Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 1 chemical reactions and equations, cbse case study questions class 10 science chemical reactions and equations, case study 1, case study : 2, case study : 3, case study : 4.
1.) Write the definition of exothermic reaction.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, sikkim scert class 4 evs chapter 14 norbu goes to school solution, nobel lecture class 11 long questions for semester 2, andhra pradesh scert class 8 physical science semester 1 chapter 5 sound solutions, andhra pradesh scert class 8 physical science semester 1 chapter 4 synthetic fibres and plastics solutions.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Last modified on: 1 month ago
- Reading Time: 11 Minutes
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Here, we have provided case based/passage based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations.

| CBSE | |
| U | Class 10 Students |
| Science | |
| Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations | |
| Case Study Questions | |
| 3 | |
| Yes |
Table of Contents
Case Study/Passage Based Questions on Chemical Reactions and Equations
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Question 1:
Corrosion is the phenomenon of deterioration of surface of metal in presence of air and moisture. It is a natural process and in the presence of a moist atmosphere, chemically active metals get corroded. This is an oxidation reaction. Rusting is the process where iron corrodes due to exposure to the atmosphere. The main circumstance of corrosion occurs with iron because it is a structural material in construction, bridges, buildings, rail transport, ships, etc. Aluminium is also an important structural metal, but even aluminium undergoes oxidation reactions. However, aluminium doesn’t corrode or oxidize as rapidly as its reactivity suggests. Copper (Cu) corrodes and forms a basic green carbonate.
(i) What is rusting?
(ii) Which two metals do not corrode easily?
(iii) Write the chemical name of the compound formed on corrosion of silver.
(iv) Corrosion is (a) a redox reaction (b) a reduction reaction (c) a displacement reaction (d) an oxidation reaction
Also read: Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Question 2:
Oxidation is the process of gaining of oxygen, or losing of hydrogen. Reduction is the process of losing of oxygen or gaining of hydrogen. The substance which undergoes oxidation is the reducing agent while the substance which undergoes reduction is known as the oxidising agent. Oxidation and reduction always take place together and these type of reactions are known as redox reactions. Some of the examples of redox reactions are given below:

(i) Give two examples of oxidation reaction from your everyday life.
(ii) Write the oxidising agent in the reaction III and VI.
(iii) Which of the following is an oxidising agent? (a) LiAlH 4 (b) Alkaline KMnO 4 (c) Acidified K 2 Cr 2 O 7 (d) Both (b) and (c)
(iv) Out of oxidation and reduction, which reaction takes place at anode?
Also read: Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Question 3:
A chemical reaction is a representation of chemical change in terms of symbols and formulae of reactants and products. There are various types of chemical reactions like combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, oxidation and reduction reactions. Reactions in which heat is released along with the formation of products are called exothermic chemical reactions. All combustion reactions are exothermic reactions.
(i) The chemical reaction in which a single substance breaks down into two or more simpler substances upon heating is known as (a) thermal decomposition reaction (b) photo decomposition reaction (c) electric decomposition reaction (d) both (a) and (c)
(ii) The massive force that pushes the rocket forward through space is generated due to the (a) combination reaction (b) decomposition reaction (c) displacement reaction (d) double displacement reaction
(iii) A white salt on heating decomposes to give brown fumes and yellow residue is left behind. The yellow residue left is of (a) lead nitrate (b) nitrogen oxide (c) lead oxide (d) oxygen gas
(iv) Which of the following reactions represents a combination reaction? (a) CaO (s) + H 2 O (l) → Ca(OH) 2 (aq) (b) CaCO 3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO 2 (g) (c) Zn(s) + CuSO 4 (aq) → ZnSO 4 (aq) + Cu(s) (d) 2FeSO 4 (s) → Fe 2 O 3 (s) +SO 2 (g) + SO 3 (g)
(v) Complete the following statements by choosing correct type of reaction for X and Y. Statement 1: The heating of lead nitrate is an example of ‘X’ reaction. Statement 2: The burning of magnesium is an example of ‘Y’ reaction. (a) X- Combination, Y- Decomposition (b) X- Decomposition, Y-Combination (c) X- Combination, Y-Displacement (d) X- Displacement, Y-Decomposition
Related Posts
Download cbse books.
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
3 thoughts on “ Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations ”
Good examples! But can you please available practical types and equations type of case based questions which we can read and learn an then they help us to solve the Boards examm. Pleaseeww🙂🙂🙂
would love to see more equation based questions. nevertheless, it proved quite useful in my revision!
after going through the above content child should develops ideas to answer based on knowledge acquired.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
CBSE Expert
Class 10 Science: Case Study Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations PDF Download
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given.

Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Questions, by practicing this Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam.
Case Study Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Question 1:
A chemical reaction is a representation of chemical change in terms of symbols and formulae of reactants and products. There are various types of chemical reactions like combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, oxidation, and reduction reactions. Reactions in which heat is released along with the formation of products are called exothermic chemical reactions. All combustion reactions are exothermic reactions.
(i) The chemical reaction in which a single substance breaks down into two or simpler substances upon heating is known as (a) thermal decomposition reaction (b) photodecomposition reaction (c) electric decomposition reaction (d) both (a) and (c)
Answer: (a) The chemical reaction in which a single substance breaks down into two or more simpler substances upon heating is known as thermal decomposition reaction.
(ii) The massive force that pushes the rocket forward through space is generated due to the (a) combination reaction (b) decomposition reaction (c) displacement reaction (d) double displacement reaction
Answer: (b) The massive force that pushes the rocket forward through space is generated due to the decomposition reaction. Hydrogen peroxide decomposes and provides it with a considerable reaction force thrust.
(iii) A white salt on heating decomposes to give brown fumes and the yellow residue is left behind. The yellow residue left is of (a) lead nitrate (b) nitrogen oxide (c) lead oxide (d) oxygen gas
Answer: (c) Lead nitrate decomposes to give brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide gas and yellow residue of lead oxide is left behind.
(iv) Which of the following reactions represents a combination reaction? (a) CaO (s) + H 2 O (l) → Ca(OH) 2 (aq) (b) CaCO 3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO 2 (g) (c) Zn(s) + CuSO 4 (aq) → ZnSO 4 (aq) + Cu(s) (d) 2FeSO 4 (s) → Fe 2 O 3 (s) +SO 2 (g) + SO 3 (g)
Answer: (a) A reaction in which two or more reactants combine to form a single product is known as a combination reaction.
(v) Complete the following statements by choosing correct type of reaction for X and Y. Statement 1: The heating of lead nitrate is an example of ‘X’ reaction. Statement 2: The burning of magnesium is an example of ‘Y’ reaction. (a) X- Combination, Y- Decomposition (b) X- Decomposition, Y-Combination (c) X- Combination, Y-Displacement (d) X- Displacement, Y-Decomposition
Answer: (b) Heating of lead nitrate to form nitrogen dioxide and lead oxide is an example of thermal decomposition reaction and the burning of magnesium ribbon in the air to form magnesium oxide is an example of combination reaction.
Question 2:
In a chemical reaction, reactants are converted into products. The conversion of reactants into products in a chemical reaction is often accompanied by some features which can be observed easily. These easily observed features which take place as a result of chemical reactions are known as characteristics of chemical reactions. Some important characteristics of chemical reactions are: (I) Evolution of heat (II) Formation of a precipitate (III) Change in color (IV) Change in temperature (V) Change in state
Anyone of these general characteristics can tell us whether a chemical reaction has taken place or not.
(i) Reaction of magnesium with air is a/an
| (a) exothermic reaction | (b) endothermic reaction |
| (c) reversible reaction | (d) substitution reaction |
Answer: (a) exothermic reaction
(ii) In the following reaction Ca 2+ (aq)+2OH−(aq)⟶Ca(OH) 2 (s)Ca(aq) 2 ++2OH(aq)−⟶Ca(OH) 2 (s) precipitate of calcium hydroxide will be of
| (b) blue colour | (c) brown colour | (d) white colour |
Answer: (d) white colour
(iii) In the given reaction, S(s)+O 2 (g)⟶SO 2 S(s)+O 2 (g)⟶SO 2 the physical state of SO 2 is
| (a) liquid | (b) solid | (c) gaseous | (d) all three |
Answer: (c) gaseous
(iv) Which one of the following processes involves chemical reactions?
| (a) Storing of oxygen gas under pressure in a gas cylinder. |
| (b) Keeping petrol in a china dish in the open. |
| (c) Liquefaction of air. |
| (d) Heating copper wire in the presence of air at high temperatures. |
Answer: (d) Heating copper wire in the presence of air at high temperature.
(v) In which of the following reactions, a high amount of heat energy will be evolved?
| (a) Electrolysis of water | (b) Dissolution of NH4Cl in water |
| (c) Burning of L.P.G. | (d) Decomposition of AgBr in the presence of light |
Answer: (c) Burning of L.P.G.
You can also practice Class 10 Science MCQ Questions for Board Exams.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Based Questions Class 10
Students who are studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to get the knowledge about the Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Based Questions. Case based questions are generally based on the seen passages from the chapter Chemical Reactions and Equations. Through solving the case based questions, students can understand each and every concept.
With the help of Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Based Questions, students don’t need to memorise each answer. As answers for these case studies are already available in the given passage. Questions are asked through MCQs so student’s won’t take time to mark the answers. These multiple choice questions can help students to score the weightage of Chemical Reactions and Equations.
Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Based Questions with Solutions
Selfstudys provides case studies for the Class 10 Science chapter Chemical Reactions and Equations with solutions. The Solutions can be helpful for students to refer to if there is a doubt in any of the case studies problems. The solutions from the Selfstudys website are easily accessible and free of cost to download. This accessibility can help students to download case studies from anywhere with the help of the Internet.
Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Based Questions with solutions are in the form of PDF. Portable Document Format (PDF) can be downloaded through any of the devices: smart phone, laptop. Through this accessibility, students don't need to carry those case based questions everywhere.
Features of Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Based Questions
Before solving questions, students should understand the basic details of Chemical Reactions and Equations. Here are the features of case based questions on Chemical Reactions and Equations are:
- These case based questions start with short or long passages. In these passages some concepts included in the chapter can be explained.
- After reading the passage, students need to answer the given questions. These questions are asked in the Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ).
- These case based questions are a type of open book test. These case based questions can help students to score well in the particular subject.
- These Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Based Questions can also be asked in the form of CBSE Assertion and Reason .
Benefits of Solving Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Based Questions
According to the CBSE board, some part of the questions are asked in the board exam question papers according to the case studies. As some benefits of solving Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Based Questions can be obtained by the students. Those benefits are:
- Through solving case studies students will be able to understand every concept included in the chapter Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Passages included in the case study are seen passages, so students don’t need to struggle for getting answers. As these questions and answers can be discussed by their concerned teacher.
- Through these students can develop their observation skills. This skill can help students to study further concepts clearly.
- Case studies covers all the concepts which are included in the Chemical Reactions and Equations
How to Download Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Based Questions?
Students studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to solve questions based on case study. It is necessary for students to know the basic idea of Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Based Questions. Students can obtain the basic idea of case based questions through Selfstudys website. Easy steps to download it are:
- Open Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards CBSE which is visible in the navigation bar.
- A pop-up menu will appear, Select case study from the list.
- New page will appear, select 10 from the list of classes.
- Select Science from the subject list.
- And in the new page, you can access the Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Based Questions.
Tips to solve Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Questions-
Students should follow some basic tips to solve Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Based Questions. These tips can help students to score good marks in CBSE Class 10 Science.
- Generally, the case based questions are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
- Students should start solving the case based questions through reading the given passage.
- Identify the questions and give the answers according to the case given.
- Read the passage again, so that you can easily answer the complex questions.
- Answer according to the options given below the questions provided in the Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Based Questions.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
CBSE Board Exam is on the way, so you must practice some good Case Studies and Passage Based Questions of Class 10 Science to boost your preparation to score 95+% on Boards. In this post, you will get Case Study and Passage Based Questions that will come in CBSE Class 10 Science Board Exams. These Case Study Questions Class 10 Science are written by experts.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
A chemical reaction is a representation of chemical change in terms of symbols and formulae of reactants and products. There are various types of chemical reactions like combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, oxidation, and reduction reactions. Reactions in which heat is released along with the formation of products are called exothermic chemical reactions. All combustion reactions are exothermic reactions.
(i) The chemical reaction in which a single substance breaks down into two or simpler substances upon heating is known as (a) thermal decomposition reaction (b) photodecomposition reaction (c) electric decomposition reaction (d) both (a) and (c)
Answer: (a) The chemical reaction in which a single substance breaks down into two or more simpler substances upon heating is known as thermal decomposition reaction.
(ii) The massive force that pushes the rocket forward through space is generated due to the (a) combination reaction (b) decomposition reaction (c) displacement reaction (d) double displacement reaction
Answer: (b) The massive force that pushes the rocket forward through space is generated due to the decomposition reaction. Hydrogen peroxide decomposes and provides it with a considerable reaction force thrust.
(iii) A white salt on heating decomposes to give brown fumes and the yellow residue is left behind. The yellow residue left is of (a) lead nitrate (b) nitrogen oxide (c) lead oxide (d) oxygen gas
Answer: (c) Lead nitrate decomposes to give brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide gas and yellow residue of lead oxide is left behind.
(iv) Which of the following reactions represents a combination reaction? (a) CaO (s) + H 2 O (l) → Ca(OH) 2 (aq) (b) CaCO 3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO 2 (g) (c) Zn(s) + CuSO 4 (aq) → ZnSO 4 (aq) + Cu(s) (d) 2FeSO 4 (s) → Fe 2 O 3 (s) +SO 2 (g) + SO 3 (g)
Answer: (a) A reaction in which two or more reactants combine to form a single product is known as a combination reaction.
(v) Complete the following statements by choosing correct type of reaction for X and Y. Statement 1: The heating of lead nitrate is an example of ‘X’ reaction. Statement 2: The burning of magnesium is an example of ‘Y’ reaction. (a) X- Combination, Y- Decomposition (b) X- Decomposition, Y-Combination (c) X- Combination, Y-Displacement (d) X- Displacement, Y-Decomposition
Answer: (b) Heating of lead nitrate to form nitrogen dioxide and lead oxide is an example of thermal decomposition reaction and the burning of magnesium ribbon in the air to form magnesium oxide is an example of combination reaction.
Question 2:
In a chemical reaction, reactants are converted into products. The conversion of reactants into products in a chemical reaction is often accompanied by some features which can be observed easily. These easily observed features which take place as a result of chemical reactions are known as characteristics of chemical reactions. Some important characteristics of chemical reactions are: (I) Evolution of heat (II) Formation of a precipitate (III) Change in color (IV) Change in temperature (V) Change in state
Anyone of these general characteristics can tell us whether a chemical reaction has taken place or not.
(i) Reaction of magnesium with air is a/an
| (a) exothermic reaction | (b) endothermic reaction |
| (c) reversible reaction | (d) substitution reaction |
Answer: (a) exothermic reaction
(ii) In the following reaction Ca 2+ (aq)+2OH−(aq)⟶Ca(OH) 2 (s)Ca(aq) 2 ++2OH(aq)−⟶Ca(OH) 2 (s) precipitate of calcium hydroxide will be of
| (b) blue colour | (c) brown colour | (d) white colour |
Answer: (d) white colour
(iii) In the given reaction, S(s)+O 2 (g)⟶SO 2 S(s)+O 2 (g)⟶SO 2 the physical state of SO 2 is
| (a) liquid | (b) solid | (c) gaseous | (d) all three |
Answer: (c) gaseous
(iv) Which one of the following processes involves chemical reactions?
| (a) Storing of oxygen gas under pressure in a gas cylinder. |
| (b) Keeping petrol in a china dish in the open. |
| (c) Liquefaction of air. |
| (d) Heating copper wire in the presence of air at high temperatures. |
Answer: (d) Heating copper wire in the presence of air at high temperature.
(v) In which of the following reactions, high amount of heat energy will be evolved?
| (a) Electrolysis of water | (b) Dissolution of NH4Cl in water |
| (c) Burning of L.P.G. | (d) Decomposition of AgBr in the presence of light |
Answer: (c) Burning of L.P.G.
Case Study 3: Chemical reactions and equations are fundamental concepts in chemistry that help us understand the transformation of substances. A chemical reaction involves the rearrangement of atoms to form new substances with different properties. In a chemical equation, the reactants are written on the left side, and the products are written on the right side, separated by an arrow. The number of atoms of each element must be balanced on both sides of the equation. This is achieved by using coefficients to adjust the number of molecules involved in the reaction. Chemical reactions can be classified into various types, such as combination reactions, decomposition reactions, displacement reactions, and redox reactions. Understanding and balancing chemical equations is crucial for studying chemical reactions, predicting the products formed, and analyzing the stoichiometry of reactions.
What do chemical reactions involve? a) Formation of new substances with different properties b) Rearrangement of atoms c) Balancing of equations d) All of the above Answer: d) All of the above
How are reactants and products represented in a chemical equation? a) Reactants on the left side, products on the right side b) Reactants on the right side, products on the left side c) Reactants and products mixed together d) Reactants and products in different equations Answer: a) Reactants on the left side, products on the right side
What must be balanced in a chemical equation? a) Number of molecules b) Number of atoms of each element c) Physical properties of substances d) Coefficients Answer: b) Number of atoms of each element
Which type of chemical reaction involves the breakdown of a compound into simpler substances? a) Combination reaction b) Decomposition reaction c) Displacement reaction d) Redox reaction Answer: b) Decomposition reaction
Why is balancing chemical equations important? a) To predict the products formed in a reaction b) To analyze the stoichiometry of reactions c) To study chemical reactions d) All of the above Answer: d) All of the above
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Assertion reason questions class 10 science chapter 15 our environment, differential calculus: defined and explained with examples, extra questions of class 10 social science civics chapter 6 political parties pdf download, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 1
Last Updated on May 10, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 10 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 10 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 10 science chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations.
| Chemical Reactions and Equations | |
| Case Study Questions | |
| Competency Based Questions | |
| CBSE | |
| 10 | |
| Science | |
| Class 10 Studying Students | |
| Yes | |
| Mentioned | |
Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on Chemical Reactions and Equations
Question 1:
Rahul is a skilled painter. He mixed a white coloured powder, compound X with water. The compound X reacted vigorously with water to produce a compound Y and a large amount of heat. Then, Rahul used the compound Y for white washing the walls. Customer was not satisfied with the work of Rahul as walls were not shining. But Rahul guaranteed him that the walls would shine after 2-3 days and after 3 days of whitewash, the walls became shiny.
Read the above passage carefully and give the answer to the following questions:
Q 1. Name the compound X, that Rahul mixed with water.
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. The compound X is calcium oxide (CaO).
Q 2. Name the compound Y, that Rahul got after mixing X with water.
Ans. Compound Y is calcium hydroxide.
Q 3. What type of reaction has occurred here?
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Combination reaction
Q 4. Write the chemical reaction responsible for shiny finish of the walls.
Ans. Ca (OH) 2 (aq) + CO 2 (g) → CaCO 3 (s) + H 2 O (l)
Q 5. Write the common name of X and Y.
Ans. Common name of CaO (X) is quick lime and that of Ca(OH) 2 is slaked lime.
Acids Bases and Salts Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 2
Topics from which case study questions may be asked.
- Understand the concept of chemical reactions and their importance in daily life.
- Learn to write chemical equations for different types of chemical reactions.
- Master the skill of balancing chemical equations.
- Identify and classify different types of chemical reactions, such as combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, and redox reactions.
- Explore the concepts of oxidation and reduction in chemical reactions.
- Understand the phenomena of corrosion and rancidity and their prevention methods.
- Recognize the applications of chemical reactions in various industries and everyday scenarios.
- Develop critical thinking skills by analyzing and predicting the outcomes of chemical reactions.
- Appreciate the role of chemical reactions in environmental processes and human activities.
This chapter deals with introducing students to the fundamental concepts of chemical reactions, equations, and their implications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Heat Case Study Questions
Q1: what are case study questions for cbse examinations.
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 10 science chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How should students approach answering case study questions for CBSE?
A3: Students should carefully read the case study, identify the key issues or problems presented, analyze the information provided, apply relevant concepts and principles of chemical reactions and equations, and formulate well-supported solutions or responses.
Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 10 science chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience. If you need more case study questions for your preparation, then you visit Physics Gurukul website.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on chemical reactions and equations for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on chemical reactions and equations class 10 science into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of chemical reactions and equations.
Q7: Name the law based on which chemical equations must be balanced.
A7: Law of conservation of mass. Mass can neither be created nor can it be destroyed during a chemical reaction.
Q8: List any two observations when ferrous sulphate is heated in a dry test tube.
A8: (i) Initial light green colour changes to reddish brown colour. (ii) Colourless gas is evolved. (iii) Gas with choking smell is evolved
Q9: Why do silver articles become black after some time, when exposed to air?
A9: They get tarnished by reacting with atmospheric air to form silver sulphide.
Q10: Give reason why do chips manufacturers usually flush bags of chips with gas such as nitrogen?
A10: To prevent the oil and fats of the chips from being oxidized or become rancid.

