
The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models


Coca-Cola’s Business And Distribution Strategy In A Nutshell
Coca-Cola’s distribution strategy involves initial investments in bottling partners, transitioning to a franchising model . Exclusivity agreements, marketing investments, and a hybrid approach balance control and independence. As bottling operations stabilize, they’re re-franchised, enabling global expansion with low capital expenditure. This differs from McDonald’s, which emphasizes real estate control in its franchising.
Coca-Cola follows a business strategy (implemented in 2006) where it invests initially in bottling partners’ operations through its operating arm – the Bottling Investment Group.
As they take off, Coca-Cola divests its equity stakes and establishes a franchising model as a long-term growth and distribution strategy .
Table of Contents
The secret isn’t in the secret formula but in its distribution strategy .
The Coca-Cola Company’s business model is based on five large independent bottling partners.
In 2019, these five bottling partners represented 40 percent of the total unit case volume the company sold.
Coca-Cola has separate agreements with bottling partners for manufacturing and selling the company’s products.
As specified by Coca-Cola,
“The bottler’s agreements generally authorize the bottlers to prepare, package, distribute and sell Company Trademark Beverages in authorized containers in an identified territory. The bottler is obligated to purchase its entire requirement of concentrates or syrups for the designated Company Trademark Beverages from the Company or Company-authorized suppliers.”
Coca-Cola typically agrees to refrain from selling or distributing, or from authorized third parties to sell or distribute, the Company Trademark Beverages throughout the identified territory, to guarantee bottling partner exclusivity under that territory and product.
However, Coca-Cola typically reserves the right to manufacture and distribute its trademarked products and brands.
In exchange, Coca-Cola also participates in its bottling partners’ sales and marketing activities.
For instance, in 2019, Coca-Cola spent $4.4 billion in promotional and marketing programs with bottling partners.
Coca-Cola’s short-term chain, long-term franchise-model
Coca-Cola’s strategy for building, growing, and maintaining its distribution system is pretty fluid.
Indeed, in most cases, Coca-Cola leverages a network of independent bottling partners.
In some cases, Coca-Cola places strategic investments in some bottling partners’ operations.
It does that either to enable entry into a local market by leveraging Coca-Cola’s group resources or to maintain control of the bottling partner.
In the long-term, Coca-Cola will divest its stake as the bottling partner operations take off, thus enabling Coca-Cola to keep its capital requirements low while keeping a minor stake in the bottling partner, thus guaranteeing control and cooperation.
Therefore, the distribution system and the bottling partners are organized as a hybrid approach between chain and franchise.
Where in the short term, Coca-Cola acts as a chain of bottling companies. Long-term, it acts more like franchising, where bottling partners are kept mostly independent yet tied to the Coca-Cola brand .
This mixed distribution system of owned and non-owned bottling partners is the Coca-Cola system which sold 30.3 billion unit cases in 2019.
Trademark Coca-Cola accounted for 43 percent of U.S. unit case volume.
Re-franchising or “going franchise”
For instance, in 2019, Coca-Cola acquired controlling interests in bottling operations in Zambia, Kenya, and Eswatini.
As those bottling operations will become stable and established over time, Coca-Cola will re-franchise them.
Therefore, it will sell its controlling stake, having a franchisor-franchisee relationship with those bottling partners.
In some cases, it might keep a minor equity stake to keep more control over the operations.
In 2018, for instance, Coca-Cola had a few hundred million in proceeds as it re-franchised its Canadian and Latin American bottling operations.
This is how Coca-Cola keeps its CAPEX low while still keeping control of the bottling operations and enabling expansion and capillary distribution !
This is how Coca-Cola represents its system:

While in the directly owned bottling facilities, Coca-Cola sells directly, independent bottling partners manage distribution in the concentrate operations.
Therefore, Coca-Cola makes money by selling its concentrate to bottling partners ( they must place an entire order for the concentrate available in that territory as part of the bottling agreement ).
To handle those operations, Coca-Cola introduced 2006 the Bottling Investment Group, which managed the bottling operations’ acquisition, divestment, and re-franchising.
The graphic below gives a good picture of the overall process and strategy which has been implemented since 2006:

Coca-Cola vs. McDonald’s distribution strategy
Here we can draw the difference between Coca-Cola’s and McDonald’s distribution strategies.
Both companies have found an ingenious way to scale up operations while maintaining control over the business.
In the case of Coca-Cola, the company employs a franchained model , where the company first controls operations in the short term.
Once those have been established, it moves to a licensing/partnership/exclusivity model , where it can keep control of its bottling partners while making its overall organization lighter.
McDonald’s also employs an interesting model , which is a heavily franchised one.
Indeed, as of 2023, most McDonald’s restaurants are franchises.

Yet, to keep lousy control over the franchising operations, McDonald’s directly negotiate lease terms, and it’s usually the owner/or primary renter of the land where the franchising operations sit.
In this way, McDonald’s lessens the cost of owning and operating franchises directly, while still allowing franchise restaurants to follow the company’s policies via its lease operations.
In that respect, McDonald’s is more of a real estate company than a restaurant business.


