

[Solved]Starbucks Delivering Customer Service Case Study Solution: 5 Questions answered
![[Solved]Starbucks Delivering Customer Service Case Study Solution: 5 Questions answered 3 Starbucks: Delivering Customer Service](https://www.simplimba.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/We-are-open-story-for-coffe-shop-and-cafe-576x1024.jpg)
Starbucks Delivering Customer Service case study comes from HBR. A link to the original case can be found here . The case can be analyzed from the perspectives of marketing, sales improvement, and from a strategic investment point of view. The company is contemplating a strategic investment of $40 Mn to bolster its systems and process to cater to the needs of new customers. We can also analyze Starbucks delivering customer service case study from the standpoint of future organizational vision and reinventing a brand
For more such solved case studies as the Starbucks Delivering Customer Service case study, please follow the link
Starbucks delivering customer service case study summary
In 1971, Gerald Baldwin, Gordan Bowker, and Ziev Siegl established a small shop in Seattle’s market. The company excelled at selling whole Arabica beans to coffee purists, a niche market. In 1982, Schultz joined Starbucks. A few years later, Schultz purchased the company. After he ascended to power, new stores opened. Starbucks delivering customer service Case Study also narrates the story of the owners and their vision for the organization in order to deliver a unique customer value
The organization went public. Both whole-bean coffee and coffee with a higher price tag were sold at the stores. By 1992, Starbucks had 140 stores in the Pacific Northwest and Chicago and was competing favorably with smaller coffee chains such as Gloria Jean’s Coffee Bean and Barnie’s Coffee & Tea. In 2002, Starbucks was the most well-known specialty coffee brand in North America. The company’s annual sales and net income grew at a rate of 40% and 50%, respectively. The company had over 5,000 stores worldwide and over 20 million customers.
It focused primarily on marketing at the point of sale and in local stores. The slogan “live coffee” encapsulated Starbucks’ brand positioning. It demonstrated how vital it was to preserve the national coffee culture , which provided customers with a “ experience” comprised of the coffee, the service, and the atmosphere. They were all baristas and were referred to as “partners. ” They believed that if partners were satisfied, so would customers. Consequently, employee turnover was low. When a partner was hired, he or she was required to complete “hard skills” and “soft skills” training in order to connect with customers more effectively.
Several types of matrices, such as monthly status reports and self-reported checklists, were used to evaluate the performance of the service. In addition, they had a mystery shopper program known as “customer overview The shopper rated four “fundamental services.” The company’s goal was to become “the most recognizable and esteemed brand in the world.” Starbucks vice president Christine Day devised a plan to invest an additional $40 million per year in the company’s 4,500 locations. This equates to an additional 20 hours of work per week. They are unsure whether to believe what customers say about customer service and its impact on sales and profits.
Starbucks Delivering Customer Service case study: What Contributed to the exceptional positioning of Starbucks in the Coffee Segment?
The extraordinary success of Starbucks in the early 1990s can be attributed to Howard Schultz, who added value propositions to the company by enhancing its services and adding quality to them. Schultz believed that coffee drinking creates an experience in the customer’s mind known as “the third place.”
Contributing to Starbucks’ extraordinary success in the 1990s were:
Starbucks works directly with its growers to maintain the superior quality of its coffee beans, and because all of its stores are company-owned, they are able to maintain tight control over its products and services.
Starbucks trains its partners in both hard and soft skills prior to hiring them in order to foster positive relationships with its customers. They instructed their employees on how to interact with customers by smiling, making eye contact, and remembering their names and preferences.
- The Customers : Their ‘Just Say Yes’ policy encourages partners to provide the best service possible, even if it exceeds company regulations, and their three-minute serving time enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Partner satisfaction : Schultz referred to Starbucks’ employees as “Partners,” and the company provides even entry-level employees with health insurance and company stock as a form of incentive. They believe that customer satisfaction depends on the satisfaction of their partners, which is why the company has one of the lowest employee turnover rates in the industry as a result of their promotion strategy of promoting partners within their rank and approximately 70% of the company store manager was an ex-partner.
- The atmosphere of Starbucks stores : Schultz’s intention is to create a drinking coffee experience, where people drink coffee not only for its taste and quality but also to enjoy the experience. It is a place where people come to relax and enjoy social interaction, which is why they have comfortable seating areas and the layout of their stores is inviting.
- Location of the stores: Starbucks stores are situated in high-traffic areas such as office buildings, shopping centers, and university campuses.
The store’s value proposition is so compelling because they provide high-quality premium coffee and services to their customers as a result of their highly controlled supply chain strategy. In addition, they serve additional menu items such as pastries, soda, and juice, and they regularly launch new products. They are so focused on their services that they are familiar with their customers if they frequent the establishment, and their attributes, ambiance, and seating environment are an added value proposition.
Starbucks Delivering Customer Service case study: What Factors led to the decline of Customer Satisfaction Scores in the Early 1990s?
The customer satisfaction rating for Starbucks has dropped as a result of a gap between the company’s primary attributes and the expectations that customers have for the brand. Paying a premium price for Starbucks did not make a whole lot of sense because the chain does not stand out in terms of either its image or its products when compared to other, smaller coffee shop chains.
Customers started believing that Starbucks had entered a money-making industry and that the company placed a higher priority on shop expansion than on their satisfaction. On many occasions, “service enhancement” and “service speed” were the areas that required the most improvement. Also shown in the presentation is the fact that 11.34 percent of people believe that improvements to the services they receive could make them feel more valued.
• As shown in Exhibit 10, the majority of respondents (83 percent) believe that maintaining a clean environment is an essential component in achieving high levels of customer satisfaction.
• Because seventy-seven percent of customers placed a high premium on convenience, Starbucks made it a point to open multiple locations across the country.
• Seventy-five percent of customers ranked being treated as a valuable customer as extremely important for the generation of customer happiness, and Starbucks partners made certain to remember their customers’ names, welcome them, and inquire about their preferred drink modification preferences, among other things.
Because of this, asserting that the company’s service has worsened in recent years would be an exaggeration, given that consumers continue to give Starbucks high marks in a variety of other categories. However, Starbucks is becoming increasingly concerned about the lengthening wait times.
Because Starbucks is more concerned with the value of its brand, expansion, and profit than with how customers perceive its coffee, the customer snapshot is not an ideal instrument for measuring customer happiness.
Starbucks Delivering Customer Service case study: How did Customer Transform from 1992 to the early 2000s?
The average customer in 2002 was younger than the average customer in 1992, and the average customer in 2002 had less education than the average customer in 1992.
•In 1992, Starbucks’ customers were mostly wealthy people, but by 2002, they also included people with lower incomes.
• The market research team also found that customers used stores, in the same way, no matter where they were or how they were set up.
• In the research, it was also found that the most frequent customers came in an average of 18 times a month, but the average customer only came in five times a month.
• The research team also found out that Starbucks’ customers had changed from wealthy, well-educated, white-collar women between the ages of 24 and 44 to younger customers with less education who wanted more options and took more work to please.
Is it advisable for Starbucks to Invest $40 Mn in its stores and staff? What is the rationale behind the investment and share a mathematical model to justify the investment?
The investment plan called for “relaxing the labor-hour restrictions in the stores” in order to increase the amount of available labor in each store by 20 hours per week at an additional annual cost of $40 million.
Starbucks Delivering Customer Service case study: Breakeven Calculations
Analysis of the Profitability of the Investment Plan Investment per Store = $40,000,000 / 5886 stores = $6795.8 per store
$172 is the revenue difference between customers who are satisfied and customers who are extremely satisfied.
For each location to be profitable, $6795.8 must be divided by 172, which equals forty customers. There are 570 customers who shop at each location on a daily basis.
For the company to become profitable, 40 of its 570 existing customers must be upgraded from satisfied to extremely satisfied. Therefore, Starbucks is recommended to invest $40 million in order to increase service speed and decrease the number of satisfied customers who become dissatisfied.
As there is a direct correlation between satisfied customers and loyal customers, this would result in the consumer base’s long-term commitment.
Starbucks Delivering Customer Service case study: The rationale behind the investment
The objective of investing $40 million in labor was to maximize customer satisfaction by converting satisfied customers into highly satisfied customers, thereby increasing revenue. This was accomplished by increasing the level of satisfaction of satisfied customers. Exhibit 10 displays the results of the 2002 consumer survey conducted by Starbucks. According to the survey, approximately 65 percent of Starbucks’ customers consider prompt service to be one of the most important factors in determining their level of satisfaction with their Starbucks coffee experience.
We have solved more than 50 Case Studies here .
If you have any comments regarding the solution, share unbiased feedback here
Follow me on LinkedIn or Quora
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Presentation on : Case study- Starbucks- Going Global Fast

