Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey


What Are Research Objectives and How to Write Them (with Examples)

Table of Contents
Introduction
Research is at the center of everything researchers do, and setting clear, well-defined research objectives plays a pivotal role in guiding scholars toward their desired outcomes. Research papers are essential instruments for researchers to effectively communicate their work. Among the many sections that constitute a research paper, the introduction plays a key role in providing a background and setting the context. 1 Research objectives, which define the aims of the study, are usually stated in the introduction. Every study has a research question that the authors are trying to answer, and the objective is an active statement about how the study will answer this research question. These objectives help guide the development and design of the study and steer the research in the appropriate direction; if this is not clearly defined, a project can fail!
Research studies have a research question, research hypothesis, and one or more research objectives. A research question is what a study aims to answer, and a research hypothesis is a predictive statement about the relationship between two or more variables, which the study sets out to prove or disprove. Objectives are specific, measurable goals that the study aims to achieve. The difference between these three is illustrated by the following example:
- Research question : How does low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) compare with a placebo device in managing the symptoms of skeletally mature patients with patellar tendinopathy?
- Research hypothesis : Pain levels are reduced in patients who receive daily active-LIPUS (treatment) for 12 weeks compared with individuals who receive inactive-LIPUS (placebo).
- Research objective : To investigate the clinical efficacy of LIPUS in the management of patellar tendinopathy symptoms.
This article discusses the importance of clear, well-thought out objectives and suggests methods to write them clearly.
What is the introduction in research papers?
Research objectives are usually included in the introduction section. This section is the first that the readers will read so it is essential that it conveys the subject matter appropriately and is well written to create a good first impression. A good introduction sets the tone of the paper and clearly outlines the contents so that the readers get a quick snapshot of what to expect.
A good introduction should aim to: 2,3
- Indicate the main subject area, its importance, and cite previous literature on the subject
- Define the gap(s) in existing research, ask a research question, and state the objectives
- Announce the present research and outline its novelty and significance
- Avoid repeating the Abstract, providing unnecessary information, and claiming novelty without accurate supporting information.
Why are research objectives important?
Objectives can help you stay focused and steer your research in the required direction. They help define and limit the scope of your research, which is important to efficiently manage your resources and time. The objectives help to create and maintain the overall structure, and specify two main things—the variables and the methods of quantifying the variables.
A good research objective:
- defines the scope of the study
- gives direction to the research
- helps maintain focus and avoid diversions from the topic
- minimizes wastage of resources like time, money, and energy
Types of research objectives
Research objectives can be broadly classified into general and specific objectives . 4 General objectives state what the research expects to achieve overall while specific objectives break this down into smaller, logically connected parts, each of which addresses various parts of the research problem. General objectives are the main goals of the study and are usually fewer in number while specific objectives are more in number because they address several aspects of the research problem.
Example (general objective): To investigate the factors influencing the financial performance of firms listed in the New York Stock Exchange market.
Example (specific objective): To assess the influence of firm size on the financial performance of firms listed in the New York Stock Exchange market.
In addition to this broad classification, research objectives can be grouped into several categories depending on the research problem, as given in Table 1.
Table 1: Types of research objectives
Characteristics of research objectives
Research objectives must start with the word “To” because this helps readers identify the objective in the absence of headings and appropriate sectioning in research papers. 5,6
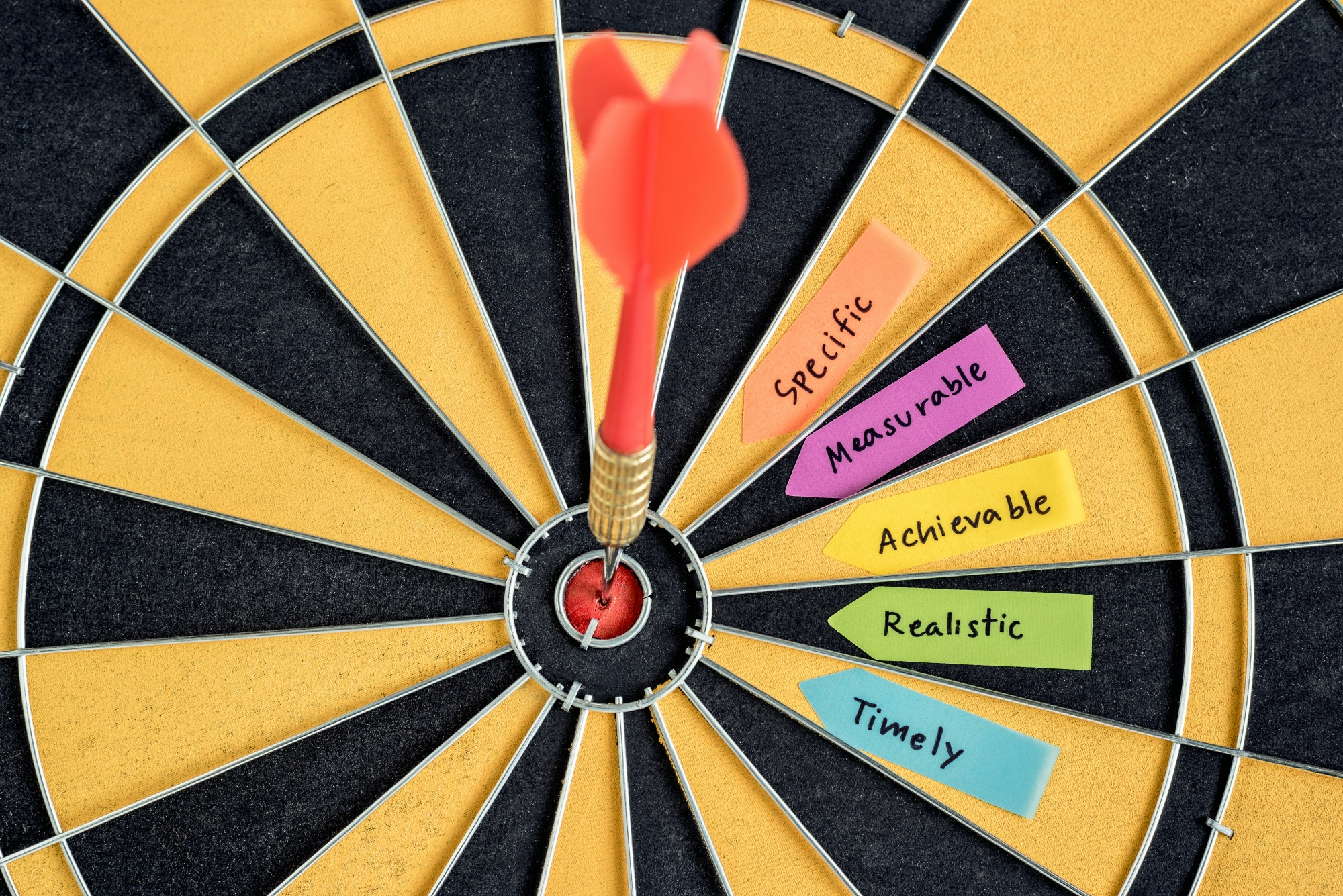
- A good objective is SMART (mostly applicable to specific objectives):
- Specific—clear about the what, why, when, and how
- Measurable—identifies the main variables of the study and quantifies the targets
- Achievable—attainable using the available time and resources
- Realistic—accurately addresses the scope of the problem
- Time-bound—identifies the time in which each step will be completed
- Research objectives clarify the purpose of research.
- They help understand the relationship and dissimilarities between variables.
- They provide a direction that helps the research to reach a definite conclusion.
How to write research objectives?
Research objectives can be written using the following steps: 7
- State your main research question clearly and concisely.
- Describe the ultimate goal of your study, which is similar to the research question but states the intended outcomes more definitively.
- Divide this main goal into subcategories to develop your objectives.
- Limit the number of objectives (1-2 general; 3-4 specific)
- Assess each objective using the SMART
- Start each objective with an action verb like assess, compare, determine, evaluate, etc., which makes the research appear more actionable.
- Use specific language without making the sentence data heavy.
- The most common section to add the objectives is the introduction and after the problem statement.
- Add the objectives to the abstract (if there is one).
- State the general objective first, followed by the specific objectives.
Formulating research objectives
Formulating research objectives has the following five steps, which could help researchers develop a clear objective: 8
- Identify the research problem.
- Review past studies on subjects similar to your problem statement, that is, studies that use similar methods, variables, etc.
- Identify the research gaps the current study should cover based on your literature review. These gaps could be theoretical, methodological, or conceptual.
- Define the research question(s) based on the gaps identified.
- Revise/relate the research problem based on the defined research question and the gaps identified. This is to confirm that there is an actual need for a study on the subject based on the gaps in literature.
- Identify and write the general and specific objectives.
- Incorporate the objectives into the study.
Advantages of research objectives
