If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.

Computers and the Internet
Course: computers and the internet > unit 2, what are the parts of a computer.
- CPU, memory, input & output
- Input & output devices
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Computer memory
- Secondary memory
- Computer components
- Exploring microcomputers
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page


- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Computer Basics - Inside a Computer
Computer basics -, inside a computer, computer basics inside a computer.

Computer Basics: Inside a Computer
Lesson 5: inside a computer.
/en/computerbasics/buttons-and-ports-on-a-computer/content/
Inside a computer
Have you ever looked inside a computer case , or seen pictures of the inside of one? The small parts may look complicated, but the inside of a computer case isn't really all that mysterious. This lesson will help you master some of the basic terminology and understand a bit more about what goes on inside a computer.
Watch the video below to learn about what's inside a desktop computer.
Looking for the old version of this video? You can still see it here :
Motherboard
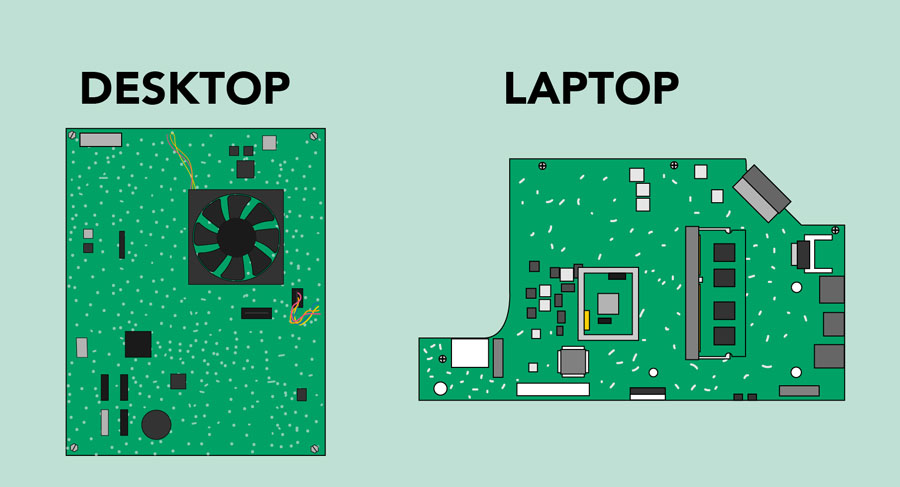
The motherboard is the computer's main circuit board . It's a thin plate that holds the CPU, memory, connectors for the hard drive and optical drives, expansion cards to control the video and audio, and connections to your computer's ports (such as USB ports). The motherboard connects directly or indirectly to every part of the computer.
CPU/processor
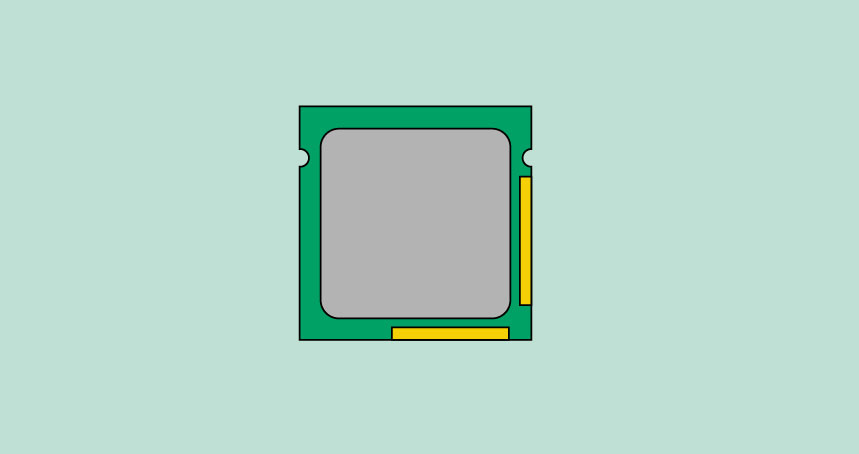
The central processing unit (CPU), also called a processor , is located inside the computer case on the motherboard. It is sometimes called the brain of the computer, and its job is to carry out commands. Whenever you press a key, click the mouse, or start an application, you're sending instructions to the CPU.
The CPU is usually a two-inch ceramic square with a silicon chip located inside. The chip is usually about the size of a thumbnail. The CPU fits into the motherboard's CPU socket , which is covered by the heat sink , an object that absorbs heat from the CPU.
A processor's speed is measured in megahertz (MHz) , or millions of instructions per second; and gigahertz (GHz) , or billions of instructions per second. A faster processor can execute instructions more quickly. However, the actual speed of the computer depends on the speed of many different components—not just the processor.
RAM (random access memory)
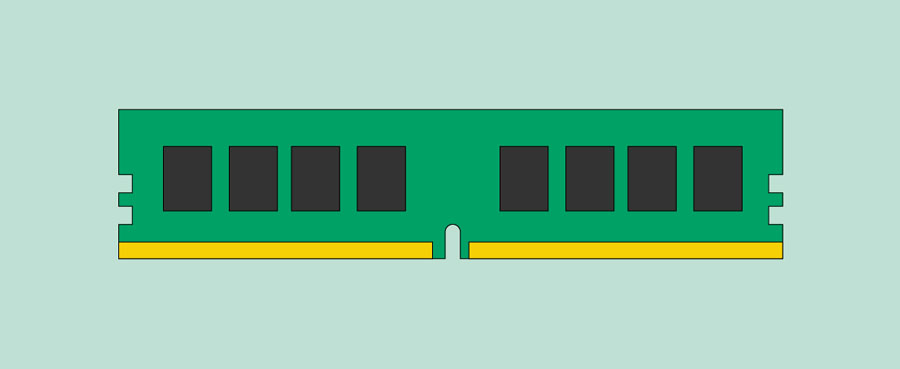
RAM is your system's short-term memory . Whenever your computer performs calculations, it temporarily stores the data in the RAM until it is needed.
This short-term memory disappears when the computer is turned off. If you're working on a document, spreadsheet, or other type of file, you'll need to save it to avoid losing it. When you save a file, the data is written to the hard drive , which acts as long-term storage .
RAM is measured in megabytes (MB) or gigabytes (GB) . The more RAM you have, the more things your computer can do at the same time. If you don't have enough RAM, you may notice that your computer is sluggish when you have several programs open. Because of this, many people add extra RAM to their computers to improve performance.
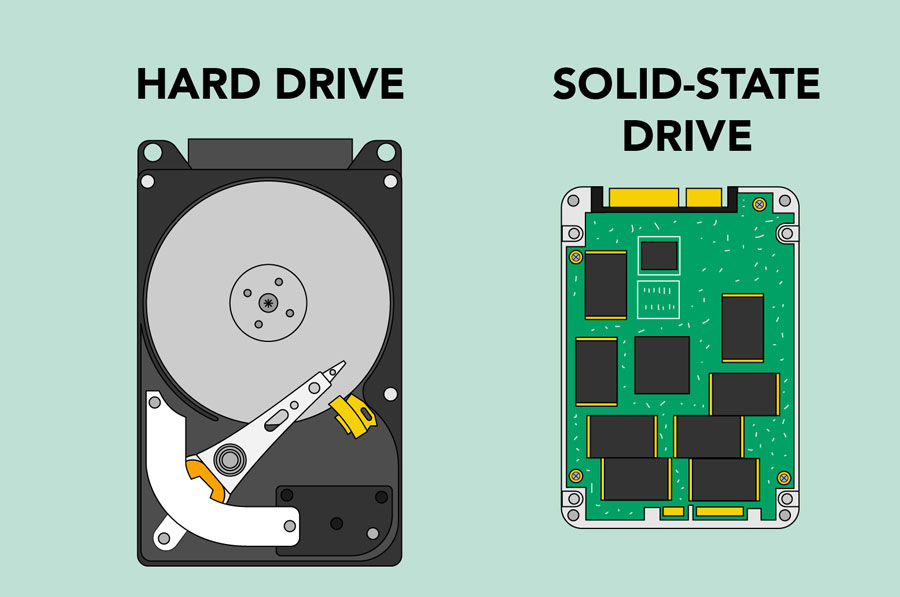
The hard drive is where your software, documents, and other files are stored. The hard drive is long-term storage , which means the data is still saved even if you turn the computer off or unplug it.
When you run a program or open a file, the computer copies some of the data from the hard drive onto the RAM . When you save a file, the data is copied back to the hard drive . The faster the hard drive, the faster your computer can start up and load programs .
Power supply unit
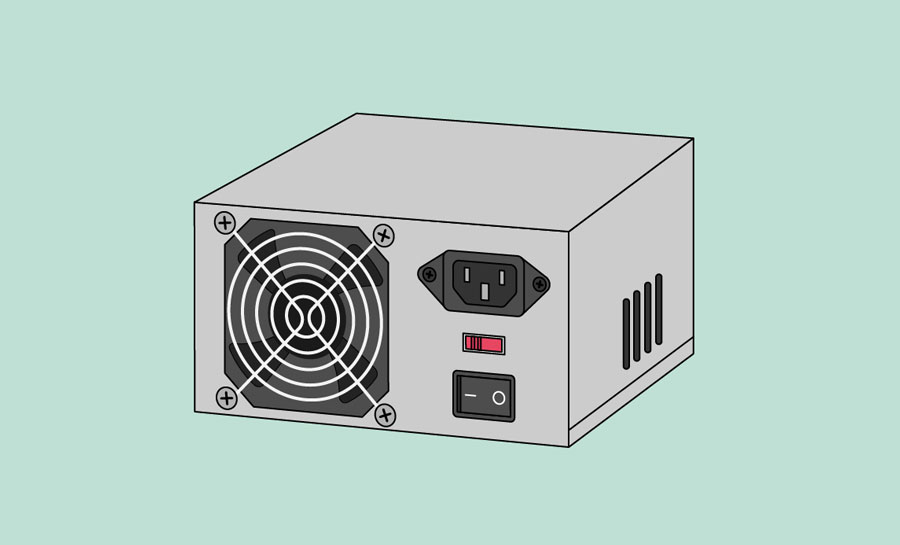
The power supply unit in a computer converts the power from the wall outlet to the type of power needed by the computer. It sends power through cables to the motherboard and other components.
If you decide to open the computer case and take a look, make sure to unplug the computer first. Before touching the inside of the computer, you should touch a grounded metal object —or a metal part of the computer casing —to discharge any static buildup. Static electricity can be transmitted through the computer circuits, which can seriously damage your machine.
Expansion cards
Most computers have expansion slots on the motherboard that allow you to add various types of expansion cards . These are sometimes called PCI (peripheral component interconnect) cards . You may never need to add any PCI cards because most motherboards have built-in video, sound, network, and other capabilities.
However, if you want to boost the performance of your computer or update the capabilities of an older computer, you can always add one or more cards. Below are some of the most common types of expansion cards.
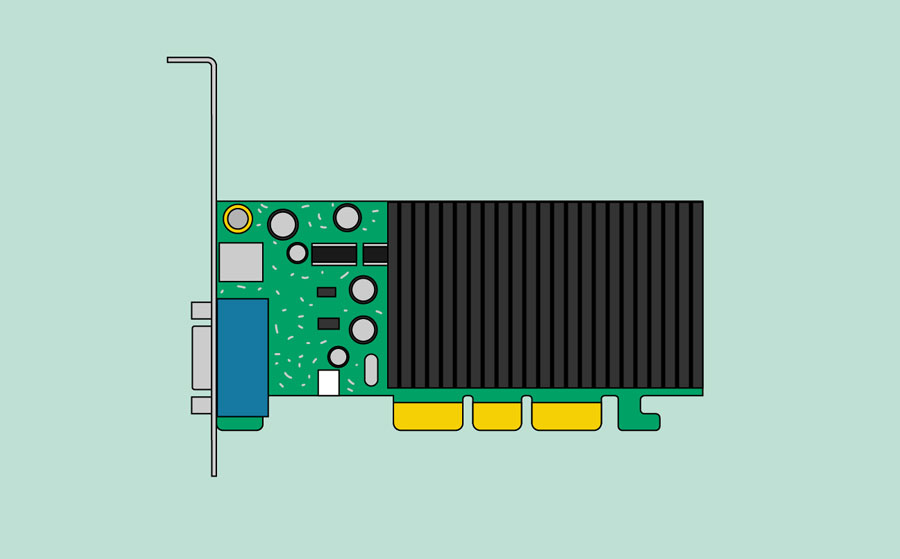
The video card is responsible for what you see on the monitor. Most computers have a GPU (graphics processing unit) built into the motherboard instead of having a separate video card. If you like playing graphics-intensive games, you can add a faster video card to one of the expansion slots to get better performance.