Related Papers
Trí Tròn Trịa
bruceharris.net
Abdelhamid Mohamed
Giovanni Morra
University of Roehampton submitted paper
kelvin M Mutegi
virginia keshishian
Paul Patterson , Kevin Goh
The astounding growth and expansion of Starbucks is outlined, both on a global scale and within Austra-lia. The focus then shifts to the abrupt closure of three-quarters of the Australian stores in mid 2008. Several reasons for these closures are described and examined, including that: Starbucks overestimated their points of differentiation and the perceived value of their supplementary services; their service standards declined; they ignored some golden rules of international marketing; they expanded too quickly and forced themselves upon an unwilling public; they entered late into a highly competitive market; they failed to communicate the brand; and their business model was unsustainable. Key lessons that may go beyond the specifics of the Starbucks case are the importance of: undertaking market research and taking note of it; thinking globally but acting locally; establishing a differential advantage and then striving to sustain it; not losing sight of what makes a brand successful in the first place; and the necessity of having a sustainable business model.
Martina Vannevel
High product quality, service reliability, and management of operations are key factors in business growth and sustainability. Analyzing " The Starbucks Experience " is a pedagogical approach to reinforcing the concepts of control and management of quality, service reliability, and efficient operations in action. The objective of this paper is to show how providing high-quality, reliable products and service at Starbucks have influenced its market share, productivity, and profitability. In turn, Starbucks has improved on these business measures by excelling in operations management. The approach taken was to research the early days at Starbucks to gain insight on what made Starbucks so successful and then to use observational research to assess the customer experience at a particular Starbucks store in a city in the state of Michigan, USA. Sitting in this Starbucks store in the city's little downtown and observing its operations and customers contact offered the opportunity to observe customers waiting in line, the baristas serving the customers, examining the store's layout, and listening to conversations that revealed what customers like and dislike about " The Starbucks Experience. " Recommendations are made to improve operations. These areas fall under operations management for a company that sells a product and provides a service. There are three reasons customers choose Starbucks: the coffee, the people serving the coffee, and the experience in the stores. By excelling in these three areas and improving operations management, Starbucks can regain its market share, and improve productivity and profitability.
DR. NAJIHAH HANISAH MARMAYA
This study pertains to the use of the brand personality measurement framework as a means to investigate the pervasiveness of Starbucks, a foreign branded coffee outlet, in Malaysia. A survey was performed to obtain 261 consumer perceptions and opinions regarding the corporate branding ofa foreign coffee outlet brand in Malaysia. Data was collected through the use of questionnaires from respondents in various cities throughout Malaysia using purposive and convenience sampling methods. Statistical analysis, including factor and reliability analysis, has been applied in order to statistically validate the findings of this research. The results of the analysis indicate that consumers identify Starbuck's to be distinctive and a confident brand.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Duncan Holtom
Environmental Science: an Indian journal
zeid qamhieh
CHEMICAL & PHARMACEUTICAL BULLETIN
Hiroaki Ohno
Asian Journal of Biological Sciences
Afework Bekele
Rafaella Oliveira Baracho
Antonella Negro
Regional Science and Urban Economics
Rosina Moreno
Revista Brasileira de Entomologia
Agnelo de Souza
ABIODUN OLUSEGUN ODUNEWU
Sustainability
Abdelmohsen. A Nassani
Ciência e Natura
Mirla Weber
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy
Ilmiyah Ahmad
Lisa Holgado
BULLETIN OF THE TRANSILVANIA UNIVERSITY OF BRASOV • VOL. 8 (57) No.2 – 2015 .SERIES IV PHILOLOGY AND CULTURAL STUDIES,
nadina visan
Tamara Benzaquén
Javed Yasin
Journal of Management
Anales De La Universidad De Murcia
CF 19 JUAN A MATEOS
Revista Venezolana de Gerencia
Jesús Monterrosas García
Observatorio (OBS*)
Elisete Correia
masoud karimi
Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science
EMMANUEL JAMES
Technology and Culture
Tim Edensor
Jurnal Pengelolaan Sumberdaya Alam dan Lingkungan (Journal of Natural Resources and Environmental Management)
Hariyadi Hariyadi
See More Documents Like This
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Starbucks Marketing Strategy Unveiled | A Case Study
Jane Ng • 31 Oct 2023 • 5 min read
Are you curious about Starbucks marketing strategy? This global coffeehouse chain has transformed the way we consume coffee, with a marketing approach that’s nothing short of genius. In this article, we’ll dive deep into Starbucks marketing strategy, exploring its core elements, the 4 Ps of Starbucks’ Marketing Mix, and its success stories.
Table Of Contents
What is starbucks marketing strategy, key components of starbucks marketing strategy, the 4 ps of starbucks’ marketing mix, starbucks marketing success stories, key takeaways.
- FAQs About Starbucks Marketing Strategy