Adding clear research objectives has the following advantages: 4,8
- Maintains the focus and direction of the research
- Optimizes allocation of resources with minimal wastage
- Acts as a foundation for defining appropriate research questions and hypotheses
- Provides measurable outcomes that can help evaluate the success of the research
- Determines the feasibility of the research by helping to assess the availability of required resources
- Ensures relevance of the study to the subject and its contribution to existing literature
Disadvantages of research objectives
Research objectives also have few disadvantages, as listed below: 8
- Absence of clearly defined objectives can lead to ambiguity in the research process
- Unintentional bias could affect the validity and accuracy of the research findings
Key takeaways
- Research objectives are concise statements that describe what the research is aiming to achieve.
- They define the scope and direction of the research and maintain focus.
- The objectives should be SMART—specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.
- Clear research objectives help avoid collection of data or resources not required for the study.
- Well-formulated specific objectives help develop the overall research methodology, including data collection, analysis, interpretation, and utilization.
- Research objectives should cover all aspects of the problem statement in a coherent way.
- They should be clearly stated using action verbs.
Frequently asked questions on research objectives
Q: what’s the difference between research objectives and aims 9.
A: Research aims are statements that reflect the broad goal(s) of the study and outline the general direction of the research. They are not specific but clearly define the focus of the study.
Example: This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.
Research objectives focus on the action to be taken to achieve the aims. They make the aims more practical and should be specific and actionable.
Example: To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation.
Q: What are the examples of research objectives, both general and specific?
A: Here are a few examples of research objectives:
- To identify the antiviral chemical constituents in Mumbukura gitoniensis (general)
- To carry out solvent extraction of dried flowers of Mumbukura gitoniensis and isolate the constituents. (specific)
- To determine the antiviral activity of each of the isolated compounds. (specific)
- To examine the extent, range, and method of coral reef rehabilitation projects in five shallow reef areas adjacent to popular tourist destinations in the Philippines.
- To investigate species richness of mammal communities in five protected areas over the past 20 years.
- To evaluate the potential application of AI techniques for estimating best-corrected visual acuity from fundus photographs with and without ancillary information.
- To investigate whether sport influences psychological parameters in the personality of asthmatic children.
Q: How do I develop research objectives?
A: Developing research objectives begins with defining the problem statement clearly, as illustrated by Figure 1. Objectives specify how the research question will be answered and they determine what is to be measured to test the hypothesis.
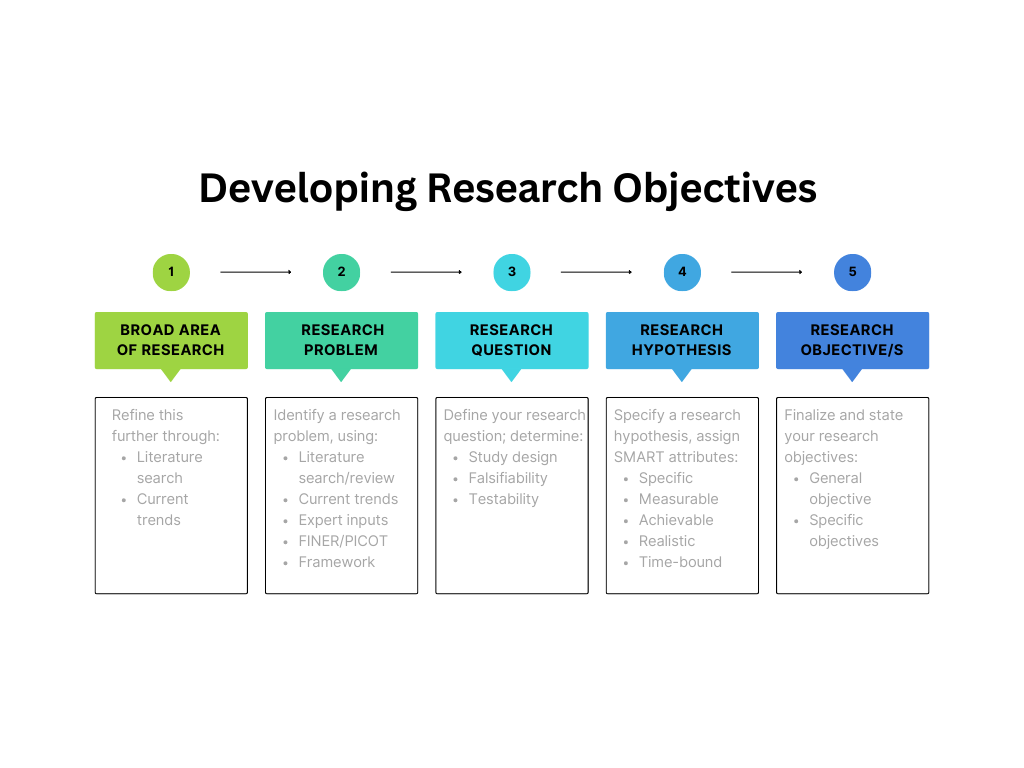
Q: Are research objectives measurable?
A: The word “measurable” implies that something is quantifiable. In terms of research objectives, this means that the source and method of collecting data are identified and that all these aspects are feasible for the research. Some metrics can be created to measure your progress toward achieving your objectives.
Q: Can research objectives change during the study?
A: Revising research objectives during the study is acceptable in situations when the selected methodology is not progressing toward achieving the objective, or if there are challenges pertaining to resources, etc. One thing to keep in mind is the time and resources you would have to complete your research after revising the objectives. Thus, as long as your problem statement and hypotheses are unchanged, minor revisions to the research objectives are acceptable.
Q: What is the difference between research questions and research objectives? 10
Q: are research objectives the same as hypotheses.
A: No, hypotheses are predictive theories that are expressed in general terms. Research objectives, which are more specific, are developed from hypotheses and aim to test them. A hypothesis can be tested using several methods and each method will have different objectives because the methodology to be used could be different. A hypothesis is developed based on observation and reasoning; it is a calculated prediction about why a particular phenomenon is occurring. To test this prediction, different research objectives are formulated. Here’s a simple example of both a research hypothesis and research objective.
Research hypothesis : Employees who arrive at work earlier are more productive.
Research objective : To assess whether employees who arrive at work earlier are more productive.
To summarize, research objectives are an important part of research studies and should be written clearly to effectively communicate your research. We hope this article has given you a brief insight into the importance of using clearly defined research objectives and how to formulate them.
- Farrugia P, Petrisor BA, Farrokhyar F, Bhandari M. Practical tips for surgical research: Research questions, hypotheses and objectives. Can J Surg. 2010 Aug;53(4):278-81.
- Abbadia J. How to write an introduction for a research paper. Mind the Graph website. Accessed June 14, 2023. https://mindthegraph.com/blog/how-to-write-an-introduction-for-a-research-paper/
- Writing a scientific paper: Introduction. UCI libraries website. Accessed June 15, 2023. https://guides.lib.uci.edu/c.php?g=334338&p=2249903
- Research objectives—Types, examples and writing guide. Researchmethod.net website. Accessed June 17, 2023. https://researchmethod.net/research-objectives/#:~:text=They%20provide%20a%20clear%20direction,track%20and%20achieve%20their%20goals .
- Bartle P. SMART Characteristics of good objectives. Community empowerment collective website. Accessed June 16, 2023. https://cec.vcn.bc.ca/cmp/modules/pd-smar.htm
- Research objectives. Studyprobe website. Accessed June 18, 2023. https://www.studyprobe.in/2022/08/research-objectives.html
- Corredor F. How to write objectives in a research paper. wikiHow website. Accessed June 18, 2023. https://www.wikihow.com/Write-Objectives-in-a-Research-Proposal
- Research objectives: Definition, types, characteristics, advantages. AccountingNest website. Accessed June 15, 2023. https://www.accountingnest.com/articles/research/research-objectives
- Phair D., Shaeffer A. Research aims, objectives & questions. GradCoach website. Accessed June 20, 2023. https://gradcoach.com/research-aims-objectives-questions/
- Understanding the difference between research questions and objectives. Accessed June 21, 2023. https://board.researchersjob.com/blog/research-questions-and-objectives
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