Related Posts
- Bihar Board
James Dyson Award
Cfa institute, srm university.
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter Wise Important Case Study Questions
Chapter wise important case study questions cbse class 10 science: cbse class 10 science board exam 2024 is just around the corner and students are working hard to score maximum marks. check these case study questions from class 10 science to ace your examination this year also download the solutions from the pdf attached towards the end. .

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter Wise Important Case Study Questions: While the CBSE Board exam for Class 10 students are ongoing, the CBSE Class 10 Science board exam 2024 is to be held on March 2, 2024. With the exams just a few days away, CBSE Class 10th Board exam candidates are rushing to prepare the remaining syllabus, practising their weak portions, trying to revise the important questions from the past year papers, practise questions, etc.
Why are CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions Important?
- Section A : 20 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B : 6 Very Short Answer type questions carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C : 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- Section D : 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E : 3 Case Based/ Source Based units of assessment (4 marks each) with sub-parts.
How to solve case study questions in CBSE Class 10 Science?
- Read the case given and the associated questions carefully.
- Read the questions attentively and analyse what they are asking.
- Apply your subject knowledge and theories in the given case to decide what the correct answers should be.
1.A chemical reaction is a representation of chemical change in terms of symbols and formulae of reactants and products. There are various types of chemical reactions like combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, oxidation and reduction reactions. Reactions in which heat is released along with the formation of products are called exothermic chemical reactions. All combustion reactions are exothermic reactions.
(i) The massive force that pushes the rocket forward through space is generated due to the
(a) combination reaction
(b) decomposition reaction
(c) displacement reaction
(d) double displacement reaction
(ii) A white salt on heating decomposes to give brown fumes and yellow residue is left behind. The yellow residue left is of
(a) lead nitrate
(b) nitrogen oxide
(c) lead oxide
(d) oxygen gas
(iii) Which of the following reactions represents a combination reaction?
(a) CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca (OH)2 (aq)
(b) CaCO3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO2(g)
(c) Zn(s) + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu(s)
(d) 2FeSO4(s) → Fe2O3 (s) +SO2(g) + SO3(g)
(iv) Complete the following statements by choosing correct type of reaction for X and Y.
Statement 1: The heating of lead nitrate is an example of ‘X’ reaction.
Statement 2: The burning of magnesium is an example of ‘Y’ reaction.
(a)X-Combination,Y-Decomposition
(b)X-Decomposition,Y-Combination
(c)X-Combination,Y-Displacement
(d) X- Displacement, Y-Decomposition
2.The earlier concept of oxidation and reduction is based on the addition or removal of oxygen or hydrogen elements so, in terms of oxygen and hydrogen, oxidation is addition of oxygen to a substance and removal of hydrogen from a substance. On the other hand, reduction is addition of hydrogen to a substance and removal of oxygen from a substance. The substance which gives oxygen to another substance or removes hydrogen from another substance in an oxidation reaction is known as oxidising agent, while the substance which gives hydrogen to another substance or removes oxygen from another substance in a reduction reaction is known as reducing agent. For example,
(i) A redox reaction is one in which
(a) both the substances are reduced
(b) both the substances are oxidised
(c) an acid is neutralised by the base
(d) one substance is oxidised while the other is reduced.
(ii) In the reaction, H2S+Cl2⟶S+2HCl
(a) H2S is the reducing agent.
(b) HCl is the oxidising agent.
(c) H2S is the oxidising agent.
(d) Cl2 is the reducing agent.
(iii) Which of the following processes does not involve either oxidation or reduction?
(a) Formation of slaked lime from quicklime.
(b) Heating mercuric oxide.
(c) Formation of manganese chloride from manganese oxide (MnO2).
(d) Formation of zinc from zinc blende.
(iv) Mg+CuO⟶MgO+Cu
Which of the following is wrong relating to the above reaction?
(a) CuO gets reduced
(b) Mg gets oxidised.
(c) CuO gets oxidised.
(d) It is a redox reaction.
3.A copper vessel gets tarnished due to formation of an oxide layer on its surface. On rubbing lemon on the vessel, the surface is cleaned, and the vessel begins to shine again. This is due to the fact that which reacts with the acid present in lemon to form a salt which is washed away with water. As a result, the layer of copper oxide is removed from the surface of the vessel and the shining surface is exposed.
1.Which of the following acids is present in lemon?
(a) Formic acid
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Citric acid
(d) Hydrochloric acid
2.The nature of copper oxide is
d) amphoteric
3.Name the salt formed in the above reaction
a) copper carbonate
b) copper chloride
c)copper citrate
d) copper citrate
4.The phenomenon of copper getting tarnished is
a) corrosion
b) rancidity
c) displacement
d)none of these
4.Metals as we know, are very useful in all fields, industries in particular. Non-metals are no less in any way. Oxygen present in air is essential for breathing as well as for combustion. Non-metals form a large number of compounds which are extremely useful, e.g., ammonia, nitric acid, sulphuric acid, etc. Non-metals are found to exist in three states of matter. Only solid non-metals are expected to be hard however, they have low density and are brittle. They usually have low melting and boiling points and are poor conductors of electricity.
i.____________ is a non-metal but is lustrous
A.Phosphorus
ii.Which of the following is known as 'King of chemicals'?
C. Sulphuric acid
D. Nitric acid
iii.Which of the following non-metals is a liquid?
iv.Hydrogen is used
A.for the synthesis of ammonia
B. for the synthesis of methyl alcohol
C.nitrogenous fertilizers
D. all of these
5.Nisha observed that the bottoms of cooking utensils were turning black in colour while the flame of her stove was yellow in colour. Her daughter suggested cleaning the air holes of the stove to get a clean, blue flame. She also told her mother that this would prevent the fuel from getting wasted.
a) Identify the reasons behind the sooty flame arising from the stove.
b) Can you distinguish between saturated and unsaturated compounds by burning them? Justify your answer.
c) Why do you think the colour of the flame turns blue once the air holes of the stove are cleaned?
6.Blood transport food, Oxygen and waste materials in our bodies. It consists of plasma as a fluid medium. A pumping organ [heart] is required to push the blood around the body. The blood flows through the chambers of the heart in a specific manner and direction. While flowing throughout the body, blood exerts a pressure against the wall or a vessel.
- Pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary vein
- Very narrow and have high resistance
- Much wide and have low resistance
- Very narrow and have low resistance
- Much wide and have high resistance
- It is a hollow muscular organ
- It is four chambered having three auricles and one ventricle.
- It has different chambers to prevent O2 rich blood from mixing with the blood containing CO2
- Both A & C
- Blood = Plasma + RBC + WBC + Platelets
- Plasma = Blood – RBC
- Lymph = Plasma + RBC
- Serum = Plasma + RBC + WBC
7.A brain is displayed at the Allen Institute for Brain Science. The human brain is a 3-pound (1.4-kilogram) mass of jelly-like fats and tissues—yet it's the most complex of all known living structures The human brain is more complex than any other known structure in the universe. Weighing in at three pounds, on average, this spongy mass of fat and protein is made up of two overarching types of cells—called glia and neurons— and it contains many billions of each. Neurons are notable for their branch-like projections called axons and dendrites, which gather and transmit electrochemical signals. Different types of glial cells provide physical protection to neurons and help keep them, and the brain, healthy. Together, this complex network of cells gives rise to every aspect of our shared humanity. We could not breathe, play, love, or remember without the brain.
1)Animals such as elephants, dolphins, and whales actually have larger brains, but humans have the most developed cerebrum. It's packed to capacity inside our skulls and is highly folded. Why our brain is highly folded?
- b) Learning
3)Which among these protects our brain?
a)Neurotransmitter
b) Cerebrospinal fluid
d) Grey matter
4.Ram was studying in his room. Suddenly he smells something burning and sees smoke in the room. He rushes out of the room immediately. Was Ram’s action voluntary or involuntary? Why?
8.Preeti is very fond of gardening. She has different flowering plants in her garden. One day a few naughty children entered her garden and plucked many leaves of Bryophyllum plant and threw them here and there in the garden. After few days, Preeti observed that new Bryophyllum plants were coming out from the leaves which fell on the ground.
1.What does the incident sited in the paragraph indicate?
(a). Bryophyllum leaves have special buds that germinate to give rise to new plant.
(b). Bryophyllum can propagate vegetatively through leaves.
(c). Bryophyllum is a flowering plant that reproduces only asexually
(d). Both (a) and (b).
2.Which of the following plants can propagate vegetatively through leaves like Bryophyllum?
3.Do you think any other vegetative part of Bryophyllum can help in propagation? If yes, then which part?
(c) Flowers
4.Which of the following plant is artificially propagated (vegetatively) by stem cuttings in horticultural practices?
(b)Snakeplant
(d)Water hyacinth
9.The growing size of the human population is a cause of concern for all people. The rate of birth and death in a given population will determine its size. Reproduction is the process by which organisms increase their population. The process of sexual maturation for reproduction is gradual and takes place while general body growth is still going on. Some degree of sexual maturation does not necessarily mean that the mind or body is ready for sexual acts or for having and bringing up children. Various contraceptive devices are being used by human beings to control the size of the population.
1) What are common signs of sexual maturation in boys?
a) Broadening of shoulders
b) Development of mammary glands
c) Broadening of waist
d) High pitch of voice
2) Common sign of sexual maturation in girls is
a) Low pitch voice
b) Appearance of moustache and beard
c) Development of mammary glands
d) Broadening of shoulders
3) Which contraceptive method changes the hormonal balance of the body?
b) Diaphragms
c) Oral pills
d) Both a) and b)
4) What should be maintained for healthy society?
a) Rate of birth and death rate
b) Male and female sex ratio
c) Child sex ratio
d) None of these
10.Pea plants can have smooth seeds or wrinkled seeds. One of the phenotypes is completely dominant over the other. A farmer decides to pollinate one flower of a plant with smooth seeds using pollen from a plant with wrinkled seeds. The resulting pea pod has all smooth seeds.
i) Which of the following conclusions can be drawn?
(1) The allele for smooth seeds is dominated over that of wrinkled seeds.
(2) The plant with smooth seeds is heterozygous.
(3) The plant with wrinkled seeds is homozygous.
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ii) Which of the following crosses will give smooth and wrinkled seeds in same proportion?
(a) RR X rr
(b) Rr X rr
(d) rr X rr
iii) Which of the following cross can be used to determine the genotype of a plant with dominant phenotype?
(a) RR X RR
(b) Rr X Rr
(c) Rr X RR
(d) RR X rr
iv) On crossing of two heterozygous smooth seeded plants (Rr), a total of 1000 plants were obtained in F1 generation. What will be the respective number of smooth and wrinkled seeds obtained in F1 generation?
(a) 750, 250
(b) 500, 500
(C) 800, 200
(d) 950, 50
11.Food chains are very important for the survival of most species.When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction of a species in some cases.The foundation of the food chain consists of primary producers.Primary producers or autotrophs,can use either solar energy or chemical energy to create complex organic compounds,whereas species at higher trophic levels cannot and so must consume producers or other life that itself consumes producers. Because the sun’s light is necessary for photosynthesis,most life could not exist if the sun disappeared.Even so,it has recently been discovered that there are some forms of life,chemotrophs,that appear to gain all their metabolic energy from chemosynthesis driven by hydrothermal vents,thus showing that some life may not require solar energy to thrive.
1.If 10,000 J solar energy falls on green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem,what percentage of solar energy will be converted into food energy?
(d)It will depend on the type of the terrestrial plant
2.Matter and energy are two fundamental inputs of an ecosystem. Movement of
(a)Energy is by directional and matter is repeatedly circulating
(b)Energy is repeatedly circulating and matter is unidirectional
(c)Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating
(d)Energy is multidirectional and matter is bidirectional
3.Raj is eating curd/yoghurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying
(a)First trophic level
(b)Second trophic level
(c)Third trophic level
(d)Fourth trophic level
4.Which of the following, limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain
(a)Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels
(b)Less availability of food
(c)Polluted air
5.The decomposers are not included in the food chain. The correct reason for the same is because decomposers
(a) Act at every trophic level at the food chain
(b) Do not breakdown organic compounds
(c) Convert organic material to inorganic forms
(d) Release enzymes outside their body to convert organic material to inorganic forms
12.Shyam participated in a group discussion in his inter school competition on the practical application of light and was very happy to win an award for his school. That very evening his father gave treat to celebrate Shyam’s win. Shyam while sitting saw an image of a person sitting at his backside in his curved plate and could see that person’s mobile drop in the flower bed. Person was not aware until Shyam went and informed him. He thanked Shyam for his clever move.
a)From which side of his plate Shyam observed the incident –
i)outward curved
ii)inward curved
iii)plane surface
b)Part of plate from which Shyam observed the incident acted like a-
i)concave mirror
ii)convex mirror
iii)plane mirror
c)The nature of the size of the image formed in above situation is –
i)real, inverted and magnified
ii)same size , laterally inverted
iii)virtual, erect and diminished
iv)real , inverted and diminished
d)Magnification of the image formed by convex mirror is –
more than 1
iii)equal to 1
iv)less than 1
- The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is
(a) at focus
(c) at optical center
- When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is
(a)real and smaller
(b) virtual and smaller
(c) virtual and inverted
- The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus ofconvex lens is
(a) highly magnified
(b) point in size
- When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is
(b) between F and optical center
(c) at infinity
(d) none of the above
14.One of the wires in domestic circuits supply, usually with a red insulation cover, is called live wire. with black insulation is called neutral wire. The earth wire, which has insulation of green colour, is usually connected to a metal plate deep in the earth near the house appliances that has a metallic body. Overloading contact, in such a situation the current in the circuit abruptly increases. circuit prevents damage to the appliances and the circuit due to overloading.
1 When do we say that an electrical appliance
2 Mention the function of earth wire in electrical line
3 How is an electric fuse connected in a domestic circuit?
4 When overloading and short circuiting are said to occur?
5 What is a live wire?
15.Light of all the colours travel at the same speed in vacuum for all wavelengths. But in any transparent medium(glass or water), the light of different colours travels at different speeds for different wavelengths, which means that the refractive index of a particular medium is different for different wavelengths. As there is a difference in their speeds, the light of different colours bend through different angles. The speed of violet colour is maximum and the speed of red colour is minimum in glass so, the red light deviates least and violet colour deviates most. Hence, higher the wavelength of a colour of light, smaller the refractive index and less is the bending of light.
(i)Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of Light of different colours of white light in air?
(a) Red light moves fastest.
(b) Blue light moves faster than green light.
(c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed.
(d) Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of the red and the violet light.
(ii)Which of the following is the correct order of wavelength?
(a) Red> Green> Yellow
(b) Red> Violet> Green
(c) Yellow> Green> Violet
(d) Red> Yellow> Orange
(iii)Which of the following is the correct order of speed of light in glass?
(a) Red> Green> Blue
(b) Blue> Green> Red
(c) Violet> Red> Green
(d) Green> Red> Blue
(iv)Which colour has maximum frequency?
16.The region around a magnet where magnetism acts is represented by the magnetic field.The force of magnetism is due to moving charge or some magnetic material. Like stationary charges produce an electric field proportional to the magnitude of charge, moving charges produce magnetic fields proportional to the current. In other words, a current carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it. The subatomic particles in the conductor, like the electrons moving in atomic orbitals, are responsible for the production of magnetic fields. The magnetic field lines around a straight conductor (straight wire) carrying current are concentric circles whose centres lie on the wire.
1)The magnetic field associated with a current carrying straight conductor is in anti- clockwise direction. If the conductor was held horizontally along east west direction,what is the direction of current through it?
2)Name and state the rule applied to determine the direction of magnetic field in a straight current carrying conductor.
3)Ramus performs an experiment to study the magnetic effect of current around a current carrying straight conductor with the help of a magnetic compass. He reports that
a)The degree of deflection of magnetic compass increases when the compass is moved away from the conductor.
b)The degree of deflection of the magnetic compass increases when the current through the conductor is increased.
Which of the above observations of the student appears to be wrong and why?
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science CBSE Chapter Wise PDF
Related resources to prepare for CBSE 10th Science Board Exam 2024
- CBSE class 10 Science syllabus 2024
- NCERT Book for Class 10th Science 2023-2024 (PDF)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- CBSE Class 10 Science sample paper
- Previous Year Questions of CBSE Class 10 Science
- CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Physics Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Biology Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Science Topper Answer Sheet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Practice Paper 2023 with Answers
- Class 10 CBSE Admit Card 2023-24
- CBSE Class 10 Date Sheet 2023
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2023 - 2024
- CBSE Class 10 DELETED Syllabus 2023-24
- CBSE Class 10th Sample Paper 2022-23: Download Sample Question Papers and Marking Scheme
- CBSE Class 10 Previous Year Question Papers for 2022-23
- CBSE Class 10 Important Questions and Answers for 2023-24 of ALL Chapters
- CBSE Class 10 Practice Papers: All Subjects
- CBSE Topper Answer Sheet Class 10: Model Answer Paper Download PDF
- CBSE Class 10 Mock Tests: All Subjects
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- UPSC Answer Key 2024
- UPSC Question Paper 2024
- UPSC Exam Analysis 2024
- UPSC Prelims Cut Off 2024
- Bihar BEd Admit Card 2024
- IAS Exam Last Minute Tips 2024
- NTA NET Admit Card 2024
- APSC SO Result 2024
- APSC SO Admit Card 2024
- UPSC CSE Admit Card 2024
- CBSE Class 10 QnA

