
COMMERCIAL LAW BLOG
Research & Updates

Sub-contracting and Assignment : Resolving the Legal Conundrum

The performance of a contract may require third party involvement towards the fulfilment of obligations under a contract. In certain specific circumstances, the contracting parties may decide to “sub-contract” or “assign” their rights and obligations to a third party depending upon the nature of the contract.
In common parlance, sub-contracting and assignment are used interchangeably, however, a significant difference lies between the two when one examines the terms from a legal stand point. This post aims to discuss the concept of Sub-Contracting and Assignment and explains the key difference between the two concepts.
Sub-contracting
Sub-contracting refers to the delegation of certain duties and obligations by contracting parties to a third party, i.e. a sub-contractor who aids in the performance of the contract. According to the Black’s Law Dictionary, a sub-contract is “where a person has contracted for the performance of certain work and he, in turn, engages a third party to perform the whole or part of that which is included in the original contract, his agreement with such third person is called a subcontract and such person is called a subcontractor .” [1] A subcontractor could be a company, self-employed professionals or an agency undertaking to fulfil obligations under a contract.
Sub-contracting is generally undertaken in complex projects where the contract has a prolonged life cycle or multiple components for completion of a project, for instance, infrastructure contracts, construction contracts, renewable energy contracts or certain information technology-related contracts. However, the rights and duties of the sub-contractor under the sub-contracting agreement are relatively similar to that of the principal contractor in the main agreement.
Furthermore, while drafting a contract, one must ensure to incorporate a clause on sub-contracting which clearly spells out that parties to the contract shall sub-contract the rights and obligations only after seeking prior written consent from the other party. The sub-contracting arrangement maybe two-fold, depending upon the nature of the main contract:
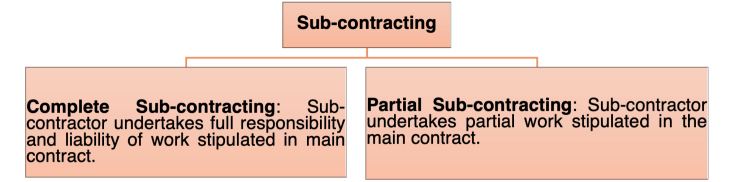
Primarily, the basic idea behind delegation of the obligations to a sub-contractor is to ensure greater flexibility in the performance of the contract. However, it is imperative to enter into a sub-contractor’s agreement that specifies all the details of the work to be performed by the subcontractor, including optimum time required to accomplish the task, payment of charges to the subcontractor, termination of the agreement, etc.
While subcontracting is time-saving and cost efficient, it may result into legal issues between the contracting parties. For instance, issues may arise with respect to the payment conditions where the payment to sub-contractor is contingent upon or linked to the principal contractor receiving its payment from the employer. Further, the courts in India have always upheld the principle of privity of contract between employer and the principal contractor on the one hand and between the principal contractor and sub-contractor(s) on the other. The Supreme Court of India in the case of Zonal General Manager, Ircon International Ltd. v. Vinay Heavy Equipments [2] upheld that in the absence of a back-to-back covenant in the main contract, “ the distinct and sole liability of the middle-contractor is presumed and that the rules in relation to privity of contract will mean that the jural relationship between the employer and the main contractor on the one hand and between the sub-contractor and the main contractor on the other will be quite distinct and separate” . Therefore, in order to avoid ambiguities and future legal squabbles, careful consideration must be given while drafting specific terms and obligation that will pass down the contractual chain.
Assignment of contract refers to an act of transferring contractual rights and liabilities under the contract to a third party with other party’s concurrence. Section 37 of the India Contract Act, 1872 (“ Contract Act ”) enables the contracting parties to dispense with the performance of a contract by way of an assignment. While the principle of assignment is well recognized under Indian law, it derives its origin from the English law.
Assignment of rights is a “complete transfer of rights to receive benefits” accruing to one party under a contract. Performance of a contract may be assigned as long as the contracting parties provide their consent towards the assignment. However, the act of assignment needs to be looked at from the perspective of the contracting parties. Essentially, there are three parties involved, namely, the assignor, assignee and obligor.
An important principle affecting assignments is that the burden or liability under a contract cannot be assigned. Essentially, the moot question that often arises is with respect to assignment of “rights” vis à vis assignment of “obligations”. The Supreme Court in the case of Khardah Company Ltd. v. Raymon & Co. (India) Private Limited [3] categorically distinguished between assignment of “rights” and “obligations”. The court upheld that, “ an assignment of a contract might result by transfer either of the rights or of the obligations thereunder. But there is a well-recognised distinction between these two classes of assignments. As a rule, obligations under a contract cannot be assigned except with the consent of the promisee, and when such consent is given, it is really a novation resulting in substitution of liabilities. On the other hand rights under a contract are assignable unless the contract is personal in its nature (or) the rights are incapable of assignment either under the law or under an agreement between the parties” . Primarily, the court clarified that obtaining prior consent to assign “obligations” under a contract would be considered as novation as it will result into substitution of liabilities and obligations to the assignee. Moreover, introduction of a new party into an existing contract will result into novation of a contract i.e. creation of a new contract between original party and new party. As the courts have interpreted that transfer of obligations can be undertaken through novation, the assignment clause in a contract must clearly deal with novation, if the intention is to transfer obligations.
Furthermore, the Supreme Court, in the case of Gopalbhai Manusudhan [4] , reaffirmed that whenever there is a case of assignment or even the transfer of the obligations, it must be acclaimed that there is the presence of the consent of the parties. Without the consent of the parties, the assignment will be not considered valid. In addition to upholding the legal point, this ruling also indicates that before establishing a commercial contract, the parties must consider the different complications of contracts, such as the objective of the contract and the presence of an assignability clause in the agreement.
Therefore, the judicial trend in India has time and again reiterated and laid down that rights under contract can be assigned unless (a) the contract is personal in nature i.e. requires personal engagement of a specific person or (b) the rights are incapable of assignment either under law or under an agreement between the parties. In the case of Robinson v. Davison [5] , the defendant’s wife pledged to perform piano at a concert on a specific date. Due to “her illness”, she was unable to fulfil her obligation, which was to play the piano at an event. The contract in this instance was ruled to be solely dependent on the defendant’s wife’s good health and personal talent, and the defendant’s wife’s illness led the contract to be void. Further, the court ruled that the defendant could not be held liable for damages as a result of the contract’s non-performance. The wife could not assign her right/obligation to a third party because the contract was founded on the “promisor’s expertise” in the aforesaid case.
While assignment is a boiler plate clause, it requires careful consideration on a case-to-case basis. For instance, in real estate transactions, a buyer would insist on retaining the right to assign the “agreement to sell” in favour of a nominee (a company, affiliate or any other third party), in order to facilitate final conveyance in favour of the intended buyer. Similarly, in lending transactions, a borrower will be prohibited from assigning rights under the contract, however, the lender will retain absolute and free right to assign/sell loan portfolios to other lenders or securitisation company.
The apex court has time and again reiterated that the best policy is to unequivocally state the intent with respect to assignment in the agreement to avoid litigation in the future. The contracting parties must expressly specify the rights and obligations stemming from assignment under a contract. Any agreed limitation on such an assignment must be expressly laid down in the contract to avoid adverse consequences.
For a person drafting a contract, it is important to understand these subtle differences, between sub-contracting and assignment. While “sub-contracting” is delegating or outsourcing the liabilities and obligations, “assignment” is literally transferring the obligations. It will be not fallacious to say that an “assignment” transfers the entire legal obligation to perform to the party assigned the obligation whereas, subcontracting leaves the primary responsibility to perform the obligation with the contracting party.
Archana Balasubramanian (Partner), Vaishnavi Vyas (Associate)
[1] Black’s Law Dictionary 4th ed. (St. Paul: West, 1951).
[2] 2006 SCC OnLine Mad 1107
[3] MANU/SC/0428/1962
[4] Kapilaben & Ors. v Ashok Kumar Jayantilal Seth through POA Gopalbhai Manusudhan 2019 (10) SCJ 269
[5] (1871) LR 6 Ex 269
Share this:
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
Leave a comment Cancel reply
- Agama Announcements
- Arbitration
- Commercial Laws
- Covid-19 Updates
- Criminal Law
- Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain
- Data Protection/Privacy
- Environmental Law
- Family Laws
- In the News
- Intellectual Property Laws
- Labour/Employment
- Labour/Employment – Women
- Real Estate
- Securities Law
- Will & Succession
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address:
This website does not provide any legal advice and is for information purposes only. Any reliance on information or opinion contained herein would be against the advice of the administrators of this website and entirely at risk and cost of the recipient or user of this information. No attorney-client relationship is formed through this website, directly or indirectly. Opinions are of authors and does not necessarily bind the administrators or owners of the website or the law firm.