How does R Discovery Translate Complex Academic Papers Accurately

What Constitutes Good Research in Academia?
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Objectives – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Objectives – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Objectives
Research objectives refer to the specific goals or aims of a research study. They provide a clear and concise description of what the researcher hopes to achieve by conducting the research . The objectives are typically based on the research questions and hypotheses formulated at the beginning of the study and are used to guide the research process.
Types of Research Objectives
Here are the different types of research objectives in research:
- Exploratory Objectives: These objectives are used to explore a topic, issue, or phenomenon that has not been studied in-depth before. The aim of exploratory research is to gain a better understanding of the subject matter and generate new ideas and hypotheses .
- Descriptive Objectives: These objectives aim to describe the characteristics, features, or attributes of a particular population, group, or phenomenon. Descriptive research answers the “what” questions and provides a snapshot of the subject matter.
- Explanatory Objectives : These objectives aim to explain the relationships between variables or factors. Explanatory research seeks to identify the cause-and-effect relationships between different phenomena.
- Predictive Objectives: These objectives aim to predict future events or outcomes based on existing data or trends. Predictive research uses statistical models to forecast future trends or outcomes.
- Evaluative Objectives : These objectives aim to evaluate the effectiveness or impact of a program, intervention, or policy. Evaluative research seeks to assess the outcomes or results of a particular intervention or program.
- Prescriptive Objectives: These objectives aim to provide recommendations or solutions to a particular problem or issue. Prescriptive research identifies the best course of action based on the results of the study.
- Diagnostic Objectives : These objectives aim to identify the causes or factors contributing to a particular problem or issue. Diagnostic research seeks to uncover the underlying reasons for a particular phenomenon.
- Comparative Objectives: These objectives aim to compare two or more groups, populations, or phenomena to identify similarities and differences. Comparative research is used to determine which group or approach is more effective or has better outcomes.
- Historical Objectives: These objectives aim to examine past events, trends, or phenomena to gain a better understanding of their significance and impact. Historical research uses archival data, documents, and records to study past events.
- Ethnographic Objectives : These objectives aim to understand the culture, beliefs, and practices of a particular group or community. Ethnographic research involves immersive fieldwork and observation to gain an insider’s perspective of the group being studied.
- Action-oriented Objectives: These objectives aim to bring about social or organizational change. Action-oriented research seeks to identify practical solutions to social problems and to promote positive change in society.
- Conceptual Objectives: These objectives aim to develop new theories, models, or frameworks to explain a particular phenomenon or set of phenomena. Conceptual research seeks to provide a deeper understanding of the subject matter by developing new theoretical perspectives.
- Methodological Objectives: These objectives aim to develop and improve research methods and techniques. Methodological research seeks to advance the field of research by improving the validity, reliability, and accuracy of research methods and tools.
- Theoretical Objectives : These objectives aim to test and refine existing theories or to develop new theoretical perspectives. Theoretical research seeks to advance the field of knowledge by testing and refining existing theories or by developing new theoretical frameworks.
- Measurement Objectives : These objectives aim to develop and validate measurement instruments, such as surveys, questionnaires, and tests. Measurement research seeks to improve the quality and reliability of data collection and analysis by developing and testing new measurement tools.
- Design Objectives : These objectives aim to develop and refine research designs, such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and observational designs. Design research seeks to improve the quality and validity of research by developing and testing new research designs.
- Sampling Objectives: These objectives aim to develop and refine sampling techniques, such as probability and non-probability sampling methods. Sampling research seeks to improve the representativeness and generalizability of research findings by developing and testing new sampling techniques.
How to Write Research Objectives
Writing clear and concise research objectives is an important part of any research project, as it helps to guide the study and ensure that it is focused and relevant. Here are some steps to follow when writing research objectives:
- Identify the research problem : Before you can write research objectives, you need to identify the research problem you are trying to address. This should be a clear and specific problem that can be addressed through research.
- Define the research questions : Based on the research problem, define the research questions you want to answer. These questions should be specific and should guide the research process.
- Identify the variables : Identify the key variables that you will be studying in your research. These are the factors that you will be measuring, manipulating, or analyzing to answer your research questions.
- Write specific objectives: Write specific, measurable objectives that will help you answer your research questions. These objectives should be clear and concise and should indicate what you hope to achieve through your research.
- Use the SMART criteria: To ensure that your research objectives are well-defined and achievable, use the SMART criteria. This means that your objectives should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
- Revise and refine: Once you have written your research objectives, revise and refine them to ensure that they are clear, concise, and achievable. Make sure that they align with your research questions and variables, and that they will help you answer your research problem.
Example of Research Objectives
Examples of research objectives Could be:
Research Objectives for the topic of “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Employment”:
- To investigate the effects of the adoption of AI on employment trends across various industries and occupations.
- To explore the potential for AI to create new job opportunities and transform existing roles in the workforce.
- To examine the social and economic implications of the widespread use of AI for employment, including issues such as income inequality and access to education and training.
- To identify the skills and competencies that will be required for individuals to thrive in an AI-driven workplace, and to explore the role of education and training in developing these skills.
- To evaluate the ethical and legal considerations surrounding the use of AI for employment, including issues such as bias, privacy, and the responsibility of employers and policymakers to protect workers’ rights.
When to Write Research Objectives
- At the beginning of a research project : Research objectives should be identified and written down before starting a research project. This helps to ensure that the project is focused and that data collection and analysis efforts are aligned with the intended purpose of the research.
- When refining research questions: Writing research objectives can help to clarify and refine research questions. Objectives provide a more concrete and specific framework for addressing research questions, which can improve the overall quality and direction of a research project.
- After conducting a literature review : Conducting a literature review can help to identify gaps in knowledge and areas that require further research. Writing research objectives can help to define and focus the research effort in these areas.
- When developing a research proposal: Research objectives are an important component of a research proposal. They help to articulate the purpose and scope of the research, and provide a clear and concise summary of the expected outcomes and contributions of the research.
- When seeking funding for research: Funding agencies often require a detailed description of research objectives as part of a funding proposal. Writing clear and specific research objectives can help to demonstrate the significance and potential impact of a research project, and increase the chances of securing funding.
- When designing a research study : Research objectives guide the design and implementation of a research study. They help to identify the appropriate research methods, sampling strategies, data collection and analysis techniques, and other relevant aspects of the study design.
- When communicating research findings: Research objectives provide a clear and concise summary of the main research questions and outcomes. They are often included in research reports and publications, and can help to ensure that the research findings are communicated effectively and accurately to a wide range of audiences.
- When evaluating research outcomes : Research objectives provide a basis for evaluating the success of a research project. They help to measure the degree to which research questions have been answered and the extent to which research outcomes have been achieved.
- When conducting research in a team : Writing research objectives can facilitate communication and collaboration within a research team. Objectives provide a shared understanding of the research purpose and goals, and can help to ensure that team members are working towards a common objective.
Purpose of Research Objectives
Some of the main purposes of research objectives include:
- To clarify the research question or problem : Research objectives help to define the specific aspects of the research question or problem that the study aims to address. This makes it easier to design a study that is focused and relevant.
- To guide the research design: Research objectives help to determine the research design, including the research methods, data collection techniques, and sampling strategy. This ensures that the study is structured and efficient.
- To measure progress : Research objectives provide a way to measure progress throughout the research process. They help the researcher to evaluate whether they are on track and meeting their goals.
- To communicate the research goals : Research objectives provide a clear and concise description of the research goals. This helps to communicate the purpose of the study to other researchers, stakeholders, and the general public.
Advantages of Research Objectives
Here are some advantages of having well-defined research objectives:
- Focus : Research objectives help to focus the research effort on specific areas of inquiry. By identifying clear research questions, the researcher can narrow down the scope of the study and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information.
- Clarity : Clearly stated research objectives provide a roadmap for the research study. They provide a clear direction for the research, making it easier for the researcher to stay on track and achieve their goals.
- Measurability : Well-defined research objectives provide measurable outcomes that can be used to evaluate the success of the research project. This helps to ensure that the research is effective and that the research goals are achieved.
- Feasibility : Research objectives help to ensure that the research project is feasible. By clearly defining the research goals, the researcher can identify the resources required to achieve those goals and determine whether those resources are available.
- Relevance : Research objectives help to ensure that the research study is relevant and meaningful. By identifying specific research questions, the researcher can ensure that the study addresses important issues and contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Topics – Ideas and Examples

Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example...

Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and...

