
We asked students how their lives have changed since the onset of this pandemic. They told us about all the things they miss, what it’s like to learn online, and how they’re dealing with the...
Students working on college admission essays often struggle to figure out how to write about their experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic. For students applying to college using the CommonApp, there are several different places where students and counselors can address the pandemic’s impact.
The pandemic marks a stretch on the timeline that tangles with a teetering democracy, a deteriorating planet, the loss of human rights that once felt unshakable.
ABSTRACT. In this personal account of living through the coronavirus pandemic as a US graduate student, I reflect on the major events and themes that defined the time: the hasty closure of university campuses, the clumsy transition to remote learning, the economic consequences, the controversial reopening of campuses, and finally, my hopes for ...