Latest Education News
UGC NET Answer Key 2024: Check Unofficial Papers PDF for Shift 1 and 2
TS PGECET 2024 Results Out, Download Rankcard At pgecet.tsche.ac.in
BEL Recruitment 2024: भारत इलेक्ट्रॉनिक्स में विभिन्न पदों पर निकली भर्तियाँ, जानें कैसे करें आवेदन
MECON AE Recruitment 2024: Notification Out for Various Engineer and other posts, Check eligibility and application process
NTA UGC NET 2024 June Question Paper: डाउनलोड करें शिफ्ट वाइज सेट A, B, C, और D पेपर 1, 2 पीडीएफ
NEET PG 2024 Admit Card Out Today, Login at natboard.edu.in to Get Hall Ticket Soon
Find 3 differences between the pictures of the frog in 10 seconds!
CG Forest Driver Recruitment 2024: Registration Begins for 144 Vacancies at forest.cg.gov.in, Apply till July 1
AP Inter Supply Result 2024 Declared for 1st, 2nd Year Releasing Today at bie.ap.gov.in, Get Latest Updates
UGC NET Question Paper 2024: Download June Session Papers for Set A, B, C, D PDF Shift 1, 2
Personality Test: Your Finger Shape Reveals Your Hidden Personality Traits
Personality Test: Your Foot Shape Reveals Your Hidden Personality Traits
Lucknow University Admit Card 2024 OUT at lkouniv.ac.in; Direct Link to Download Even Semester Exam Hall Ticket PDF
Union Territories of India: Ladakh, Chandigarh, Puducherry, Jammu And Kashmir And More
UP Board Class 11 Maths Syllabus 2024-2025: Download in PDF
Picture Puzzle IQ: Time’s Ticking! Can You Spot the Odd Camel In 12 Seconds?
जानें यूपी में एसडीएम और डीएसपी में से किसे मिलती है ज्यादा सैलरी?
CG Forest Driver Recruitment 2024: छत्तीसगढ़ वन विभाग में वाहन चालक के 144 पदों के लिए आवेदन शुरू, जानें कैसे करें Apply
Only highly intelligent readers can spot three hidden faces in 6 seconds!
TS ECET Counselling 2024: 1st Phase Seat Allotment Result Out at tgecet.nic.in, List of Required Documents
- RS Aggarwal
- ML Aggarwal
- Merchant of Venice
- NCERT Books
- Questions and Answers
- NCERT Notes
- Important Questions
- Chemical Reactions and Equations
Case Based Questions for Ch 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science
(i) The massive force that pushes the rocket forward through space is generated due to the
(a) combination reaction
(b) decomposition reaction
(c) displacement reaction
(d) double displacement reaction
(ii) A white salt on heating decomposes to give brown fumes and yellow residue is left behind. The yellow residue left is of
(a) lead nitrate
(b) nitrogen oxide
(c) lead oxide
(d) oxygen gas
(iii) Which of the following reactions represents a combination reaction?
(a) CaO (s) + H 2 O (l) ⟶ Ca(OH) 2 (aq)
(b) CaCO 3 (s) ⟶ CaO (s) + CO 2 (g)
(c) Zn(s) + CuSO 4 (aq) ⟶ ZnSO 4 (aq) + Cu(s)
(d) 2FeSO 4 (s) ⟶ Fe 2 O 3 (s) + SO 2 (g) + SO 3 (g)
(iv) Complete the following statements by choosing correct type of reaction for X and Y.
Statement 1: The heating of lead nitrate is an example of ‘X’ reaction.
Statement 2: The burning of magnesium is an example of ‘Y’ reaction.
(a) X-Combination, Y-Decomposition
(b) X-Decomposition, Y-Combination
(c) X-Combination, Y-Displacement
(d) X- Displacement, Y-Decomposition
Lead nitrate decomposes to give lead oxide and nitrogen oxide. Thus, X is a decomposition reaction.
2Pb(NO 3 ) 2 (s) ⟶ 2PbO(s) + 4NO 2 (g)
Magnesium burns in the presence of oxygen gas to magnesium oxide. Thus, Y is a combination reaction.
2Mg + O 2 ⟶ 2MgO
(b) combustion
(c) decomposition reaction
(d) photosynthesis
(ii) Which of the following is essential for photosynthesis?
(a) Sunlight
(b) Chlorophyll
(c) Glucose
(d) Both 'a' and 'b’
(iii) When a chemical compound decomposes on absorbing light and energy, then the reaction which takes place is known as:
(a) photosynthesis
(b) photodecomposition
(c) combination
(d) thermal decomposition
(iv) Which of the following reactions is an example of combustion reaction?
(a) C(s) + O 2 (g) ⟶ CO 2 (g)
(b) Zn(s) + H 2 SO 4 (aq) ⟶ ZnSO 4 + H 2 (g)
(c) Zn(s) +2HCl(aq) ⟶ ZnCl 2 (aq) + H 2 (g)
(d) 3Mg(s) + N 2 (g) ⟶ Mg 3 N 2 (s)
(v) Which of the following is an example of combination reaction?
(a) H 2 + Cl 2 ⟶ 2HCl
(b) Fe + S ⟶ FeS
(c) 2H 2 + O 2 ⟶ 2H 2 O
(d) All of them
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesis nutrients from carbon dioxide and water.
(iii) (b) photodecomposition
A combustion reaction is a reaction in which a substance reacts with oxygen gas, releasing energy in the form of light and heat.
(v) (d) All of them
The values of x and y are:
(a) 3 and 5
(b) 8 and 6
(c) 4 and 2
(d) 7 and 1
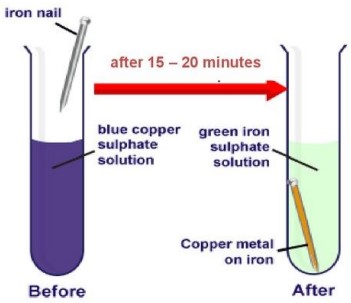
(ii) What happens when copper rod is dipped in iron sulphate solution:
(a) Copper displaces iron
(b) Blue colour of copper sulphate solution is obtained
(c) No reaction takes place
(d) Reaction is exothermic
(iii) A substance which oxidised itself and reduces other is known as:
(a) Oxidising agent
(b) Reducing agent
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
(iv) Fe 2 O 3 + 2Al ⟶ Al 2 O 3 + 2Fe
The above reaction is an example of a:
(a) Combination reaction
(b) Double displacement reaction
(c) Decomposition reaction
(d) Displacement reaction
(v) Name the products formed when iron filings are heated with dilute hydrochloric acid.
(a) Fe (III) chloride and water
(b) Fe (II) chloride and water
(c) Fe (II) chloride and hydrogen gas
(d) Fe (III) chloride and hydrogen gas
After balancing the equation, we get
Cu + 4HNO 3 ⟶ Cu(NO 3 ) 2 + 2NO 2 + 2H 2 O
(ii) (c) No reaction takes place.
(iii) (b) Reducing agent
Reducing agents reduce the other substance and in turn, get oxidized.
(iv) (d) Displacement reaction
(v) (c) Fe (II) chloride and hydrogen gas
When dilute Hydrochloric acid is added to iron filings, iron chloride & hydrogen gas is produced.
Fe + 2HCl ⟶ FeCl 2 + H 2
The iron displaces hydrogen from hydrochloric acid to form iron (II) chloride & hydrogen gas. This is a single displacement reaction.
(a) bleaching agent in the textile, paper and jute industry
(b) disinfectant for water to make water free of germs
(c) oxidising agent in many industries
(d) all of these
(ii) Bleaching powder is also known as:
(a) calcium oxychloride
(b) calcium hypochlorite
(c) chloride of lime
(iii) Bleaching powder gives smell of chlorine because it:
(a) is unstable
(b) gives chlorine on exposure to atmosphere
(c) is a mixture of chlorine and slaked lime
(d) contains excess of chlorine.
(iv) Select the correct statement(s) regarding bleaching powder.
(a) It is pale yellow powder having smell of chlorine.
(b) It is sparingly soluble in water and gives milky suspension when dissolved in water.
(c) As bleaching powder gives nascent oxygen, it shows bleaching property.
(d) All of these.
(v) Identify the product ‘X’ in the given reaction.
Ca(OH) 2 + Cl 2 ⟶ X + H 2 O
(a) CaOCl 2
(c) Ca(ClO 3 ) 2
Bleaching powder gives chlorine on exposure to air by reacting with CO 2 .
CaOCl 2 + CO 2 ⟶ CaCO 3 + Cl 2
Ca(OH) 2 + Cl 2 ⟶ CaOCl 2 + H 2 O
CaOCl 2 : calcium oxychloride (bleaching powder)
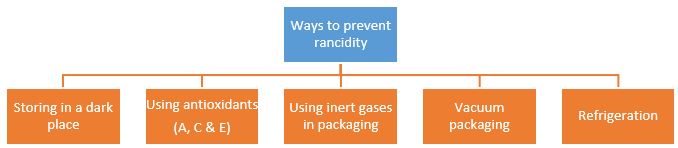
(i) Rancidity can be prevented by:
(a) adding antioxidants
(b) packaging oily food in nitrogen gas
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these.
(ii) Combination of phosphorus and oxygen is an example of:
(a) oxidation
(b) reduction
(c) rancidity
(d) none of these
(iii) A science teacher wrote the following statements about rancidity:
(I) When fats and oils are reduced, they become rancid.
(II) In chips packet, rancidity is prevented by oxygen.
(III) Rancidity is prevented by adding antioxidants.
Select the correct option
(a) (I) only
(b) (II) and (III) only
(c) (III) only
(d) (I), (II) and (III)
(iv) Two statements are given below regarding rusting of iron.
(I) The rusting of iron is a redox reaction and reaction occurs as,
4Fe + 3O 2 ⟶ 4Fe 3+ + 6O 2–
(II) The metallic iron is oxidised to Fe 2+ and O 2 is reduced to O 2– .
Select the correct statement(s).
(b) II only
(c) Both I and II
(v) Which of the following measures can be adopted to prevent or slow down rancidity?
(I) Food materials should be packed in air tight container.
(II) Food should be refrigerated.
(III)Food materials and cooked food should be kept away from direct sunlight.
(a) Only II and III
(b) Only I and III
(c) Only II and III
(d) I, II and III
Antioxidants and nitrogen gas prevent oxidation of food.
(ii) (a) oxidation
4P + 3O 2 ⟶ 2P 2 O 3 ,
4P + 5O 2 ⟶ 2P 2 O 5
(iii) (III) only
The oils and fats are slowly oxidised to certain bad smelling compounds, which release foul smell. This is known as rancidity. Rancidity is prevented by filling nitrogen gas in chips packets.
(iv) (a) I only
(v) (d) I, II and III
(i) Consider the following reaction:
pMg 3 N 2 + qH 2 O ⟶ rMg(OH) 2 + sNH 3
When the equation is balanced, the coefficients p, q, r, s respectively are:
(a) 1, 3, 3, 2
(b) 1, 6, 3, 2
(c) 1, 2, 3, 2
(d) 2, 3, 6, 2
(ii) Which of the following information is not conveyed by a balanced chemical equation?
(a) Physical states of reactants and products
(b) Symbols and formulae of all the substances involved in a particular reaction
(c) Number of atoms/molecules of the reactants and products formed
(d) Whether a particular reaction is actually feasible or not
(iii) The balancing of chemical equations is in accordance with
(a) law of combining volumes
(b) law of constant proportions
(c) law of conservation of mass
(d) both (b) and (c)
(iv) Which of the following chemical equations is an unbalanced one?
(a) 2NaHCO 3 ⟶ Na 2 CO 3 + H 2 O + CO 2
(b) 2C 4 H 10 + 12O 2 ⟶ 8CO 2 + 10H 2 O
(c) 2Al + 6H 2 O ⟶ 2Al(OH) 3 + 3H 2
(d) 4NH 3 + 5O 2 ⟶ 4NO + 6H 2 O
(v) Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(a) A chemical equation tells us about the substances involved in a reaction.