Starbucks marketing strategy is all about creating exceptional experiences for its customers. They do this by:
Starbucks’ Core Business Level Strategy
Starbucks is unique in the coffee world because it doesn’t just compete on price. Instead, it stands out by making special and high-quality products. They always aim for something new and innovative, which makes them different from others.
Starbucks Global Expansion Strategy
As Starbucks grows all over the world, it doesn’t use a one-size-fits-all approach. In places like India, China, or Vietnam, they change things up to suit what people there like while keeping the Starbucks style.
1/ Uniqueness and Product Innovation
Starbucks focuses on offering unique products and constant innovation.
- Example: Starbucks’ seasonal drinks like the Pumpkin Spice Latte and the Unicorn Frappuccino are excellent illustrations of product innovation. These limited-time offerings generate excitement and draw in customers seeking something different.

2/ Global Localization
Starbucks adapts its offerings to cater to local tastes while maintaining its core brand identity.
- Example: In China, Starbucks introduced a range of tea-based beverages and mooncakes for the Mid-Autumn Festival , respecting local traditions while keeping the Starbucks experience intact.
3/ Digital Engagement
Starbucks embraces digital channels to enhance customer experiences.
- Example: The Starbucks mobile app is a prime example of digital engagement. Customers can order and pay through the app, earning rewards and receiving personalized offers, simplifying and enriching their visits.
4/ Personalization and the “Name-on-Cup” Strategy

Starbucks connects with customers on a personal level through the famous “ name-on-cup ” approach.
- Example : When Starbucks baristas misspell customers’ names or write messages on cups, it often results in customers sharing their unique cups on social media. This user-generated content showcases personal connections and serves as free, authentic promotion for the brand.
5/ Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
Starbucks promotes ethical sourcing and sustainability.
- Example: Starbucks’ commitment to buying coffee beans from ethical and sustainable sources is evident through initiatives like C.A.F.E. Practices (Coffee and Farmer Equity) . This reinforces the brand’s commitment to environmental and social responsibility, attracting customers who value sustainability.
Product Strategy
Starbucks offers an array of products, not just coffee. From specialty beverages to snacks, including specialty beverages (e.g., Caramel Macchiato, Flat White), pastries, sandwiches, and even branded merchandise (mugs, tumblers, and coffee beans). Starbucks caters to a wide range of customer preferences. The company continually innovates and customizes its product offerings to maintain a competitive edge.
Price Strategy
Starbucks positions itself as a premium coffee brand. Their pricing strategy reflects this position, charging higher prices compared to many competitors. However, they also offer value through their loyalty program, which rewards customers with free drinks and discounts, promoting customer retention and attracting price-conscious consumers.
Place (Distribution) Strategy
Starbucks’ global network of coffee shops and partnerships with supermarkets and businesses ensures the brand is accessible and convenient for customers. It’s not just a coffee shop; it’s a lifestyle choice.