Research Approach – Types Methods and Examples

Research Problem – Examples, Types and Guide

- Aims and Objectives – A Guide for Academic Writing
- Doing a PhD
One of the most important aspects of a thesis, dissertation or research paper is the correct formulation of the aims and objectives. This is because your aims and objectives will establish the scope, depth and direction that your research will ultimately take. An effective set of aims and objectives will give your research focus and your reader clarity, with your aims indicating what is to be achieved, and your objectives indicating how it will be achieved.
Introduction
There is no getting away from the importance of the aims and objectives in determining the success of your research project. Unfortunately, however, it is an aspect that many students struggle with, and ultimately end up doing poorly. Given their importance, if you suspect that there is even the smallest possibility that you belong to this group of students, we strongly recommend you read this page in full.
This page describes what research aims and objectives are, how they differ from each other, how to write them correctly, and the common mistakes students make and how to avoid them. An example of a good aim and objectives from a past thesis has also been deconstructed to help your understanding.
What Are Aims and Objectives?
Research aims.
A research aim describes the main goal or the overarching purpose of your research project.
In doing so, it acts as a focal point for your research and provides your readers with clarity as to what your study is all about. Because of this, research aims are almost always located within its own subsection under the introduction section of a research document, regardless of whether it’s a thesis , a dissertation, or a research paper .
A research aim is usually formulated as a broad statement of the main goal of the research and can range in length from a single sentence to a short paragraph. Although the exact format may vary according to preference, they should all describe why your research is needed (i.e. the context), what it sets out to accomplish (the actual aim) and, briefly, how it intends to accomplish it (overview of your objectives).
To give an example, we have extracted the following research aim from a real PhD thesis:
Example of a Research Aim
The role of diametrical cup deformation as a factor to unsatisfactory implant performance has not been widely reported. The aim of this thesis was to gain an understanding of the diametrical deformation behaviour of acetabular cups and shells following impaction into the reamed acetabulum. The influence of a range of factors on deformation was investigated to ascertain if cup and shell deformation may be high enough to potentially contribute to early failure and high wear rates in metal-on-metal implants.
Note: Extracted with permission from thesis titled “T he Impact And Deformation Of Press-Fit Metal Acetabular Components ” produced by Dr H Hothi of previously Queen Mary University of London.
Research Objectives
Where a research aim specifies what your study will answer, research objectives specify how your study will answer it.
They divide your research aim into several smaller parts, each of which represents a key section of your research project. As a result, almost all research objectives take the form of a numbered list, with each item usually receiving its own chapter in a dissertation or thesis.
Following the example of the research aim shared above, here are it’s real research objectives as an example:
Example of a Research Objective
- Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
- Investigate the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup.
- Determine the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types.
- Investigate the influence of non-uniform cup support and varying the orientation of the component in the cavity on deformation.
- Examine the influence of errors during reaming of the acetabulum which introduce ovality to the cavity.
- Determine the relationship between changes in the geometry of the component and deformation for different cup designs.
- Develop three dimensional pelvis models with non-uniform bone material properties from a range of patients with varying bone quality.
- Use the key parameters that influence deformation, as identified in the foam models to determine the range of deformations that may occur clinically using the anatomic models and if these deformations are clinically significant.
It’s worth noting that researchers sometimes use research questions instead of research objectives, or in other cases both. From a high-level perspective, research questions and research objectives make the same statements, but just in different formats.
Taking the first three research objectives as an example, they can be restructured into research questions as follows:
Restructuring Research Objectives as Research Questions
- Can finite element models using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum together with explicit dynamics be used to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion?
- What is the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup?
- What is the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types?
Difference Between Aims and Objectives
Hopefully the above explanations make clear the differences between aims and objectives, but to clarify:
- The research aim focus on what the research project is intended to achieve; research objectives focus on how the aim will be achieved.
- Research aims are relatively broad; research objectives are specific.
- Research aims focus on a project’s long-term outcomes; research objectives focus on its immediate, short-term outcomes.
- A research aim can be written in a single sentence or short paragraph; research objectives should be written as a numbered list.
How to Write Aims and Objectives
Before we discuss how to write a clear set of research aims and objectives, we should make it clear that there is no single way they must be written. Each researcher will approach their aims and objectives slightly differently, and often your supervisor will influence the formulation of yours on the basis of their own preferences.
Regardless, there are some basic principles that you should observe for good practice; these principles are described below.
Your aim should be made up of three parts that answer the below questions:
- Why is this research required?
- What is this research about?
- How are you going to do it?
The easiest way to achieve this would be to address each question in its own sentence, although it does not matter whether you combine them or write multiple sentences for each, the key is to address each one.
The first question, why , provides context to your research project, the second question, what , describes the aim of your research, and the last question, how , acts as an introduction to your objectives which will immediately follow.
Scroll through the image set below to see the ‘why, what and how’ associated with our research aim example.

Note: Your research aims need not be limited to one. Some individuals per to define one broad ‘overarching aim’ of a project and then adopt two or three specific research aims for their thesis or dissertation. Remember, however, that in order for your assessors to consider your research project complete, you will need to prove you have fulfilled all of the aims you set out to achieve. Therefore, while having more than one research aim is not necessarily disadvantageous, consider whether a single overarching one will do.
Research Objectives
Each of your research objectives should be SMART :
- Specific – is there any ambiguity in the action you are going to undertake, or is it focused and well-defined?
- Measurable – how will you measure progress and determine when you have achieved the action?
- Achievable – do you have the support, resources and facilities required to carry out the action?
- Relevant – is the action essential to the achievement of your research aim?
- Timebound – can you realistically complete the action in the available time alongside your other research tasks?
In addition to being SMART, your research objectives should start with a verb that helps communicate your intent. Common research verbs include:
Table of Research Verbs to Use in Aims and Objectives
Last, format your objectives into a numbered list. This is because when you write your thesis or dissertation, you will at times need to make reference to a specific research objective; structuring your research objectives in a numbered list will provide a clear way of doing this.
To bring all this together, let’s compare the first research objective in the previous example with the above guidance:
Checking Research Objective Example Against Recommended Approach
Research Objective:
1. Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
Checking Against Recommended Approach:
Q: Is it specific? A: Yes, it is clear what the student intends to do (produce a finite element model), why they intend to do it (mimic cup/shell blows) and their parameters have been well-defined ( using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum ).
Q: Is it measurable? A: Yes, it is clear that the research objective will be achieved once the finite element model is complete.
Q: Is it achievable? A: Yes, provided the student has access to a computer lab, modelling software and laboratory data.
Q: Is it relevant? A: Yes, mimicking impacts to a cup/shell is fundamental to the overall aim of understanding how they deform when impacted upon.
Q: Is it timebound? A: Yes, it is possible to create a limited-scope finite element model in a relatively short time, especially if you already have experience in modelling.
Q: Does it start with a verb? A: Yes, it starts with ‘develop’, which makes the intent of the objective immediately clear.
Q: Is it a numbered list? A: Yes, it is the first research objective in a list of eight.
Mistakes in Writing Research Aims and Objectives
1. making your research aim too broad.
Having a research aim too broad becomes very difficult to achieve. Normally, this occurs when a student develops their research aim before they have a good understanding of what they want to research. Remember that at the end of your project and during your viva defence , you will have to prove that you have achieved your research aims; if they are too broad, this will be an almost impossible task. In the early stages of your research project, your priority should be to narrow your study to a specific area. A good way to do this is to take the time to study existing literature, question their current approaches, findings and limitations, and consider whether there are any recurring gaps that could be investigated .
Note: Achieving a set of aims does not necessarily mean proving or disproving a theory or hypothesis, even if your research aim was to, but having done enough work to provide a useful and original insight into the principles that underlie your research aim.
2. Making Your Research Objectives Too Ambitious
Be realistic about what you can achieve in the time you have available. It is natural to want to set ambitious research objectives that require sophisticated data collection and analysis, but only completing this with six months before the end of your PhD registration period is not a worthwhile trade-off.
3. Formulating Repetitive Research Objectives
Each research objective should have its own purpose and distinct measurable outcome. To this effect, a common mistake is to form research objectives which have large amounts of overlap. This makes it difficult to determine when an objective is truly complete, and also presents challenges in estimating the duration of objectives when creating your project timeline. It also makes it difficult to structure your thesis into unique chapters, making it more challenging for you to write and for your audience to read.
Fortunately, this oversight can be easily avoided by using SMART objectives.
Hopefully, you now have a good idea of how to create an effective set of aims and objectives for your research project, whether it be a thesis, dissertation or research paper. While it may be tempting to dive directly into your research, spending time on getting your aims and objectives right will give your research clear direction. This won’t only reduce the likelihood of problems arising later down the line, but will also lead to a more thorough and coherent research project.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
Research Objectives: The Compass of Your Study
Table of contents
- 1 Definition and Purpose of Setting Clear Research Objectives
- 2 How Research Objectives Fit into the Overall Research Framework
- 3 Types of Research Objectives
- 4 Aligning Objectives with Research Questions and Hypotheses
- 5 Role of Research Objectives in Various Research Phases
- 6.1 Key characteristics of well-defined research objectives
- 6.2 Step-by-Step Guide on How to Formulate Both General and Specific Research Objectives
- 6.3 How to Know When Your Objectives Need Refinement
- 7 Research Objectives Examples in Different Fields
- 8 Conclusion
Embarking on a research journey without clear objectives is like navigating the sea without a compass. This article delves into the essence of establishing precise research objectives, serving as the guiding star for your scholarly exploration.
We will unfold the layers of how the objective of study not only defines the scope of your research but also directs every phase of the research process, from formulating research questions to interpreting research findings. By bridging theory with practical examples, we aim to illuminate the path to crafting effective research objectives that are both ambitious and attainable. Let’s chart the course to a successful research voyage, exploring the significance, types, and formulation of research paper objectives.
Definition and Purpose of Setting Clear Research Objectives
Defining the research objectives includes which two tasks? Research objectives are clear and concise statements that outline what you aim to achieve through your study. They are the foundation for determining your research scope, guiding your data collection methods, and shaping your analysis. The purpose of research proposal and setting clear objectives in it is to ensure that your research efforts are focused and efficient, and to provide a roadmap that keeps your study aligned with its intended outcomes.
To define the research objective at the outset, researchers can avoid the pitfalls of scope creep, where the study’s focus gradually broadens beyond its initial boundaries, leading to wasted resources and time. Clear objectives facilitate communication with stakeholders, such as funding bodies, academic supervisors, and the broader academic community, by succinctly conveying the study’s goals and significance. Furthermore, they help in the formulation of precise research questions and hypotheses, making the research process more systematic and organized. Yet, it is not always easy. For this reason, PapersOwl is always ready to help. Lastly, clear research objectives enable the researcher to critically assess the study’s progress and outcomes against predefined benchmarks, ensuring the research stays on track and delivers meaningful results.
How Research Objectives Fit into the Overall Research Framework
Research objectives are integral to the research framework as the nexus between the research problem, questions, and hypotheses. They translate the broad goals of your study into actionable steps, ensuring every aspect of your research is purposefully aligned towards addressing the research problem. This alignment helps in structuring the research design and methodology, ensuring that each component of the study is geared towards answering the core questions derived from the objectives. Creating such a difficult piece may take a lot of time. If you need it to be accurate yet fast delivered, consider getting professional research paper writing help whenever the time comes. It also aids in the identification and justification of the research methods and tools used for data collection and analysis, aligning them with the objectives to enhance the validity and reliability of the findings.
Furthermore, by setting clear objectives, researchers can more effectively evaluate the impact and significance of their work in contributing to existing knowledge. Additionally, research objectives guide literature review, enabling researchers to focus their examination on relevant studies and theoretical frameworks that directly inform their research goals.
Types of Research Objectives
In the landscape of research, setting objectives is akin to laying down the tracks for a train’s journey, guiding it towards its destination. Constructing these tracks involves defining two main types of objectives: general and specific. Each serves a unique purpose in guiding the research towards its ultimate goals, with general objectives providing the broad vision and specific objectives outlining the concrete steps needed to fulfill that vision. Together, they form a cohesive blueprint that directs the focus of the study, ensuring that every effort contributes meaningfully to the overarching research aims.
- General objectives articulate the overarching goals of your study. They are broad, setting the direction for your research without delving into specifics. These objectives capture what you wish to explore or contribute to existing knowledge.
- Specific objectives break down the general objectives into measurable outcomes. They are precise, detailing the steps needed to achieve the broader goals of your study. They often correspond to different aspects of your research question , ensuring a comprehensive approach to your study.
To illustrate, consider a research project on the impact of digital marketing on consumer behavior. A general objective might be “to explore the influence of digital marketing on consumer purchasing decisions.” Specific objectives could include “to assess the effectiveness of social media advertising in enhancing brand awareness” and “to evaluate the impact of email marketing on customer loyalty.”