(b) A chemical equation informs us about the symbols and formulae of the substances involved in a reaction.
(c) A chemical equation tells us about the atoms or molecules of the reactants and products involved in a reaction.
(d) All the above.
(i) (b) 1, 6, 3, 2
Mg 3 N 2 + 6H 2 O ⟶ 3Mg(OH) 2 + 2NH 3
(ii) (d) Whether a particular reaction is actually feasible or not
(iii) (c) law of conservation of mass
In a balanced chemical equation, total mass of reactants must be equal to the total mass of products. This is the statement of law of conservation of mass.
(iv) (b) 2C 4 H 10 + 12O 2 ⟶ 8CO 2 + 10H 2 O
(v) (d) All the above.
(i) Which of the following is a redox reaction?
(a) CaCO 3 ⟶ CaO + CO 2
(b) H 2 + Cl 2 ⟶ 2HCl
(c) CaO + 2HCl ⟶ CaCl 2 + H 2 O
(d) NaOH + HCl ⟶ NaCl + H 2 O
(ii) Identify the reaction in which H2O2 is acting as a reducing agent.
(a) H 2 SO 3 + H 2 O 2 ⟶ H 2 SO 4 + H 2 O
(b) 2HI + H 2 O 2 ⟶ 2H 2 O + I 2
(c) Cl 2 + H 2 O 2 ⟶ 2HCl + O 2
(d) 2FeCl 2 + 2HCl + H 2 O 2 ⟶ 2FeCl 3 + 2H 2 O
(iii) For the following reactions, identify the one in which H2S acts as a reducing agent.
(a) CuSO 4 + H 2 S ⟶ CuS + H 2 SO 4
(b) Cd(NO 3 ) 2 + H 2 S ⟶ CdS + 2HNO 3
(c) 2FeCl 3 + H 2 S ⟶ 2FeCl 2 + 2HCl + S
(iv) For the following reaction, identify the correct statement.
ZnO + CO ⟶ Zn + CO 2
(a) ZnO is being reduced.
(b) CO 2 is being oxidised.
(c) CO is being reduced.
(d) ZnO is being oxidised.
(v) In the following reaction, which substance is reduced?
Pbs + 4H 2 O 2 ⟶ PbSO 4 + 4H 2 O
(b) H 2 O 2
(i) (b) H 2 + Cl 2 ⟶ 2HCl
H 2 is oxidised to HCl while Cl 2 is reduced to HCl.
(ii) (c) Cl 2 + H 2 O 2 ⟶ 2HCl + O 2
(iii) (c) 2FeCl 3 + H 2 S ⟶ 2FeCl 2 + 2HCl + S
H 2 S itself gets oxidised to S and reduces FeCl 3 to FeCl 2 .
(iv) (a) ZnO is being reduced. ZnO is reduced to Zn and CO is oxidised to CO 2 .
(v) (b) H 2 O 2 is reduced to water by removal of oxygen.
In a chemical reaction, reactants are converted into products. The conversion of reactants into products in a chemical reaction is often accompanied by some features which can be observed easily. These easily observed features which take place as a result of chemical reaction are known as characteristics of chemicals reactions. Some important characteristics of chemical reactions are:
(I) Evolution of heat
(II) Formation of precipitate
(III) Change in colour
(IV) Change in temperature
(V) Change in state
Any one of these general characteristics can tell us whether a chemical reaction has taken place or not.
(i) Reaction of magnesium with air is a/an:
(a) exothermic reaction
(b) endothermic reaction
(c) reversible reaction
(d) substitution reaction
(ii) In the following reaction,
Ca 2+ (aq) + 2OH - (aq) ⟶ Ca(OH) 2 (s)
precipitate of calcium hydroxide will be of:
(a) green colour
(b) blue colour
(c) brown colour
(d) white colour.
(iii) In the given reaction,
S(s) + O 2 (g) ⟶ SO 2
the physical state of SO 2 is
(c) gaseous
(d) all three.
(iv) Which one of the following processes involve chemical reactions?
(a) Storing of oxygen gas under pressure in a gas cylinder.
(b) Keeping petrol in a china dish in the open.
(c) Liquefaction of air.
(d) Heating copper wire in the presence of air at high temperature.
(v) In which of the following reactions, high amount of heat energy will be evolved?
(a) Electrolysis of water
(b) Dissolution of NH 4 Cl in water
(c) Burning of L.P.G.
(d) Decomposition of AgBr in the presence of light.
(i) (a) exothermic reaction
(ii) (d) white colour.
Calcium hydroxide is a white colour solid.
(iii) (c) gaseous
SO 2 is gaseous in nature.
(iv) (d) Heating copper wire in the presence of air at high temperature.
When copper is heated in the presence of air in a very high temperature, a chemical reaction takes place. Copper reacts with oxygen of the air to form a thin layer of copper oxide on the surface of metallic copper.
(v) (c) Burning of L.P.G.
On burning of L.P.G., heat is evolved.
(i) Copper displaces which of the following metals from its salt solution?
(ii) When zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric acid, the gas evolved is
(a) red in colour and have a sweet smelling.
(b) green in colour and have a foul smell.
(c) colourless, odourless and burns with a pop sound.
(d) colourless, pungent smelling and burns with a pop sound.
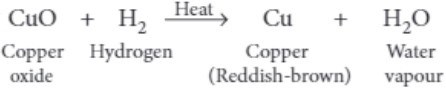
(iii) When dry hydrogen is passed over a heated oxide of metal X using the apparatus shown below, a reddish-brown residue is obtained.
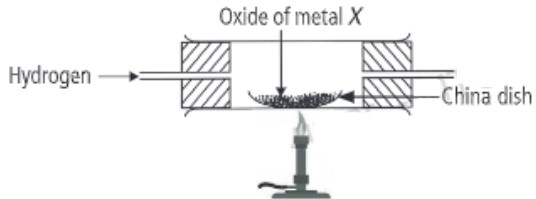
The reddish-brown residue could be
(iv) Which of the following reactions is a displacement reaction?
(a) CaO + H 2 O ⟶ Ca(OH) 2
(c) Mg + CuSO 4 ⟶ MgSO 4 + Cu
(b) MgCO 3 ⟶ Mg + CO 2
(d) H 2 + Cl 2 ⟶ 2HCl
(v) When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to granulated zinc placed in a test tube, the observation made is
(a) the surface of the metal turns shining
(b) the reaction mixture turns milky
(c) greenish yellow gas is evolved
(d) the colourless and odourless gas evolves burns with a pop sound.
(i) (c) AgNO 3
Cu + 2AgNO 3 ⟶ Cu(NO 3 ) 2 + 2Ag
Copper can displace silver from its salt solution since, copper is more reactive than silver.
(ii) (c) colourless, odourless and burns with a pop sound.
Zn + H 2 SO 4 (dil.) ⟶ ZnSO 4 + H 2 ↑
H 2 is a colourless, odourless gas and burns with a pop sound.
(iii) (a) Copper is the reddish-brown residue as shown in below reaction.
(iv) (c) Mg + CuSO 4 ⟶ MgSO 4 + Cu
It is a single displacement reaction.
(v) (d) the colourless and odourless gas evolves burns with a pop sound.
Hydrogen gas is evolved in this reaction as shown in the reaction.
Zn + 2HCl ⟶ ZnCl 2 + H 2 ↑
Hydrogen gas is colourless and odourless which burns with a pop sound.
Those reactions in which two compounds react by an exchange of ions to form two new compounds are called double displacement reactions. A double displacement reaction usually occurs in solution and one of the products, being insoluble, precipitate out (separates as a solid). Any reaction in which an insoluble solid (called precipitate) is formed that separates from the solution is called a precipitation reaction. The reaction in which acid or acidic oxide reacts with base or basic oxide to form salt and water is called neutralisation reaction.
For example, 2NaOH + H 2 SO 4 ⟶ Na 2 SO 4 + H 2 O
(i) When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through a blue solution of copper sulphate, a black precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained and the sulphuric acid so formed remains in the solution. The reaction is an example of a:
(b) displacement reaction
(ii) Which of the following is not a double displacement reaction?
(a) AgNO 3 (aq) + NaCl(aq) ⟶ AgCl(s) + NaNO 3 (aq)
(b) Zn(s) + H 2 SO 4 (aq) ⟶ ZnSO 4 (aq) + H 2 (g)
(c) CuSO 4 (aq) + H 2 S (aq) ⟶ CuS(s) + H 2 SO 4 (aq)
(d) Pb(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) ⟶ PbI 2 (s) + 2KNO 3 (aq)
(iii) Barium chloride on reaction with ammonium sulphate forms barium sulphate and ammonium chloride. Which of the following correctly represents the type of the reaction involved?
(I) Displacement reaction
(II) Precipitation reaction
(III) Combination reaction
(IV) Double displacement reaction
(b) (II) only
(c) (III) and (IV) only
(d) (II) and (IV) only
(iv) Identify A in the following reaction.
AlCl 3 (aq) + 3NH 4 OH(aq) ⟶ A + 3NH 4 Cl(aq)
(a) Al(OH) 3
(b) Al 2 O 3
(v) Consider the following reaction,
BaCl 2 + Na 2 SO 4 ⟶ BaSO 4 + 2NaCl
Identify the precipitate in the reaction.
(c) Na 2 SO 4
(i) (d) double displacement reaction
CuSO 4 + H 2 S ⟶ CuS + H 2 SO 4
Both CuSO 4 and H 2 S exchange their ions to give new compounds- CuS and H 2 SO 4 . Hence, this is a double displacement reaction.
(ii) (b) Zn(s) + H 2 SO 4 (aq) ⟶ ZnSO 4 (aq) + H 2 (g)
It is an example of single displacement reaction.
(iii) (d) (II) and (IV) only
BaCl 2 + (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ⟶ BaSO 4 ↓ + 2NH 4 Cl
(BaSO 4 : white ppt.)
It is a precipitation reaction as well as double displacement reaction.
(iv) (a) Al(OH) 3
AlCl 3 + 3NH 4 OH ⟶ Al(OH) 3 + 3NH 4 Cl
(v) (b) BaSO 4
BaCl 2 (aq) + Na 2 SO 4 (aq) ⟶ BaSO 4 (s) ↓ + 2NaCl(aq)
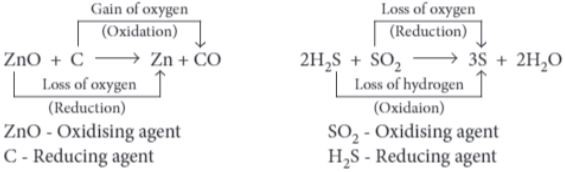
(i) A redox reaction is one in which:
(a) both the substances are reduced
(b) both the substances are oxidized
(c) an acid is neutralised by the base
(d) one substance is oxidised while the other is reduced.
(ii) In the reaction, H 2 S + Cl 2 ⟶ S + 2HCI
(a) H 2 S is the reducing agent.
(c) H 2 S is the oxidising agent.
(b) HCl is the oxidising agent.
(d) Cl 2 is the reducing agent.
(iii) Which of the following processes does not involve either oxidation or reduction?
(a) Formation of slaked lime from quick lime.
(b) Heating mercuric oxide.
(c) Formation of manganese chloride from manganese oxide (MnO 2 ).
(d) Formation of zinc from zinc blend.
(iv) Mg + CuO ⟶ MgO + Cu
Which of the following is wrong relating to the above reaction?
(a) CuO gets reduced.
(b) Mg gets oxidised.
(c) CuO gets oxidised.
(d) It is a redox reaction.
(v) Identify the correct oxidising agent and reducing agent in the following reaction.
Fe 2 O 3 + 2AI ⟶ 2Fe + Al 2 O 3
(a) Al - Oxidising agent, Fe 2 O 3 - Reducing agent
(b) Fe 2 O 3 - Oxidising agent, Al - Reducing agent
(c) Fe - Oxidising agent, Al 2 O 3 - Reducing agent
(b) Fe 2 O 3 - Oxidising agent, Al 2 O 3 - Reducing agent
(i) (d) one substance is oxidised while the other is reduced.
In a redox reaction, one reactant is reduced while other reactant is oxidised.
(ii) (a) H 2 S is the reducing agent.
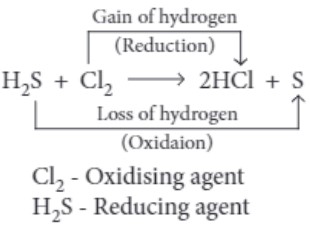
(iii) (a) Formation of slaked lime from quick lime