The sound card —also called an audio card —is responsible for what you hear in the speakers or headphones. Most motherboards have integrated sound, but you can upgrade to a dedicated sound card for higher-quality sound.
Network card
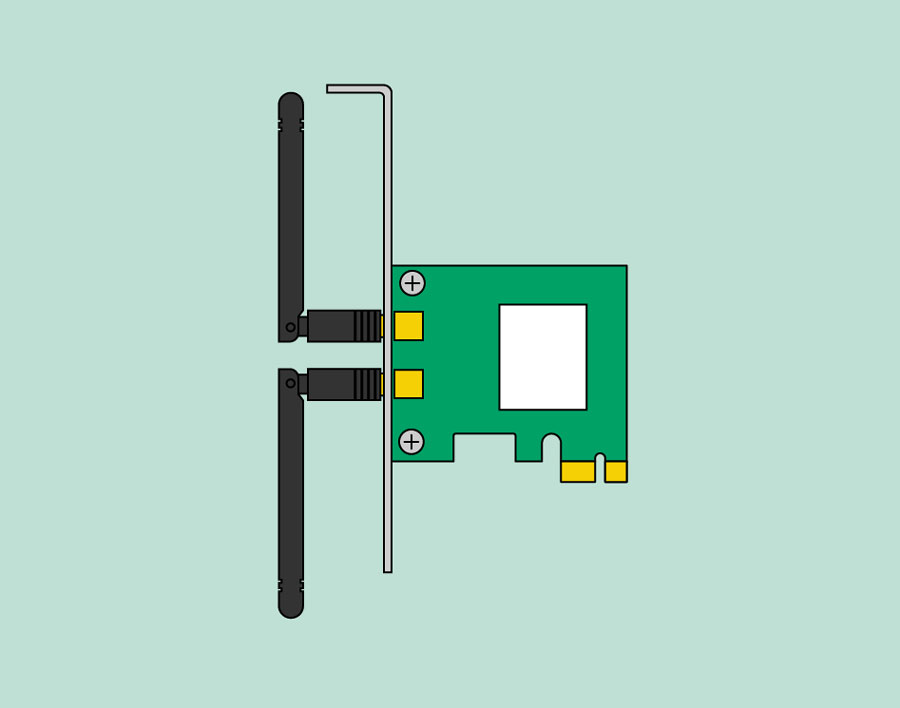
The network card allows your computer to communicate over a network and access the Internet. It can either connect with an Ethernet cable or through a wireless connection (often called Wi-Fi ). Many motherboards have built-in network connections, and a network card can also be added to an expansion slot.
Bluetooth card (or adapter)
Bluetooth is a technology for wireless communication over short distances. It's often used in computers to communicate with wireless keyboards , mice , and printers . It's commonly built into the motherboard or included in a wireless network card . For computers that don't have Bluetooth, you can purchase a USB adapter, often called a dongle .
/en/computerbasics/laptop-computers/content/
- Engineering Mathematics
- Discrete Mathematics
- Operating System
- Computer Networks
- Digital Logic and Design
- C Programming
- Data Structures
- Theory of Computation
- Compiler Design
- Computer Org and Architecture
Computer Organization and Architecture Tutorial
- Basic Computer Instructions
- What is Computer
- Issues in Computer Design
- Difference between assembly language and high level language
- Addressing Modes
- Difference between Memory based and Register based Addressing Modes
- Computer Organization | Von Neumann architecture
- Harvard Architecture
- Interaction of a Program with Hardware
- Simplified Instructional Computer (SIC)
- Instruction Set used in simplified instructional Computer (SIC)
- Instruction Set used in SIC/XE
- RISC and CISC in Computer Organization
- Vector processor classification
- Essential Registers for Instruction Execution
- Introduction of Single Accumulator based CPU organization
- Introduction of Stack based CPU Organization
- Machine Control Instructions in Microprocessor
- Very Long Instruction Word (VLIW) Architecture
- Input and Output Systems
- Computer Organization | Different Instruction Cycles
- Machine Instructions
- Computer Organization | Instruction Formats (Zero, One, Two and Three Address Instruction)
- Difference between 2-address instruction and 1-address instructions
- Difference between 3-address instruction and 0-address instruction
- Register content and Flag status after Instructions
- Debugging a machine level program
- Vector Instruction Format in Vector Processors
- Vector instruction types
- Instruction Design and Format
- Introduction of ALU and Data Path
- Computer Arithmetic | Set - 1
- Computer Arithmetic | Set - 2
- Difference between 1's Complement representation and 2's Complement representation Technique
- Restoring Division Algorithm For Unsigned Integer
- Non-Restoring Division For Unsigned Integer
- Computer Organization | Booth's Algorithm
- How the negative numbers are stored in memory?
- Microprogrammed Control
- Computer Organization | Micro-Operation
- Microarchitecture and Instruction Set Architecture
- Types of Program Control Instructions
- Difference between CALL and JUMP instructions
- Computer Organization | Hardwired v/s Micro-programmed Control Unit
- Implementation of Micro Instructions Sequencer
- Performance of Computer in Computer Organization
- Introduction of Control Unit and its Design
- Computer Organization | Amdahl's law and its proof
- Subroutine, Subroutine nesting and Stack memory
- Different Types of RAM (Random Access Memory )
- Random Access Memory (RAM) and Read Only Memory (ROM)
- 2D and 2.5D Memory organization
Input and Output Organization
- Priority Interrupts | (S/W Polling and Daisy Chaining)
- I/O Interface (Interrupt and DMA Mode)
- Direct memory access with DMA controller 8257/8237
- Computer Organization | Asynchronous input output synchronization
- Programmable peripheral interface 8255
- Synchronous Data Transfer in Computer Organization
- Introduction of Input-Output Processor
- MPU Communication in Computer Organization
- Memory mapped I/O and Isolated I/O
- Memory Organization
- Introduction to memory and memory units
- Memory Hierarchy Design and its Characteristics
- Register Allocations in Code Generation
- Cache Memory
- Cache Organization | Set 1 (Introduction)
- Multilevel Cache Organisation
- Difference between RAM and ROM
- What's difference between CPU Cache and TLB?
- Introduction to Solid-State Drive (SSD)
- Read and Write operations in Memory
- Instruction Level Parallelism
- Computer Organization and Architecture | Pipelining | Set 1 (Execution, Stages and Throughput)
- Computer Organization and Architecture | Pipelining | Set 3 (Types and Stalling)
- Computer Organization and Architecture | Pipelining | Set 2 (Dependencies and Data Hazard)
- Last Minute Notes Computer Organization
COA GATE PYQ's AND COA Quiz
- Computer Organization and Architecture
- Digital Logic & Number representation
- Number Representation
- Microprocessor
- GATE CS Preparation