Aligning Objectives with Research Questions and Hypotheses
The harmony between what research objectives should be, questions, and hypotheses is critical. Objectives define what you aim to achieve; research questions specify what you seek to understand, and hypotheses predict the expected outcomes.
This alignment ensures a coherent and focused research endeavor. Achieving it necessitates a thoughtful consideration of how each component interrelates, ensuring that the objectives are not only ambitious but also directly answerable through the research questions and testable via the hypotheses. This interconnectedness facilitates a streamlined approach to the research process, enabling researchers to systematically address each aspect of their study in a logical sequence. Moreover, it enhances the clarity and precision of the research, making it easier for peers and stakeholders to grasp the study’s direction and potential contributions.
Role of Research Objectives in Various Research Phases
Throughout the research process, objectives guide your choices and strategies – from selecting the appropriate research design and methods to analyzing data and interpreting results. They are the criteria against which you measure the success of your study. In the initial stages, research objectives inform the selection of a topic, helping to narrow down a broad area of interest into a focused question that can be explored in depth. During the methodology phase, they dictate the type of data needed and the best methods for obtaining that data, ensuring that every step taken is purposeful and aligned with the study’s goals. As the research progresses, objectives provide a framework for analyzing the collected data, guiding the researcher in identifying patterns, drawing conclusions, and making informed decisions.
Crafting Effective Research Objectives

The effective objective of research is pivotal in laying the groundwork for a successful investigation. These objectives clarify the focus of your study and determine its direction and scope. Ensuring that your objectives are well-defined and aligned with the SMART criteria is crucial for setting a strong foundation for your research.
Key characteristics of well-defined research objectives
Well-defined research objectives are characterized by the SMART criteria – Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Specific objectives clearly define what you plan to achieve, eliminating any ambiguity. Measurable objectives allow you to track progress and assess the outcome. Achievable objectives are realistic, considering the research sources and time available. Relevant objectives align with the broader goals of your field or research question. Finally, Time-bound objectives have a clear timeline for completion, adding urgency and a schedule to your work.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Formulate Both General and Specific Research Objectives
So lets get to the part, how to write research objectives properly?
- Understand the issue or gap in existing knowledge your study aims to address.
- Gain insights into how similar challenges have been approached to refine your objectives.
- Articulate the broad goal of research based on your understanding of the problem.
- Detail the specific aspects of your research, ensuring they are actionable and measurable.
How to Know When Your Objectives Need Refinement
Your objectives of research may require refinement if they lack clarity, feasibility, or alignment with the research problem. If you find yourself struggling to design experiments or methods that directly address your objectives, or if the objectives seem too broad or not directly related to your research question, it’s likely time for refinement. Additionally, objectives in research proposal that do not facilitate a clear measurement of success indicate a need for a more precise definition. Refinement involves ensuring that each objective is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound, enhancing your research’s overall focus and impact.
Research Objectives Examples in Different Fields
The application of research objectives spans various academic disciplines, each with its unique focus and methodologies. To illustrate how the objectives of the study guide a research paper across different fields, here are some research objective examples:
- In Health Sciences , a research aim may be to “determine the efficacy of a new vaccine in reducing the incidence of a specific disease among a target population within one year.” This objective is specific (efficacy of a new vaccine), measurable (reduction in disease incidence), achievable (with the right study design and sample size), relevant (to public health), and time-bound (within one year).
- In Environmental Studies , the study objectives could be “to assess the impact of air pollution on urban biodiversity over a decade.” This reflects a commitment to understanding the long-term effects of human activities on urban ecosystems, emphasizing the need for sustainable urban planning.
- In Economics , an example objective of a study might be “to analyze the relationship between fiscal policies and unemployment rates in developing countries over the past twenty years.” This seeks to explore macroeconomic trends and inform policymaking, highlighting the role of economic research study in societal development.
These examples of research objectives describe the versatility and significance of research objectives in guiding scholarly inquiry across different domains. By setting clear, well-defined objectives, researchers can ensure their studies are focused and impactful and contribute valuable knowledge to their respective fields.
Defining research studies objectives and problem statement is not just a preliminary step, but a continuous guiding force throughout the research journey. These goals of research illuminate the path forward and ensure that every stride taken is meaningful and aligned with the ultimate goals of the inquiry. Whether through the meticulous application of the SMART criteria or the strategic alignment with research questions and hypotheses, the rigor in crafting and refining these objectives underscores the integrity and relevance of the research. As scholars venture into the vast terrains of knowledge, the clarity, and precision of their objectives serve as beacons of light, steering their explorations toward discoveries that advance academic discourse and resonate with the broader societal needs.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.

Research Aims, Objectives & Questions
By: David Phair (PhD) and Alexandra Shaeffer (PhD) | June 2022

T he research aims , objectives and research questions (collectively called the “golden thread”) are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you’re crafting a research proposal , dissertation or thesis . We receive questions almost every day about this “holy trinity” of research and there’s certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we’ve crafted this post to help you navigate your way through the fog.
Overview: The Golden Thread
- What is the golden thread
- What are research aims ( examples )
- What are research objectives ( examples )
- What are research questions ( examples )
- The importance of alignment in the golden thread
What is the “golden thread”?
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims , research objectives , and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Importantly, the golden thread needs to weave its way through the entirety of any research project , from start to end. In other words, it needs to be very clearly defined right at the beginning of the project (the topic ideation and proposal stage) and it needs to inform almost every decision throughout the rest of the project. For example, your research design and methodology will be heavily influenced by the golden thread (we’ll explain this in more detail later), as well as your literature review.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope ( the delimitations ) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can “go deep” and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity. They also help keep you on track , as they act as a litmus test for relevance. In other words, if you’re ever unsure whether to include something in your document, simply ask yourself the question, “does this contribute toward my research aims, objectives or questions?”. If it doesn’t, chances are you can drop it.
Alright, enough of the fluffy, conceptual stuff. Let’s get down to business and look at what exactly the research aims, objectives and questions are and outline a few examples to bring these concepts to life.