It is a decomposition reaction.
(iv) (c) CuO gets oxidised.
Addition of oxygen is called oxidation while the removal of oxygen is called reduction.
Thus, Mg gets oxidised and CuO gets reduced and it is a redox reaction.
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialisation Class 10 History
Related chapters.
- Acids, Bases and Salts
- Metals and Non-metals
- Carbon and its Compounds
- Periodic Classification of Elements (Not in Syllabus)
Related Questions
- NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science
- NCERT Revision Notes for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science
- VSAQ for Ch 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science NCERT
- Assertion and Reason for Ch 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science
Report a problem
- Question is incorrect
- Answer is Incorrect
- Spelling Mistakes
- Not explained in detail
- Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 10 Chemistry
- Important Questions Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations Important Questions with Answers
Class 10 chemistry important questions with answers are provided here for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations. These important questions are based on CBSE board curriculum and correspond to the most recent Class 10 chemistry syllabus. By practising these Class 10 important questions, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas covered in the chapter and prepare for the Class 10 Annual examinations.
Download Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Important Questions with Answers PDF by clicking on the button below. Download PDF
Recommended Videos
Chemical reactions and equations class 10 in one-shot.

Class 10 Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Important Questions with Answers
Multiple choice type questions.
Q1. Which of the following gases is used to store fat and oil-containing foods for a long time?
- Carbon dioxide
(3) Nitrogen gas is used to store fat and oil-containing foods for a long time.
Q2. The chemical reaction between Hydrogen sulphide and iodine to give Hydrogen iodide and sulphur is given below:
H 2 S + I 2 → 2HI + S.
The reducing and oxidising agents involved in this redox reaction are:
- Iodine and sulphur, respectively
- Iodine and hydrogen sulphide, respectively
- Sulphur and iodine, respectively
- Hydrogen sulphide and sulphur, respectively
(2) Iodine is an oxidising agent, and hydrogen sulphide is the reducing agent in the reaction mentioned above.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions and identify the type of reaction in each case.
(a )Nitrogen gas is treated with hydrogen gas in the presence of a catalyst at 773K to form ammonia gas.
(b )Sodium hydroxide solution is treated with acetic acid to form sodium acetate and water.
(c ) Ethanol is warmed with ethanoic acid to form ethyl acetate in the presence of concentrated H 2 SO 4 .
(d) Ethene is burnt in the presence of oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water and releases heat and light.
It is an addition reaction.
(b ) NaOH (aq) + CH 3 COOH (aq) → CH 3 COONa (aq) + H 2 O (l)
It is a double displacement or a neutralisation reaction.
It is a double displacement or an esterification reaction.
(d ) C 2 H 4 (g) + 3 O 2 (g) → 2 CO 2 (g) + 2 H 2 O (g) + Heat + light
It is a redox or a combustion reaction.
Q2. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions and identify the type of
reaction in each case.
(a ) In the thermite reaction, iron (III) oxide reacts with aluminium and gives molten iron and aluminium oxide.
(b ) Magnesium ribbon is burnt in an atmosphere of nitrogen gas to form solid magnesium nitride.
(c ) Chlorine gas is passed in an aqueous potassium iodide solution to form potassium
chloride solution and solid iodine.
(d ) Ethanol is burnt in the air to form carbon dioxide and water and releases heat.
(a ) Fe 2 O 3 (s) + 2 Al (s) → Al 2 O 3 (s) + 2 Fe (l) + Heat
It is a displacement or redox reaction.
(b ) 3 Mg (s) + N 2 (g) → Mg 3 N 2 (s)
It is a combination reaction.
(c ) 2 KI (aq) + Cl 2 (g) → 2 KCl (aq) + I 2 (s)
Q3. Complete the missing components / variables given as x and y in the following reactions
(a) Pb(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) + 2 KI (aq) → Pbl 2 (x) + 2 KNO 3 (y)
(b) Cu (s) + 2 AgNO 3 (aq) → Cu(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) + x(s)
(c) Zn (s) + H 2 SO 4 (aq) → ZnSO 4 (x) + H 2 (y)
(a) Pb(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) + 2 KI (aq) → Pbl 2 (s) + 2 KNO 3 (aq)
(b) Cu (s) + 2 AgNO 3 (aq) → Cu(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) + 2 Ag(s)
(c) Zn (s) + H 2 SO 4 (aq) → ZnSO 4 (aq) + H 2 (g)
Q4. Which among the following changes are exothermic or endothermic in nature?
(a) Decomposition of ferrous sulphate
(b) Dilution of sulphuric acid
(c) Dissolution of sodium hydroxide in water
(d) Dissolution of ammonium chloride in water
(a ) The decomposition of ferrous sulphate is an example of an endothermic reaction because heat is absorbed during this reaction.
(b ) The dilution of sulphuric acid is an example of an exothermic reaction because heat is released during this reaction.
(c ) The dissolution of sodium hydroxide in water is an example of an exothermic reaction because heat is released during this reaction.
(d ) The dissolution of ammonium chloride in water is an example of an endothermic reaction because heat is absorbed during this reaction.
Q5. Identify the reducing agent in the following reactions
(a ) 4 NH 3 + 5 O 2 → 4 NO + 6 H 2 O
(b ) H 2 O + F 2 → HF + HOF
(c ) Fe 2 O 3 + 3 CO → 2 Fe + 3 CO 2
(d ) 2 H 2 + O 2 → 2 H 2 O
(a ) Here, ammonia (NH 3 ) is the reducing agent.
(b ) Here, water (H 2 O) is the reducing agent.
(c ) Here, carbon monoxide (CO) is the reducing agent.
(d ) Here, hydrogen (H 2 ) is the reducing agent.
Q6. Identify the oxidising agent (oxidant) in the following reactions
(a ) Pb 3 O 4 + 8 HCI → 3 PbCl 2 + Cl 2 + 4 H 2 O
(b ) 2 Mg + O 2 → 2 MgO
(c ) CuSO 4 + Zn → Cu + ZnSO 4
(d ) V 2 O 5 + 5 Ca → 2 V + 5 CaO
(e ) 3 Fe + 4 H 2 O → Fe 3 O 4 + 4 H 2
(f ) CuO + H 2 → Cu + H 2 O
(a ) Pb 3 O 4 is the oxidising agent here. The oxidation state of Pb in Pb 3 O 4 reduces from + 6 to + 2 in PbCl 2. Thus it acts as an oxidising agent.
(b ) O 2 is the oxidising agent here. The oxidation state of oxygen in elemental form O 2 reduces from 0 to – 2 in MgO . Thus it acts as an oxidising agent.
(c ) CuSO 4 is the oxidising agent here. The oxidation state of Cu in CuSO 4 reduces from + 2 to 0 in Cu . Thus it acts as an oxidising agent.
(d ) V 2 O 5 is the oxidising agent here. The oxidation state of V in V 2 O 5 reduces from + 5 to 0 in V . Thus, it acts as an oxidising agent.
(e ) H 2 O is the oxidising agent here. The oxidation state of oxygen in H 2 O reduces from – 2 to – 3 in H 2 O . Thus it acts as an oxidising agent.
(f ) CuO is the oxidising agent here. The oxidation state of Cu in CuO reduces from + 2 to 0 in Cu . Thus, it acts as an oxidising agent.
Q7. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions
(a ) Sodium carbonate on reaction with hydrochloric acid in equal molar concentrations gives sodium chloride and sodium hydrogen carbonate.
(b ) Sodium hydrogen carbonate on reaction with hydrochloric acid gives sodium chloride, water and liberates carbon dioxide.
(c ) On treatment with potassium iodide, copper sulphate precipitates cuprous iodide (Cu 2 I 2 ), liberates iodine gas and forms potassium sulphate.
(a ) Na 2 CO 3 + HCl → NaCl + NaHCO 3
(b ) NaHCO 3 + HCl → NaCl + H 2 O + CO 2
(c ) 2 CuSO 4 + 4 KI → Cu 2 I 2 + 2 K 2 SO 4 + I 2
Q8. A solution of potassium chloride, when mixed with silver nitrate solution, an insoluble white substance is formed. Write the chemical reaction involved and also mention the type of the chemical reaction?
Chemical reaction: KCl + AgNO 3 → KNO 3 + AgCl
It is a double displacement reaction.
Q9. Ferrous sulphate decomposes with the evolution of a gas having a characteristic dour of burning sulphur. Write the chemical reaction involved and identify the type of reaction.
FeSO 4 (s) + Heat → Fe 2 O 3 (s) + SO 2 (g) + SO 3 (g)
It is a thermal decomposition reaction.
Q10. Why do fireflies glow at night?
Fireflies glow at night because of a chemical reaction involving light’s emission. Fireflies store a protein (luciferin) that combines with oxygen in the air to form a new substance (oxyluciferin) and the evolution of energy in light.
Q11. Grapes hanging on the plant do not ferment, but after being plucked from the plant can be
fermented. Under what conditions do these grapes ferment? Is it a chemical or a physical
When attached to the plants, Grapes are living, and therefore, their immune system prevents fermentation. The microbes can grow in the plucked grapes, which can be fermented under anaerobic conditions. This is a chemical change.
Q12. Which among the following are physical or chemical changes?
(a ) Evaporation of petrol
(b ) Burning of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG)
(c ) Heating of an iron rod to red hot.
(d ) Curdling of milk
(e ) Sublimation of solid ammonium chloride
(a ) Evaporation of petrol is a physical change as it only gets converted from one physical state to another.
(b ) Burning of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) is a chemical change as heating produces carbon dioxide and water.
(c ) The heating of an iron rod to red hot is a physical change as heating involves only temperature change.
(d ) The curdling of milk is a chemical change as it affects the chemical composition of the milk.
Q13. We made the following observations during the reaction of some metals with dilute hydrochloric acid.
(a) Silver metal does not show any change
(b) The temperature of the reaction mixture rises when aluminium (Al) is added.
(c) The sodium metal reaction is highly explosive.
(d) Some gas bubbles are seen when lead (Pb) is reacted with the acid.
Explain these observations giving suitable reasons.
(a ) Silver does not show any characteristics change because silver is less reactive than hydrogen. Thus, it cannot displace hydrogen from dilute hydrochloric acid.
(b ) The reaction between aluminium (Al) and hydrochloric acid is highly exothermic. Thus, the temperature of the reaction mixture rises.
(c ) Sodium is a highly reactive metal. It reacts with hydrochloric acid, vigorously forming hydrogen gas and a large amount of heat.
(d ) When lead reacts with hydrochloric acid, the gas bubbles observed are hydrogen gas.
Pb (s) + 2 HCl (aq) → PbCl 2 (s) + H 2 (g)
Q14. A substance X, an oxide of a group 2 element, is used intensively in the cement industry. This element is present in bones also. On treatment with water, it forms a solution which turns red litmus blue. Identify X and also write the chemical reactions involved.
Here, X is calcium oxide.
- Calcium oxide is used intensively in the cement industry.
- The element present in it (in bones also) is calcium.
- On treatment with water, calcium oxide forms a solution of calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH) 2 ], which is an alkali. Hence, it turns red litmus blue.
CaO (s) + H 2 O (l) → Ca(OH) 2 (aq) + Heat
Q15. Write a balanced chemical equation for each following reaction and classify
(a ) Lead acetate solution is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid to form lead chloride and acetic acid solution.
(b ) A piece of sodium metal is added to absolute ethanol to form sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas.
(c ) Iron (III) oxide on heating with carbon monoxide gas reacts to form solid iron and liberates carbon dioxide gas.
(d ) Hydrogen sulphide gas reacts with oxygen gas to form solid sulphur and liquid water
(a ) Pb(CH 3 COO) 2 + 2 HCl → PbCl 2 + 2 CH 3 COOH
(b ) 2 Na + 2 C 2 H 5 OH → 2 C 2 H 5 ONa+ H 2
It is a displacement or a redox reaction.
It is a redox reaction.
(d ) 2 H 2 S + O 2 → 2 S + 2 H 2 O
Q16. Why do we store silver chloride in dark coloured bottles?
We store silver chloride in the dark-coloured bottles because silver chloride decomposes into silver and chlorine gas in sunlight.
Q17. Balance the following chemical equations and identify the type of chemical reaction.
(a ) Mg (s) + Cl 2 (g) → MgCI 2 (s)
(b ) HgO (s) + Heat → Hg (l) + O 2 (g)
(c ) Na (s) + S (s) → Na 2 S (s)
(d ) TlCl 4 (l) + Mg (s) → Tl (s) + MgCl 2 (s)
(e ) CaO (s) + SiO 2 (s) → CaSiO 3 (s)
(f ) H 2 O 2 (l) + UV → H 2 O (l) + O 2 (g)
(b ) 2 HgO (s) + Heat → 2 Hg (l) + O 2 (g)
(c ) 2 Na (s) + S (s) → Na 2 S (s)
(d ) TlCl 4 (l) + 2 Mg (s) → Tl (s) + 2 MgCl 2 (s)
It is a displacement reaction.
(f ) 2 H 2 O 2 (l) + UV → 2 H 2 O (l) + O 2 (g)
It is a decomposition reaction.
Q18. A magnesium ribbon is burnt in oxygen to give a white compound X accompanied by light emission. If the burning ribbon is now placed in an atmosphere of nitrogen, it continues to burn and forms a compound Y.
(a) Write the chemical formulae of X and Y.
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation when X is dissolved in water.
Here, X is magnesium oxide, and Y is magnesium nitride.
(a ) The chemical formulae of X are MgO and Y is Mg 3 N 2 .
(b ) When X is dissolved in water following reaction occurs.
MgO + H 2 O → Mg(OH) 2
Q19. Zinc liberates hydrogen gas when reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid, whereas copper does not. Explain why?
Zinc is more reactive than copper as Zinc is placed above hydrogen, and copper is placed below hydrogen in the activity series of metals. Thus, zinc liberates hydrogen gas when reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid, whereas copper does not.
Q20. A silver article generally turns black when kept in the open for a few days. The article, when rubbed with toothpaste again, starts shining.
(a ) Why do silver articles turn black when kept in the open for a few days? Name the phenomenon involved.
(b ) Name the black substance formed and give its chemical formula.
(a ) The silver article turns black when kept in the air because the silver article reacts with sulphur compounds such as hydrogen sulphide (H 2 S) present in the air to form silver sulphide Ag 2 S. This phenomenon is called corrosion. It is also known as tarnishing of silver.
(b ) The black substance is silver sulphide. Its chemical formula is Ag 2 S.
Related Videos
Balancing of chemical equations.

