- FAFSA Updates
- Interactive
- JagTran Tracker
- JagMail Login
- Faculty & Staff
- Directories
- Faculty/Staff
- College of Arts and Sciences
- Earth Sciences
The University of South Alabama offers a Bachelor of Science in Geology that prepares students to enter the scientific workforce or continue studies in graduate school. Students who major in geology receive extensive hands-on training through multiple field trips and research opportunities conducted in diverse geological regions, including Alabama, Texas and New Mexico. Students can also choose to minor in Geology.
Geology students study the Earth’s physical, chemical, and biological features and evolution over a wide range of spatial and temporal scales. Geology course sizes at South are small, which allows faculty to provide individualized attention. Students are mentored by experienced faculty advisors and receive personalized advice on seeking geology careers or pursuing graduate research opportunities following graduation.

The Bachelor of Science in Geology at South prepares students to enter the scientific workforce.
Geologists work in the following fields:
- mining and mineral exploration
- petroleum exploration
- engineering geology
- environmental geology
- research and academia
- volcanology
- planetary geology
- paleontology
- remote sensing and geographic information systems
- landfill design
- military planning
- urban planning
- hazards mitigation
- police and legal work
- state and federal government
Students in the geology program at South are mentored by experienced faculty advisors and receive personalized advice on seeking geology careers or pursuing graduate research opportunities following graduation. South maintains close contact with alumni who are currently employed as geologists in the mining, petroleum, environmental, water supply and research fields.
For more information on potential careers in geology, please visit the following websites:
- Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS)
- Geology and Earth Science Jobs (geology.com)
- Geoscience Workforce (American Geosciences Institute)

- Preferences


Types of Faults and seismic waves - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

Types of Faults and seismic waves
Types of faults and seismic waves what is a fault a fault is a break in the rocks that make up the earth s crust, along which rocks on either side have moved past ... – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- A fault is a break in the rocks that make up the Earths crust, along which rocks on either side have moved past each other.
- The direction of movement along the fault plane determines the fault type.
- An earthquake is caused by a sudden slip on a fault. The tectonic plates are always slowly moving, but they get stuck at their edges due to friction. When the stress on the edge overcomes the friction, there is an earthquake that releases energy in waves that travel through the earth's crust and cause the shaking that we feel.
- Slippage along fault initiates seismic waves in all directions radiating from the focus.
- Seismic waves are vibrations that travel through the Earth carrying the energy released during earthquakes
- There are two categories of seismic waves
- Body Waves Can travel through Earths inner layers (core, mantle, crust)-
- Primary and Secondary waves
- Surface Waves Can only travel through the surface layers (crust)
- Love and Rayleigh
- P waves- are the first waves to arrive at a seismograph station.
- -fastest form of wave, sometimes called compression waves.
- Can move through both liquids and solids.
- These waves cause rock particles to move back and forth in the same direction as the wave is traveling (push-pull).
- S-Waves- arrive after the primary waves at the seismograph station.
- -Can travel through solids only.
- -Cause particles to move back and forth at right angles to the line of wave movement
- Rayleigh wave-surface wave causing the ground to shake in an elliptical motion
- Because of its motion, it moves the ground up and down, and side-to-side in the same direction that the wave is moving
- Most of EQ shaking is due to this type of wave
- Love wave- produce entirely horizontal motion
- Moves the ground side-to-side
- Named after A.E.H. Love a British mathematician
- Magnitude- the amount of energy released during an EQ
- Richter Scale- based on the largest seismic waves generated by the EQ on a factor of 10.
- Moment Magnitude Scale- considers the size of the fault rupture, the amount of movement, and rocks stiffness
- Measures the intensity of the EQ using a rating system of the damage
- Scientists compile information from various observers within different zip codes to get a better understanding of the devastation caused by an EQ to determine its intensity.
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.