Research Aims: What are they?
Simply put, the research aim(s) is a statement that reflects the broad overarching goal (s) of the research project. Research aims are fairly high-level (low resolution) as they outline the general direction of the research and what it’s trying to achieve .
Research Aims: Examples
True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording “this research aims to…”, “this research seeks to…”, and so on. For example:
“This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.” “This study sets out to assess the interaction between student support and self-care on well-being in engineering graduate students”
As you can see, these research aims provide a high-level description of what the study is about and what it seeks to achieve. They’re not hyper-specific or action-oriented, but they’re clear about what the study’s focus is and what is being investigated.
Need a helping hand?
Research Objectives: What are they?
The research objectives take the research aims and make them more practical and actionable . In other words, the research objectives showcase the steps that the researcher will take to achieve the research aims.
The research objectives need to be far more specific (higher resolution) and actionable than the research aims. In fact, it’s always a good idea to craft your research objectives using the “SMART” criteria. In other words, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound”.
Research Objectives: Examples
Let’s look at two examples of research objectives. We’ll stick with the topic and research aims we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic:
To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation. To assess employee perceptions of digital transformation in retail HR. To identify the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR.
And for the student wellness topic:
To determine whether student self-care predicts the well-being score of engineering graduate students. To determine whether student support predicts the well-being score of engineering students. To assess the interaction between student self-care and student support when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students.
As you can see, these research objectives clearly align with the previously mentioned research aims and effectively translate the low-resolution aims into (comparatively) higher-resolution objectives and action points . They give the research project a clear focus and present something that resembles a research-based “to-do” list.

Research Questions: What are they?
Finally, we arrive at the all-important research questions. The research questions are, as the name suggests, the key questions that your study will seek to answer . Simply put, they are the core purpose of your dissertation, thesis, or research project. You’ll present them at the beginning of your document (either in the introduction chapter or literature review chapter) and you’ll answer them at the end of your document (typically in the discussion and conclusion chapters).
The research questions will be the driving force throughout the research process. For example, in the literature review chapter, you’ll assess the relevance of any given resource based on whether it helps you move towards answering your research questions. Similarly, your methodology and research design will be heavily influenced by the nature of your research questions. For instance, research questions that are exploratory in nature will usually make use of a qualitative approach, whereas questions that relate to measurement or relationship testing will make use of a quantitative approach.
Let’s look at some examples of research questions to make this more tangible.
Research Questions: Examples
Again, we’ll stick with the research aims and research objectives we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic (which would be qualitative in nature):
How do employees perceive digital transformation in retail HR? What are the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR?
And for the student wellness topic (which would be quantitative in nature):
Does student self-care predict the well-being scores of engineering graduate students? Does student support predict the well-being scores of engineering students? Do student self-care and student support interact when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students?
You’ll probably notice that there’s quite a formulaic approach to this. In other words, the research questions are basically the research objectives “converted” into question format. While that is true most of the time, it’s not always the case. For example, the first research objective for the digital transformation topic was more or less a step on the path toward the other objectives, and as such, it didn’t warrant its own research question.
So, don’t rush your research questions and sloppily reword your objectives as questions. Carefully think about what exactly you’re trying to achieve (i.e. your research aim) and the objectives you’ve set out, then craft a set of well-aligned research questions . Also, keep in mind that this can be a somewhat iterative process , where you go back and tweak research objectives and aims to ensure tight alignment throughout the golden thread.
The importance of strong alignment
Alignment is the keyword here and we have to stress its importance . Simply put, you need to make sure that there is a very tight alignment between all three pieces of the golden thread. If your research aims and research questions don’t align, for example, your project will be pulling in different directions and will lack focus . This is a common problem students face and can cause many headaches (and tears), so be warned.
Take the time to carefully craft your research aims, objectives and research questions before you run off down the research path. Ideally, get your research supervisor/advisor to review and comment on your golden thread before you invest significant time into your project, and certainly before you start collecting data .
Recap: The golden thread
In this post, we unpacked the golden thread of research, consisting of the research aims , research objectives and research questions . You can jump back to any section using the links below.
As always, feel free to leave a comment below – we always love to hear from you. Also, if you’re interested in 1-on-1 support, take a look at our private coaching service here.

You Might Also Like:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Dissertation While Working: A How-To Guide
Struggling to balance your dissertation with a full-time job and family? Learn practical strategies to achieve success.

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
41 Comments
Thank you very much for your great effort put. As an Undergraduate taking Demographic Research & Methodology, I’ve been trying so hard to understand clearly what is a Research Question, Research Aim and the Objectives in a research and the relationship between them etc. But as for now I’m thankful that you’ve solved my problem.
Well appreciated. This has helped me greatly in doing my dissertation.
An so delighted with this wonderful information thank you a lot.
so impressive i have benefited a lot looking forward to learn more on research.
I am very happy to have carefully gone through this well researched article.
Infact,I used to be phobia about anything research, because of my poor understanding of the concepts.
Now,I get to know that my research question is the same as my research objective(s) rephrased in question format.
I please I would need a follow up on the subject,as I intends to join the team of researchers. Thanks once again.
Thanks so much. This was really helpful.
I know you pepole have tried to break things into more understandable and easy format. And God bless you. Keep it up
i found this document so useful towards my study in research methods. thanks so much.
This is my 2nd read topic in your course and I should commend the simplified explanations of each part. I’m beginning to understand and absorb the use of each part of a dissertation/thesis. I’ll keep on reading your free course and might be able to avail the training course! Kudos!
Thank you! Better put that my lecture and helped to easily understand the basics which I feel often get brushed over when beginning dissertation work.
This is quite helpful. I like how the Golden thread has been explained and the needed alignment.
This is quite helpful. I really appreciate!
The article made it simple for researcher students to differentiate between three concepts.
Very innovative and educational in approach to conducting research.
I am very impressed with all these terminology, as I am a fresh student for post graduate, I am highly guided and I promised to continue making consultation when the need arise. Thanks a lot.
A very helpful piece. thanks, I really appreciate it .
Very well explained, and it might be helpful to many people like me.
Wish i had found this (and other) resource(s) at the beginning of my PhD journey… not in my writing up year… 😩 Anyways… just a quick question as i’m having some issues ordering my “golden thread”…. does it matter in what order you mention them? i.e., is it always first aims, then objectives, and finally the questions? or can you first mention the research questions and then the aims and objectives?
Thank you for a very simple explanation that builds upon the concepts in a very logical manner. Just prior to this, I read the research hypothesis article, which was equally very good. This met my primary objective.
My secondary objective was to understand the difference between research questions and research hypothesis, and in which context to use which one. However, I am still not clear on this. Can you kindly please guide?
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study. Research questions are broader and guide the overall study, while hypotheses are specific and testable statements used in quantitative research. Research questions identify the problem, while hypotheses provide a focus for testing in the study.
Exactly what I need in this research journey, I look forward to more of your coaching videos.
This helped a lot. Thanks so much for the effort put into explaining it.
What data source in writing dissertation/Thesis requires?
What is data source covers when writing dessertation/thesis
This is quite useful thanks
I’m excited and thankful. I got so much value which will help me progress in my thesis.
where are the locations of the reserch statement, research objective and research question in a reserach paper? Can you write an ouline that defines their places in the researh paper?
Very helpful and important tips on Aims, Objectives and Questions.
Thank you so much for making research aim, research objectives and research question so clear. This will be helpful to me as i continue with my thesis.
Thanks much for this content. I learned a lot. And I am inspired to learn more. I am still struggling with my preparation for dissertation outline/proposal. But I consistently follow contents and tutorials and the new FB of GRAD Coach. Hope to really become confident in writing my dissertation and successfully defend it.
As a researcher and lecturer, I find splitting research goals into research aims, objectives, and questions is unnecessarily bureaucratic and confusing for students. For most biomedical research projects, including ‘real research’, 1-3 research questions will suffice (numbers may differ by discipline).
Awesome! Very important resources and presented in an informative way to easily understand the golden thread. Indeed, thank you so much.
Well explained
The blog article on research aims, objectives, and questions by Grad Coach is a clear and insightful guide that aligns with my experiences in academic research. The article effectively breaks down the often complex concepts of research aims and objectives, providing a straightforward and accessible explanation. Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced researcher, this article provides practical insights that contribute to the foundational aspects of a successful research endeavor.
A great thanks for you. it is really amazing explanation. I grasp a lot and one step up to research knowledge.
I really found these tips helpful. Thank you very much Grad Coach.
I found this article helpful. Thanks for sharing this.
thank you so much, the explanation and examples are really helpful
This is a well researched and superbly written article for learners of research methods at all levels in the research topic from conceptualization to research findings and conclusions. I highly recommend this material to university graduate students. As an instructor of advanced research methods for PhD students, I have confirmed that I was giving the right guidelines for the degree they are undertaking.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
- Defining Research Objectives: How To Write Them