Long Answer Type Questions
Q1. On heating blue coloured powder of copper (I) nitrate in a boiling tube, copper oxide
(black), oxygen gas, and a brown gas X is formed
(a) Write a balanced chemical equation of the reaction.
(b) Identity the brown gas X evolved.
(c) Identify the type of reaction.
(d) What could be the pH range of the aqueous solution of the gas X?
(a ) 2 CuNO 3 (s) + Heat → 2 CuO (s) + 4 NO 2 (g) + O 2 (g)
(b ) The brown gas is of nitrogen dioxide.
(c ) It is a thermal decomposition reaction.
(d ) NO 2 gas reacts with water to produce nitric acid. Thus, its pH range will be less than 7.
Q2. Give the characteristic tests for the following gases
The characteristics test for
(a ) CO 2 : CO 2 turns lime water milky due to the formation of insoluble calcium carbonate.
CO 2 + Ca(OH) 2 → CaCO 3 + H 2 O
(b ) SO 2 : SO 2 turns purple coloured acidic potassium permanganate solution colourless.
5 SO 2 + 2 KMnO 4 + 2 H 2 O → K 2 SO 4 + 2 MnSO 4 + 2 H 2 SO 4
(c ) O 2 : We can confirm the evolution of oxygen gas by bringing a burning candle near the mouth of the test tube containing the reaction mixture. The intensity of the flame increases because oxygen supports burning.
(d ) H 2 : Hydrogen (H 2 ) gas burns with a pop sound when a burning candle is brought near it.
Q3. What happens when a piece of
(a) Zinc metal is added to copper sulphate solution?
(b) Aluminium metal is added to dilute hydrochloric acid?
(c) Silver metal is added to copper sulphate solution?
Also, write the balanced chemical equation if the reaction occurs
(a ) Zinc metal reacts with copper sulphate solution and forms colourless zinc sulphate and reddish-brown copper metal.
Zn (s) + CuSO 4 (aq) → ZnSO 4 (aq) + Cu (s)
(b ) Aluminium metal reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form aluminium chloride and hydrogen gas.
2 Al (s) + 6 HCl (aq) → 2 AlCl 3 (aq) + 3 H 2 (g)
(c ) Silver is less reactive than copper. Hence, no reaction will occur.
Q4. When zinc granules are treated with a dilute solution of H 2 SO 4 , HCI, HNO 3 , NaCI and NaOH. Write the chemical equations if a reaction occurs.
- Zinc granules react with dilute sulphuric acid to form zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas.
Zn (s) + H 2 SO 4 (aq) → ZnSO 4 (aq) + H 2 (g)
- Zinc granules react with dilute hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.
Zn (s) + H 2 SO 4 (aq) → ZnCl 2 (aq) + H 2 (g)
- Zinc granules react with dilute nitric acid to form zinc nitrate, water and dinitrogen gas.
Zn (s) + H 2 SO 4 (aq) → Zn(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) + H 2 O (l) + N 2 O (g)
- Zinc does not react with sodium chloride
Zn (s) + NaCl → No Reaction.
- Zinc granules react with dilute sodium hydroxide to form zinc hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Zn (s) + NaOH (aq) → Zn(OH) 2 (aq) + Na (g)
Q5. A white precipitate is obtained when adding a drop of barium chloride solution to an aqueous sodium sulphite solution.
(a ) Write a balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved
(b ) What other name can be given to this precipitation reaction?
(c ) On adding dilute hydrochloric acid to the reaction mixture, white residue disappears. Why?
(a ) BaCl 2 + Na 2 SO 3 ⟶ BaSO 3 + 2 NaCl
(b ) It can be assigned as a double displacement reaction.
(c ) On adding dilute hydrochloric acid to the reaction mixture, white residue disappears due to the formation of barium chloride.
BaSO 3 + 2 HCl ⟶ BaCl 2 + SO 2 + H 2 O
Q6. You are provided with two containers made up of copper and aluminium. You are also
provided with dilute HCI, HNO 3 , ZnCl 2 and H 2 O solutions. In which of the above
containers we can keep these solutions?
The solution of dilute HCI, HNO 3 , ZnCl 2 and H 2 O can be kept in a container made of copper since copper is a less reactive metal and is placed below the hydrogen in the reactivity series. Hence it does not react with HCI, HNO 3 , ZnCl 2 and H 2 O. At the same time, aluminium is a highly reactive metal and can react with these solutions. Thus container made of copper is suitable to keep the given solutions.
Chemical Reactions and Equations – Previous Year Questions