Create a website or blog at WordPress.com

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
- Constitution of India
- Indian Penal Code
- Indian Contract Act
- Indian Evidence Act
- Transfer of Property
- Intellectual Property Rights
- Consumer Protection
- Right to Information
- Human Rights
- Voice of Women
- Expert Corner
- Case Summary
- Legal Maxims
- Internships
- General Knowledge
- Submit Post
Assignment of Contract

An agreement enforceable by law becomes a contract. A contract involves both rights and obligations because a contract is an agreement enforceable by law. An agreement involves promises from both sides, and thus, there is the creation of both rights and obligations. For instance, X promises to sell his car to Y, and Y promises to pay Rs. 5,00,000 for his car. This constitutes a valid contract between X and Y. Here, the right on the part of X is to get Rs. 5,00,000 as consideration for selling his car, and the obligation for X is to deliver the car to Y as consideration for Rs. 5,00,000 paid to X by Y for selling his car.
Similarly, the right on the part of Y is to get the car delivered as consideration for Rs. 5,00,000 paid, and the obligation for Y is to pay Rs. 5,00,000 as consideration for the vehicle. If either X or Y fails to discharge their responsibility, there will be a breach of contract. In this way, a contract leads to the creation of both rights and obligations for both parties.
Assignment of contract refers to transferring contractual rights and liabilities under the contract to the third party with or without the other party’s concurrence. For instance, X owes Y Rs. 1,000, and Y owes Z the same amount. In this case, Y is under obligation to pay Rs. One thousand to Z and has the right to receive Rs. 1,000 from Z. In this case if Y asks Z to directly pay Rs. 1,000 to X, and if X accepts the same, there will be an assignment of Y’s right to Z. But, if in a similar situation, instead of transferring his ownership, Y would have transferred any of his obligations, then it would amount to novation. Section 37 of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, enables the parties to dispense the performance by way of the contract’s Assignment. Apart from conforming with the Indian Contract Act, 1872, there are exceptional circumstances where the contract assignment must be duly stamped in conformity with the provisions of the Indian Stamp Act, 1899.
The common law system did give effect to three kinds of transactions, viz., acknowledgment, novation, and power of attorney, which to some extent did work of an assignment. Under the Indian Contract Law, any form of contract can be assigned as long as consent is involved in the Assignment. The consent of the ‘promisee’ is necessary for assigning any obligation under the contract. There are three parties involved in contracts of Assignment, namely, the assignor, assignee, and obligor. The working and application of the contract assignment depend on a multiplicity of factors such as the contract’s language, applicability, availability of the assignment clause in the agreement, etc. There are contracts that contain a clause prohibiting Assignment, while other contracts require the consent of the other party to the Assignment.
But if a contract between two parties relies entirely on the’ promisor’s skill or expertise, then such a contract cannot be assigned under any circumstances. This is because the ‘promisee’ has entered into the contract based on the’ promisor’s skill or expertise. The case of Robinson v Davison is important case law in this regard . In this case, the defendant’s wife promised to play piano on a particular at a concert. She was unable to discharge her liability, that is, to play piano at the concert because of her illness. In this case, it was held that the contract was directly dependent on the good health and the personal skill of the defendant’s wife, and the illness of his wife discharged the contract. It was also stated that the defendant could not be made liable to pay compensation for the non-performance of the contract. As the contract was based on the ‘promisor’s skill in the above case law, the wife could not assign her right/obligation to any third party.
Case Study: Kapilaben & Ors. v Ashok Kumar Jayantilal Seth through POA Gopalbhai Manusudhan Case
Kapilaben & Ors. v Ashok Kumar Jayantilal Seth through POA Gopalbhai Manusudhan is a recent judgment delivered by the Supreme Court of India on November 25, 2019, concerning the Assignment of rights and Interests in a contract. In this judgment, the Supreme Court reaffirmed that a party to a contract could not assign its liabilities or obligations without the consent of the other party.
The facts of the case are: The appeals to the Supreme Court resulted from the Gujrat High Court’s decision that had allowed the appeals of the respondent against the trial court’s decision. The dispute, in this case, is related to a property owned by the appellants (Vendor). The appellant has had formulated an agreement to sell in favor of some of the respondents in 1986 regarding the above-mentioned property. The respondents, who were the original vendees, had paid a part of the consideration part. The Original Vendees, in 1987, assigned the former’s rights in favor of Respondent 1 and executed an agreement in favor of Respondent 1. This led to several disputes, and subsequently, Respondent 1 filed suits against the Original Vendees and the vendor demanding specific performance of the agreement executed in 1987. The Respondent’s suits were dismissed by the trial courts stating that the Original Vendees could not have assigned their outstanding obligation of paying Vendor the remaining money to Respondent 1 without the consent of the Vendor. On the other hand, Gujrat High Court reversed the decision of the trial court and declared the Assignment of rights in favor of Respondent 1 as valid.
The Supreme Court in its judgment reaffirmed the view of the trial courts and stated that: “ It is further relevant to note that under the 1987 agreements, payment of the outstanding consideration amount is to be made to the original vendees, not the Appellants, and possession/ownership of the suit property is to be handed over by the original vendees. The 1987 agreements nowhere provide for the discharge of the original vendees’ pending obligations towards the Appellants by Respondent Nos. 1. Hence, we are inclined to accept the Appellants’ argument that the 1987 agreements were not a case of Assignment but appear to be independent/sovereign agreements for sale which were contingent and dependent on the execution and implementation of the 1986 agreement. Therefore, the only way Respondent Nos. 1 can seek specific performance of the 1986 agreement against the Appellants is by proving the Appellants’ knowledge of and consent to transfer the original vendees’ rights and liabilities Respondent Nos. 1.”
From the above discussion, it is clear that the Assignment of contract refers to transferring contractual rights and liabilities under the contract to the third party with or without the other party’s concurrence. Section 37 of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, thatenables the parties to dispense is the performance by way of Assignment of the contract. Under the Indian Contract Law, any form of contract can be assigned as long as consent is involved in the Assignment. The consent of the ‘promisee’ is necessary for assigning any obligation under the contract. The working and application of the contract assignment depend on a multiplicity of factors such as the contract’s language, applicability, availability of the assignment clause in the agreement, etc. There are contracts that contain a clause prohibiting Assignment, while other contracts require the consent of the other party to the Assignment. The Assignment of obligations/liabilities is not possible in the case of contracts solely relying on the personal skill or expertise of the ‘promisor’.
The recent judgment of the Supreme Court in Kapilaben & Ors. v Ashok Kumar Jayantilal Seth, through POA Gopalbhai Manusudhan Case, also reaffirms that in case of transfer/assigning of outstanding obligations under the contract, the consent of the other party is a necessary condition to make the Assignment valid. Even though this judgment reaffirms the point upheld by law, it still suggests the parties to a contract consider the various complexities of contracts, the intent contract, the availability of the assignability clause in the written agreement, etc., before drafting a commercial contract.
References:
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872, No. 2(h) (Indian).
- Dr. R.K. Bangia, The Indian Contract Act, 2 (12 th Edition, 2005), Allahabad Law Agency, Haryana.
- Krishnendu Kanungo & Pritisha Chakraborty , Assignment Of Rights And Its Practical Relevance In Financial Transactions: A Lender’s Perspective Manupatra, http://docs.manupatra.in/newsline/articles/Upload/E915DA6B-361C-493B-91D1-96D8EB703128.pdf (last accessed Mar. 12, 2021).
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872, No. 37 (Indian)
- Sir Oshley Roy Marshall, The Assignment of Choses in Action (Pitman Publishing 1950).
- Krishnendu, supra note 3, at 1.
- Khared & Co. Ltd. v Ramon & Co. Ltd., AIR 1962 SC 1810.
- Krishnendu, supra note 3, at 2.
- Robinson v Davison, (1871) L.R. Ex. 269.
- BANGIA, supra note 1, at 255.
- Ramesh Vaidyanathan & Aishini Mandal, Assignment Of Contractual Obligations – Is Consent Necessary Advayalegal (Dec. 6, 2019) https://www.advayalegal.com/blog/contractual-rights/ (last accessed Mar. 13, 2021).
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
A detailed analysis of provisions related to coercions under the indian contract law, free consent (section 13 & 14), a detailed analysis of provisions related to compensation for loss or damage caused by breach of contract under the indian contract law, editor picks, popular posts, maneka gandhi vs union of india – case summary, contract of bailment and pledge, adm jabalpur vs shivkant shukla (1976) 2 scc 521 – case..., popular category.
- NEWS UPDATE 1750
- Bare Act PDF 919
- Case Summary 363
- Legal Maxims 269
- Articles 177
- Indian Penal Code 104
- Articles 86
- Voice of Women 72