Computer Organization and Architecture is used to design computer systems. Computer Architecture is considered to be those attributes of a system that are visible to the user like addressing techniques, instruction sets, and bits used for data, and have a direct impact on the logic execution of a program, It defines the system in an abstract manner, It deals with What does the system do.
Whereas, Computer Organization is the way in which a system has to structure and It is operational units and the interconnections between them that achieve the architectural specifications, It is the realization of the abstract model, and It deals with How to implement the system.
In this Computer Organization and Architecture Tutorial, you’ll learn all the basic to advanced concepts like pipelining, microprogrammed control, computer architecture, instruction design, and format.
Recent Articles on Computer Organisation
- Computer Arithmetic
- Miscellaneous
- Quick Links
Basic Computer Instructions :
- A simple understanding of Computer
- Computer System Level Hierarchy
- Computer Architecture and Computer Organization
- Timing diagram of MOV Instruction in Microprocessor
- Assembly language and High level language
- Memory based Vs Register based addressing modes
- Von Neumann architecture
- Data Transfer instructions in AVR microcontroller
- Arithmetic instructions in AVR microcontroller
- Conditional Branch Instructions in AVR Microcontroller
- CALL Instructions and Stack in AVR Microcontroller
- Branch Instructions in AVR Microcontroller
- Logical Instructions in AVR Microcontroller
- Data Manipulation Instructions
Instruction Design and Format :
- Different Instruction Cycles
- Instruction Formats (Zero, One, Two and Three Address Instruction)
- 2-address instruction and 1-address instructions
- 3-address instruction and 0-address instruction
- 3-address instruction and 2-address instructions
Computer Arithmetic :
- Computer Arithmetic | ALU and Data Path
- Computer Arithmetic | Set 1
- Computer Arithmetic | Set 2
- Difference between 1’s complement and 2’s complement
- Booth’s Algorithm
Microprogrammed Control :
- Micro-Operation
- Hardwired v/s Micro-programmed Control Unit
Memory Organization :
- What’s difference between CPU Cache and TLB?
- Different Types of RAM
- Types of computer memory (RAM and ROM)
- Introduction to solid-state drive (SSD)
Input and Output Systems :
- Asynchronous input output synchronization
Pipelining :
- Execution, Stages and Throughput
- Types and Stalling
- Dependencies and Data Hazard
IEEE Number Statndards
Miscellaneous :
- Generations of computer
- Introduction to quantum computing
- Conventional Computing vs Quantum Computing
- Flynn’s taxonomy
- Clusters In Computer Organisation
- Program for Binary To Decimal Conversion
- Program for Decimal to Binary Conversion
- Program for decimal to octal conversion
- Program for octal to decimal conversion
- Program for hexadecimal to decimal
Quick Links :
- ‘Quizzes’ on Computer Organization and Architecture !
- ‘Practice Problems’ on Computer Organization and Architecture !
Please Login to comment...
Related articles.
- What are Tiktok AI Avatars?
- Poe Introduces A Price-per-message Revenue Model For AI Bot Creators
- Truecaller For Web Now Available For Android Users In India
- Google Introduces New AI-powered Vids App
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Home PowerPoint Templates Shapes Computer Illustration Concept Diagram for PowerPoint
Computer Illustration Concept Diagram for PowerPoint
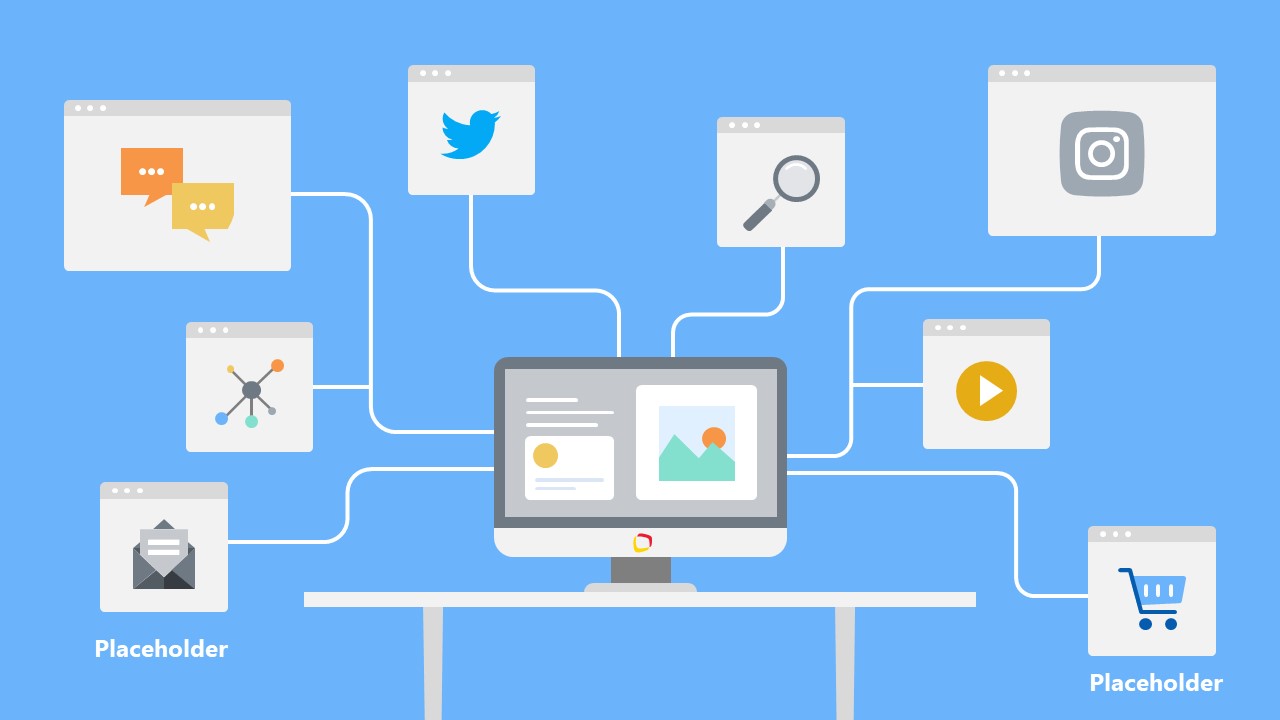
The Computer Illustration Concept Diagram for PowerPoint is a flat vector presentation of technology and networks. The computer template design includes various infographic icons relevant to digital terms. This PowerPoint network diagram template presents two slide layouts to describe multiple process flow concepts. For example, the first slide shows a tree diagram design which could also illustrate work break down structure ideas. Similarly, the second slide displays a visual presentation of cause and effect diagram, also known as fishbone diagram. All segments of PowerPoint diagram depict browser or folder windows. Because this computer concept diagram illustrates multi-processing in digital technology devices.
The Computer Illustration Concept Diagram for PowerPoint includes useful infographic icons. Such as chat massages, twitter, search, Instagram, video play, shopping cart, email, and sharing. These icons demonstrate possible functions and features of computer. Therefore, these slides will be ideal learning material for computer literacy students. The second slide of this concept diagram could be used as timeline template. Here, desktop screen will represent starting point and shipping cart for end goal. But users can replace shapes and icons of these diagram slides in few clicks. Simply remove any icon and copy paste a desire graphic on its place.
The PowerPoint diagram templates of computer concept contain editable shapes, icons, and backgrounds. Apart from changing colors or size of diagram icons, users can also use many background format options. For instance, adding background image, pattern, or gradient effects. Moreover, both slides are presentable as slide cover for digital technology and marketing presentations.
You must be logged in to download this file.
Favorite Add to Collection
Details (2 slides)