Oxidation & Reduction – Concept + Quiz

| CHEMISTRY Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Class 10th Science - Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 10 Science Subject - Chemical Reactions and Equations, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Chemical reactions and equations case study questions with answer key.
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Chemical equation is a method of representing a chemical reaction with the help of symbols and formulae of the substances involved in it. In a chemical equation, the substances which combine or react are called reactants and new substances produced are called products. A chemical equation is a short hand method of representing a chemical reaction. A balanced chemical equation has equal number of atoms of different elements in the reactants and products side. An unbalanced chemical equation has unequal number of atoms of one or more elements in reactants and products. Formulae of elements and compounds are not changed to balance an equation. (i) Consider the following reaction: pMg 3 N 2 + qH 2 O ⇾ rMg(OH) 2 + sNH 3 When the equation is balanced, the coefficients p, q, r, s respectively are
(ii) Which of the following information is not conveyed by a balanced chemical equation?
(iii) The balancing of chemical equations is in accordance with
(iv) Which of the following chemical equations is an unbalanced one?
(v) Which of the following statements is/are correct?
In decomposition reactions, a single reactant breaks down to form two or more products. A decomposition reaction is opposite to combination reaction. Thermal decomposition reactions use the energy in form of heat for the decomposition of reactants. Electrolytic decomposition reactions involve the use of electrical energy for the decomposition of reactant molecules. Photolysis or photochemical decomposition involves the use of light energy for the purpose of decomposition. (i) Which of the following reactions is a decomposition reaction?
\({ (ii) \ } 2 \mathrm{~Pb}\left(\mathrm{NO}_{3}\right)_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{PbO}+n A+\mathrm{O}_{2}\) What is nA in the given reaction?
(iii) Amino acid is formed by the decomposition of which component of our diet?
(iv) Silver chloride on exposure to sunlight for a long duration turns grey due to (I) the formation of silver by decomposition of silver chloride (II) sublimation of silver chloride (III) decomposition of chlorine gas from silver chloride (IV) oxidation of silver chloride The correct statement(s) is/are
(v) What type of chemical reaction takes place when electricity is passed through water?
Redox reactions are those reactions in which oxidation and reduction occur Simultaneously. A redox reaction is made up of two half reactions. In the first half reaction, oxidation takes place and in second half reaction, reduction occurs. Oxidation is a process in which a substance loses electrons and in reduction, a substance gains electrons. The substance which gains electrons is reduced and acts as an oxidising agent. On the other hand, a substance which loses electrons is oxidised and acts as a reducing agent. (i) Which of the following is a redox reaction?
| \({ (a) \ } \mathrm{CaCO}_{3} \rightarrow \mathrm{CaO}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}\) | \(\text { (b) } \mathrm{H}_{2}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{HCl}\) |
| \({ (c) \ } \mathrm{CaO}+2 \mathrm{HCl} \rightarrow \mathrm{CaCl}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) | \(\text { (d) } \mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{HCl} \rightarrow \mathrm{NaCl}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) |
(ii) Identify the reaction in which H2 02 is acting as a reducing agent.
| \(\text { (a) } \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) | \(\text { (b) } 2 \mathrm{Hl}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{I}_{2}\) |
| \(\text { (c) } \mathrm{Cl}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{HCl}+\mathrm{O}_{2}\) | \(\text { (d) } 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{2}+2 \mathrm{HCl}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{3}+2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) |
(iii) For the following reactions, identify the one in which H 2 S acts as a reducing agent.
| \(\text { (a) } \mathrm{CuSO}_{4}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CuS}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}\) | \(\text { (b) } \mathrm{Cd}\left(\mathrm{NO}_{3}\right)_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CdS}+2 \mathrm{HNO}_{3}\) |
| \(\text { (c) } 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{2}+2 \mathrm{HCl}+\mathrm{S}\) | (d) None of these |
(iv) For the following reaction, identify the correct statement. \(\mathrm{ZnO}+\mathrm{CO} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Zn}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}\)
| is being oxidised | |
(v) In the following reaction, which substance is reduced? \(\mathrm{PbS}+4 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow \mathrm{PbSO}_{4}+4 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\)
| O | O |
In a balanced chemical reaction, equal number of atoms are present on both sides of reaction. A balanced chemical reaction is based on law of conservation of mass which means that total mass of reactants and products participating in a reaction must be equal. For example, a balanced chemical equation of burning of magnesium in oxygen to form magnesium oxide is written as : \(2 \mathrm{Mg}+\mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{MgO}\) The mass of reactants (2 x 24 + 32 = 80) is equal to the mass of products [2 x (24 + 16) = 80] (i) In a reaction, 35 g of reactant, PQ breaks down into 20 g of product, P and an unknown amount of product, Q. Using the law of conservation of mass, weight of products, Q will be
| ( |
(ii) When solid mercury (II) oxide is heated, liquid mercury and oxygen gas are produced. Which of the following statements is true regarding the balanced chemical equation for this process? (a) 1 mole of mercury (II) oxide produces two moles of mercury and one mole of oxygen gas (b) 2 moles of mercury (II) oxide produce one mole of mercury and one mole of oxygen gas (c) 1 mole of mercury (II) oxide produces half mole of mercury and half mole of oxygen gas (d) 2 moles of mercury (II) oxide produce 2 moles of mercury and one mole of oxygen gas (iii) Which of the following laws is satisfied by a balanced chemical equation?
(iv) In the given chemical reaction \(\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{6(l)}+15 \mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \longrightarrow m \mathrm{CO}_{2(g)}+n \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(l)}\) The values of m and n are respectively
| ( |
(v) Sulphur dioxide reacts with oxygen to form sulphur trioxide. What would be the molar ratio of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide?
In a chemical reaction, reactants are converted into products. The conversion of reactants into products in a chemical reaction is often accompanied by some features which can be observed easily. These easily observed features which take place as a result of chemical reaction are known as characteristics of chemicals reactions. Some important characteristics of chemical reactions are: (I) Evolution of heat (II) Formation of precipitate (III) Change in colour (IV) Change in temperature (V) Change in state Anyone of these general characteristics can tell us whether a chemical reaction has taken place or not. (i) Reaction of magnesium with air is a/an
(ii) In the following reaction \(\mathrm{Ca}_{(a q)}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{OH}_{(a q)}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_{2(s)}\) precipitate of calcium hydroxide will be of
(iii) In the given reaction, \(\mathrm{S}_{(s)}+\mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{SO}_{2}\) the physical state of SO 2 is
(iv) Which one of the following processes involve chemical reactions?
(v) In which of the following reactions, high amount of heat energy will be evolved?
A reaction in which two or more reactants combine to form a single product is called a combination reaction. For example, calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to form calcium hydroxide. The reaction is highly exothermic in nature, as lots of heat is produced during the reaction. \(\mathrm{CaO}_{(s)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(l)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_{2(a q)}+\text { Heat }\) Calcium oxide Water Calcium hydroxide Solution of Ca(OH) 2 is used for white wash the walls. Calcium hydroxide reacts slowly with carbon dioxide in air to form a thin layer of calcium carbonate on the wall which gives a shiny appearance to wall. Calcium carbonate will form after two or three days of white wash. (i) What is the chemical name of quick lime?
(ii) When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water,
(iv) Quick lime combines Vigorously with water to form (A) which reacts slowly with the carbon dioxide in air to form (B) Identify the compounds(A) and (B)
(v) Among the following, the endothermic reaction is
Reactions in which one element takes place of another element in a compound, are known as displacement reactions. In general, more reactive elements displaces a less reactive element from its compound. In all single displacement reactions, only one element displaces another element from its compound. The single displacement reactions are, however, written as just displacement reactions. The displacement reaction between iron (III) oxide and powdered aluminium produces so much heat that iron metal obtained is in molten form. (i) Copper displaces which of the following metals from its salt solution?
| ( |
(ii) When zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric acid, the gas evolved is
(iv) Which of the following reactions is a displacement reaction?
(v) When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to granulated zinc placed in a test tube, the observation made is
Those reactions in which two compounds react by an exchange of ions to form two new compounds are called double displacement reactions. A double displacement reaction usually occurs in solution and one of the products, being insoluble, precipitate out (separates as a solid). Any reaction in which an insoluble solid (called precipitate) is formed that separates from the solution is called a precipitation reaction. The reaction in which acid or acidic oxide reacts with base or basic oxide to form salt and water is called neutralisation reaction. For example, \(2 \mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) (i) When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through a blue solution of copper sulphate, a black precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained and the sulphuric acid so formed remains in the solution. The reaction is an example of a
(ii) Which of the following is not a double displacement reaction?
| \(\text { (a) } \mathrm{AgNO}_{3(a q)}+\mathrm{NaCl}_{(a q)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{AgCl}_{(s)}+\mathrm{NaNO}_{3(a q)}\) | \(\text { (b) } \mathrm{Zn}_{(s)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4(a q)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{ZnSO}_{4(a q)}+\mathrm{H}_{2(g)}\) |
| \(\text { (c) } \mathrm{CuSO}_{4(a q)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S}_{(a q)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CuS}_{(s)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4(a q)}\) | \(\text { (d) } \mathrm{Pb}\left(\mathrm{NO}_{3}\right)_{2(a q)}+2 \mathrm{KI}_{(a q)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{PbI}_{2(s)}+2 \mathrm{KNO}_{3(a q)}\) |
(iii) Barium chloride on reaction with ammonium sulphate forms barium sulphate and ammonium chloride. Which of the following correctly represents the type of the reaction involved? (I) Displacement reaction (II) Precipitation reaction (III) Combination reaction (IV) Double displacement reaction
(iv) Identify A in the following reaction. \(\mathrm{AlCl}_{3(a q)}+3 \mathrm{NH}_{4} \mathrm{OH}_{(a q)} \longrightarrow A+3 \mathrm{NH}_{4} \mathrm{Cl}_{(a q)}\)
| O |
(v) Consider the following reaction, \(\mathrm{BaCl}_{2}+\mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4} \longrightarrow \mathrm{BaSO}_{4}+2 \mathrm{NaCl}\) identify the precipitate in the reaction,
(ii) In the reaction, \(\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2} \longrightarrow \mathrm{S}+2 \mathrm{HCl}\)
| S is the reducing agent. | |
| S is the oxidising agent. | is the reducing agent. |
(iii) Which ofthe following processes does not involve either oxidation or reduction?
| ). |
\(\text { (iv) } \mathrm{Mg}+\mathrm{CuO} \longrightarrow \mathrm{MgO}+\mathrm{Cu}\)
Which of the following is wrong relating to the above reaction?
| . |
(v) Identify the correct oxidising agent and reducing agent in the following reaction. \(\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}+2 \mathrm{Al} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{Fe}+\mathrm{Al}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}\)
| O Reducing agent | - Oxidising agent, AI- Reducing agent |
| O - Reducing agent | - Oxidising agent, Al O - Reducing agent |
Oxidation has damaging effect on metals as well as on food. The damaging effect of oxidation on metal is studied as corrosion and that on food is studied as rancidity. The phenomenon due to which metals are slowly eaten away by the reaction of air, water and chemicals present in atmosphere, is called corrosion. For example, iron articles are shiny when new, but get coated with a reddish brown powder when left for sometime. This process is known as rusting of iron. Rancidity is the process of slow oxidation of oil and fat (which are volatile in nature) present in the food materials resulting in the change of smell and taste in them. (i) Rancidity can be prevented by
(ii) Combination of phosphorus and oxygen is an example of
(iii) A science teacher wrote the following statements about rancidity : (I) When fats and oils are reduced, they become rancid. (II) In chips packet, rancidity is prevented by oxygen. (III) Rancidity is prevented by adding antioxidants. Select the correct option.
(iv) Two statements are given below regarding rusting of iron. (I) The rusting of iron is a redox reaction and reaction occurs as, \(4 \mathrm{Fe}+3 \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 4 \mathrm{Fe}^{3+}+6 \mathrm{O}^{2-}\) (II) The metallic iron is oxidised to \(\mathrm{Fe}^{2+} \text { and } \mathrm{O}_{2} \text { is reduced to } \mathrm{O}^{2-}\) Select the correct statement(s).
(v) Which of the following measures can be adopted to prevent or slow down rancidity? (I) Food materials should be packed in air tight container. (II) Food should be refrigerated. (III) Food materials and cooked food should be kept away from direct sunlight
Chemical reaction, a process in which one or more substances, the reactants, are converted to one or more different substances, the products. Substances are either chemical elements or compounds. A chemical reaction rearranges the constituent atoms of the reactants to create different substances as products. Study this table related to the different types of reactions / processes and answer the questions that follow.
| i | Combustion | \(\text { Magnesium }+\text { Oxygen } \stackrel{\text { heat }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Magnesium dioxide }\) |
| ii | Photosynsthesis | \(\text { Carbon dioxide }+\text { Water } \frac{\text { sunlight }}{\text { chlorophyll }} \longrightarrow \text { Glucose }+\text { Oxygen }+\text { Water }\) |
| iii | Combination | \(\text { Iron }+\text { Sulphur } \stackrel{\text { heat }}{\rightarrow} \text { Iron sulphide }\) |
| iv. | Photodecomposition | \(\text { Silver bromide } \stackrel{\text { light }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Silver }+\text { Bromine }\) |
(i) The reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a single substance under suitable conditions is (a) combination reaction (b) combustion (c) decomposition reaction (d) photosynthesis (ii) Which of the following is essential for photosynthesis? (a) Sunlight (b) Chlorophyll (c) Glucose (d) Both 'a' and 'b’ Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesis nutrients from carbon dioxide and water. (iii) When a chemical compound decomposes on absorbing light and energy, then the reaction which takes place is known as (a) photosynthesis (b) photodecomposition (c) combination (d) thermal decomposition. A photodecomposition is a chemical reaction in which an inorganic chemical (or an organic chemical) is broken down by photons and is the interaction of one or more photons with one target molecule. (iv) Which of the following reactions is an example of combustion reaction ? \((a) \mathrm{C}_{(s)}+\mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CO}_{2(g)}\\ (b) \mathrm{Zn}_{(s)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4(a q)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{ZnSO}_{4(a q)}+\mathrm{H}_{2(g)}\\ (c) \mathrm{Zn}_{(s)}+2 \mathrm{HCl}_{(a q)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{ZnCl}_{2(a q)}+\mathrm{H}_{2(g)}\\ (d) 3 \mathrm{Mg}_{(s)}+\mathrm{N}_{2(g)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Mg}_{3} \mathrm{~N}_{2(s)}\) A combustion reaction is a reaction in which a substance reacts with oxygen gas, releasing energy in the form of light and heat. (v) Which of the following is an example of combination reaction? \((a) \mathrm{H}_{2(g)}+\mathrm{Cl}_{2(g)} \stackrel{\text { light }}{\longrightarrow} 2 \mathrm{HCl}_{(g)}\\ (b) \mathrm{Fe}_{(s)}+S_{(s)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{FeS}_{(g)}\\ (c) 2 \mathrm{H}_{2(g)}+\mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(l)}\\ (d) All \ of \ them\) A combination reaction (also known as a synthesis reaction) is a reaction where two or more elements or compounds (reactants) combine to form a single compound (product).
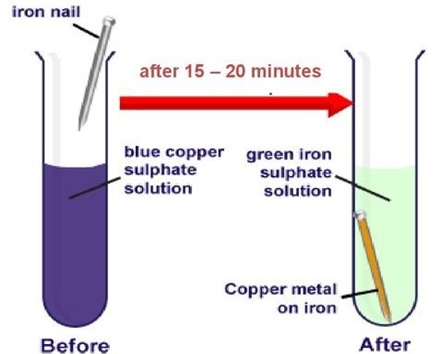
*****************************************
Related 10th standard cbse science materials, other 10th standard cbse materials.

CBSE 10th Maths Probability Chapter Case Study Question with Answers
Cbse 10th maths statistics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths surface areas and volumes chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths areas related to circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths some applications of trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths introduction to trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths coordinate geometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths triangles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths arithmetic progressions chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th maths quadratic equations chapter case study questions with answers.

CBSE 10th Social Science The Making Of A Global World Chapter Case Study Question with Answers
Cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths pair of linear equation in two variables chapter case study question with answers, tamilnadu stateboard 10th standard cbse study materials.

Tamilnadu Stateboard 10th Standard CBSE Subjects

Stateboard Tamil Nadu
Neet study materials.
- JEE Study Materials
- Banking first yr Study Materials
- TNPSC Study Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Study Materials
- 5th Standard Study Materials
- 1st Standard - CVBHSS Study Materials
- 2nd Standard - CVBHSS Study Materials
- 3rd Standard - CVBHSS Study Materials
- 4th Standard - CVBHSS Study Materials
- 5th Standard - CVBHSS Study Materials
- 12th Standard Study Materials
- 11th Standard Study Materials
- 10th Standard Study Materials
- 9th Standard Study Materials
- 8th Standard Study Materials
- 7th Standard Study Materials
- 6th Standard Study Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Study Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Study Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Study Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Study Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Study Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Study Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Study Materials
- NEET Syllabus
- NEET Exam Pattern
Chemical Communications
Facile synthesis of cu-based catalysts from cu 3 si and their catalysis properties study †.

* Corresponding authors
a State Key Laboratory of Organic Electronics and Information Displays & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 9 Wenyuan Road, Nanjing 210023, China E-mail: [email protected]
b Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (KLOFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Jiangsu National Synergistic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials (SICAM), Nanjing Tech University (NanjingTech), 30 South Puzhu Road, Nanjing 211816, China
Supported copper species are well-known for their remarkable catalytic properties across numerous reactions. However, the current preparation methods pose challenges for large-scale production. In this study, we present a cost-effective method for the facile preparation of a series of copper–silicon composites using Cu 3 Si@Si particles as precursors. We evaluate the catalytic properties of these composites in the conversion of 4-nitrophenol to 4-amionphenol. Notably, the Cu@SiO x /Si composite exhibits exceptional catalytic performance, attributed to the synergy effect between Cu and Si, and the formation of a metastable Si–H 2 complex that enhances the reaction kinetics. This research introduces a novel approach for creating efficient and stable catalysts for hydrogenation reactions.

Supplementary files
- Supplementary information PDF (840K)
Article information
Download citation, permissions.
Facile synthesis of Cu-based catalysts from Cu 3 Si and their catalysis properties study
Y. Li, X. Liu, G. Zu, Z. Yang, X. Huang and S. Li, Chem. Commun. , 2024, Advance Article , DOI: 10.1039/D4CC01870B
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements
Hydrogeochemical assessment and modeling of groundwater processes and pollution: a case study of the Grombalia aquifer in Northeast Tunisia
- khezami, Farah
- Khiari, Nouha
- Drouiche, Abdelmalek
- Chkirbene, Anis
- Zahi, Faouzi
- Debieche, Taha-Hocine
- Khadhar, Samia
Groundwater in the Grombalia region often represents the main source of water, which is intensively exploited to meet the needs of human consumption and irrigation, threatening its quality. This study aims to assess the quality of groundwater in the Grombalia shallow aquifer, and to identify the hydrogeochemical processes controlling its mineralization, based on chemical analysis results of thirteen (13) groundwater samples taken in October 2020. The results show that the chemical element content of most groundwater samples exceeds WHO standards. Based on the abundance of cations and anions, the groundwater is characterized by a single hydrochemical facies (Cl-Ca-Mg), revealing the combination of natural and anthropogenic processes governing water chemistry in the study area. Multivariate statistical analysis, including principal component analysis, Pearson correlation and hierarchical cluster analysis, revealed the main processes controlling groundwater chemistry are agricultural activities and dissolution of evaporitic formations. Bivariate diagrams show that cation exchange reactions leading to the adsorption of Na + into clay minerals and the simultaneous release of Ca 2+ ions, as well as the dissolution of silicates, are also processes that influence groundwater chemistry. Finally, calculation of the nitrate pollution index (NPI) reveals that most groundwater samples are very heavily polluted (NPI > 3), which may be linked to anthropogenic activities, such as the return of irrigation water, as well as untreated urban waste. The suitability of groundwater for drinking was determined by using WHO guidelines and Water Quality Index (WQI) revealed the Grombalia aquifer have poor to very poorly quality water for drinking purposes.
- Hydrogeochemistry;
- Groundwater;
- Factorial analysis;
- Water-rock interactions;
- Nitrate contamination;

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

Case Study: Battery Types
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 286
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Ranging from the very crude to the highly sophisticated, batteries come in a plethora of variety. Batteries in short are electrochemical cells that produce a current of electricity via chemical reactions. More specifically, batteries produce electrical energy from oxidation-reduction reactions. A collection of electrochemical cells wired in series is properly called a battery. A flashlight battery is really a single electrochemical cell, while a car battery is really a battery since it is three electrochemical cells in series.
Introduction
About 2000 years later the Voltaic Pile, a stack of individual cells of zinc and copper disks immersed in sulfuric acid, was created by the Italian Count Volta and effectively replaced the use of the Leyden Jar, an instrument that stored static electricity for future use. Volta's battery is considered the first electrochemical cell and the reaction for which is as follows:
oxidation half-reaction : \(Zn \rightarrow Zn^{2+} + 2e^-\)
reduction half-reaction : \(2H^+ + 2e^- \rightarrow H_2\)
Because zinc is higher in the electrochemical series, the zinc anode reacts with sulfate anions and is oxidized whilst protons are reduced to hydrogen gas. The copper cathode remains unchanged and acts only as electrode for the chemical reaction. Because the Voltaic pile was unafe to use and the cell power diminished over time, it was abandoned.
Electrochemical cells typically consist of an anode (the negative electrode where oxidation occurs), a cathode (the positive electrode where reduction occurs), and an electrolyte (the medium conducting anions and cations within a reaction) all contained within a cell. Electrons flow in a closed circuit from the anode to the cathode. Depending on the configuration of the cell and the electrolyte used, a salt bridge may be necessary to conduct ions from one half cell to another as an electric charge is created when electrons move from electrode to another. The difference created would keep electrons from flowing any further. Because a salt bridge permits the flux of ions, a balance in charge is kept between the half cells whilst keeping them separate.
Types of Batteries
The two main categories of batteries are primary and secondary. Essentially, primary cells are batteries which cannot be recharged while secondary cells are rechargeable. The distinction begs the question as to why primary cells are still in use today, and the reason being is that primary cells have lower self-discharge rates meaning that they can be stored for longer periods of time than rechargeable batteries and maintain nearly the same capacity as before. Reserve and backup batteries present a unique example of this advantage of primary cells. In reserve, or stand-by, batteries components of the battery containing active chemicals are separated until the battery is needed, thus greatly decreasing self-discharge. An excellent example is the Water-Activated Battery. As opposed to inert reserve batteries, backup batteries are already activated and functional but not producing any current until the main power supply fails.
Biobatteries
Devices that generate electric energy via the digestion of carbohydrates, fats, and protiens by enzymes. The most common biobatteries are the lemon or potato battery and the frog or ox-head battery better described as a "muscular pile". In a lemon cell, the energy for the battery is not produced by the lemon but by the metal electrodes. Usually zinc and copper electrodes are inserted into a lemon (the electrolyte being citric acid) and connected by a circuit. The zinc is oxidized in the lemon in order to reach a preferred lower energy level and the electrons discharged provide the energy. Using zinc and copper electrodes, a lemon can produce about 0.9 Volts.
While not technically a biobattery, an Earth battery is comprised of two different electrodes which are either buried underground or immersed in natural bodies of water which tap into Telluric currents to produce electric energy.
Dry-Cell Batteries
During the 1860s, a French man named George Lelanche developed the Lelanche cell also known today as the dry-cell battery. A dry-cell battery is a battery with a paste electrolyte (as opposed to a wet-cell battery with a liquid electrolyte) in the the middle of its cylinder and attached are metal electrodes. A dry-cell battery is a primary cell that cannot be reused. In order to function, each dry-cell battery has a cathode and an anode. Some examples of dry-cell batteries used in everyday objects today are remote controls, clocks, and calculators.