Indian Contract Act 1872 Notes [Law of Contracts Notes]
- Contract Act Blogs Subject-wise Law Notes
- Aishwarya Agrawal
- July 27, 2024

This article provides Contracts Law Notes notes with case laws .
Law of Contracts dealing with matters relating to Contracts. A contract is made when an agreement becomes enforceable by law. There is no legal obligation as long as it is a mere agreement. Once the agreement becomes a contract, there is a legal obligation by the parties involved.
Hello Readers!
As a learner, you can consider this Indian Contract Act 1872 notes as a free, online, and self-paced course.
As a competitive exams aspirant, you will find it perfect for Judicial Service Exams, UPSC CSE Law Optional, etc.
As a reader, this Law of Contracts notes is sufficient for you to learn or research on Indian Contract Act, 1872!
Happy Learning!
Note: For books on Law of Contracts, click here .
Introduction to the Law of Contracts
Agreement under indian contract act (section 2 to 9, indian contract act), capacity to contract under indian contract act (sections: 10, 11, 12, 64, 65, 68), free consent (sections 13 to 22, indian contract act), consideration under indian contract act (sections 23 to 25 indian contract act), lawful object in contracts, void agreements: limitations on freedom of contract (s. 24 – 30, indian contract act), quasi – contracts and unjust enrichment (section 68 to 72, indian contract act), discharge of a contract (section 37 to 67, indian contract act), breach of contract (ss. 73, 74 & 75), contract of indemnity, contract of guarantee under indian contract act, bailment under indian contract act, pledge under indian contract act, agency under indian contract act, other concepts.
For notes on other subjects, click here .
For case briefs and analysis, click here .
We hope you found Indian Contract Act notes’ on every topic related to the Law of Contracts .
If you think we missed anything, help us by mentioning the details in this form.
Disclaimer:
We have done our best to provide the right information. However, we don’t claim the content to be genuine. We suggest readers to do check it.
You might like

What Is Probation Period?

Law on Abortion in India: An Overview

A.K. Roy v Union of India (1982)
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Add Comment *
Post Comment
- Search Menu
Sign in through your institution
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Numismatics
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Social History
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Meta-Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Legal System - Costs and Funding
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Restitution
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Social Issues in Business and Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Research Methodology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Social Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Sustainability
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- Ethnic Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Religion
- Politics and Law
- Politics of Development
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Qualitative Political Methodology
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Disability Studies
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >

7 Parties and Assignment
- Published: September 2024
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This chapter discusses the privity of contract, which is one of the pillars of English contract law. Indian law accepts the common law’s starting position and the strength of the edifice built through repeated judicial affirmation. The privity of contract deals with the effect of a contract on third parties, while the privity of consideration instead covers what role, if any, third parties may play in the formation of a contract. The chapter then considers the exceptions to the privity of contract, including collateral contracts, implied contracts, trusts, marriage settlements, and assignments. It explains that the assignment of contractual rights is subject to restrictions on the transfer of property under Indian law.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.

Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Assignment clause: stating intent clearly in contract is the best policy
Kluwer Arbitration Blog
Does the assignment of a contract assign the arbitration agreement: the indian perspective.
Under the Indian Contract Act 1872 (“ ICA ”), an arbitration agreement is a distinct and separate contract. Like all other contracts, it can be transferred by way of assignment to third parties under Section 37 of the ICA. The Supreme Court of India in Khardah Company Ltd vs Raymon & Co. (India) Private Ltd has held that there is a distinction between the assignment of “rights” and “liabilities.” A contract stands novated when assigning rights and liabilities to a third party. This raises a fundamental question – does the arbitration agreement also stand novated when the principal contract is assigned to a third party? If it does, then as held by the Supreme Court in Kapilaben v. Ashok Kumar Jayantilal Sheth the assignment of every obligation, such as the obligation to refer the dispute to arbitration, requires the parties’ fresh consent.
If, on the other hand, the arbitration agreement does not stand novated on assignment of the principal contract, does it mean that the arbitration agreement is automatically transferred along with the principal contract to the third party without the need for fresh consent (“ Automatic Transfer Approach ”)?
The United States courts have always been divided in their approach. Some earlier decisions, such as Hosiery Mfrs’ Corp. v. Goldston and Nissan Motor Acceptance Corp v. Ross , support the Automatic Transfer Approach. On the contrary, decisions like Lachmar v. Trunkline LNG Co . require express consent of the assignee (third party). However, in recent years courts have critically analysed the principal contract than merely choosing sides to ascertain assignment of the arbitration agreement, adopting an approach similar to the highest court of Bulgaria .
In similar vein, the Indian courts have been inconsistent in their decisions on whether the assignment of a contract also amounts to the assignment of the arbitration agreement to a third party.
Requirement of Specific Consent
In Delhi Iron and Steel Co. Ltd. v. U.P. Electricity Board , the Delhi High Court took the view that the assignment of the principal contract does not ipso facto result in the assignment of the arbitration agreement. The principal contract is assignable, but the arbitration agreement is not. Since an arbitration agreement is a distinct and separate agreement, the arbitral intent between the original party and the assignee of the other party must be made manifest. A similar view was adopted in Vishranti CHSL v. Tattva Mittal Corpn. (P) Ltd . holding that in the absence of specific consent to the assignment of the arbitration agreement, the arbitration agreement would not be assigned to the third party, even if the principal contract has been assigned.
The basis for this view can be found in the judgement of the Indian Supreme Court in M.C. Chacko v. State of Travancore which held that a person who is not a party to the contract cannot enforce the terms of the contract. However, it is pertinent to note that even in this judgement, the Supreme Court had recognised the assignment exception. Thus, the requirement of specific consent by the assignee to transfer the arbitration agreement is an approach adopted by Indian courts only in a handful cases.
No Separate Consent Required
The predominant view by Indian courts has been that the doctrine of separability enshrined under Section 16 of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act 1996 (“ Act ”) relates to the right of the arbitral tribunal to rule on its own jurisdiction. The doctrine of separability and its jurisprudence cannot be extended to mean that a separate arbitration agreement is to be executed between the parties at the time of assignment of a contract. Therefore, as held by the Bombay High Court in DLF Power Ltd. v. Mangalore Refinery & Petrochemicals Ltd . (“ DLF ”), a third party, to whom the principal contract is assigned, can enforce the arbitration agreement.
Specifically, if the rights and obligations under the principal contract are assigned to a third party and this third party also performs obligations under the contract, such as making payments, seeking extension of time or approval, joint survey, etc., this third party is entitled to invoke arbitration.
Consensual Theory of Arbitration
Taking a similar approach, the Delhi High Court in Rajesh Gupta v. Mohit Lata Sunda held that if the parties to the principal contract knew of the assignment and were fully aware that a third party ‘had stepped into the shoes’ of another party, the arbitration agreement stood assigned. These views are essentially based on the consensual theory in arbitration stated in Aerens Goldsouk International Co. Ltd. v. Samit Kavdia , which recognises that non-signatories to the arbitration agreement can invoke the arbitration clause and are thus ‘parties’ to the arbitration agreement under Section 2(1)(h) of the Act.
Consequently, the consensual theory aims to infer consent from the parties’ behaviour if an agreement is not self-evident. Agency, assignment, and group of companies doctrine are among such theories. Recently, the Delhi High Court in Tomorrow Sales Agency (P) Ltd. v. SBS Holdings Inc. , held that the non-signatories may either invoke the arbitration agreement, being the beneficiaries of the contract, or otherwise be bound by the same. The Court noted, “ 30. Gary B. Born, has explained that the legal basis for holding that a non-signatory is bound by an arbitration agreement includes “both purely consensual theories (e.g., agency, assumption, assignment) and non-consensual theories ( e.g. , estoppels, alter ego).” However, this decision has been challenged in an appeal which is currently pending. It would be interesting to see how the court deals with the question of third parties invoking arbitration, especially in cases of assignment of the principal contract.
Nonetheless, the Bombay High Court in DLF echoed a similar view and held that the arbitration clause does not take away the right of assignment of a party to a contract if it is otherwise assignable. The High Court noted that there is a clear distinction between the assignment of rights under a contract by a party who has performed its obligations under the contract and the assignment of a claim. The latter is a mere claim which cannot be assigned in law. It further observed that once the other party has accepted the assignment and insisted on compliance with rights, duties and obligations, the assignee steps into the shoes of the assignor and will be entitled to all rights, obligations and benefits, including the arbitration agreement forming part of the said agreement.
Similarly, in Bestech India (P) Ltd. v. MGF Developments Ltd. , the Delhi High Court considered the parties’ conduct post-assignment of the contract and rejected the submissions of the original party that the assignee had no locus standi to file an application for appointment of an arbitrator or that the assignee had no privity of the contract with the original party.
While Indian courts have been inconsistent in following the Automatic Transfer Approach when the principal contract is assigned, the predominant view aligns with international practices. Though the minority view requiring specific consent for assignment of the arbitration agreement may be correct on a strict reading of the requirement of express consent to refer the dispute to arbitration, a more practical and pragmatic approach requires inferring such consent by the assignment.
As explained by the Singapore Court of Appeal in the case of BXH v. BXI , “an arbitration agreement does not have a purpose or life independent of the substantive obligations that it attaches to.” Thus, the requirement of express consent, though sound, defies a more holistic understanding of the purpose of the arbitration agreement, i.e. , to refer disputes arising out of the obligations under the principal contract to arbitration.
While the views discussed above were from different Indian High Courts, the applicability and binding nature of the arbitration agreement to non-signatories through assignment has now been recognised in the recent landmark judgment by the Indian Supreme Court in Cox and Kings Ltd. v. SAP India Pvt. Ltd. and Another which has been discussed on the Blog here . Though the Supreme Court has not explicitly addressed the issue of the requirement of express consent for assignment of the arbitration agreement, the extension of the arbitration agreement to non-signatories implies that specific consent may not be required for assignment of the arbitration agreement when the principal contract is assigned.
The author would like to thank Mr. Ankit Singh, Senior Associate, Mr. Ayush Kumar, Associate, ANR LAW LLP and Ms. Ramya Singh, Final Year Student, Ram Manohar Lohia National Law University, Lucknow for their research assistance.
________________________
To make sure you do not miss out on regular updates from the Kluwer Arbitration Blog, please subscribe here . To submit a proposal for a blog post, please consult our Editorial Guidelines .
References [ + ]

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Browse Categories
- UK & Ireland