Supported Versions:
Subscribe today and get immediate access to download our PowerPoint templates.
Related PowerPoint Templates
Megaphone Concept Design PowerPoint Template
4M Root Cause Analysis PowerPoint Template
5-Level Pyramid Diagram PowerPoint Template
4-Item Key Focus Area PowerPoint Template

Parts Of A Computer And Their Functions (All Components)
Whether you need to know the essential parts of a computer and their functions for academic reasons or to begin immersing yourself in the world of computers, this is the right resource for you.
Some parts include the case, motherboard, CPU, RAM, graphics card, SSD, HDD, keyboard, and mouse. Read on to discover more about the functions of all components.
Parts Of A Computer And Their Functions
1. the computer case or chassis.

This component holds all of the physical parts of a computer system.
It is usually designed to fit a motherboard, wiring, and primary and secondary storage devices easily. Some are designed so well that it is easy to make everything look tidy and presentable.
They can also accommodate CD or DVD drives, allowing users to listen to music using compact discs or watch Blu-ray movies from their computer.
Cases come in all different sizes and shapes to accommodate various computer components and satisfy the consumer’s needs. Computer builders need to ensure compatibility between components and the case.
In addition to the power button, cases typically have extra connectors on the front for more convenience. USB ports and headphone jacks are commonly found. These all connect up to the motherboard using pin header connectors.
Computer cases rely on fans inside them to create proper airflow to keep all the internals cool and working reliably.
Laptops have their case or chassis designed specifically for each model to hole all the parts and the screen in a conveniently compact design that can fold closed to make it even more mobile.
List of computer case sizes (known as form factor):
- Very small form factor : Supports Mini ITX motherboards
- Small form factor : Supports micro ATX motherboards.
- Standard form factor : Supports standard ATX motherboards.
- Larger form factors : Supports ATX and XL-ATX motherboards.
2. Motherboard

The motherboard is the main board mounted directly inside the computer case. All other cards plug directly into the motherboard, hence its name.
It is a printed circuit board in which the CPU, RAM, drives, power supply, expansion cards, and more are plugged into it. Its function involves integrating all the physical components to communicate and operate together.
A good motherboard offers a wide amount of connectivity options. It also has the least amount of bottlenecks possible. This allows all the components to operate efficiently and to fulfill their maximum potential as they were designed to do.
As the physical size is reduced, connectivity options and functionality are limited.
Motherboards come in the following sizes:
3. Central Processing Unit (CPU)

The CPU or central processing unit is like the brain of computer systems. It processes all the information on a computational level. It takes all the processes from the RAM and processes them to perform the tasks required by the computer system.
The faster the processor, the more instructions it can execute at any given time.
The central processing unit is usually seated in a socket that utilizes a lever or a latch with a hinged plate and a cut-out in the center to secure the CPU onto the motherboard.
It has many copper pads underneath it for the socket contacts to push up against them to make electrical contact. There are other ways CPUs can be attached to the motherboard.
Here are some common examples:
- ZIF (Zero Insertion Force) : Although this is a more desirable socket, they are mostly found on older computer motherboards. It has a lever-operated mechanism to clamp the pins of the processor.
- PGA (Pin Grid Array) : It is also a ZIF socket with a different pin pitch and count.
- LGA (Land Grid Array) : More commonly found on motherboards today. A levered hinged plate with a center cut-out clamps down on the processor.
- BGA (Ball Grid Array) : The CPU is soldered directly onto the motherboard. This makes it a non-user-swappable component. It is susceptible to bad connectivity.
Processors have various amounts of cores . These cores can handle specific operations, allowing each core to work on a different task.
They also have a clock speed most commonly measured in MHz or Ghz. While a higher clock speed can indicate a faster CPU, many more factors come into play to determine the overall performance of a processor.
A processor generates a decent amount of heat , especially when working under high loads. It will run even hotter when set to a higher clock speed to make it run faster. This is called overclocking.
This is why a heatsink and fan assembly are required to draw the heat away from the central processing unit and distribute it to thin sheets or metal fins for the fan to cool down.
There are so many different types of computer processors. The largest manufacturers of processors are Intel, AMD, and NVidia.
4. Random Access Memory (RAM)

RAM is a data storage device that can provide fast read and write access. RAM is volatile memory, meaning it loses all the stored data when power is lost. The RAM keeps data ready for the CPU to process. The RAM speed is a big contributor to the overall speed of a computer system.
It plugs directly into a long slot that has contacts on either side of the slot.
It, too, has a clock speed (usually also measured in MHz), just like a processor. So, it can also be overclocked to deliver increased performance beyond the intended specification. The clock speed is not the only deciding factor regarding memory speed. Memory timing also plays a big part.
Certain RAM modules are sold with a heat spreader. It helps dissipate the heat from the individual memory ICs, keeping them cooler.
RAM has evolved like any other component. RAM used on the motherboard often uses DDR (Double Data Rate) SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) type memory.
RAM Amount always comes in powers of 2, so you will always see numbers like 16GB, 32GB, or 64GB of RAM, to mention some examples of memory units.

5. Graphics Card or Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)

A graphics card is an output device that processes the data from the motherboard and sends the appropriate information to the computer’s screen for display.
You can connect monitors to it using HDMI, DisplayPort, DVI, or VGA connectors. It can also be referred to as a video or display card. A video card takes the burden of all the video processing from the main CPU. This gives a computer a big boost in performance.
Fans are almost a given because of the large processing requirements for a gaming GPU.
A video card plugs into a PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slot on the motherboard. It is a serial expansion bus slot capable of high bandwidth in two directions.
A graphics card has a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), the main part of a computer system that requires cooling. A GPU is slower than a CPU but is designed to deal with mathematical operations required for video rendering.
The card’s memory amount varies depending on the manufacturer’s design. Video cards use GDDR (Graphics Double Data Rate) SDRAM, specially designed to optimize graphics performance.
GDDR is built to handle a higher bandwidth compared to plain DDR RAM.
A laptop’s GPU is usually mounted directly onto the motherboard, much like the CPU. Some models use integrated graphics with the GPU and CPU in one processing unit.
This can also be true for some CPUs on desktop computers. The GPU can be integrated with the CPU, and the motherboard’s output ports are used instead of a graphics card’s ports.
Integrated graphics do not offer great performance, so most gamers or individuals using their computers for work that involves more GPU-intensive tasks opt for systems with discrete GPUs.
6. Sound Card

Most of the time, the sound chip built into the motherboard is used for audio output. But, if you are a sound enthusiast or prefer high-quality audio output while playing a game, you might be inclined to use a sound card.
Sound cards plug into a computer in multiple ways. It can be through USB, PCI slot, or PCI Express x 1 slot. External DACs have gained popularity and help deliver clearer and more defined audio or high-definition sound output.
They connect up using an IO cable like a USB cable to your computer or laptop and provide a line out for your speakers or headphones. A sound processing chip on the card does all of the audio processing and is usually not a very powerful processor.
A sound card can offer a wide range of connectivity with audio equipment. Examples could be optical audio, a 1/4-inch jack, or RCA connectors.
7. Hard Disk Drive (HDD)

A hard drive is still found in many PCs to this day. A mechanical drive’s purpose is to store all your information for retrieval at any time.
Apart from storing information for your computer, hard disk drives also function as a boot drive to run the operating system (OS) from it. You can install operating systems of many different kinds depending on your needs.
An OS software program, like Microsoft Windows, makes a computer useable. The biggest vulnerability of a mechanical drive is its physically fragile nature.
They have fragile components
One bump the wrong way can destroy a whole drive. A mechanical hard drive contains one or more platters that spin anywhere between 5200 to 10000 RPM (revolutions per minute).
The read and write heads are about 0.002 (51 micro M) inches from the platter. This gives you an idea about the physical limitations of its fragile nature.
Small areas on the platter can represent a 1 or a 0. It can be changed using the drive head to alter the material to represent the correct value magnetically. This is how data is written to the drive.
There are various categories of hard drives made for various real-world applications.
Some examples include:
- General use for desktops or laptops.
- Gaming optimized for desktops or laptops.
- General high-capacity storage.
- NAS Devices.
- Video recording.
They can also be purchased as an external drive that usually connects to your computer by USB cable.
An uninterruptible power supply is sometimes used to prevent data loss with mechanical drives where a sudden power outage is experienced, or the power cord is accidentally disconnected while the computer is running. This allows proper shutdowns for desktop systems that have experienced sudden power loss.
8. Solid State Drive (SSD)

An SSD is also a type of hard drive, but it doesn’t have any moving bits. It consists of a bank of flash memory that can hold a reasonable amount of information.
While the capacity of SSDs is increasing, they aren’t cost-effective for storing large amounts. A mechanical drive has a cheaper gigabyte-to-dollar ratio.
However, the SSD is a high-performance drive. It’s fast and cannot be as easily damaged by dropping it or taking a few bumps. SSDs are available as 2.5-inch laptop encapsulated drives, and an M.2 SDD is the most commonly used kind on the market.
That’s why I always recommend SSDs for portable-type computers where possible. In our other article, you can read more about whether or not SSD’s are worth it.
9. Power Supply Unit (PSU)

A power supply unit mounts inside the computer case. It converts the AC mains supply from the power cord from a wall socket and supplies the correct DC voltages to all the parts of a computer.
A computer power supply supplies the following voltages:
- +3.3v : This voltage is supplied to the motherboard.
- +5V : This voltage is supplied to the motherboard and other computer hardware.
- +12V : This voltage is supplied to the motherboard and other components.
- -12V : This voltage is supplied to the motherboard.
A PSU is one of the most important system components
It plays an important role in keeping a computer running reliably.
You get different wattage ratings for power supplies. The higher the wattage, the higher the electrical current that can be made available to everything that needs it to function properly.
The higher you go in Watts, the more the power supply will likely cost. A power supply usually also comes with a cooling fan. This helps all the internal components of your computer stay cool when the power supply is subjected to bigger loads.
10. Monitor or Visual Display Unit (VDU)