Faults and Earthquakes
Mar 16, 2012
560 likes | 1.18k Views
Faults and Earthquakes . Take-Away Points. Earthquakes generate waves that travel through the earth Earthquakes occur when rocks slip along faults Faults are classified by the kinds of movement that occur along them Earthquakes don’t kill people, buildings kill people Magnitude and Intensity
Share Presentation
- great earthquake lasts minutes
- lengthen historical data base
- strong earthquake feels
- harbor shape
- first revealed importance

Presentation Transcript
Take-Away Points • Earthquakes generate waves that travel through the earth • Earthquakes occur when rocks slip along faults • Faults are classified by the kinds of movement that occur along them • Earthquakes don’t kill people, buildings kill people • Magnitude and Intensity • Seismic waves are used to map the earth’s interior • Predicting earthquakes is not yet possible
Some Important Earthquakes 1755 - Lisbon, Portugal • Killed 70,000, Raised Waves in Lakes all over Europe • First Scientifically Studied Earthquake 1811-1812 - New Madrid, Missouri • Felt over 2/3 of the U.S. • Few Casualties 1886 - Charleston, South Carolina • Felt All over East Coast, Killed Several Hundred. • First Widely-known U.S. Earthquake
Some Important Earthquakes 1906 - San Francisco • Killed 500 (later studies, possibly 2,500) • First Revealed Importance of Faults 1923 – Tokyo - Killed 140,000 in firestorm 1964 - Alaska • Killed about 200 • Wrecked Anchorage. • Tsunamis on West Coast. 1976 - Tangshan, China • Hit an Urban Area of Ten Million People • Killed 650,000
How Seismographs Work 1. Earthquakes generate waves that travel through the earth
Seismic Waves 1. Earthquakes generate waves that travel through the earth
Locating Earthquakes 1. Earthquakes generate waves that travel through the earth
Locating Earthquakes - Depth 1. Earthquakes generate waves that travel through the earth
Elastic Rebound 2. Earthquakes occur when rocks slip along faults
Epicenter and Focus Focus • Location within the earth where fault rupture actually occurs Epicenter • Location on the surface above the focus 2. Earthquakes occur when rocks slip along faults
Types of Faults Faults Are Classified According to the Kind of Motion That Occurs on Them • Joints - No Movement • Strike-Slip - Horizontal Motion • Dip-Slip - Vertical Motion 3. Faults are classified by the kinds of movement that occur along them
Strike-Slip Fault – Left Lateral 3. Faults are classified by the kinds of movement that occur along them
Strike-Slip Fault – Right Lateral 3. Faults are classified by the kinds of movement that occur along them
Dip-Slip Fault - Normal 3. Faults are classified by the kinds of movement that occur along them
Dip-Slip Fault - Reverse 3. Faults are classified by the kinds of movement that occur along them
Dip-Slip Faults • Normal Faults: Extension • Reverse Faults: Compression • Reverse Faults are often called Thrust Faults 3. Faults are classified by the kinds of movement that occur along them
Normal Fault Structures 3. Faults are classified by the kinds of movement that occur along them
Reverse Fault Structures 3. Faults are classified by the kinds of movement that occur along them
Major Hazards of Earthquakes • Building Collapse • Landslides • Fire • Tsunamis (Not Tidal Waves!) 4. Earthquakes don’t kill people, buildings kill people
Safest & Most Dangerous Buildings • Small, Wood-frame House - Safest • Steel-Frame • Reinforced Concrete • Unreinforced Masonry • Adobe - Most Dangerous 4. Earthquakes don’t kill people, buildings kill people
Tsunamis Probably Caused by Submarine Landslides Travel about 400 M.p.h. Pass Unnoticed at Sea, Cause Damage on Shore Warning Network Around Pacific Can Forecast Arrival Whether or Not Damage Occurs Depends on: • Direction of Travel • Harbor Shape • Bottom • Tide & Weather 4. Earthquakes don’t kill people, buildings kill people
Magnitude and Intensity Intensity • How Strong Earthquake Feels to Observer Magnitude • Related to Energy Release • Determined from Seismic Records • Rough correlation between the two for shallow earthquakes 5. Magnitude and Intensity
Intensity How Strong Earthquake Feels to Observer Depends On: • Distance to Quake • Geology • Type of Building • Observer! Varies from Place to Place • Mercalli Scale- 1 to 12 5. Magnitude and Intensity
Isoseismals from the 1906 San Francisco Earthquake 5. Magnitude and Intensity
Intensity and Geology in San Francisco, 1906 5. Magnitude and Intensity
Intensity and Bedrock Depth in San Francisco, 1906 5. Magnitude and Intensity
San Francisco and New Madrid Compared 5. Magnitude and Intensity
Magnitude - Determined from Seismic Records Richter Scale: • Related to Energy Release • Exponential • No Upper or Lower Bounds • Largest Quakes about Mag. 8.7 • Magnitude-Energy Relation • 4 - 1 • 5 - 30 • 6 - 900: • 1 Megaton = about 7 • 7 - 27,000 • 8 - 810,000 5. Magnitude and Intensity
Seismic - Moment Magnitude A Seismograph Measures Ground Motion at One Instant But -- • A Really Great Earthquake Lasts Minutes • Releases Energy over Hundreds of Kilometers • Need to Sum Energy of Entire Record • Modifies Richter Scale, doesn't replace it • Adds about 1 Mag. To 8+ Quakes 5. Magnitude and Intensity
Magnitude and Energy 5. Magnitude and Intensity
Seismology and Earth's Interior Successive Approximation in Action 6. Seismic waves are used to map the earth’s interior
1. Assume the Earth is uniform. • We know it isn't, but it's a useful place to start. It's a simple matter to predict when a seismic signal will travel any given distance. 6. Seismic waves are used to map the earth’s interior
2. Actual seismic signals don't match the predictions • If we match the arrival times of nearby signals, distant signals arrive too soon • If we match the arrival times of distant signals, nearby signals arrive too late. • Signals are interrupted beyond about 109 degrees 6. Seismic waves are used to map the earth’s interior
3. We conclude: • Distant signals travel through deeper parts of the Earth, therefore .. • Seismic waves travel faster through deeper parts of the Earth, therefore …. • They travel curving paths (refract) • Also, there is an obstacle in the center (the core). 6. Seismic waves are used to map the earth’s interior
Why Refraction Occurs 6. Seismic waves are used to map the earth’s interior
Waves Travel The Fastest Path 6. Seismic waves are used to map the earth’s interior
Seismic Waves in the Earth 6. Seismic waves are used to map the earth’s interior
Inner Structure of the Earth 6. Seismic waves are used to map the earth’s interior
The overall structure of the Earth 6. Seismic waves are used to map the earth’s interior
Strategies of Earthquake Prediction Lengthen Historical Data Base • Historical Records • Paleoseismology Short-term Prediction • Precursors Long-term Prediction • Seismic Gaps • Risk Levels Modeling • Dilatancy - Diffusion • Stick - Slip • Asperities (kinks) • Crack Propagation 7. Predicting earthquakes is not yet possible
Seismic Gaps 7. Predicting earthquakes is not yet possible
Are Earthquakes Getting More Frequent? 7. Predicting earthquakes is not yet possible
Earthquake Fatalities Since 1800 7. Predicting earthquakes is not yet possible
- More by User