How is this helpful for me?
- Claim the judgments where you have appeared by linking them directly to your profile and maintain a record of your body of work.
- Interact directly with CaseMine users looking for advocates in your area of specialization.
- Creating a unique profile web page containing interviews, posts, articles, as well as the cases you have appeared in, greatly enhances your digital presence on search engines such Google and Bing, resulting in increased client interest.
- The cases linked on your profile facilitate Casemine's artificial intelligence engine in recommending you to potential clients who might be interested in availing your services for similar matters.
Know more
SUGGESTIONS
- Visual Try our Visuals feature which gives you an instant snapshot of the most relevant and landmark case laws.">
Cases cited for the legal proposition you have searched for.
- Judgments 17995
...whether it is transferable or non-transferable. There was considerable argument before us on the question as to assignability of a contract . The law on the subject is well settled and might be stated in simple terms. An ...assignments. As a rule obligations under a contract cannot be assigned except with the consent of the promisee, and when such consent is given, it is really a novation resulting in substitution of liabilit... contract is personal in its character and incapable of assignment on that ground. But it is settled law that an arbitration clause does not take away the right of a party to a contract to...
...clients of ICICI Bank in favour of the assignee”. That, the assignment of a debt can never carry with it the assignment of the obligations of the assignor. Unless there is ...the borrower(s), an assignment of a debt can never carry with it the assignment of the obligations of the assignor unless there is a novation of the contract by all part...the borrower(s), the impugned deed of assignment is legally unsustainable without novation of original contract between ICICI Bank Ltd. (assignor) and the borrower(s) (assignee). We find no merit in the above argum...
...make assignment of the plot. The real question is whether the assignee has a legal right to claim performance of any part from the allottor. The answer of the said question depends upon the terms ... assignment of a contract might result by transfer either of the rights or of the obligations thereunder. But there is a well-recognised distinction between these two classes of assignments. As a rule...obligations under a contract cannot be assigned except with the consent of the promisee, and when such consent is given, it is really a novation resulting in substitution of liabilities. On the other hand ...
..., the Supreme Court held the compensation as falling in the latter category of a capital receipt. But, so far as the case before us is concerned, the assignment of the contract and the payment received...impaired the assessee in any manner in carrying on its business. In these circumstances, the payment for assignment of the contract , in our view, clearly is in the nature of a revenue receipt...business receipt. In the present case also the amount which is received by the assessee-company for assignment of a contract which it had entered into and which formed a part of its business activ...
...property, and the contract to assign thus becomes a complete assignment .”Applying the above principles to the facts of the instant case the High Court came to the... contract would, in equity, transfer the beneficial “interest” and of Jessel, M.R, in Collyer v. Isaacsthat “the contract to assign thus becomes a complete assignment ”. I find...mortgage security on existing chattels and also the benefit of what in form was an assignment of non-existing chattels which might be afterwards brought on to the premises. That assignment , in fact, constituted onl...
...appreciating that the assignor bank is only transferring its rights under a contract and its own asset, namely, the debt as also the mortgagee's rights in the mortgaged properties without in any manner affecting the rights ...held that the law on the subject of assignment of a contract is well settled. An assignment of a contract might result by transfer either of the rights or by transfer of...is a well recognized distinction between the two classes of assignments. As a rule, obligations under a contract cannot be assigned except with the consent of the promisee, and when such consent is given, it is really ...
...other party for assignment under Section 15(b) of the Specific Relief Act is only applicable in cases where the obligation is of a personal nature or where there is an express bar in the contract prohibiti...regarding development of housing scheme in the suit property shows that there was implied consent for assignment of rights under the 1986 agreement in favour of Respondent Nos. 1.III. Validity ...particularly deal with the assignability of contracts, this Court has opined time and again that a party to a contract cannot assign their obligations/liabilities without the consent of the other party. A ...
...No.1, but what the learned Single Judge has overlooked is that there is a distinction between assignment of an obligation and the assignment of a right. The Constitution Bench of the ...obligations under a contract cannot be assigned except with the consent of the promise, and when such consent is given, it is really a novation resulting in sub-situation of liabili...concerned was situated. 14. Concerning the assignment of the right under the contract , on hiving off the business of defendant No.1 and the hived off business vested in defendant No.2...
...P. Somarajan, J.:— The accused Nos. 4 and 5 respectively came up in two criminal cases foisted against them under Section 500 IPC, on the basis of a news item published in ‘Madhyamam Daily’ newspaper dated 29/06/2011. It...give the contract to Keltron, subsequently it was cancelled. It is at that juncture a news item was published in ‘Madhyamam Daily’ newspaper detailing the history of the alleged contract and attempt on...the part of the government to give the contract work to the defacto complainant, company. Now the company came up claiming that it would constitute defamation as against the company. 2...
...us, however, have no bearing on the point in question. They relate to sub-letting or assignment of a contract , contrary to the terms on which the contract was granted. For example there are cases in...own allegations. A large number of cases were cited before us as to whether the agreement was vitiated, as found by the learned Judge of the court below. Most of the cases cited before...contracts obtained from the railway company, that the defendants worked as the plaintiff's servants and that all the profits received by the carrying out of the contract ought to go to the plaintiff...
...vested in the insurer.16. The equitable assignment of the rights and remedies of the assured in favour of the insurer, implied in a contract of indemnity, known as “sub...is part of the law of contract and the other part of the law of restitution.”23. An “ assignment ” on the other hand, refers to a transfer of a.... Subrogation, as an equitable assignment , is inherent, incidental and collateral to a contract of indemnity, which occurs automatically, when the insurer settles the claim under the policy, by...
....20. In Kapilaben's case (supra) this Court had considered that assignment of a contract might result in transfer of either rights or obligations thereunder. The transfer of oblig...particularly deal with the assignability of contracts, this Court has opined time and again that a party to a contract cannot assign their obligations/liabilities without the consent of the other party. A ...between these two classes of assignments. As a rule obligations under a contract cannot be assigned except with the consent of the promisee, and when such consent is given, it is really a novation resulting in subs...
...essential from the assignment of a contract already broken, under which the only surviving right is the right to sue for damages? This right, it is to be observed, is quite distinct from and must not be...transferee of the reversion no question arises here, and we have nothing to do with it. But as between the lessor and the lessee the case is different. They had entered into a contract of leasing on...notice and thereupon to sue on the contract and enforce the penalty. That is the very point. Could he? For what is this, thus isolated, but a mere right to sue? How can it be distinguished in any...
...action, but as the enforcement of a cause of action legitimately supported by the underwriter's interest in recouping himself in respect of the amount of the loss which he had paid under the policy as ...insurance money or the right to claim the benefit of a contract not coupled with any liability.14. Section 6(e) of the Transfer of Property Act states that a mere right...maintenance. That interest must exist apart from the assignment and to that extent must be independent of it.15. A chose in action for breach of contract was not assignable at...
...he took the assignment of the policy on October 18, 1945 he was merely indulging in a gamble on Mahajan Deolal's life; the contract was therefore, void by reason of s. 30 of the Indian ...these contentions; because if Mahajan Deolal was himself guilty of a fraudulent suppression of material facts on which the respondent company was discharged from performing its part of the contract , the ap.... On behalf of the appellant, however, the contention was that s. 38 of the insurance Act provided a complete code for assignment and transfer of insurance policies and the assignment made in favour of...
...sales-tax again, which the appellants contended, was not demandable as there were no second sales; the delivery of a kutcha delivery order did not amount to a sale of goods, but was only an assignment ...was only an assignment of a forward contract . Held, that the agreements...and the delivery of the kutcha delivery order did not amount to a sale of goods, but was only an assignment of a right to obtain delivery of the gunnies, which were not in existence ...
...plaintiff in his evidence that the ' contract of bailment had been entered into by his agent. 4. I need not consider the case of assignment of a contract because in the in...filed by the consignor who was a party to the contract of consignment, the suit should have been dismissed, as it was a suit filed by a bare consignee against the Railway. The contention is well founded.... This is a case of bailment of goods to the Railway. The word "bailment" is thus defined in Section 148 of the Indian Contract Act :- "A "bailment" is the...
...substitute the original contract with a new contract or rescind or alter. It cannot be done unilaterally…”33. In any case, obligations under a contract cannot be assigned, wit.... Novatio, rescission or alteration of a contract under Section 62 of the Indian Contract Act can only be done with the agreement of both the parties of a contract . Both the parties have to agree to... a ...
...Khardah Company Ltd. v. Raymon & Co. (India) Private Ltd. and Company, AIR 1962 SC 1810, the Supreme Court observed that an assignment of a ...rights or of the obligations thereunder. But there is well recognised distinction between these two classes of assignments. As a rule obligations under a contract cannot be assigned, except with the consent of the promisee ...the law or under an agreement between the parties.The doctrine of assignment is also known to the insurance law and an assignment of the policy is a transfer of the ...
...any case there was no evidence of compliance with Section 16(c) of the Act either by the seventh defendant or by the plaintiff. It is also contended that the assignment of the agreement in favour of the pl...bar for the allottee to make assignment of the plot. The real question is whether the assignee has a legal right to claim performance of any part from the allottor. Answer of the said question depends upon...well settled and might be stated in simple terms. An assignment of a contract might result by transfer either of the rights or of the obligations thereunder. But there is a well-recognized distinction...
Keyword Alert(s)
Create alert, update courts.
- Supreme Court & High Court
Overruled By
Our algorithms sense that you may get better results by trying out the same excerpt in our CaseIQ interface.
Sub-Contracting And Assignment : Resolving The Legal Conundrum
Contributor.