A monitor is an output device that interprets and displays the graphics information sent from the computer’s GPU. There are various types of monitors on the market. An LED (Light Emitting Diode) backlit LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) monitor is the most commonly used with a modern PC.
There are also various computer screen sizes with different aspect ratios. The aspect ratio is simply the ratio between height and width. For example, a 16:9 aspect ratio screen will have 16 parts wide to 9 parts in height.
There are also curved computer monitors, but they are more expensive displays. Monitors also have a fast response time to meet the high demands required to eliminate delays with user input for gaming.
11. Keyboard

A keyboard is an input device that is one of the ways to communicate with a computer. Typing a key from the keyboard sends a small portion of information to tell it which key was pressed.
Once the computer receives input from the keyboard, it can use the keystrokes in digital form to produce a specific task in any software being used. The computer system can use this information in many ways. An example could be a command or a character that can be used in a document.
There are two main different types of keyboards. Mechanical and membrane types.
12. Mouse or Trackpad

A mouse is an input device that allows the user to move a pointer displayed on the monitor and experience a more intuitive interaction with computer systems.
These days, mice have more buttons than the common three and offer way more functions than mice in the early days. However, the three main buttons allow users to select, grab, scroll, and access extra menus and options.
A computer mouse is a handy pointing device that can be wired or wireless. The latter requires batteries. Optical mice of today allow for very accurate precision and smooth movement.
Laptops have a built-in trackpad, which works almost like a mouse. Many people don’t like working with them, so they usually plug a mouse into the laptop instead.
Common peripheral parts for computers
Some common peripherals connect to a computer and extend their usefulness.
A printer can take an image sent by a computer and deliver it onto a sheet of paper. It does this by using the information from the computer, and by either using toner or ink, it deposits one of these in a controlled and accurate manner to form the image.
A scanner can take anything on paper, and it functions by scanning it to produce a replicated digital image for a computer to save. This is also handy for saving physical photos you want to preserve.
Once the photo is stored digitally, it won’t decay as a physical photo does over time. The flatbed scanner is one of the most commonly used today.
Multifunction printers
Many all-in-one, multifunction devices have printer and scanning capabilities in one reasonably compact product, which has dominated the market over recent years and continues to grow.
The most common models include an inkjet printer and scanner for home use and a laser printer version for home and other office applications.
Computer Speakers
Speakers can connect to the sound card at the rear of the computer. Another way they can be connected is by a monitor that already has built-in speakers.
Generally, the sound quality of a monitor’s speakers is poor. That’s why most people buy a set of computer speakers for their desks. You can even connect up a 7.1 surround speaker system to certain sound cards for a computer.
This can add a nicer experience to gaming, playing music, or watching a film.
A microphone
A microphone is essential for anyone who requires decent audio recording or capturing. They can range widely in price, from extremely cheap to very expensive, depending on the individual’s profession or application. They are usually connected to an audio interface before connecting to the computer.
There are so many uses for a microphone connected to a computer, but some include:
- Recording singing or musical instruments for composing music.
- Game streaming or commentary.
- Communication for calls.
- Creating podcasts.
A camera or webcam
Desktop users often use cameras when not using a laptop or other portable communication device with an inbuilt camera. Again, quality can vary depending on how much someone is willing to spend. They allow many applications, including video or conference calls, webinars, or presentations, and gamers to be streamed from their seats.
Many models have microphones built into them, but they won’t deliver the audio quality that a high-end dedicated microphone can produce.
A video summary of this article on YouTube

Marlo brings over 20 years of IT expertise to his role as the founder and driving force behind Computer Info Bits. With a lifelong passion for technology, he has dedicated his career to not only working within the IT industry but also sharing that knowledge extensively. Since 2019, Marlo has turned his focus to writing, aiming to demystify technology and make accessible, reliable information available to both tech novices and professionals.
Through his articles, Marlo covers everything from basic computer tips to complex hardware discussions, always with the aim of helping readers better understand and use their technology. He continues to stay at the forefront of the tech world, dedicating countless hours to researching and interacting with the latest developments.

Computer Basics Diagram
Mar 31, 2019
420 likes | 620 Views
Computer Basics Diagram. Computer System. A complete working computer that has all of the necessary parts to make the computer function. . Hardware. Software. Hardware. The physical components of the computer. The actual equipment you can see and touch. . Hardware. Peripheral.
Share Presentation
- computer system
- storage devices
- computer basics diagram
- command line interface os

Presentation Transcript
Computer System A complete working computer that has all of the necessary parts to make the computer function. Hardware Software
Hardware The physical components of the computer. The actual equipment you can see and touch.
Hardware Peripheral A peripheral is an external piece of hardware that is important, but not necessary for a computer system to work.
Hardware Input Devices Processing Output Devices Storage Devices
Input Devices Hardware that enables a computer user to enter data and programs into a computer.
Input Devices Hardware that enables a computer user to enter data and programs into a computer. Keyboard
Input Devices Hardware that enables a computer user to enter data and programs into a computer. Keyboard Mouse
Input Devices Hardware that enables a computer user to enter data and programs into a computer. Keyboard Mouse Scanner
Input Devices Hardware that enables a computer user to enter data and programs into a computer. Keyboard Mouse Scanner Microphone
Input Devices Hardware that enables a computer user to enter data and programs into a computer. Keyboard Mouse Scanner Microphone Barcode Reader
Input Devices Hardware that enables a computer user to enter data and programs into a computer. Keyboard Mouse Scanner Microphone Barcode Reader Webcam
Processing The main parts of a computer system that process information.
Processing The main parts of a computer system that process information. CPU Central Processing Unit The CPU is often called the “brains” of the computer.
Processing The main parts of a computer system that process information. CPU Central Processing Unit The CPU is often called the “brains” of the computer. ROM Read Only Memory ROM is permanent internal memory that cannot be changed.
Processing The main parts of a computer system that process information. CPU Central Processing Unit The CPU is often called the “brains” of the computer. ROM Read Only Memory ROM is permanent internal memory that cannot be changed. RAM Random Access Memory RAM is temporary memory that can be changed.
Output Devices Hardware that represents data as either hard copy or soft copy after is has been processed by the computer.
Output Devices Hardware that represents data as either hard copy or soft copy after is has been processed by the computer. Monitor Represents data as “soft copy.” Some common monitors are CRT or flat-panel.
Output Devices Hardware that represents data as either hard copy or soft copy after is has been processed by the computer. Monitor Represents data as “soft copy.” Some common monitors are CRT or flat-panel. Printer Represents data as “hard copy.” Some common printers are laser or inkjet.
Output Devices Hardware that represents data as either hard copy or soft copy after is has been processed by the computer. Monitor Represents data as “soft copy.” Some common monitors are CRT or flat-panel. Printer Represents data as “hard copy.” Some common printers are laser or inkjet. Speakers
Storage Devices Needed for permanently storing important information such as computer programs, files, and data.
Storage Devices Needed for permanently storing important information such as computer programs, files, and data. Magnetic Storage Hard Disk Floppy Disk Videotape Plastic or metal platters that are coated with oxide and store data magnetically.
Storage Devices Needed for permanently storing important information such as computer programs, files, and data. Magnetic Storage Hard Disk Floppy Disk Videotape Plastic or metal platters that are coated with oxide and store data magnetically. Optical Storage CDs DVDs A storage medium on which data is recorded and read by two lasers
Storage Devices Needed for permanently storing important information such as computer programs, files, and data. Magnetic Storage Hard Disk Floppy Disk Videotape Plastic or metal platters that are coated with oxide and store data magnetically. Optical Storage CDs DVDs A storage medium on which data is recorded and read by two lasers USB Storage
In September 1956 IBM launched the 305 RAMAC, the first computer with a hard disk drive (HDD). The HDD weighed over a ton and stored 5MB of data. IBM leased this machine for $35,000 a year.
Network Computers that are connected in order to share information and resources. The main computer on a network is called a file server. LAN – Local Area NetworkComputers are in close proximity to each other. WAN – Wide Area NetworkComputers are in a larger geographical area.
Software A set of instructions or programs that tell a computer what to do.
Software Operating System or Platform Applications or Programs
This type of software manages RAM, controls peripheral devices, manages file operations (saving, opening, deleting, renaming, etc.), monitors system performance, and provides a user interface Operating System or Platform
This type of software manages RAM, controls peripheral devices, manages file operations (saving, opening, deleting, renaming, etc.), monitors system performance, and provides a user interface Operating System or Platform Windows is a GUI OS environment that works with DOS. It uses icons and menus to make computers easy to use. You can multitask with Windows. DOS & Windows DOS is a command-line interface OS. It is not very user-friendly!
This type of software manages RAM, controls peripheral devices, manages file operations (saving, opening, deleting, renaming, etc.), monitors system performance, and provides a user interface Operating System or Platform Windows is a GUI OS environment that works with DOS. It uses icons and menus to make computers easy to use. You can multitask with Windows. DOS & Windows DOS is a command-line interface OS. It is not very user-friendly! Macintosh Macintosh computers have their own operating system.
This type of software manages RAM, controls peripheral devices, manages file operations (saving, opening, deleting, renaming, etc.), monitors system performance, and provides a user interface Operating System or Platform Windows is a GUI OS environment that works with DOS. It uses icons and menus to make computers easy to use. You can multitask with Windows. DOS & Windows DOS is a command-line interface OS. It is not very user-friendly! Macintosh Macintosh computers have their own operating system. Other Operating Systems: Linux, UNIX, OS/2
Application Software or Programs Programs that allow users to perform specific tasks.
Application Software or Programs Programs that allow users to perform specific tasks. Word Processing Letters, reports, text
Application Software or Programs Programs that allow users to perform specific tasks. Word Processing Letters, reports, text Spreadsheets Numbers
Application Software or Programs Programs that allow users to perform specific tasks. Word Processing Letters, reports, text Spreadsheets Numbers Slide Shows Electronic Presentations
Application Software or Programs Programs that allow users to perform specific tasks. Word Processing Letters, reports, text Spreadsheets Numbers Slide Shows Electronic Presentations Browser World Wide Web
Application Software or Programs Programs that allow users to perform specific tasks. Word Processing Letters, reports, text Spreadsheets Numbers Slide Shows Electronic Presentations Browser World Wide Web Database Large collections of data
Application Software or Programs Programs that allow users to perform specific tasks. Word Processing Letters, reports, text Spreadsheets Numbers Slide Shows Electronic Presentations Browser World Wide Web Database Large collections of data Real Player & Media Player Multimedia
Virus A small computer program or piece of code that is put on a computer (usually without the user knowing about it) that is destructive to the computer.
- More by User