Faults and Earthquakes . BASIC DEFINITIONS. FAULT : A surface or narrow zone along which one side has moved relative to the other. Faults are classified based upon their direction of movement. . HANGING WALL vs FOOTWALL. A fault divides rock into two fault blocks
855 views • 32 slides

Faults and Earthquakes . Some Important Earthquakes . 1755 - Lisbon, Portugal Killed 70,000, Raised Waves in Lakes all over Europe First Scientifically Studied Earthquake 1811-1812 - New Madrid, Missouri Felt over 2/3 of the U.S. Few Casualties 1886 - Charleston, South Carolina
640 views • 48 slides

Faults & Earthquakes
Faults & Earthquakes. Deforming the Earth’s Crust. Deformation. The process by which the shape of a rock changes because of stress is called deformation . There are two basic types of deformation: Plastic deformation Elastic deformation.
616 views • 17 slides

Traps and Faults
Traps and Faults. Review: Mode and Space. C. B. A. data. data. user mode. kernel mode. “kernel space”. Review: the Role of Events. A CPU event is an “unnatural” change in control flow. Like a procedure call, an event changes the PC.
301 views • 18 slides

Faults, Earthquakes and Uplift
Faults, Earthquakes and Uplift. Move it, move it !!. What are they?. Fault: a break or fracture in the crust of Earth. Earthquakes: shaking or trembling of the earth caused by movement along a fault. Uplift: upward movement of Earth’s crust. Faults.
385 views • 13 slides

Earthquakes: Waves, Faults and Folds
Earthquakes: Waves, Faults and Folds. By: Marg Dyan D. Fernandez Princess Amaryah P. Ejares NatSci1-A7. Earthquake.
282 views • 13 slides
Faults and Earthquakes ______________ – the shaking and trembling that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth’s surface ______________ – a force that acts on rock to change its shape or volume
920 views • 64 slides


Faults and Mountains
Faults and Mountains . Fault- a break along which the rock on either side moves. Hanging wall- the rock on the side of the fault that is on top of the fault (in non-vertical faults). Footwall- is the rock under the fault (in non-vertical faults). Vocabulary.
273 views • 9 slides