Promotion Strategy
Starbucks excels in promotion through various methods, including seasonal advertising campaigns, social media engagement, and limited-time offerings. Their holiday promotions, such as the “ Red Cup ” campaign, create anticipation and excitement among customers, increasing footfall and sales.
1/ The Starbucks Mobile App
Starbucks’ mobile app has been a game-changer in the coffee industry. This app seamlessly integrates into the customer experience, allowing users to place orders, make payments, and earn rewards all within a few taps. The convenience offered by the app keeps customers engaged and encourages repeat visits.
Additionally, the app is a data goldmine, providing Starbucks with insights into customer preferences and behaviors, enabling more personalized marketing.
2/ Seasonal and Limited-Time Offerings
Starbucks has mastered the art of creating anticipation and excitement with its seasonal and limited-time offerings. Examples like the Pumpkin Spice Latte (PSL) and the Unicorn Frappuccino have become cultural phenomena. The launch of these unique, time-limited drinks creates a buzz that extends beyond coffee enthusiasts to a broader audience.
Customers eagerly await the return of these offerings, turning seasonal marketing into a potent force for customer retention and acquisition.
3/ My Starbucks Rewards
Starbucks’ My Starbucks Rewards program is a model of loyalty program success. It puts the customer at the center of the Starbucks experience. It offers a tiered system where customers can earn stars for each purchase. These stars translate into various rewards, from free drinks to personalized offers, creating a sense of value for regular patrons. It boosts customer retention, elevates sales, and cultivates brand loyalty.
In addition, it enhances the emotional connection between the brand and its customers. Through personalized offers and birthday rewards, Starbucks makes its customers feel valued and appreciated. This emotional bond encourages not only repeat business but also positive word-of-mouth marketing.
Starbucks marketing strategy is a testament to the power of creating memorable customer experiences. By emphasizing uniqueness, sustainability, personalization, and embracing digital innovations, Starbucks has solidified its position as a global brand that extends far beyond coffee.
To enhance your own business’s marketing strategy, consider incorporating AhaSlides. AhaSlides offers interactive features that can engage and connect with your audience in novel ways. By harnessing the power of AhaSlides, you can gather valuable insights, personalize your marketing efforts, and cultivate stronger customer loyalty.
FAQs About Starbucks Marketing Strategy
What is the marketing strategy of starbucks.
Starbucks’ marketing strategy is built on delivering unique customer experiences, embracing digital innovation, ensuring product quality, and promoting sustainability.
What is Starbucks most successful marketing strategy?
Starbucks’ most successful marketing strategy is personalization through its “name-on-cup” approach, engaging customers and creating social media buzz.
What are the 4 P’s of marketing Starbucks?
Starbucks’ marketing mix consists of Product (diverse offerings beyond coffee), Price (premium pricing with loyalty programs), Place (global network of stores and partnerships), and Promotion (creative campaigns and seasonal offerings).
References: CoSchedule | IIMSkills | Mageplaza | MarketingStrategy.com

A writer who wants to create practical and valuable content for the audience
More from AhaSlides


Provide details on what you need help with along with a budget and time limit. Questions are posted anonymously and can be made 100% private.

Studypool matches you to the best tutor to help you with your question. Our tutors are highly qualified and vetted.

Your matched tutor provides personalized help according to your question details. Payment is made only after you have completed your 1-on-1 session and are satisfied with your session.

- Homework Q&A
- Become a Tutor
All Subjects
Mathematics
Programming
Health & Medical
Engineering
Computer Science
Foreign Languages
Access over 20 million homework & study documents
Starbucks case study ppt.

Sign up to view the full document!


24/7 Homework Help
Stuck on a homework question? Our verified tutors can answer all questions, from basic math to advanced rocket science !

Similar Documents
working on a homework question?
Studypool is powered by Microtutoring TM
Copyright © 2024. Studypool Inc.
Studypool is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university.
Ongoing Conversations

Access over 20 million homework documents through the notebank
Get on-demand Q&A homework help from verified tutors
Read 1000s of rich book guides covering popular titles

Sign up with Google
Sign up with Facebook
Already have an account? Login
Login with Google
Login with Facebook
Don't have an account? Sign Up
The marketplace for case solutions.
Starbucks – Case Solution
This case study analysis focuses on the identification and examination of the forces in the competitive environment surrounding Starbucks and the company's ability in relation to the coffee industry. It discusses the core competencies of Starbucks and the alternatives and opportunities for growing its retail operations.
Mary M. Crossan; Ariff Kachra Harvard Business Review ( 98M006-PDF-ENG ) June 18, 1998
Case questions answered:
Case study questions answered in the first solution:
- Section I: Situation Analysis. Write a summary of the situation of the market Starbucks is operating in at the time of the case. The purpose of the Situation Analysis is to frame the environment in which Starbucks is operating and planning to grow. In order to assist in this section, a copy of a well-respected tool entitled the 5Cs. This is a format you can use as a general reference in order to develop a picture of Starbucks’ opportunities and challenges.
- Section II: Starbucks Position. Describe Starbucks’ apparent position in the market. Describe the primary values that Starbucks brings to its target audience(s). Highlight critical features and attributes that make the Starbucks brand “real” and believable in the eyes of consumers.
- Section III: Options. In your analysis of the Market and Starbucks position, develop 3 options you believe Starbucks should consider as they move to expand and grow the business. Cite and briefly explain one primary reward that might be achieved for each option and one primary risk that might cause the option to fail.
- Section IV: Proposal. Develop a set of Guidelines for Starbucks management to follow in making decisions to adopt options and expand the business while staying true to the delivery of market expectations. This section should be reasonably specific as to the things and values Starbucks would want to include in any expansion of its brand, including internal growth and external opportunities (e.g., Frappuccino).
Case study questions answered in the second solution:
- What is your assessment of the impact of each of the five competitive forces on the retail coffee-house industry?
- Based on your assessment of these forces, how attractive is this industry? Explain your answer.
Not the questions you were looking for? Submit your own questions & get answers .
Starbucks Case Answers
You will receive access to two case study solutions! The second is not yet visible in the preview.
Problem Statement – Starbucks Case Study
The problem statement, in this case, is trying to figure out where to take Starbucks from here.
Situational Analysis – The Starbucks Company
The market size and growth are consistently expanding, which means consumers are not worried about spending their money on quality drinks. Consumers’ perception of coffee has changed as the lifestyle behind coffee has changed.
If Starbucks tackles the international market, it would only benefit the company as it could be ahead of competitors and have the first mover’s advantage. Making sure they maintain their brand locally and internationally will increase consumers’ brand loyalty as well as their cash flow.
PESTEL Analysis
Political/legal.
Starbucks should keep in mind the taxation policy. Some countries impose high taxation on farmers, for example. Any sort of fluctuation in taxes on supplies will be apparent in products and will affect consumers.
The company should also keep in mind trade regulations. Some countries like Argentina and Saudi Arabia have stricter laws when it comes to trade. The company needs to make sure, when it goes globally, that it keeps its mission, vision, and product intact while respecting the culture.
Starbucks needs to keep in mind certain aspects, such as the inflation rate, growth in average income, and the growth of the economy .
There are certain risks that come with going internationally. For example, if the economy stops growing as opposed to what the company predicts, then that could affect the business majorly. Consumers will not spend on the company’s products, and it will leave the company with a dent in its profitability.
Porter’s Five Forces: Competitive Rivalry
Starbucks has shown tremendous growth and strength in its brand. However, competitors are able to affect their success. The company’s US competitors are Green Mountain, Brothers, Coffee People, Diedrich, and other products such as juice, soft drinks, and non-coffee-related drinks.
As shown in Exhibit 1, the company seems to be the lead in the industry compared to U.S. and Canadian companies.
The company should keep in mind the consumers in order to beat any incoming competitor, whether it is a coffee drink, place, or a non-coffee drink. The mind of the market is based on consumers’ needs and wants, and based on that, the company should cater to the consumer.
At the same time, they should keep in mind their vision, mission, and environment while catering to their consumer.
Starbucks Position
Starbucks positions itself in the market as a…
Unlock Case Solution Now!
Get instant access to this case solution with a simple, one-time payment ($24.90).
After purchase:
- You'll be redirected to the full case solution.
- You will receive an access link to the solution via email.
Best decision to get my homework done faster! Michael MBA student, Boston
How do I get access?
Upon purchase, you are forwarded to the full solution and also receive access via email.
Is it safe to pay?
Yes! We use Paypal and Stripe as our secure payment providers of choice.
What is Casehero?
We are the marketplace for case solutions - created by students, for students.
- Preferences