The performance of a contract may require third party involvement towards the fulfilment of obligations under a contract. In certain specific circumstances, the contracting parties may decide to "sub-contract" or "assign" their rights and obligations to a third party depending upon the nature of the contract.
In common parlance, sub-contracting and assignment are used interchangeably, however, a significant difference lies between the two when one examines the terms from a legal stand point. This post aims to discuss the concept of Sub-Contracting and Assignment and explains the key difference between the two concepts.
Sub-contracting
Sub-contracting refers to the delegation of certain duties and obligations by contracting parties to a third party, i.e. a sub-contractor who aids in the performance of the contract. According to the Black's Law Dictionary, a sub-contract is "where a person has contracted for the performance of certain work and he, in turn, engages a third party to perform the whole or part of that which is included in the original contract, his agreement with such third person is called a subcontract and such person is called a subcontractor ." 1 A subcontractor could be a company, self-employed professionals or an agency undertaking to fulfil obligations under a contract.
Sub-contracting is generally undertaken in complex projects where the contract has a prolonged life cycle or multiple components for completion of a project, for instance, infrastructure contracts, construction contracts, renewable energy contracts or certain information technology-related contracts. However, the rights and duties of the sub-contractor under the sub-contracting agreement are relatively similar to that of the principal contractor in the main agreement.
Furthermore, while drafting a contract, one must ensure to incorporate a clause on sub-contracting which clearly spells out that parties to the contract shall sub-contract the rights and obligations only after seeking prior written consent from the other party. The sub-contracting arrangement maybe two-fold, depending upon the nature of the main contract:
Primarily, the basic idea behind delegation of the obligations to a sub-contractor is to ensure greater flexibility in the performance of the contract. However, it is imperative to enter into a sub-contractor's agreement that specifies all the details of the work to be performed by the subcontractor, including optimum time required to accomplish the task, payment of charges to the subcontractor, termination of the agreement, etc.
While subcontracting is time-saving and cost efficient, it may result into legal issues between the contracting parties. For instance, issues may arise with respect to the payment conditions where the payment to sub-contractor is contingent upon or linked to the principal contractor receiving its payment from the employer. Further, the courts in India have always upheld the principle of privity of contract between employer and the principal contractor on the one hand and between the principal contractor and sub-contractor(s) on the other. The Supreme Court of India in the case of Zonal General Manager, Ircon International Ltd. v. Vinay Heavy Equipments 2 upheld that in the absence of a back-to-back covenant in the main contract, " the distinct and sole liability of the middle-contractor is presumed and that the rules in relation to privity of contract will mean that the jural relationship between the employer and the main contractor on the one hand and between the sub-contractor and the main contractor on the other will be quite distinct and separate" . Therefore, in order to avoid ambiguities and future legal squabbles, careful consideration must be given while drafting specific terms and obligation that will pass down the contractual chain.
Assignment of contract refers to an act of transferring contractual rights and liabilities under the contract to a third party with other party's concurrence. Section 37 of the India Contract Act, 1872 (" Contract Act ") enables the contracting parties to dispense with the performance of a contract by way of an assignment. While the principle of assignment is well recognized under Indian law, it derives its origin from the English law.
Assignment of rights is a "complete transfer of rights to receive benefits" accruing to one party under a contract. Performance of a contract may be assigned as long as the contracting parties provide their consent towards the assignment. However, the act of assignment needs to be looked at from the perspective of the contracting parties. Essentially, there are three parties involved, namely, the assignor, assignee and obligor.
An important principle affecting assignments is that the burden or liability under a contract cannot be assigned. Essentially, the moot question that often arises is with respect to assignment of "rights" vis à vis assignment of "obligations". The Supreme Court in the case of Khardah Company Ltd. v. Raymon & Co. (India) Private Limited 3 categorically distinguished between assignment of "rights" and "obligations". The court upheld that, " an assignment of a contract might result by transfer either of the rights or of the obligations thereunder. But there is a well-recognised distinction between these two classes of assignments. As a rule, obligations under a contract cannot be assigned except with the consent of the promisee, and when such consent is given, it is really a novation resulting in substitution of liabilities. On the other hand rights under a contract are assignable unless the contract is personal in its nature (or) the rights are incapable of assignment either under the law or under an agreement between the parties" . Primarily, the court clarified that obtaining prior consent to assign "obligations" under a contract would be considered as novation as it will result into substitution of liabilities and obligations to the assignee. Moreover, introduction of a new party into an existing contract will result into novation of a contract i.e. creation of a new contract between original party and new party. As the courts have interpreted that transfer of obligations can be undertaken through novation, the assignment clause in a contract must clearly deal with novation, if the intention is to transfer obligations.
Furthermore, the Supreme Court, in the case of Gopalbhai Manusudhan 4 , reaffirmed that whenever there is a case of assignment or even the transfer of the obligations, it must be acclaimed that there is the presence of the consent of the parties. Without the consent of the parties, the assignment will be not considered valid. In addition to upholding the legal point, this ruling also indicates that before establishing a commercial contract, the parties must consider the different complications of contracts, such as the objective of the contract and the presence of an assignability clause in the agreement.
Therefore, the judicial trend in India has time and again reiterated and laid down that rights under contract can be assigned unless (a) the contract is personal in nature i.e. requires personal engagement of a specific person or (b) the rights are incapable of assignment either under law or under an agreement between the parties. In the case of Robinson v. Davison 5 , the defendant's wife pledged to perform piano at a concert on a specific date. Due to "her illness", she was unable to fulfil her obligation, which was to play the piano at an event. The contract in this instance was ruled to be solely dependent on the defendant's wife's good health and personal talent, and the defendant's wife's illness led the contract to be void. Further, the court ruled that the defendant could not be held liable for damages as a result of the contract's non-performance. The wife could not assign her right/obligation to a third party because the contract was founded on the "promisor's expertise" in the aforesaid case.
While assignment is a boiler plate clause, it requires careful consideration on a case-to-case basis. For instance, in real estate transactions, a buyer would insist on retaining the right to assign the "agreement to sell" in favour of a nominee (a company, affiliate or any other third party), in order to facilitate final conveyance in favour of the intended buyer. Similarly, in lending transactions, a borrower will be prohibited from assigning rights under the contract, however, the lender will retain absolute and free right to assign/sell loan portfolios to other lenders or securitisation company.
The apex court has time and again reiterated that the best policy is to unequivocally state the intent with respect to assignment in the agreement to avoid litigation in the future. The contracting parties must expressly specify the rights and obligations stemming from assignment under a contract. Any agreed limitation on such an assignment must be expressly laid down in the contract to avoid adverse consequences.
For a person drafting a contract, it is important to understand these subtle differences, between sub-contracting and assignment. While "sub-contracting" is delegating or outsourcing the liabilities and obligations, "assignment" is literally transferring the obligations. It will be not fallacious to say that an "assignment" transfers the entire legal obligation to perform to the party assigned the obligation whereas, subcontracting leaves the primary responsibility to perform the obligation with the contracting party.
1. Black's Law Dictionary 4th ed. (St. Paul: West, 1951).
2. 2006 SCC OnLine Mad 1107
3. MANU/SC/0428/1962
4. Kapilaben & Ors. v Ashok Kumar Jayantilal Seth through POA Gopalbhai Manusudhan 2019 (10) SCJ 269
5. (1871) LR 6 Ex 269
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