Computer Basics
Computer Basics Which computer should I buy? What do I get for an extra $775 and do I even need it ? Desktop We need to understand several things before going out and buying a computer . What are the different components of a computer system and how do they work?
2.82k views • 31 slides

Computer Basics. Computer Hardware and Software 2008-2009. The Information Processing Cycle. What is a computer?. accepts data processes data produces output stores results. A computer is an electronic device that executes the instructions in a program.
1.14k views • 22 slides
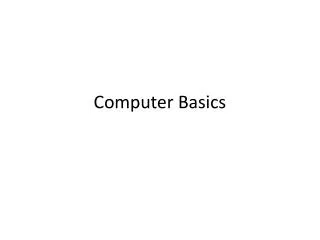
Computer Basics. The Computer (Generic). Processor executes commands. Memory stores program and data. Input devices transfer information from outside world into computer. Output devices are vice versa. Inputs. Memory. Outputs. Processor. NXT. USB communications port.
664 views • 11 slides
Computer Basics. Introduction to Computer. Computer Types. Operating Systems. By Gustavo Alatta. Introduction to Computers.
888 views • 18 slides
Computer Basics. Mr. Reese. Introduction to Computers. Lesson 1. 1.1 Describe the Importance of Computers in Today’s World. Computer an electronic device that you can use to store and process information. 1.1 Describe the Importance of Computers in Today’s World.
795 views • 46 slides

Class Diagram Basics
Class Diagram Basics. Beginning the Class Diagram . Beginning the Class Diagram. Objectives Familiarisation with basic class diagram notation Learn to identify class names from the domain vocabulary Contents Class diagram Classes Attributes Operations Objects Identifying classes
576 views • 28 slides

Computer Basics. Chris G7j. What is a computer?. An electronic device Store Receive Process. What are the types of computer?. Desktop Computer Laptop Computer Tablet Computers Mobile phones Gaming consoles TV. How are they used?. Communicating Socializing Doing work Playing games.
1.15k views • 25 slides

Computer Basics. Lesson 5 - Output. What is Output?. Output is data that has been processed into useful form, now called Information. Types of Output: Hard copy: printed on paper or other permanent media Soft copy: displayed on screen or by other non-permanent means.
538 views • 29 slides

Computer Basics. Lesson 2 - Applications. What is an Application?. An application is another word for a program running on the computer. Whether or not it is a good application depends on how well it performs the tasks it is designed to do and how easy it is for the user to use.
542 views • 17 slides
COMPUTER BASICS
COMPUTER BASICS. WHAT IS A COMPUTER?. A device, usually electronic, that processes data according to a set of instructions. TYPES OF COMPUTER. There are four main categories, namely: Super Computer Mainframe Computer Mini Computer Micro Computer. COMPONENTS OF THE COMPUTER SYSTEM.
1.16k views • 7 slides

Computer Basics. Instructors: Connie Hutchison & Christopher McCoy. Objectives. Describe the importance of computers in today's world. Explain the basics of computer performance and how it relates to productivity. Explain the difference between memory and storage. Objectives.
1.37k views • 38 slides

Computer Basics. Tech Lit Mrs. Lesher. Keyboard. Media Center. Function Keys. Special or Dedicated Keys. Function Keys. Special or Dedicated Keys. Alphanumeric Keys. Numeric, Insertion Point Control, and Special Keys. Insertion Point Control Keys. Windows Desktop. Shortcuts Start
658 views • 39 slides

Computer Basics. Unit 1. Getting to Know Computers. Ch. 1. Computer. An electronic device that manipulates information, or "data." Watch What is a computer?. Computer. Has the ability to store , retrieve , and process data. Computers Simplified. Two basic parts Hardware
1.11k views • 40 slides

COMPUTER BASICS. Module Review. After completing the Computer Basics Terms Worksheet, use this presentation to review any concepts you had questions on or to check your answers to the worksheet.
24.38k views • 25 slides

Computer Basics. What’s that thingamagige?. Parts of a computer. Tower. The container for the CPU , memory, motherboard, video graphic card and drives. Floppy Disk Drive. A drive used to read a floppy disk. CD ROM Drive and Burner.
732 views • 26 slides

Computer basics
Computer basics. How to build your own pc. Choosing parts. Motherboard Processor Memory (RAM) Disk drive Graphics card Power supply Case Blu-ray/DVD drive Cooling Operating system. motherboard. Most important component Links all other parts together and supplies them with power
792 views • 12 slides

Computer Basics. Topic 1: The Role of Computers. Objective: Describe the role of computers in our daily life. The Role of Computers:.
4.13k views • 131 slides

Computer Basics. There are many types of computers including:. Types of Computers. Supercomputers...are used to process very large amounts of information including processing information to predict hurricanes, satellite images and navigation, and process military war scenarios.
676 views • 25 slides

Computer Basics. Kitsap Regional Library. Lesson Plan Objectives. Students will gain a basic understanding of the library computers Students will be able to log-on and off the library computers using their library card and pin
1.03k views • 19 slides

1.17k views • 25 slides

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

Computer Diagrams PPT Designs

- You're currently reading page 5

Stages // require(['jquery'], function ($) { $(document).ready(function () { //removes paginator if items are less than selected items per page var paginator = $("#limiter :selected").text(); var itemsPerPage = parseInt(paginator); var itemsCount = $(".products.list.items.product-items.sli_container").children().length; if (itemsCount ? ’Stages’ here means the number of divisions or graphic elements in the slide. For example, if you want a 4 piece puzzle slide, you can search for the word ‘puzzles’ and then select 4 ‘Stages’ here. We have categorized all our content according to the number of ‘Stages’ to make it easier for you to refine the results.
Category reset // require(['jquery'], function ($) { $(document).ready(function () { //removes paginator if items are less than selected items per page var paginator = $("#limiter :selected").text(); var itemsperpage = parseint(paginator); var itemscount = $(".products.list.items.product-items.sli_container").children().length; if (itemscount.
- 3D Man (2767)
- Anatomy (593)
- Animated (15)
- Block Chain (82)
- Branding (181)