Starbucks Case Study - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

Starbucks Case Study
Starbucks case study john baab, charly costigan, tyler kleckner, ashley kreuer, ellen park, ashley wooding outline background and history gerald baldwin, gordon ... – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- John Baab, Charly Costigan,
- Tyler Kleckner, Ashley Kreuer,
- Ellen Park, Ashley Wooding
- Gerald Baldwin, Gordon Bowker, and Ziev Siegl opened a small coffee shop in Seattles Pike Place Market in 1971
- Howard Schultz Joined the Starbucks marketing team
- Traveled to Italy and became interested in the espresso bars and tried to bring it to America
- Founders sold the company to Shultz
- Began to open new stores and had 140 stores by 1992
- Decided to take the company public and succeeded by opening more stores
- Shultz continued to take the position as chairman and chief global strategist and hired CEO Orin Smith in 2002
- To satisfy customers and to create a third place environment
- Three components to branding strategy the coffee itself, service, and atmosphere
- 5,886 stores(4574 National, 1312 International)
- Customers(20 million total, 570 per week per store)
- Net Income of 215 million
- Customer Demographic (Traditional vs. New)
- Menu (Average price of drink 3.85, 30 drinks, and 23 whole bean coffee blends)
- Partners 360 total labor hours and an average pay rate of 9.00 per hour
- Partnerships (Pepsi Bottling Co., Kraft Foods, and Dreyers Ice cream)
- Starbucks Share of Specialty Coffee Market 50 (estimate) 20.5 Total Market Share
- Well developed and established brand strategy live coffee
- Product Mix
- Customization of Drinks
- Caused tension between product quality and customer focus
- Increased menu size
- Lacked a strategic marketing group
- Very little image product differentiation
- Increase Customer Satisfaction
- Customer Quota
- Increase the number of stores
- Domestically/Internationally
- Create New Products Services
- Competition
- Donut Bagel Chains
- Small scale specialty coffee chains
- Key Problem Maintaining a customer focused brand image while continuing expansion
- Customer Satisfaction
- Lost sight of the consumer
- Lost connection between customers and growing business
- Service gap
- Investment Plan
- 40 million annually
- Add 20 labor hours a week
- Maintain 3 minute service time goal
- Increase customer satisfaction
- Goal All stores achieve 20,000 increase in weekly sales
- New Incentives for customer
- Ideas Drink of the day, membership cards, serve at your seat
- Incentives for Partners
- Adding 20 hours during peak hours to maintain 3 minute time
- More authority to regional retail managers
- Install a rolling menu policy
- Moving into new domestic and international markets
- Not saturating existing markets
- Instead move into untapped domestic markets and increase through put at current stores through added hours
- Advantages Will appear more customer focused locally, faster
- customer service
- brand image
- Marketing plan
- International
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.


Starbucks Case Study
Jul 09, 2014
320 likes | 1.09k Views
Starbucks Case Study. The Acquisition of Seattle’s Best Brad Gilbert Jessica Iversen Holly Kunz Methodist University . Overview. Who? What? When? Where? How? Why? Courses of Action Solution/Results. Who?. HISTORY Starbucks is the largest coffeehouse company in the world
Share Presentation
- financial management issue
- grocery stores
- wet whisker
- starbucks specialty barista bar

Presentation Transcript
Starbucks Case Study The Acquisition of Seattle’s Best Brad GilbertJessica IversenHolly KunzMethodist University
Overview • Who? • What? • When? • Where? • How? • Why? • Courses of Action • Solution/Results
Who? HISTORYStarbucks is the largest coffeehouse company in the world -Founded in Seattle in 1971 -Over 17,009 locations in over 50 countries -2010 Net income $945,600
Who? Seattle’s Best Coffee HISTORY: -1970 Whidbey Island, Washington (Wet Whisker)-Stewart Brothers Coffee Pier 70 -Pike Place Market -1988 SBC- local restaurant blind taste test -1998 AFC Enterprises
Starbucks vs. Seattle’s Best 2003 Comparison • 4,952 location in North America • 90 Seattle locations • # of employees • Retained Earnings • 129 locations in North America • 22 Seattle locations • # of employees • Annual sales (2002) $
What? • The Acquisition of Seattle’s Best Coffee (Set the scene, give background) • AFC Enterprises accounting scandal • Seattle’s Best and Cinnabon up for sale • (The sale of these companies has allowed AFC Enterprises to shift focus to Popeye’s and maximize the value of their portfolio)
When? • April 2003 (timeframe)
Where? • Seattle, Washington (location)
How? • Both Starbucks and Seattle’s Best Coffee are major companies in the Seattle and the Pacific Northwest coffee scene. They are often competitors for the same retail space. Both have loyal fans with an almost cult-like devotion to their preferred brand. (Identify main players/relationships/interactions)
Why? • Should Starbucks continue to compete with Seattle’s Best Coffee? Starbucks had the money and saw an opportunity to acquire their competitor. Should they purchase them to close them down, prevent them from growing, or use them to expand the overall corporation? (address financial management issue-issue that forces an examination of all courses of action)
Courses of Action • 1. Do not buy Seattle’s Best. Continue to compete and operate as before. • 2. Buy SBC and close them down and completely absorb them. • 3. Buy SBC and keep them as a separate company. Create differentiation between brands. Use SBC distribution network to help Starbucks enter grocery stores.
The Future of Starbucks • Starbucks/Peet’s Merger • Starbucks/Green Mountain • Starbucks Specialty Barista Bar • Regional Beer/Wine/Cheese
References • http://www.seattlepi.com/business/article/Starbucks-to-buy-Seattle-s-Best-Coffee-1112367.php • http://adage.com/print/96033
Starbucks vs. Seattle’s Best
- More by User