Corporate/Commercial Law
Mondaq uses cookies on this website. By using our website you agree to our use of cookies as set out in our Privacy Policy.

The Legal Quotient
In Legal Matters, Legal Quotient Matters

Introduction to Indian Contract Act, 1872
Adv Hemant More
Law and You > Business Laws > Indian Contract Act, 1872 > Introduction to Indian Contract Act, 1872
Prior to the Indian Contract Act, English law of the contract was followed in India. The extent of modifications made in the Act as per the Indian conditions and its adaptability to the Indian economy. Before the act was enacted , the contractual relationship was governed by the personal laws of different religious communities like different laws for Hindu and Muslims. In this article, let us have Introduction to Indian Contract Act, 1872

Introduction to Indian Contract Act, 1872:
Purpose or Objectives of the Act:
- According to the preamble of the Act, the main purpose is to define and amend certain parts of the law relating to contracts.
- To ensure reasonable fulfilment of expectations created by the promises of the parties and also enforcement of obligations prescribed by an agreement between the parties.
- The object of the Act is also to introduce definiteness in commercial transactions.
Salient Features of the Act:
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872 has 11 chapters.
- Law of contract creates jus in personum and not in jus in rem. The Latin word ‘Jus in personum’ means right against person. It is a right impose a particular person’s duty by initiating an action against such person. “Jus in rem” means a right enforceable against anyone in the world interfering with that right founded on some specific relationship, status, or particular property accorded legal protection from interference by anyone.
- The Indian Contract Act consists of the following two parts: (a) General principals of the Law of Contract and (b) Special kinds of contracts. The general principals of the Law of Contract are contained in Sections 1 to 75 of the Indian Contract Act. These principles apply to all kinds of contracts irrespective of their nature. Special contracts are contained in Sections 124 to 238 of the Indian Contract Act. These special contracts are Indemnity, Guarantee, Bailment, pledge, and Agency.
- The Act is neither retrospective (dealing with past events or situations) nor exhaustive (considering all elements). It seals mainly with the general principles of embodying contracts and Special Contract.
- The Act doesn’t cover the whole field of contract law. Besides the contract act, other regulating laws are the Transfer of Property Act (deals with the transfer of immovable property), the Sale of Goods Act (deals with the sale of goods), the Partnership Act (deals with the partnership agreements), etc.
- The Act applies only to those agreements which are valid and enforceable by law. An agreement which does not give rise to any legal obligations will not be enforceable by law.
- Social, religious and moral obligations, like marriage, conveyance of gifts, etc., are not enforceable by law as contracts.
- The Act only provides rules and regulations for the purpose of the contract.
- The Act does not list any rights and liabilities between parties to the contract. The contracting parties are at liberty to make rules and regulations about the enforcement of their rights and the fulfilment of their duties. Rights and liabilities and their manner of performance are decided by the parties themselves under the contract but it is within the purview of the act.
- The Act does not affect particular customs and usages of trade, which are not inconsistent with any of the provisions of law.
- The Act does not cover the agreements which result in the transfer or the destruction of rights.
- In case, a particular matter is not covered by any section of the Contract Act or by any other law in force in India, the courts may follow the principles of English Common Law, provided they are not inconsistent with Indian conditions and circumstances.
According to Section 1 of the Indian Contract Act, the Act may be called the Indian Contract Act, 1872. It extends to the whole of India and it shall come into force on the first day of September, 1872. The Act is enacted on 25th April, 1872.
Conclusion:
The Indian Contract Act, 1872, serves as a foundational framework for contract law in India, establishing essential principles governing agreements and their enforcement. Its primary aim is to create a legal environment where parties can enter into agreements with certainty and security, fostering trust and facilitating commerce.
The Act delineates the essential elements of a valid contract: offer, acceptance, consideration, and the intention to create legal relations. It emphasizes that for an agreement to be enforceable, it must be supported by consideration, which is a crucial aspect distinguishing enforceable contracts from mere social agreements.
Furthermore, the Act categorizes contracts into various types—such as valid, void, voidable, and contingent contracts—providing clarity on the enforceability of different agreements. This classification is significant for parties seeking legal recourse, as it helps ascertain their rights and obligations under various circumstances.
The provisions regarding performance of contracts and breach are pivotal in defining the liabilities of parties. The Act outlines rules for fulfilling contractual obligations and the consequences of non-performance, including remedies such as damages, specific performance, and injunctions. This framework ensures that parties have recourse in the event of a breach, thereby promoting accountability in contractual dealings.
Another critical aspect of the Act is its provisions on voidable contracts and the capacity to contract. The law recognizes that certain individuals, such as minors or persons of unsound mind, may lack the capacity to enter into contracts, thus protecting vulnerable parties. It also addresses issues of coercion, undue influence, fraud, and misrepresentation, emphasizing the need for genuine consent.
While the Indian Contract Act is comprehensive, it also interacts with various other laws, such as the Sale of Goods Act and the Specific Relief Act, which deal with specific types of contracts and remedies. This interplay creates a holistic legal ecosystem for commercial transactions.
In conclusion, the Indian Contract Act, 1872, plays a vital role in the Indian legal landscape by ensuring that contracts are enforceable and that the principles of fairness and justice govern contractual relationships. Its adaptability and comprehensive nature allow it to evolve with changing societal needs, making it an enduring pillar of commercial law in India.
For More Articles on the Indian Contract Act Click Here
For More Articles on Different Acts, Click Here
Share this:
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Administrative Law
- Alternate Dispute Resolution
- Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita
- Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita
- Careers in Law
- Christian Laws
- Code of Criminal Procedure
- Collective Bargaining
- Collective Violence
- Companies Act
- Constitutional Law
- Criminal Jurisprudence
- Criminology
- Environmental Laws
- Family Laws
- Forensic Science
- Human Rights
- Indian Contract Act
- Indian Evidence Act
- Indian Partnership Act
- Indian Penal Code
- Indian Succession Act
- Industrial Disputes Act
- Industrial Relations Code
- Information Technology Act
- Judicial Process
- Jurisprudence
- Juvenile Justice Act
- Labour Laws