You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
- How To Draw Network Diagram In Powerpoint
Powerful Drawing Solution
How To Add a Computer Network Diagram to a PowerPoint Presentation
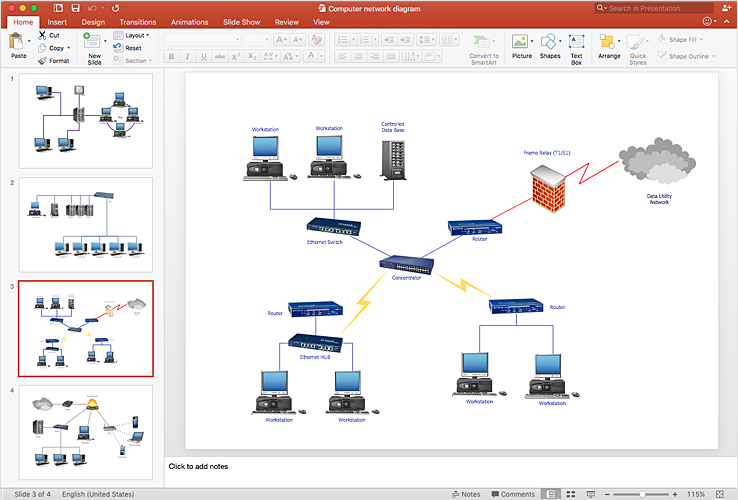
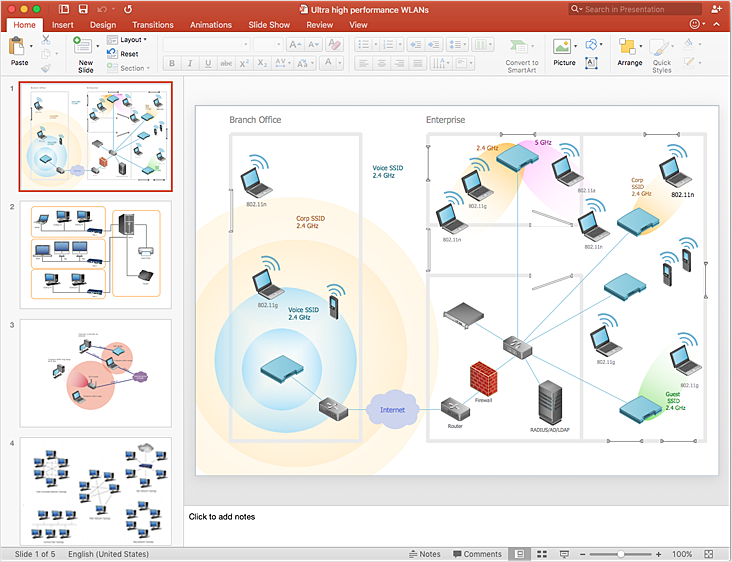
How to Add a Wireless Network Diagram to a PowerPoint Presentation
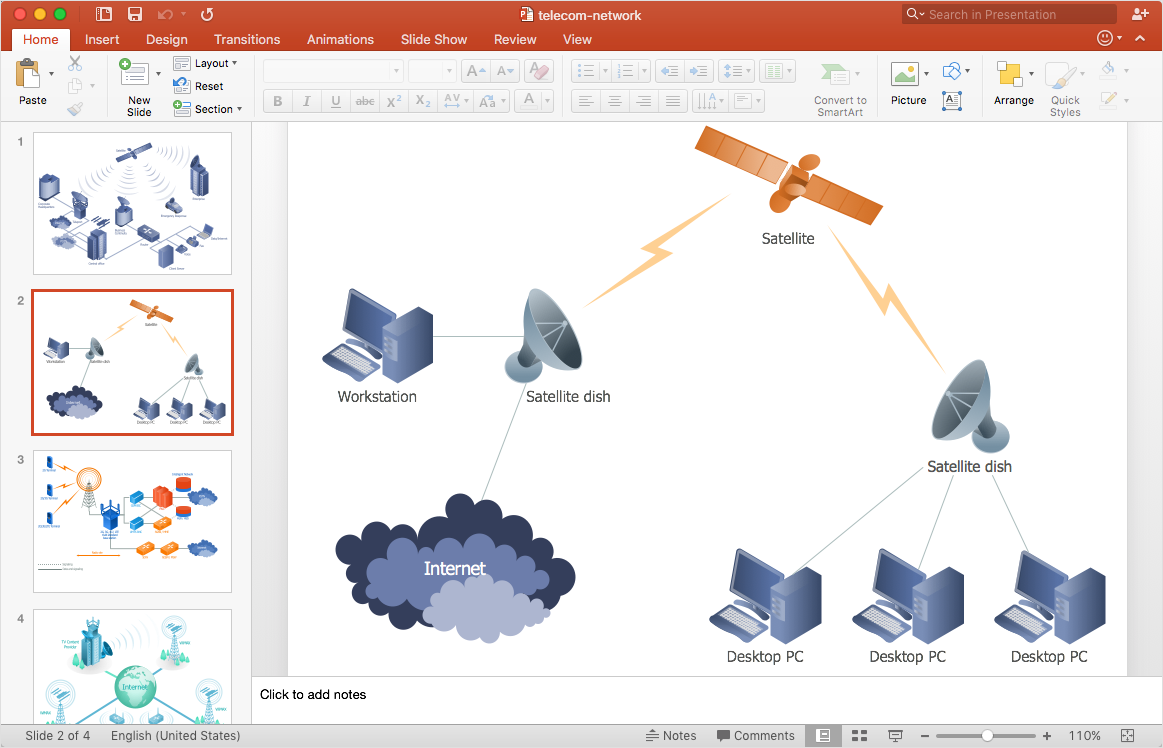
How to Add a Telecommunication Network Diagram to a PowerPoint Presentation
How to Create a Wireless Network Diagram Using ConceptDraw Solutions
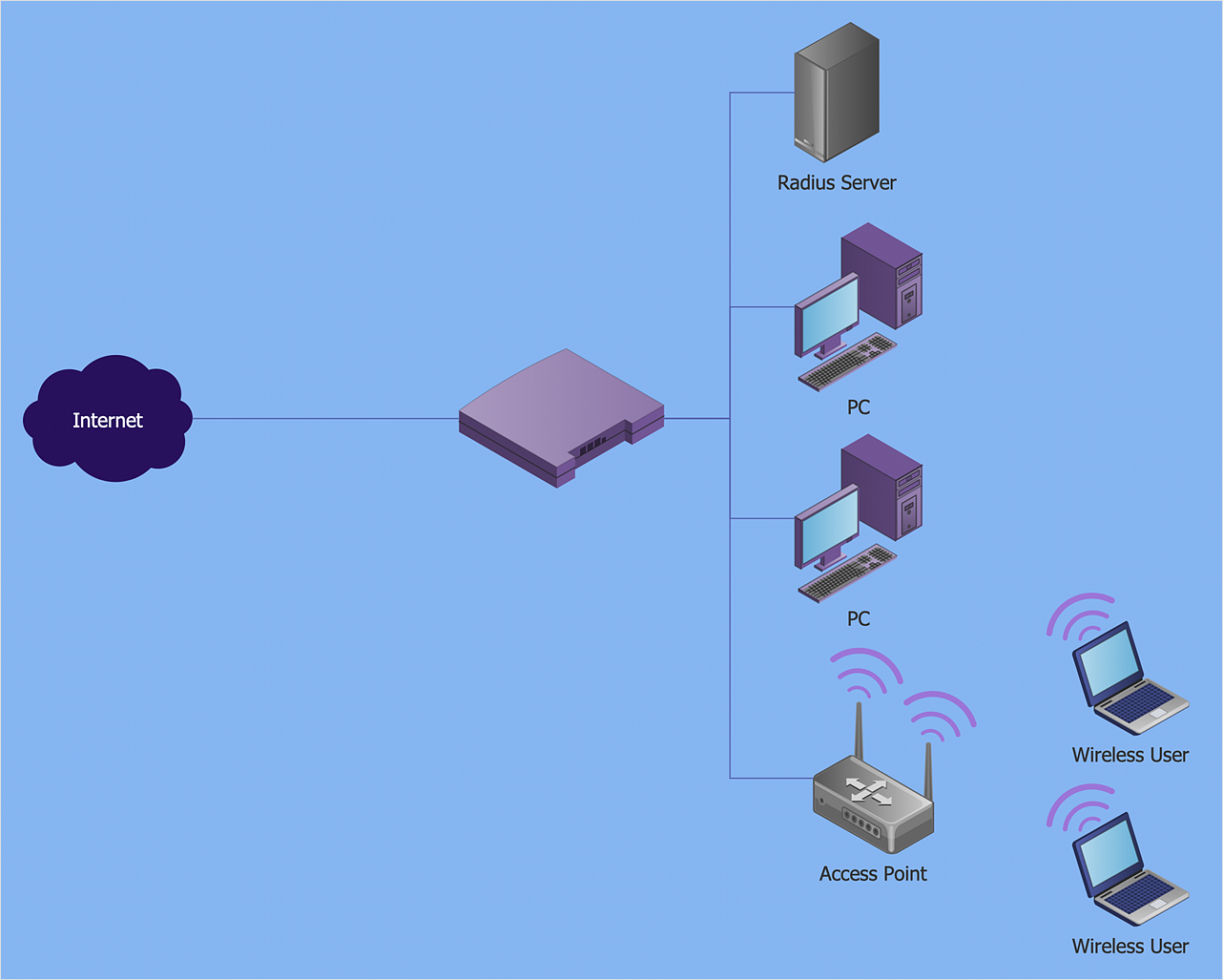
Network Diagram Examples
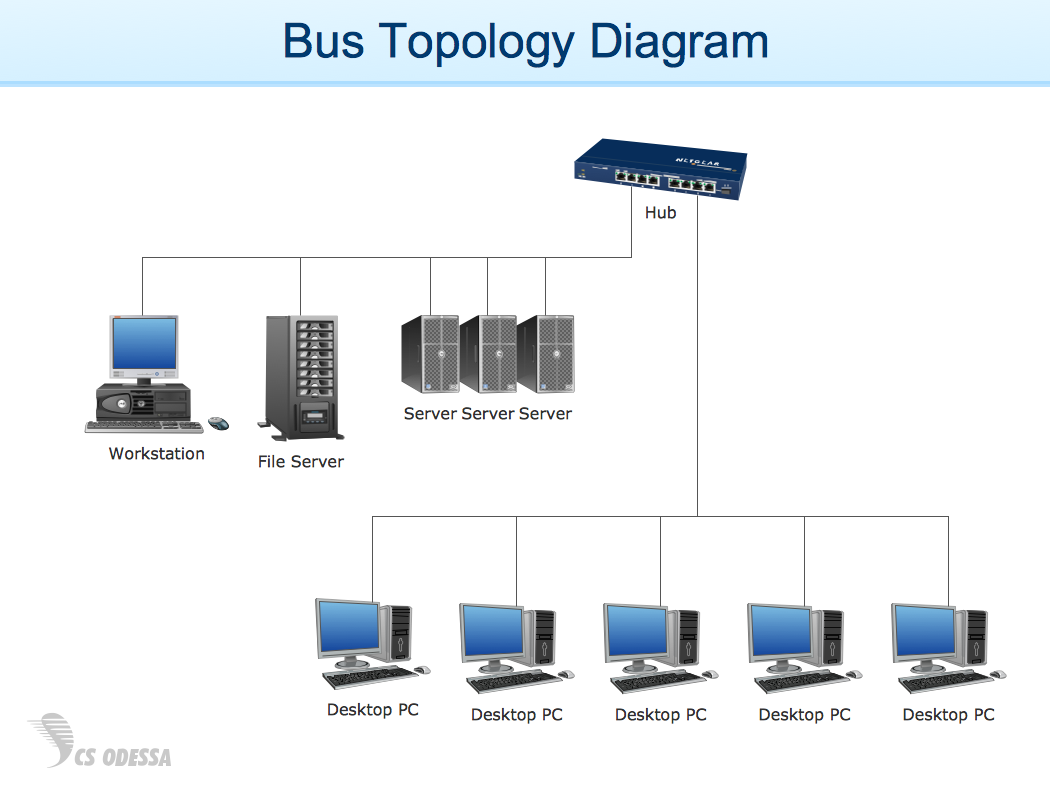
- How To Add a Computer Network Diagram to a PowerPoint ...
- Network Diagram Symbols For Powerpoint
- How to Create a Telecommunication Network Diagram in ...
- Network Diagram Examples | Wan And Lan Diagram Ppt
- How to Add a Wireless Network Diagram to a PowerPoint ...
- Sample Network Diagram Icons Ppt
- How to Add a Telecommunication Network Diagram to a PowerPoint ...
- ERD | Entity Relationship Diagrams, ERD Software for Mac and Win
- Flowchart | Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning
- Flowchart | Flowchart Design - Symbols, Shapes, Stencils and Icons
- Flowchart | Flow Chart Symbols
- Electrical | Electrical Drawing - Wiring and Circuits Schematics
- Flowchart | Common Flowchart Symbols
Slidesgo.net is an independent website that offers free powerpoint templates and is not part of Freepik/any particular brand. Read the privacy policies
computer Powerpoint templates and Google Slides themes
Discover the best computer PowerPoint templates and Google Slides themes that you can use in your presentations.
Humanoid Robot Industry PowerPoint Templates
Cyber security powerpoint templates, e-commerce powerpoint diagram, cloud computing -business powerpoint templates, computer repairs-business ppt templates, area ppt chart diagram, computer recovery powerpoint diagram, online computer repair powerpoint diagram, computer bug recovery powerpoint diagram, computer bugs recovery powerpoint diagram, slidesgo categories.
- Abstract 13 templates
- Agency 15 templates
- All Diagrams 1331 templates
- Brand Guidelines 3 templates
- Business 195 templates
- Computer 66 templates
- Education 97 templates
- Finance 54 templates
- Food 57 templates
- Formal 60 templates
- Fun 6 templates
- Industry 91 templates
- Lesson 67 templates
- Marketing 57 templates
- Marketing Plan 19 templates
- Medical 71 templates
- Military 21 templates
- Nature 119 templates
- Newsletter 5 templates
- Real Estate 46 templates
- Recreation 53 templates
- Religion 30 templates
- School 557 templates
- Simple 5 templates
- Social Media 8 templates
- Sports 46 templates
- Travel 26 templates
- Workshop 4 templates
Slidesgo templates have all the elements you need to effectively communicate your message and impress your audience.
Suitable for PowerPoint and Google Slides
Download your presentation as a PowerPoint template or use it online as a Google Slides theme. 100% free, no registration or download limits.
Want to know more?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Google Slides Help
- PowerPoint help
- Who makes Slidesgo?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Block diagram of a computer. Mar 16, 2013 •. 73 likes • 94,095 views. Z. ZTE Nepal. 1 of 14. Download Now. Download to read offline. Block diagram of a computer - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
At a high level, all computers are made up of a processor (CPU), memory, and input/output devices. Each computer receives input from a variety of devices, processes that data with the CPU and memory, and sends results to some form of output. This diagram visualizes that flow:
The computer case is the metal and plastic box that contains the main components of the computer, including the motherboard, central processing unit (CPU), and power supply. The front of the case usually has an On/Off button and one or more optical drives.. Computer cases come in different shapes and sizes. A desktop case lies flat on a desk, and the monitor usually sits on top of it.
The power supply unit in a computer converts the power from the wall outlet to the type of power needed by the computer. It sends power through cables to the motherboard and other components. If you decide to open the computer case and take a look, make sure to unplug the computer first. Before touching the inside of the computer, you should touch a grounded metal object—or a metal part of ...
The document provides a simplified block diagram of a typical computer, outlining the major components and their interconnections. The components include the central processing unit (CPU) for controlling instructions, memory for temporary and permanent storage, input devices like keyboards for entering data, and output devices like monitors for displaying information.
Computer Organization and Architecture is used to design computer systems. Computer Architecture is considered to be those attributes of a system that are visible to the user like addressing techniques, instruction sets, and bits used for data, and have a direct impact on the logic execution of a program, It defines the system in an abstract manner, It deals with What does the system do.