Starbucks. Emilia Margherita Janek Kostis Diana Nicole. Starbucks ´ strategy. The Starbucks ' strategy consistent in the ability to balance financial profitability and social impact. Starbucks´ strategy. Enterprise's location Advertising through social medias
833 views • 16 slides

case: starbucks
Domestic Growth. Main goal is to continuously expand its retail operations and to selectively pursue more opportunities to advance the Starbucks brand throughout the United States.Starbucks ended 2001 with a total of 4,709 retail locations. At the end of 2004 they had a whopping 8,337 locations with a forecast of over 10,000 retail establishments by the close of 2005.US will occupy over 8,000 of the 10,000 locations..
416 views • 0 slides

Corporate and Industry Background as presented by Group One: Jessica Baker, Tonya McGonigal, Emily Porter, Tim Porter and Robert Seitzinger. Starbucks. Profiling Starbucks. Size 6,793 Company Operated Stores 3,891 Licensed Stores (In Safeway, Albertson’s Etc.)
1.17k views • 19 slides

Starbucks. Back to the Basics. Promotional Strategy . What model does Starbucks use? Push Model Pull Model Current marketing/promotion strategy Analysis of promotion strategy Future marketing recommendations . Starbucks Marketing Model. Push Promote to wholesaler Pull
4.72k views • 17 slides

Starbucks Coffee France SAS Best in France Case Study
Starbucks Coffee France SAS Best in France Case Study. Alexandre Borsari Damien Hammouchi Stéphanie Jaccaz. The Company. Why in France ?. A label. Constraints. Adaptation. Conclusion. Key numbers : Annual Sales Turnover in billions of US dollars :. The Starbucks company (1/2).
328 views • 8 slides

Global Marketing Management Case Study: Starbucks
Global Marketing Management Case Study: Starbucks. MKTG 3215-001 Spring 2013 Mrs. Tamara L. Cohen. Class #7. Starbucks. Readings for this class: Course Pack reading # 11: “Starbucks’ quest for healthy growth: An interview with Howard Schultz”
733 views • 11 slides

Presented by: Alex Arellano Luis Mendoza Maurice Hinrich Thomas Dimitriou November 21, 2013 Practicum #8 Bus 306-01. Starbucks. Entering a Foreign Market. Agenda. Company Background Introducing Venezuela Marketing Mix Integrating The Four P’s Timeline Long Term Planning
1.08k views • 19 slides

Starbucks. Evelyn - Chanel - Balazs - Natalie - Alicia. History. The first Starbucks was opened in Seattle , on March 30, 1971 by three teachers. Starbucks got it’s name from a character in the book Moby Dick. .
1.14k views • 22 slides

Starbucks. Ethan Stone Erica Amaya. History of Starbucks. The history of Starbucks starts back in 1971 when the first store opened in Seattle, Washington.
1.4k views • 19 slides

Starbucks. Starbuck’s. Starbucks has been the largest coffee house organization Starbuck sold coffee products through its coffee house chain 17,000 distribution stores globally with its produce diversity Coffee Food Snacks Salads
1.41k views • 10 slides

1.07k views • 17 slides

Starbucks observational study
Starbucks observational study. Analyze the Data. Present Task: Analyze the Data. What did we learn from the data? Does this sample convince you that more than half of all customers at this store are female? What do you think the real percentage is? 60%, 70%, 80%?
281 views • 6 slides

Starbucks. Madalyn Dunn. Starbucks: The Beginning. Expansion. Expansion Problems: Economic. Declining economic conditions Unexperienced workforce Shortage of acceptable real estate Local price range of commodities Saturated market/self cannibalization. Expansion Problems: Political.
3.17k views • 17 slides

Live Case: Starbucks
Live Case: Starbucks. Starbucks. The problem: http://video.aol.com/video-detail/starbucks-earnings-analysis/1182319667/?icid=VIDURVBUS05 http://finance.google.com/finance?client=ob&q=NASDAQ:SBUX. Starbucks. Your task: Develop a solution to their malaise.
308 views • 3 slides

STARBUCKS A Case Analysis
STARBUCKS A Case Analysis. PREPARED AND PRESENTED BY: WASSEM AMIN, DARREN APPLEGATE, TIM KELLY, BARBARA KERSHNER, ERALD SINO, EWA SITARSKI, KLITON XHEMALI. GR 732 Marketing Management 2007. Case Analysis Outline. I. Executive Summary ~ T. Kelly
782 views • 47 slides

Questions to Consider for Starbucks Case
Questions to Consider for Starbucks Case. What has made Starbucks successful? What business is Starbucks in? When consumers buy Starbucks coffee what are they buying? What are Starbucks core competencies and key strategic assets? Which growth strategy should Starbucks choose? Why?
1.08k views • 7 slides

Portfolio Managers: Honglu Liu Min Min Chen Rafi Qi He Presented April 17, 2012. Starbucks. Introduction. SBUX Current Price @2012/4/16: $ 59.65 GICS map: 30201030 Industry: Coffee Production Founded in 1971 as a coffee bean roaster and retailer
1.24k views • 33 slides