Earthquakes and Faults
Earthquakes and Faults. 1. Faults. A fault is a break or fracture between two blocks of rocks in response to stress. Three types of stresses produce faults Tension Compression Shear One block has moved relative to the other block.
1.42k views • 16 slides

Earthquakes and Faults. Definition, Cause and Anatomy. Science Department Corpus Christi School. Short Review. What is an Earthquake?.
381 views • 13 slides

Earthquakes occur on faults
Earthquakes occur on faults. Active Fault. Earthquakes Create Seismic Waves. (also hypocenter). 3 Types of Seismic Waves. P wave: Primary S wave: Secondary Surface waves. Fastest Slowest. Depiction of Seismic Waves. Types of Earthquake Waves. Wave terminology
699 views • 45 slides
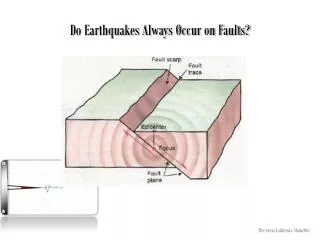
Do Earthquakes Always Occur on Faults?
Do Earthquakes Always Occur on Faults?. The Great California ShakeOut. NO. Caused by sudden release of energy Tectonic earthquakes are focused on a fault Induced seismicity Volcanism. The Great California ShakeOut. Volcanism.
191 views • 5 slides

Evidence about Past Earthquakes From Faults
Evidence about Past Earthquakes From Faults. By: Thomas Solowynsky, Tom Mulally, Victoria Flis, Omar Oregel . Faults. There are many faults that tell us different effects and are caused by earthquakes. Faults form because of extension or compression.
259 views • 14 slides

Earthquakes: Faults and Waves
Earthquakes: Faults and Waves. Sarah Bennek Grade 9. Objectives. To be able to describe what happens to the earth at normal, reverse and strike slip faults. To be able to compare and contrast P-waves, S-waves, R-waves, and L-waves. Location of Earthquakes. Earthquakes happen along faults
322 views • 11 slides

Modeling Earthquakes Faults and Statistics
Modeling Earthquakes Faults and Statistics. M. O. Robbins & K. M. Salerno, Johns Hopkins University C. Maloney, Carnegie Mellon University. Example of simulations where follow “particles†representing atoms or chunks of solid or fluid
408 views • 30 slides

Faults and Earthquakes. Take-Away Points. Earthquakes generate waves that travel through the earth Earthquakes occur when rocks slip along faults Faults are classified by the kinds of movement that occur along them Earthquakes don’t kill people, buildings kill people Magnitude and Intensity
722 views • 47 slides

Earthquakes: Faults, Hazards, & the Bay Area
Earthquakes: Faults, Hazards, & the Bay Area. Richard Sedlock, SJSU Geology/BAESI 408 924-5020 [email protected] http://www.baesi.org -- click on “Workshop Links”. What is an Earthquake?. A release of energy stored on a fault. What is a fault?.
411 views • 29 slides

Stresses, Faults, Folds, and Earthquakes
Stresses, Faults, Folds, and Earthquakes. Types of Stresses on Layers of Rocks:. Types of Folds Anticline - an upward fold in the rock Syncline - a downward fold in the rock. Syncline “sinks”. Syncline. Anticline folds up like a capital “A”. Anticline. Syncline. Anticline.
750 views • 27 slides

Faults and Earthquakes. Take-Away Points. Earthquakes generate waves that travel through the earth Earthquakes occur when rocks slip along faults Faults are classified by the kinds of movement that occur along them Earthquakes don ’ t kill people, buildings kill people
635 views • 47 slides

Faults & Earthquakes. These can be either constructive or destructive forces 3 basic types of geologic forces 1. Tension: pulling force ← → 2. Compression: pushing force → ← 3. Shearing: forces sliding past each other in opposite directions. ↑↓.
361 views • 21 slides
Folds and Faults
Folds and Faults. Tectonic Plates. Types of Differential Stress. 1. 2. 3. Ductile Deformation Rock will flow in response to stress Rock will change shape during flow Example: Copper penny on train tracks. Brittle Deformation Rock will break in response to stress
343 views • 26 slides

Lesson 2. Faults and Earthquakes. 3 Types of Faults associated with Earthquakes. Strike-Slip Fault occurs at a Transform Boundary. What type of fault is this?. Reverse Fault occurs at a Convergent Boundary. What type of fault?. Normal Faults occur at Divergent Boundaries.
197 views • 11 slides