Figure: Modern dry cell batteries. from Wikipedia
Types of dry-cell batteries are zinc-carbon batteries, alkaline-cell batteries, and mercury batteries. Before zinc-carbon batteries were used, mercury batteries were the main resource. It was not until mercury was known to become harmful that zinc-carbon batteries replaced it. Batteries may produce the following potential problems or hazards:
- Pollute the lakes and streams as the metals vaporize into the air when burned.
- Contribute to heavy metals that potentially may leach from solid waste landfills.
- Expose the environment and water to lead and acid.
- Contain strong corrosive acids.
- May cause burns or danger to eyes and skin.
Dry-cell batteries are the most common battery type used today. Essentially, the battery is comprised of a metal electrode (or graphite rod) surrounded by a moist electrolyte paste that is enclosed in a metal cylinder. 1.5 volts is the most commonly used voltage for dry-cell batteries. The sizes of dry-cell batteries vary, however, it does not change the voltage of the battery.
Zinc-carbon cells
Zinc-carbon cells were the first really portable energy source. These cells have a short lifetime and the zinc casings become porous as the zinc is converted to zinc chloride. The substances in the cell that leak out are corrosive to metal and can terminally destroy electronic equipment or flashlights. Zinc-carbon cells produce 1.5 volts.
For a dry-cell battery to operate, oxidation will occur from the zinc anode and reduction will take place in the cathode. The most common type of cathode is a carbon graphite. Once reactants have been turned into products, the dry-cell battery will work to produce electricity. For example, in a dry-cell battery, once \(Zn^{2+}\) has been oxidized to react with \(NH_3\), it will produce chloride salt to insure that too much \(NH_3\) will not block the current of the cathode.
\[Zn^{2+}_{(aq)} + 2NH_{3\;(g)} + 2Cl^-_{(aq)} \rightarrow [Zn(NH_3)_2]Cl_{2\; (s)} \nonumber \]
How does the reaction work? While the zinc anode is being oxidized, it is producing electrons that will be captured by reducing Maganese from an oxidation state of +4 to a +3.
- Reduction of Maganese: \(2MnO_{2\;(s)} + H_2O_{(l)} + 2e^- \rightarrow Mn_2O_{2\; (s)} + 2OH^-_{ (aq)}\)
The electrons produced by Zinc will then connect to the cathode to produce it's product.
- Oxidization of Zinc : \(Zn_{(s)} \rightarrow Zn^{2+}_{(aq)} +2e^-\)
Alkaline cells
Recently, the most popular dry-cell battery to be used has been the alkaline-cell battery. In the zinc-carbon battery shown above, the zinc is not easily dissolved in basic solutions. Though it is fairly cheap to construct a zinc-carbon battery, the alkaline-cell battery is favored because it can last much longer. Instead of using \(NH_4Cl\) as an electrolyte, the alkaline-cell battery will use \(NaOH\) or \(KOH\) instead. The reaction will occur the same where zinc is oxidized and it will react with \(OH^-\) instead.
\[Zn^{2+}_{(aq)} + 2OH^-_{(aq)} \rightarrow Zn(OH)_{2\; (s)} \nonumber \]
Once the chemicals in the dry-cell battery can no longer react together, the dry-cell battery is dead and cannot be recharged. Alkaline electrochemical cells have a much longer lifetime but the zinc case still becomes porous as the cell is discharged and the substances inside the cell are still corrosive. Alkaline cells produce 1.54 volts.
Mercury cells
Mercury batteries are small, circular metal batteries that were used in watches. Mercury cells offer a long lifetime in a small size but the mercury produced as the cell discharges is very toxic. This mercury is released into the atmosphere if the cells are incinerated in the trash. About 90% of the 1.4 million pounds of mercury in our garbage comes from mercury cells. Mercury cells only produce 1.3 Volts.
\[HgO + Zn + H_2O \rightarrow Hg + Zn(OH)_2 \nonumber \]
Mercury batteries utilize either pure mercuric oxide or a mix of mercuric oxide with manganese dioxide as the cathode. The anode is made with zinc and is separated from the cathode with a piece of paper or other porous substance that has been soaked in the electrolyte (which is generally either sodium or potassium oxide).
In the past, these batteries were widely used because of their long shelf life of about 10 years, and also because of their stable, steady voltage output. Also, they had the highest capacity per size. They were popular for use in button-type battery applications, such as watches or hearing aids. However, the environmental impact for the amount of mercury present in the batteries became an issue, and the mercury batteries were discontinued from public sale.
lead-acid batteries
The lead-acid battery used in cars and trucks consists of six electrochemical cells joined in series. Each cell in a lead-acid battery produces 2 volts. The electrodes are composed of lead and are immersed in sulfuric acid. The negative electrodes are spongy lead metal and the positive electrodes are lead impregnated with lead oxide. As the battery is discharged, metallic lead is oxidized to lead sulfate at the negative electrodes and lead oxide is reduced to lead sulfate at the positive electrodes. When a lead-acid battery is recharged by an alternator, electrons are forced to flow in the opposite direction which reverses the reaction.
\[Pb + PbO_2 + 2 H_2SO_4 \rightarrow 2 PbSO_4 + 2 H_2O \nonumber \]
Nickel-cadmium cells
Nickel-cadmium cells can also be regenerated by reversing the flow of the electrons in a battery charger. The cadmium is oxidized in these cells to cadmium hydroxide and the nickel is reduced. Nickel-cadmium cells generate 1.46 Volts.
\[Cd + NiO_2 + 2 H_2O \rightarrow Cd(OH)_2 + Ni(OH)_2 \nonumber \]
A Nickel-metal Hyride battery is a secondary cell very similar to the nickel-cadmium cell except that it uses a hydrogen-absorbing alloy in place of cadmium. The Nickel-metal Hyride battery has 2-3 times the capacity of a nickel-cadmium cell.
- Why are lead-acid batteries used in cars?
- What is the specific, more scientific name for a battery?
- how do batteries generally work?
- What kind of reaction occurs at the Cathode?
- What kind of reaction occurs at the anode?
- What type of battery can be recharged? Which cannot?
- If mercury batteries are so long lasting and efficient, then why are they not used anymore?
- What is the purpose of a salt bridge?
- Lead acid batteries produce two volts each and last a relatively long time. This type of battery is good for cars because of its ability to be recharged by the alternator. The batteries are connected in a series to produce the necessary voltage. They are larger than most other batteries, but work well for large energy-consuming machinery such as vehicles.
- Batteries are actually called electrochemical cells.
- Batteries work through a series of oxidation-reduction reactions that produces a waste product and a known amount of energy.
- Reduction reaction.
- Oxidation reaction.
- Secondary batteries can be recharged. Primary batteries cannot be recharged because the reaction is not reversible.
- Mercury batteries are often disposed incorrectly, which causes large amounts mercury to seep into the environment. Most or the mercury present in our environment today is the result of improper mercury battery disposal.
- Salt bridges conduct ions from one half cell to another to balance changing charges that could cause a halt to the flow of electrons in an electrochemical cell.
Contributors and Attributions
- Richard Banks (Boise State University)
- Erica Chen (UCD)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Questions With Solution 2021. 10th Standard CBSE. Reg.No. : Science. Time : 00:30:00 Hrs. Total Marks : 20. Chemical equation is a method of representing a chemical reaction with the help of symbols and formulae of the substances involved in it.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study 1. A solution of slaked lime produced by the reaction is used for white washing walls. Calcium hydroxide reacts slowly with the carbon dioxide in air to form a thin layer of calcium carbonate on the walls. Calcium carbonate is formed after two to three days ...
Case Study/Passage Based Questions on Chemical Reactions and Equations. Case Study/Passage Based Questions. Question 1: Corrosion is the phenomenon of deterioration of surface of metal in presence of air and moisture. It is a natural process and in the presence of a moist atmosphere, chemically active metals get corroded. This is an oxidation ...
Case Study Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations. Question 1: A chemical reaction is a representation of chemical change in terms of symbols and formulae of reactants and products. There are various types of chemical reactions like combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, oxidation, and reduction reactions.
Students who are studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to get the knowledge about the Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Based Questions. Case based questions are generally based on the seen passages from the chapter Chemical Reactions and Equations. Through solving the case based questions, students can understand each and every concept.
Catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower activation energy. Catalysts can be homogenous (in the same phase as the reactants) or heterogeneous (a different phase than the reactants). 7.5: Case Study- Balancing Acts in Pharmacological Synthesis; 7.E: Exercises
Case Study 3: Chemical reactions and equations are fundamental concepts in chemistry that help us understand the transformation of substances. A chemical reaction involves the rearrangement of atoms to form new substances with different properties. In a chemical equation, the reactants are written on the left side, and the products are written on the right side, separated by an arrow.
General, Organic, and Biochemistry with Problems, Case Studies, and Activities 7: Chemical Equations and Reactions Expand/collapse global location 7: Chemical Equations and Reactions Last updated; Save as PDF ... 7.1: Balancing Chemical Equations; 7.2: Energy in chemical reactions; 7.3: Equilibrium; 7.4: Catalysis;
Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations. The reaction between MnO2 with HCl is depicted in the following diagram. It was observed that a gas with bleaching abilities was released . (b) MnO2 is getting oxidized whereas HCl is getting reduced. (c) MnO2 and HCl both are getting reduced.
🟢Chemical Reaction and Equation | Case Based Questions - CBSE 10 | Anubha Ma'am @VedantuClass910 _____👉🏻 A...
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Questions 2021. A reaction in which two or more reactants combine to form a single product is called a combination reaction. For example, calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to form calcium hydroxide. The reaction is highly exothermic in nature, as lots of ...
Read the above passage carefully and give the answer to the following questions: Q 1. Name the compound X, that Rahul mixed with water. Difficulty Level: Medium. Ans. The compound X is calcium oxide (CaO). Q 2. Name the compound Y, that Rahul got after mixing X with water. Difficulty Level: Medium.
The Chapter wise Important case study based questions with their solved answers in CBSE Class 10 Science can be accessed from the table below: CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions ...
Writing Equations for Chemical Reactions. Chemical reaction equations truly represent changes of materials. For many reactions, we may only be able to write equations for the overall reactions. For example, common sense tells us that when sugar is fully oxidized, carbon dioxide and water are the final products.
Learn Class 10 chemistry chapter 1 | Chemical Reactions and Equations | case study Questions | case study based question | case study questions and answers ...
Answer. (i) (b) 1, 6, 3, 2. After balancing the equation, we get. Mg 3 N 2 + 6H 2 O 3Mg (OH) 2 + 2NH 3. (ii) (d) Whether a particular reaction is actually feasible or not. (iii) (c) law of conservation of mass. In a balanced chemical equation, total mass of reactants must be equal to the total mass of products.
It is a double displacement or an esterification reaction. (d ) C 2 H 4 (g) + 3 O 2 (g) → 2 CO 2 (g) + 2 H 2 O (g) + Heat + light. It is a redox or a combustion reaction. Q2. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions and identify the type of
LOGIN. TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chemical Reactions and Equations chapter. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem-solving skills with expert advice.
A balanced chemical equation has equal number of atoms of different elements in the reactants and products side. An unbalanced chemical equation has unequal number of atoms of one or more elements in reactants and products. Formulae of elements and compounds are not changed to balance an equation. (i) Consider the following reaction:
General, Organic, and Biochemistry with Problems, Case Studies, and Activities ... Chemical Equations and Reactions 7.3: Chemical Equilibrium Expand/collapse global location ... and then only when the chemical reaction produces a change in the total number of gas molecules in the system. An easy way to recognize such a system is to look for ...
Given the wealth of studies addressing post-traumatic stress reactions in children since the early 1980s (Yule and Williams 1990; Bergman, Axberg, and Hanson 2017), exploring the impact of disturbing childhood experiences on Teresa's spirituality from a trauma-informed lens is long overdue.
Supported copper species are well-known for their remarkable catalytic properties across numerous reactions. However, the current preparation methods pose challenges for large-scale production. In this study, we present a cost-effective method for the facile preparation of a series of copper-silicon composites usin
Groundwater in the Grombalia region often represents the main source of water, which is intensively exploited to meet the needs of human consumption and irrigation, threatening its quality. This study aims to assess the quality of groundwater in the Grombalia shallow aquifer, and to identify the hydrogeochemical processes controlling its mineralization, based on chemical analysis results of ...
This case study explores the importance of balancing chemical equations in the synthesis of new drugs and how this relates to enzyme kinetics in the body. Scenario: In the high-tech research laboratory of Apex Pharmaceuticals, a team of researchers, including Dr. Sophie Lee, is on the verge of a breakthrough. They have developed a promising new ...
Background: Postpartum post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) has a prevalence of 3-4% in women, rising to 15-19% in the presence of risks during pregnancy or childbirth, and reaching 39% in the case of neonatal death. Perinatal complications can trigger a real or perceived threat to maternal or neonatal life, which can evoke intense emotional reactions equivalent to a traumatic stressor ...
Kinetics and the Rate Equation. 5.7. Potential Energy Diagrams for Chemical Reactions. 5.8. Selectivity in Halogenation. 5.9. Carbon Reactive Intermediates. Chapter 5 Outline. Chapter 5: The Study of Chemical Reactions is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.
A dry-cell battery is a battery with a paste electrolyte (as opposed to a wet-cell battery with a liquid electrolyte) in the the middle of its cylinder and attached are metal electrodes. A dry-cell battery is a primary cell that cannot be reused. In order to function, each dry-cell battery has a cathode and an anode.