Case Study # 10 Starbucks Going Global Fast Group 5
Case Study # 10 Starbucks Going Global Fast Group 5. Group Members. Mauricio Gonzalez Bui Thi Thuy Chantharas Kanchanakool Nina Krapf Vincent Tenchavez Julia Vassiljeva. Outline. Starbucks Case Study Background Entering the Global Market Controllable Elements Uncontrollable Elements
1.11k views • 51 slides

Live Case: Starbucks. January 12, 2009. Starbucks. The problem: http://www.reuters.com/finance/stocks/keyDevelopments?symbol=SBUX.O&timestamp=20081204202900&rpc=66 http:// finance.google.com/finance?client=ob&q=NASDAQ:SBUX
199 views • 4 slides

Live Case: Starbucks. January 12, 2009. External Environmental Factors Shaping A Company’s Choice of Strategy. Porter’s Five Forces Model of Competition. Complementors. Starbucks. The problem:
303 views • 5 slides

Starbucks Rewards Case Study – What Makes It Work?
Starbucks offers one of the most sought-after loyalty programs u2018Starbucks Rewardsu2019 program that offers freebies and discounts to members giving them plenty of reasons to choose Starbucks over other players. Read the insightful case study blog post to know more.
74 views • 6 slides
- Social Media
Ppt on Starbucks Case Study
Embed Size (px):
Transcript of Ppt on Starbucks Case Study

STARBUCKS CORPORATION

Group members
Darpan GoswamiDurlov Protim BoruaTanvi HussainPranami BorahDimpal Bharali
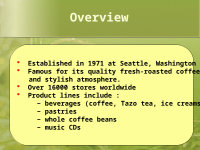
Established in 1971 at Seattle, Washington Famous for its quality fresh-roasted coffee beans and stylish atmosphere. Over 16000 stores worldwide Product lines include :
− beverages (coffee, Tazo tea, ice creams)− pastries− whole coffee beans− music CDs

1971 – Starbucks opened in Seattle’s Pike Place Market.
1982 – Howard Schultz joined Starbucks .1983 – Schultz travelled to Italy
1985– Howard Schultz established Il Giornale Coffee bar.
1987 – Il Giornale acquired Starbucks and changed the name into Starbucks Corporation.
1992 – Starbucks went public at $17 a share
1996 – Starbucks Coffee International opens its first non-North American store in Japan at Tokyo

1996 – Starbucks’ began selling bottled Frappuccino.
1998 – Acquired Seatle Coffee company.
1999 – Starbucks acquired Tazo Tea company. 1999 – Acquired Hear Music, a San Francisco-based company 1999 – Starbucks opened in China(Beijing) 2002 – Starbucks opened in Mexico ( first store in an origin country)

Mission Statements
Company Mission Statement: “Establish Starbucks as the premier
purveyor of the finest coffee in the world while maintaining our uncompromising principles while we grow.”
Environmental Mission Statement: “Starbucks is committed to a role of
environmental leadership in all facets of our business.”

Strengths Efficient Management Sound financial position Valued and motivated employees Effective distribution channel Increase in Product line Good corporate image Well trained staff Industry market leader Ambience of Starbuck stores

Profit generation slowed downProduct pricing(expensive)SizePromotion strategySelf cannibalization

Opportunities
Emerging International marketsGood relations with suppliers and
partnersSatisfied customersHigh visibility locationsLocal themed food items Alliance and acquisitionsExclusive purveyor of Narino Supremo

US market saturationAntiglobalizationFierce competitionMediaCultural and political issues in Foreign

Core Competencies
Starbucks branding High quality Good reputation
Ability to innovate, adapt to the culture Product: adapt to the taste Service: maintain the customer loyalty
Value creation Customers Employees Suppliers

The problem is anti-globalization which makes more difficult for Starbucks to enter in new markets
Symptoms:• Protests from anti-globalization activists• Those activists have enough media power it leads to
international scandals.• They receive push-backs in new markets

Analysis using porters five forces model
Other beverages apart from star bucks coffee and tea –include soda fruit juice, water, beer and other alcoholic drinks
Lower end or “less luxurious” coffee places Places that offer people a place to hang out, chat, relax or even
work e.g. tea houses, fast food places, bars.. Entry barrier for coffee industry is relatively low, even for premium
brands like star bucks Threat of new entrants include fast food chains such as
McDonalds, Burger King etc.
Threat of substitution

Competitive rivalry
Other coffee chains. examples include Café Nero, Coffee Republic & Costa Coffee.
Smaller privately owned coffee houses Secondary coffee houses like McDonalds, Burger King

Bargaining power of suppliers
Low bargaining power of suppliers due to importance of star bucks business to any individual suppliers
Suppliers of plastic products like cups,napkins,lids etc have little amount of bargaining power as large amount of alternatives are available
With new entrants like McDonalds who claim to offer premium roast coffee of reasonable quality for lower price which increases the bargaining power of buyers

Starbucks’ Strategy
Rapid store expansion strategy
• Domestic store expansion− “Starbucks everywhere” approach
• International store expansion− Company-owned and company-operated stores or licensing − Created a new subsidiary, Starbucks Coffee International− Expanded its consumer products channel in Asia Pacific region

• Employee Training and Recognition− Systems to recruit, hire and train baristas and store managers
training programs awards for partners
• Store Design, Planning, and Construction− High-traffic, high-visibility store locations− Control of average store opening costs
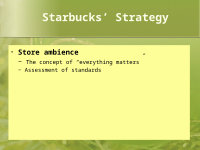
• Store ambience− The concept of “everything matters”
− Assessment of standards

Product Line
•Wide range of products choices•Selling music CDs •Joint ventures
PepsiCoDreyer’s Grand Ice Cream
•Acquisitions Hear Music Seatle coffee company