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Explain the 3 different types of faults. Land Plates. Indicates forces on the land. This is a Strike Slip Fault. or a Transverse Fault. San Andres Fault . Fault Types. Plate Motion: Major Fault Type; Transform. Strike-Slip Fault. ... PowerPoint Presentation Last modified by: Melanie Loe Company:
Presentation Transcript. Types of Faults • Strike Slip Fault: Two layers of rock are shifted horizontally or parallel to the fault plane. 1) "Hanging Wall"- The surface of block that is ontop of the plane of the fault. • 2) "Footwall"- The surface or block that lies below the plane of the fault. Reverse Fault: The hanging wall has slipped ...
PowerPoint Presentation. Ground Deformation: Faulting and FoldingEarthquakes and Mountain- Building. An Earthquake is a rapid vibration of the Earth's surface created by a sudden movement of a part of a plate along a fault. Energy released radiates in all directions from its source, the focus.
Faults • Is a break in Earth's crust where slabs of crust slip past each other. • Usually occur along plate boundaries , where the forces of plate motion compress, pull, or shear the crust so much that the crust breaks. Three Types of Faults • Normal Faults • Reverse Faults • Strike-Slip Faults. Fault Terminology • Fault Plane ...
Geologists recognize two distinct classes of faults, (1) dip slip faults, where movement is in the dip direction of the fault plane, and (2) strike slip faults, where movement is in the strike direction of the fold. You will (hopefully!) recall the terms strike and dip from earlier lectures about inclined bedding and folds.
Strike-Slip Fault. Plates move past each other. This fault is caused by shearing stress. Three major Faults Strike-slip Reverse Normal 1. Normal Fault This fault is caused by tension stress. Normal Fault Normal Fault Normal Fault 2. - A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as an HTML5 slide show) on PowerShow.com - id: 5baa46-MDk2O.
Rocks & Landforms. Folding & Faulting. Folding. When Earth's crust bends, folds occur. Folding occurs under compression when forces act towards each other, such as when plates collide. Folding & Faulting Definitions Compression Is a process of forcing something into smaller compass, reducing it in volume by pressing it together Tension Is a ...
Earthquake sources are a double couple force system which is equivalent to Fault Slip 2. The moment tensor describes the Force System for earthquakes and can be used to determine the geometry of the faulting 3. Earthquake ruptures begin from a point (hypocenter) and spread out over the fault plane 4.
San Andres Fault is a strike-slip. Types of Faults • Thrust Fault--When thrust faults are exposed on the surface overburden material lies over the main block. They are normally associated with areas of folded surfaces and or mountainous regions. Types of Faults. Reverse fault-- a normal fault except the general movement of the fault blocks is ...
Lesson 2. Faults and Earthquakes. 3 Types of Faults associated with Earthquakes. Strike-Slip Fault occurs at a Transform Boundary. What type of fault is this?. Reverse Fault occurs at a Convergent Boundary. What type of fault?. Normal Faults occur at Divergent Boundaries. 196 views • 11 slides
EARTHQUAKES AND FAULTS (Grade-8 science).pptx - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
ground Epicenter-where the shaking is first felt. above ground directly above the focus. 19. Slippage along fault initiates seismic waves in. all directions radiating from the focus. Seismic waves are vibrations that travel through. the Earth carrying the energy released during. earthquakes. 20.
Presentation Transcript. Types of Faults and Folds • Faults: when rocks break due to force. • Normal FaultCaused by tension (pulling apart) • Reverse FaultCaused by compression (pushing together) • Strike-Slip FaultCaused by shear (lateral) forces (sideways) • Folds: when rocks bend due to force. • AnticlineCaused by ...
A diagram illustrates the fault management system architecture. The two types of situations, i.e., Known and Unknown, in fault management have been described in a comprehensible manner. Impressive Features. We offer hassle-free customization options; you can instantly edit the content and visual objects to create impressive presentations.
Presentation Transcript. Earthquakes and Faults. 1. Faults • A fault is a break or fracture between two blocks of rocks in response to stress. • Three types of stresses produce faults • Tension • Compression • Shear • One block has moved relative to the other block. • The surface along which the blocks move is called a fault plane.
Earthquakes generate waves that travel through the earth Earthquakes occur when rocks slip along faults Faults are classified by the kinds of movement that occur along them Earthquakes don't kill people, buildings kill people Magnitude and Intensity. Download Presentation. great earthquake lasts minutes. lengthen historical data base.