Block Diagram of a Computer - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Block Diagram of a Computer
The Computer Illustration Concept Diagram for PowerPoint is a flat vector presentation of technology and networks. The computer template design includes various infographic icons relevant to digital terms. This PowerPoint network diagram template presents two slide layouts to describe multiple process flow concepts.
1. The computer case or chassis. This component holds all of the physical parts of a computer system. It is usually designed to fit a motherboard, wiring, and primary and secondary storage devices easily. Some are designed so well that it is easy to make everything look tidy and presentable.
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF COMPUTER. Five basic operations performed by computer are Inputting Storing Processing Outputting controlling. All computer perform the following basic operations for converting raw input data into usefull information and presenting it to the user. Slideshow 5118909 by duman.
1.97k likes | 4.76k Views. Computer Basics 1. Computer Basic 1 includes two lessons: Lesson 1: Introduction to Computers Lesson 2: Common Computer Terminology. Lesson 1 - Introduction to Computer Objectives. After completing lesson 1, you will be able to: Describe the importance of computers in today's world. Download Presentation.
Computer Concepts INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY 3 Fig. 1.1.1: Different Computer Operations Input: A computer accepts data that is provided by means of an input device, such as a keyboard. Processing: A computer performs operations on the data to transform it in some way. Output: A computer produces output on a device, such as a printer or a monitor, that shows
Presentation Transcript. What is block diagram of computer A computer's block diagram is a visual representation of its major components and how they are interconnected. It provides a high-level overview of the computer's architecture and helps to understand how data flows and is processed within the system. Input Devices: These devices allow ...
Download Free and Premium Computer Diagrams PowerPoint Templates. Choose and download Computer Diagrams PowerPoint templates, and Computer Diagrams PowerPoint Backgrounds in just a few minutes.And with amazing ease of use, you can transform your "sleep-inducing" PowerPoint presentation into an aggressive, energetic, jaw-dropping presentation in nearly no time at all.
C. CUO VEERANAN VEERANAN. 1.1.7 Block diagram and Working Principle of Computer. Education. 1 of 12. Download Now. Download to read offline. 1.1.7 Block diagram and Working Principle of Computer - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
How to Create Amazing PowerPoint Diagrams: Choose the Right Type of Diagram Begin by selecting the diagram type that best represents the data or process you want to illustrate. Common types ...
Create any diagram required of your data. With our diagram maker, you can show structures, relationships, and business processes—everything from org charts, circuit diagrams, to cycle diagrams. Design diagrams for your pitch decks, class presentations, marketing campaigns, reports—the list goes on. Professional or personal, Canva's ...
Download Free and Premium Computer Network Diagram PowerPoint Templates. Choose and download Computer Network Diagram PowerPoint templates, and Computer Network Diagram PowerPoint Backgrounds in just a few minutes.And with amazing ease of use, you can transform your "sleep-inducing" PowerPoint presentation into an aggressive, energetic, jaw-dropping presentation in nearly no time at all.
Computer Diagram found in: 0414 computer network diagram powerpoint presentation, Cluster computing diagram powerpoint slide rules, Internet computers diagram template presentation visual aids, Bf multi staged cloud computing..
Presentation Transcript. Computer Basics Diagram. Computer System A complete working computer that has all of the necessary parts to make the computer function. Hardware Software. Hardware The physical components of the computer. The actual equipment you can see and touch.
Download these innovative computer diagrams PPT slides and create impressive presentations instantly. Easy-to-use, fully customizable, elegant designs. Toggle Nav. Search. Search. Search . 5. Notifications 5. See what the world is downloading for a kickass presentation. Check out our most popular products and get inspired.
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM allows you to easily create telecommunication network diagrams and then make a PowerPoint Presentation from your network documentation in a few clicks. Telecommunication network diagrams are used to show components and connections in a telecommunications network: how they are interacted between each other and with end-users.
46 templates. Travel. 26 templates. Workshop. 4 templates. computer Powerpoint templates and Google Slides themes -Slidego.