Almost all industries use research for growth and development. Research objectives are how researchers ensure that their study has direction and makes a significant contribution to growing an industry or niche.
Research objectives provide a clear and concise statement of what the researcher wants to find out. As a researcher, you need to clearly outline and define research objectives to guide the research process and ensure that the study is relevant and generates the impact you want.
In this article, we will explore research objectives and how to leverage them to achieve successful research studies.
What Are Research Objectives?
Research objectives are what you want to achieve through your research study. They guide your research process and help you focus on the most important aspects of your topic.
You can also define the scope of your study and set realistic and attainable study goals with research objectives. For example, with clear research objectives, your study focuses on the specific goals you want to achieve and prevents you from spending time and resources collecting unnecessary data.
However, sticking to research objectives isn’t always easy, especially in broad or unconventional research. This is why most researchers follow the SMART criteria when defining their research objectives.
Understanding SMART Criteria in Research
Think of research objectives as a roadmap to achieving your research goals, with the SMART criteria as your navigator on the map.
SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. These criteria help you ensure that your research objectives are clear, specific, realistic, meaningful, and time-bound.
Here’s a breakdown of the SMART Criteria:
Specific : Your research objectives should be clear: what do you want to achieve, why do you want to achieve it, and how do you plan to achieve it? Avoid vague or broad statements that don’t provide enough direction for your research.
Measurable : Your research objectives should have metrics that help you track your progress and measure your results. Also, ensure the metrics are measurable with data to verify them.
Achievable : Your research objectives should be within your research scope, timeframe, and budget. Also, set goals that are challenging but not impossible.
Relevant: Your research objectives should be in line with the goal and significance of your study. Also, ensure that the objectives address a specific issue or knowledge gap that is interesting and relevant to your industry or niche.
Time-bound : Your research objectives should have a specific deadline or timeframe for completion. This will help you carefully set a schedule for your research activities and milestones and monitor your study progress.
Characteristics of Effective Research Objectives
Clarity : Your objectives should be clear and unambiguous so that anyone who reads them can understand what you intend to do. Avoid vague or general terms that could be taken out of context.
Specificity : Your objectives should be specific and address the research questions that you have formulated. Do not use broad or narrow objectives as they may restrict your field of research or make your research irrelevant.
Measurability : Define your metrics with indicators or metrics that help you determine if you’ve accomplished your goals or not. This will ensure you are tracking the research progress and making interventions when needed.
Also, do use objectives that are subjective or based on personal opinions, as they may be difficult to accurately verify and measure.
Achievability : Your objectives should be realistic and attainable, given the resources and time available for your research project. You should set objectives that match your skills and capabilities, they can be difficult but not so hard that they are realistically unachievable.
For example, setting very difficult make you lose confidence, and abandon your research. Also, setting very simple objectives could demotivate you and prevent you from closing the knowledge gap or making significant contributions to your field with your research.
Relevance : Your objectives should be relevant to your research topic and contribute to the existing knowledge in your field. Avoid objectives that are unrelated or insignificant, as they may waste your time or resources.
Time-bound : Your objectives should be time-bound and specify when you will complete them. Have a realistic and flexible timeframe for achieving your objectives, and track your progress with it.
Steps to Writing Research Objectives
Identify the research questions.
The first step in writing effective research objectives is to identify the research questions that you are trying to answer. Research questions help you narrow down your topic and identify the gaps or problems that you want to address with your research.
For example, if you are interested in the impact of technology on children’s development, your research questions could be:
- What is the relationship between technology use and academic performance among children?
- Are children who use technology more likely to do better in school than those who do not?
- What is the social and psychological impact of technology use on children?
Brainstorm Objectives
Once you have your research questions, you can brainstorm possible objectives that relate to them. Objectives are more specific than research questions, and they tell you what you want to achieve or learn in your research.
You can use verbs such as analyze, compare, evaluate, explore, investigate, etc. to express your objectives. Also, try to generate as many objectives as possible, without worrying about their quality or feasibility at this stage.
Prioritize Objectives
Once you’ve brainstormed your objectives, you’ll need to prioritize them based on their relevance and feasibility. Relevance is how relevant the objective is to your research topic and how well it fits into your overall research objective.
Feasibility is how realistic and feasible the objective is compared to the time, money, and expertise you have. You can create a matrix or ranking system to organize your objectives and pick the ones that matter the most.
Refine Objectives
The next step is to refine and revise your objectives to ensure clarity and specificity. Start by ensuring that your objectives are consistent and coherent with each other and with your research questions.
Make Objectives SMART
A useful way to refine your objectives is to make them SMART, which stands for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Specific : Objectives should clearly state what you hope to achieve.
- Measurable : They should be able to be quantified or evaluated.
- Achievable : realistic and within the scope of the research study.
- Relevant : They should be directly related to the research questions.
- Time-bound : specific timeframe for research completion.
Review and Finalize Objectives
The final step is to review your objectives for coherence and alignment with your research questions and aim. Ensure your objectives are logically connected and consistent with each other and with the purpose of your study.
You also need to check that your objectives are not too broad or too narrow, too easy or too hard, too many or too few. You can use a checklist or a rubric to evaluate your objectives and make modifications.
Examples of Well-Written Research Objectives
Example 1- Psychology
Research question: What are the effects of social media use on teenagers’ mental health?
Objective : To determine the relationship between the amount of time teenagers in the US spend on social media and their levels of anxiety and depression before and after using social media.
What Makes the Research Objective SMART?
The research objective is specific because it clearly states what the researcher hopes to achieve. It is measurable because it can be quantified by measuring the levels of anxiety and depression in teenagers.
Also, the objective is achievable because the researcher can collect enough data to answer the research question. It is relevant because it is directly related to the research question. It is time-bound because it has a specific deadline for completion.
Example 2- Marketing
Research question : How can a company increase its brand awareness by 10%?
Objective : To develop a marketing strategy that will increase the company’s sales by 10% within the next quarter.
How Is this Research Objective SMART?
The research states what the researcher hopes to achieve ( Specific ). You can also measure the company’s reach before and after the marketing plan is implemented ( Measurable ).
The research objective is also achievable because you can develop a marketing plan that will increase awareness by 10% within the timeframe. The objective is directly related to the research question ( Relevant ). It is also time-bound because it has a specific deadline for completion.
Research objectives are a well-designed roadmap to completing and achieving your overall research goal.
However, research goals are only effective if they are well-defined and backed up with the best practices such as the SMART criteria. Properly defining research objectives will help you plan and conduct your research project effectively and efficiently.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- research goals
- research objectives
- research roadmap
- smart goals
- SMART research objectives
- Moradeke Owa

You may also like:
Research Summary: What Is It & How To Write One
Introduction A research summary is a requirement during academic research and sometimes you might need to prepare a research summary...

Desk Research: Definition, Types, Application, Pros & Cons
If you are looking for a way to conduct a research study while optimizing your resources, desk research is a great option. Desk research...
Subgroup Analysis: What It Is + How to Conduct It
Introduction Clinical trials are an integral part of the drug development process. They aim to assess the safety and efficacy of a new...
Projective Techniques In Surveys: Definition, Types & Pros & Cons
Introduction When you’re conducting a survey, you need to find out what people think about things. But how do you get an accurate and...
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..