Financial Analysis
Proprietory ratio or equity ratio= Shareholders fund/ Total assets= 0.75
Gross profit ratio= 73% Operating ratio= Cost of goods sold+ operating
expenses/net sales *100 = 57.45% Debt-equity ratio= outsiders fund/shareholders

Recommendations
Increase spending on advertisement Create a specific brand for European expansion,
or acquire an already well established brand with still growth potential left
Expand and enhance the existing network by targeting new markets
Rethink their blanket strategy Involvement in more social responsibility
campaign They should come up with more food products

Starbucks should come up with more vending machines in places of high footfall
They should establish coffee lounge with sections dedicated to movies, music, books in big cities
They should also increase its presence in developing countries
Try to develop good relations with NGOs

Starbucks Case Analysis

Starbucks Consulting Case

Case Study: Starbucks

Starbucks Case

Week 5 starbucks ppt draft

Starbucks Marketing Case

Final Ppt ( Advertising) Starbucks

Starbucks Corporation Ppt Ashok Lahoty

Study Case - Starbucks

Starbucks ppt for marketing assignment

Starbucks Case Mine

Starbucks Scm PPT

Starbucks corporation (indian coffee) PPT

Starbucks Corporation A Case Study Should Starbucks enter Vietnam?

Starbucks case-study

Starbucks final ppt

The Starbucks Case

Starbucks Case Study.docx

STARBUCKS CASE STUDY.pdf

Case study Starbucks
- Cookie policy
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2022 FDOCUMENTS

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Strategic Analysis Of Starbucks Corporation Starbucks, with its size and scale, has the power to take advantage of its suppliers but it maintains a Fair trade certified coffee under its coffee and farmer equity (C.A.F.E) program, which gives its suppliers a fair partnership status, which yields them some moderately, low power. 7
Starbucks Delivering Customer Service case study: Breakeven Calculations. Analysis of the Profitability of the Investment Plan Investment per Store = $40,000,000 / 5886 stores = $6795.8 per store. $172 is the revenue difference between customers who are satisfied and customers who are extremely satisfied.
Introduction. Starbucks Corporation is an American multinational chain of coffeehouses and roastery reserves headquartered in Seattle, Washington. The company operates in over 30,000 locations in 70 countries worldwide as of early 2020. This blog is an in-depth analysis of Starbucks' marketing strategies, complete with touching upon their ...
Paul Patterson, Kevin Goh. The astounding growth and expansion of Starbucks is outlined, both on a global scale and within Austra-lia. The focus then shifts to the abrupt closure of three-quarters of the Australian stores in mid 2008. Several reasons for these closures are described and examined, including that: Starbucks overestimated their ...
Starbucks marketing strategy is a testament to the power of creating memorable customer experiences. By emphasizing uniqueness, sustainability, personalization, and embracing digital innovations, Starbucks has solidified its position as a global brand that extends far beyond coffee. To enhance your own business's marketing strategy, consider ...
Starbucks Company.pptx - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
Students Name Institutional Affiliation Course Date Introduction The case involves Starbucks founded in 1971 to sell high quality whole beans coffee. In 2017, Seattle-sited worldwide coffee chain Starbucks was ranked the third most appreciated firm in the globe. Currently, the firm is the ultimate coffee entity around the globe with an effective expansion strategy. The growth of Starbucks is ...
Seattle's Best Coffee HISTORY: -1970 Whidbey Island, Washington (Wet Whisker)-Stewart Brothers Coffee Pier 70 -Pike Place Market -1988 SBC- local restaurant blind taste test -1998 AFC Enterprises. Starbucks vs. Seattle's Best 2003 Comparison • 4,952 location in North America • 90 Seattle locations • # of employees • Annual sales ...
Summary Starbucks Corporation, an American company founded in 1971 in Seattle, WA, is a premier roaster, marketer and retailer of specialty coffee around world. Starting as a single shop specializing in high quality coffee and brewing products the company grew to be the largest roaster in Washington with multiple locations until the early 80's. In 1987, Howard Schultz led a group of ...
Case study questions answered in the first solution: Section I: Situation Analysis. Write a summary of the situation of the market Starbucks is operating in at the time of the case. The purpose of the Situation Analysis is to frame the environment in which Starbucks is operating and planning to grow. In order to assist in this section, a copy ...
Solutions Available. Louisiana State University, Shreveport. MADM 760. homework. Week 4 Quiz Attempt 3.docx. Solutions Available. Ashford University. HCA 421. Tm16_Wk2.pptx. ... MADM760 - Spring 2019 PPT DECK ASSIGNMENT #1 Starbucks Case Study Dr. Michael D. Meeks <[email protected] ...
Starbucks Case Presentation 1: P31: Make a list of Starbucks' goals. Describe what type of goal each is. Then, describe how that stated goal might affect how the following employees do their job: (b) a quality assurance technician at the company's roasting plant in Amsterdam (c) a regional sales manager Make a list of Starbucks' goals. Goals: Goals (objectives) are desired outcomes or targets.
Description: Starbucks Case Study John Baab, Charly Costigan, Tyler Kleckner, Ashley Kreuer, Ellen Park, Ashley Wooding Outline Background and History Gerald Baldwin, Gordon ... - PowerPoint PPT presentation. Number of Views: 4405. Avg rating:3.0/5.0.
Seattle's Best Coffee HISTORY: -1970 Whidbey Island, Washington (Wet Whisker)-Stewart Brothers Coffee Pier 70 -Pike Place Market -1988 SBC- local restaurant blind taste test -1998 AFC Enterprises. Starbucks vs. Seattle's Best 2003 Comparison • 4,952 location in North America • 90 Seattle locations • # of employees • Retained ...
Howard Schultz joined Starbucks . Schultz travelled to Italy. 1985 1987. Howard Schultz established Il Giornale Coffee bar. Il Giornale acquired Starbucks and changed the name into Starbucks Corporation. 19921996. Starbucks went public at $17 a share Starbucks Coffee International opens its first non-North American store in Japan at Tokyo. Timeline