- Law and Society
- Legal Services Authorities Act
- Maharashtra Cooperative Society Act
- MRTU and PULP Act
- Research Methodology
- Sale of goods Act
- Teaching Aptitude
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Section 2 (h) of the Indian Contract Act, 1872 defines a contract as "an agreement enforceable by law". It is characterised by an offer and an acceptance along with consideration and is backed by the power of law. An agreement is a promise by one party to another. A proposal once accepted becomes a promise.
Assignment of contract refers to an act of transferring contractual rights and liabilities under the contract to a third party with other party's concurrence. Section 37 of the India Contract Act, 1872 ("Contract Act") enables the contracting parties to dispense with the performance of a contract by way of an assignment. While the principle of ...
Assignment. Assignment of contract refers to an act of transferring contractual rights and liabilities under the contract to a third party with other party's concurrence. Section 37 of the India Contract Act, 1872 ("Contract Act") enables the contracting parties to dispense with the performance of a contract by way of an assignment.
Section 37 of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, thatenables the parties to dispense is the performance by way of Assignment of the contract. Under the Indian Contract Law, any form of contract can be assigned as long as consent is involved in the Assignment. The consent of the 'promisee' is necessary for assigning any obligation under the ...
Section 37 of the Indian Contract Act, 1872 enables parties to dispense with performance by way of assignment. The debtor is not a party to ... Nevertheless, in law, there is a clear distinction between assignment of rights under a contract by a party who has performed his obligations there under, and assignment of a claim for
n. The agreement is void, as its object is unlawful.A's estate is sold for arrears of revenue under the provisions of an Act of the Legislature, by which t. e defaulter is prohibited from purchasing the estate. B, upon an understanding with A, becomes the purchaser, and agrees to convey the estate to.
Introduction - 1) INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872 governs law relating to contracts in India. 2) The Act was passed by British India and is based on the principles of English Common Law. 3) This Act is applicable to whole of India including Jammu and Kashmir. 4) The Act came into effect from 1st September, 1872 and applies to all contracts in India. Important Definitions under the Act -
INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872 1 ICA, 1872 : NATURE, MEANING, ESSENTIALS AND KINDS OF CONTRACT 1.1 Introduction 3 1.2 Extent and commencement 3 1.3 Limitations or nature 3 1.4 Definition of contract 4 1.5 All contracts are agreements but all agreements are not contracts 5 1.6 Essentials of a Valid Contract 6
Under the Indian Contract Act, 1872 ("Act") an agreement becomes a contract when it fulfills certain essential elements, transforming it from a mere agreement to a legally enforceable contract. A contract is an agreement which gives rise to obligations which are recognized by law. Section 2 (h) of the Act defines contract as "An agreement ...
As a reader, this Law of Contracts notes is sufficient for you to learn or research on Indian Contract Act, 1872! Happy Learning! 1. Note: For books on Law of Contracts, click here. 2. Introduction to the Law of Contracts. 3. Agreement under Indian Contract Act (Section 2 to 9, Indian Contract Act) 4.
The Indian Contract Act, 1872 1.5. enforceable by law becomes void when it ceases to be enforceable". Thus a void contract is one which cannot be enforced by a court of law. Example : Mr. X agrees to write a book with a publisher. After few days, X dies in an accident. Here the contract becomes void due to the impossibility of performance of the
Indian law accepts the common law's starting position, which is to answer both these questions in the negative. 3 While its position under Indian law may rest on weak foundations, 4 the strength of the edifice built through repeated judicial affirmation arguably puts privity of contract into a rarefied category of Indian private law principles that may be considered fundamental.
Where a contract is silent or incomplete as regards the parties' intention concerning assignment, one will have to rely on the provisions of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, and the principles of ...
Indian Contract Act, 1872 General Principles of ContractINTRODUCTI. NThe law of contract is the most important branch of Mercantile Law. Without such a law it would be difficult, if. not impossible, to carry on any trade or business in a smooth manner. The law of contract is applica. le not only to business but also to all day-to-day personal ...
1.1.Short title.-This Act may be called the Indian Contract Act, 1872. Extent, Commencements.-It extends to the whole of India 2*[except the State of Jammu and Kashmir]; and it shall come into force on the first day of September, 1872. 3* Nothing herein contained shall affect the provisions of any Statute, Act or Regulation not hereby expressly ...
The Act was enacted on 25 April 1872 and commenced on 1 September 1872. The Act as enacted originally had 266 Sections, divided into 11 chapters. Later, sections of Chapter 7 and 11 were repealed, as they became part of separate legislations namely, Sale of Goods Act, 1930 and Indian Partnership Act, 1932. At present the Indian Contract Act may ...
Under the Indian Contract Act 1872 ("ICA"), an arbitration agreement is a distinct and separate contract. Like all other contracts, it can be transferred by way of assignment to third parties under Section 37 of the ICA. The Supreme Court of India in Khardah Company Ltd vs Raymon & Co. (India) Private Ltd has held... Continue reading
Position under the Indian contract act is different than under English Law Under English Law. It is an established rule under English law that the third party cannot sue a contract made for his own benefit. Apart from special circumstances. A person who is not a part of the contract cannot enforce or rely for protection on its provisions.
An assignment of a contract might result by transfer either of the rights or by tr...is a well recognized distinction between the two classes of assignments. As a rule, obligations under a contract cannot be assigned except with the consent of the promisee, and when such consent i... Vishveshwar Vighneshwar Shastri v.
Assignment. Assignment of contract refers to an act of transferring contractual rights and liabilities under the contract to a third party with other party's concurrence. Section 37 of the India Contract Act, 1872 ("Contract Act") enables the contracting parties to dispense with the performance of a contract by way of an assignment. While the ...
The general principals of the Law of Contract are contained in Sections 1 to 75 of the Indian Contract Act. These principles apply to all kinds of contracts irrespective of their nature. Special contracts are contained in Sections 124 to 238 of the Indian Contract Act. These special contracts are Indemnity, Guarantee, Bailment, pledge, and Agency.
The Indian Contract Act of 1872 is a law governing contracts and agreements in India. This act provides guidance and helps resolve any dispute that arises during the period of the contract or in ensuring its compliance. The Indian Contract Law is divided into two parts: the first deals with the general principles that apply to all contracts ...