Research Aims and Objectives: The dynamic duo for successful research
Picture yourself on a road trip without a destination in mind — driving aimlessly, not knowing where you’re headed or how to get there. Similarly, your research is navigated by well-defined research aims and objectives. Research aims and objectives are the foundation of any research project. They provide a clear direction and purpose for the study, ensuring that you stay focused and on track throughout the process. They are your trusted navigational tools, leading you to success.
Understanding the relationship between research objectives and aims is crucial to any research project’s success, and we’re here to break it down for you in this article. Here, we’ll explore the importance of research aims and objectives, understand their differences, and delve into the impact they have on the quality of research.
Understanding the Difference between Research Aims and Objectives
In research, aims and objectives are two important components but are often used interchangeably. Though they may sound similar, they are distinct and serve different purposes.
Research Aims:
Research aims are broad statements that describe the overall purpose of your study. They provide a general direction for your study and indicate the intended achievements of your research. Aims are usually written in a general and abstract manner describing the ultimate goal of the research.
Research Objectives:
Research objectives are specific, measurable, and achievable goals that you aim to accomplish within a specified timeframe. They break down the research aims into smaller, more manageable components and provide a clear picture of what you want to achieve and how you plan to achieve it.
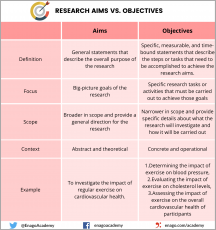
In the example, the objectives provide specific targets that must be achieved to reach the aim. Essentially, aims provide the overall direction for the research while objectives provide specific targets that must be achieved to accomplish the aims. Aims provide a broad context for the research, while the objectives provide smaller steps that the researcher must take to accomplish the overall research goals. To illustrate, when planning a road trip, your research aim is the destination you want to reach, and your research objectives are the specific routes you need to take to get there.
Aims and objectives are interconnected. Objectives play a key role in defining the research methodology, providing a roadmap for how you’ll collect and analyze data, while aim is the final destination, which represents the ultimate goal of your research. By setting specific goals, you’ll be able to design a research plan that helps you achieve your objectives and, ultimately, your research aim.
Importance of Well-defined Aims and Objectives
The impact of clear research aims and objectives on the quality of research cannot be understated. But it’s not enough to simply have aims and objectives. Well-defined research aims and objectives are important for several reasons:
- Provides direction: Clear aims and well-defined objectives provide a specific direction for your research study, ensuring that the research stays focused on a specific topic or problem. This helps to prevent the research from becoming too broad or unfocused, and ensures that the study remains relevant and meaningful.
- Guides research design: The research aim and objectives help guide the research design and methodology, ensuring that your study is designed in a way that will answer the research questions and achieve the research objectives.
- Helps with resource allocation: Clear research aims and objectives helps you to allocate resources effectively , including time, financial resources, human resources, and other required materials. With a well-defined aim and objectives, you can identify the resources required to conduct the research, and allocate them in a way that maximizes efficiency and productivity.
- Assists in evaluation: Clearly specified research aims and objectives allow for effective evaluation of your research project’s success. You can assess whether the research has achieved its objectives, and whether the aim has been met. This evaluation process can help to identify areas of the research project that may require further attention or modification.
- Enhances communication: Well-defined research aims and objectives help to enhance communication among the research team, stakeholders, funding agencies, and other interested parties. Clear aims and objectives ensure that everyone involved in your research project understands the purpose and goals of the study. This can help to foster collaboration and ensure that everyone is working towards the same end goal.
How to Formulate Research Aims and Objectives
Formulating effective research aims and objectives involves a systematic process to ensure that they are clear, specific, achievable, and relevant. Start by asking yourself what you want to achieve through your research. What impact do you want your research to have? Once you have a clear understanding of your aims, you can then break them down into specific, achievable objectives. Here are some steps you can follow when developing research aims and objectives:
- Identify the research question : Clearly identify the questions you want to answer through your research. This will help you define the scope of your research. Understanding the characteristics of a good research question will help you generate clearer aims and objectives.
- Conduct literature review : When defining your research aim and objectives, it’s important to conduct a literature review to identify key concepts, theories, and methods related to your research problem or question. Conducting a thorough literature review can help you understand what research has been done in the area and what gaps exist in the literature.
- Identify the research aim: Develop a research aim that summarizes the overarching goal of your research. The research aim should be broad and concise.
- Develop research objectives: Based on your research questions and research aim, develop specific research objectives that outline what you intend to achieve through your research. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Use action verbs: Use action verbs such as “investigate,” “examine,” “analyze,” and “compare” to describe your research aims and objectives. This makes them more specific and measurable.
- Ensure alignment with research question: Ensure that the research aim and objectives are aligned with the research question. This helps to ensure that the research remains focused and that the objectives are specific enough to answer your research question.
- Refine and revise: Once the research aim and objectives have been developed, refine and revise them as needed. Seek feedback from your colleagues, mentors, or supervisors to ensure that they are clear, concise, and achievable within the given resources and timeframe.
- Communicate: After finalizing the research aim and objectives, they should be communicated to the research team, stakeholders, and other interested parties. This helps to ensure that everyone is working towards the same end goal and understands the purpose of the study.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid While Formulating Aims and Objectives
There are several common mistakes that researchers can make when writing research aims and objectives. These include:
- Being too broad or vague: Aims and objectives that are too general or unclear can lead to confusion and lack of focus. It is important to ensure that the aims and objectives are concise and clear.
- Being too narrow or specific: On the other hand, aims and objectives that are too narrow or specific may limit the scope of the research and make it difficult to draw meaningful conclusions or implications.
- Being too ambitious: While it is important to aim high, being too ambitious with the aims and objectives can lead to unrealistic expectations and can be difficult to achieve within the constraints of the research project.
- Lack of alignment: The aims and objectives should be directly linked to the research questions being investigated. Otherwise, this will lead to a lack of coherence in the research project.
- Lack of feasibility: The aims and objectives should be achievable within the constraints of the research project, including time, budget, and resources. Failing to consider feasibility may cause compromise of the research quality.
- Failing to consider ethical considerations: The aims and objectives should take into account any ethical considerations, such as ensuring the safety and well-being of study participants.
- Failing to involve all stakeholders: It’s important to involve all relevant stakeholders, such as participants, supervisors, and funding agencies, in the development of the aims and objectives to ensure they are appropriate and relevant.
To avoid these common pitfalls, it is important to be specific, clear, relevant, and realistic when writing research aims and objectives. Seek feedback from colleagues or supervisors to ensure that the aims and objectives are aligned with the research problem , questions, and methodology, and are achievable within the constraints of the research project. It’s important to continually refine your aims and objectives as you go. As you progress in your research, it’s not uncommon for research aims and objectives to evolve slightly, but it’s important that they remain consistent with the study conducted and the research topic.
In summary, research aims and objectives are the backbone of any successful research project. They give you the ability to cut through the noise and hone in on what really matters. By setting clear goals and aligning them with your research questions and methodology, you can ensure that your research is relevant, impactful, and of the highest quality. So, before you hit the road on your research journey, make sure you have a clear destination and steps to get there. Let us know in the comments section below the challenges you faced and the strategies you followed while fomulating research aims and objectives! Also, feel free to reach out to us at any stage of your research or publication by using #AskEnago and tagging @EnagoAcademy on Twitter , Facebook , and Quora . Happy researching!
This particular material has added important but overlooked concepts regarding my experiences in explaining research aims and objectives. Thank you
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Academic Essay Writing Made Simple: 4 types and tips
The pen is mightier than the sword, they say, and nowhere is this more evident…

- Old Webinars
- Webinar Mobile App
Improving Research Manuscripts Using AI-Powered Insights: Enago reports for effective research communication
Language Quality Importance in Academia AI in Evaluating Language Quality Enago Language Reports Live Demo…

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
Simplifying the Literature Review Journey — A comparative analysis of 5 AI summarization tools
Imagine having to skim through and read mountains of research papers and books, only to…

Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Industry News
- Publishing Research
- Promoting Research
- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Open Access Week 2024
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What factors would influence the future of open access (OA) publishing?

COMMENTS
Lots of resources will recommend the SMART approach for developing and writing your research objectives. SMART means that your research objectives are. S pecific. M easurable. A chievable. R elevant. T ime-bound. Here’s an example of a poorly framed research objective: We aim to explore what affects life expectancy.
Research objectives describe the intended outcomes of a research project. They should be specific, clear, and achievable.
A research question is what a study aims to answer, and a research hypothesis is a predictive statement about the relationship between two or more variables, which the study sets out to prove or disprove. Objectives are specific, measurable goals that the study aims to achieve.
A research objective is defined as a clear and concise statement of the specific goals and aims of a research study. It outlines what the researcher intends to accomplish and what they hope to learn or discover through their research.
Research objectives refer to the specific goals or aims of a research study. They provide a clear and concise description of what the researcher hopes to achieve by conducting the research. The objectives are typically based on the research questions and hypotheses formulated at the beginning of the study and are used to guide the research process.
A research aim describes the main goal or the overarching purpose of your research project. In doing so, it acts as a focal point for your research and provides your readers with clarity as to what your study is all about.
Research objectives are integral to the research framework as the nexus between the research problem, questions, and hypotheses. They translate the broad goals of your study into actionable steps, ensuring every aspect of your research is purposefully aligned towards addressing the research problem.
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study.
Defining Research Objectives: How To Write Them. Almost all industries use research for growth and development. Research objectives are how researchers ensure that their study has direction and makes a significant contribution to growing an industry or niche.
Research objectives are specific, measurable, and achievable goals that you aim to accomplish within a specified timeframe. They break down the research aims into smaller, more manageable components and provide a clear picture of what you want to achieve and how you plan to achieve it.