Key takeaways
- An ingenious distribution network and the system drive the Coca-Cola business model.
- Beginning in 2006, Coca-Cola established the Bottling Investment Group, which invests initially in bottling companies by bringing them under the control and ownership of Coca-Cola.
- As local operations are established, and marketing and distribution activities run efficiently, Coca-Cola divests its controlling stakes, thus forming a franchising relationship with its bottling partners.
- Bottling partners keep an exclusivity agreement with other third-parties bottling companies to produce or distribute under the territories those bottling partners control. For the products they bottle up, Coca-Cola also reserves its right to manufacture and distribute its products.
- Coca-Cola, in turn, sells concentrate to those bottling companies, which act as franchisees for the branded Coca-Cola products.
Key Highlights of Coca-Cola’s Distribution Strategy:
- Investment and Franchising Model : Coca-Cola’s distribution strategy , implemented in 2006, involves initially investing in bottling partners’ operations through the Bottling Investment Group (BIG) and later transitioning to a franchising model for long-term growth and distribution .
- Distribution as a Key Factor : The success of Coca-Cola’s distribution strategy is seen as a crucial element in the company’s overall business strategy , even more so than the secret formula of its beverages.
- Five Large Independent Bottling Partners : Coca-Cola relies on five major independent bottling partners to handle a significant portion of its distribution . These partners accounted for 40 percent of the total unit case volume sold by the company in 2019.
- Bottling Agreements : Coca-Cola has specific agreements with its bottling partners for manufacturing and selling its products. These agreements grant bottlers the rights to prepare, package, distribute, and sell Coca-Cola products within authorized territories.
- Exclusivity and Control : Coca-Cola typically grants exclusivity to its bottling partners within their designated territories and products. However, Coca-Cola reserves the right to manufacture and distribute its trademarked products and brands, allowing it to maintain some control.
- Investment in Marketing : Coca-Cola actively participates in its bottling partners’ sales and marketing activities, investing substantial amounts in promotional and marketing programs. For example, in 2019, the company spent $4.4 billion on such activities.
- Hybrid Distribution Approach : Coca-Cola’s distribution system is a hybrid approach, combining elements of both company-owned bottling facilities (short-term chain) and franchising (long-term). This allows Coca-Cola to maintain control while keeping bottling partners independent.
- Re-Franchising Strategy : As bottling operations become stable and established over time, Coca-Cola re-franchises them by selling its controlling stake. In some cases, the company retains a minor equity stake to ensure control.
- Global Expansion and Capillary Distribution : Coca-Cola’s distribution strategy enables it to expand globally while keeping capital expenditure (CAPEX) low. This approach allows the company to maintain control over bottling operations and ensure widespread distribution .
- Comparison with McDonald’s : Coca-Cola’s distribution model differs from that of McDonald’s, which also employs franchising but focuses on controlling real estate and lease terms to maintain control over franchise operations.
Read Next: Coca-Cola’s Business And Distribution , Coca-Cola Mission Statement and Vision , Coca-Cola Competitors , What Does Coca-Cola Own? , Coca-Cola PESTEL Analysis , Coca-Cola SWOT Analysis , Coca-Cola Vs. Pepsi.
Related Visual Stories
Coca-Cola Business Strategy

Who Owns Coca-Cola

Coca-Cola Revenue

Coca-Cola Profits

Coca-Cola Revenue vs. Profits

Coca-Cola Employees

Coca-Cola Revenue Per Employee

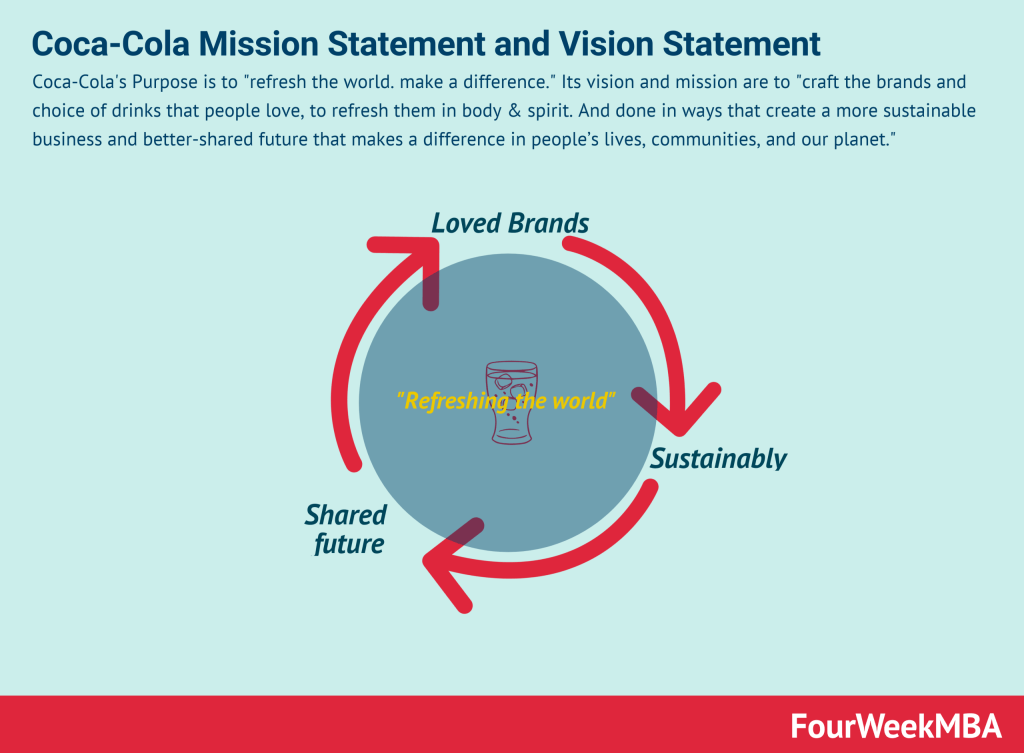
Coca-Cola Mission Statement
Coca-Cola SWOT Analysis

Coca-Cola PESTEL Analysis

What Does Coca-Cola Own?

Coca-Cola Competitors

Coca-Cola vs. PepsiCo

Who Owns Pepsi

What Does PepsiCo Own?

Pepsi Competitors

PepsiCo Revenue

PepsiCo Profits

More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- Business Models

IMAGES